Current Affairs January 05, 2024: Antibiotic Resistance, Bitcoin Ponzi Scheme, Hasdeo Arand, Prerana Programme, Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO), Cybercrimes, Blasts in Iran
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – Geo – EG – Mineral Resources} Graphene
- Context (LM): Researchers created a functional semiconductor from graphene.
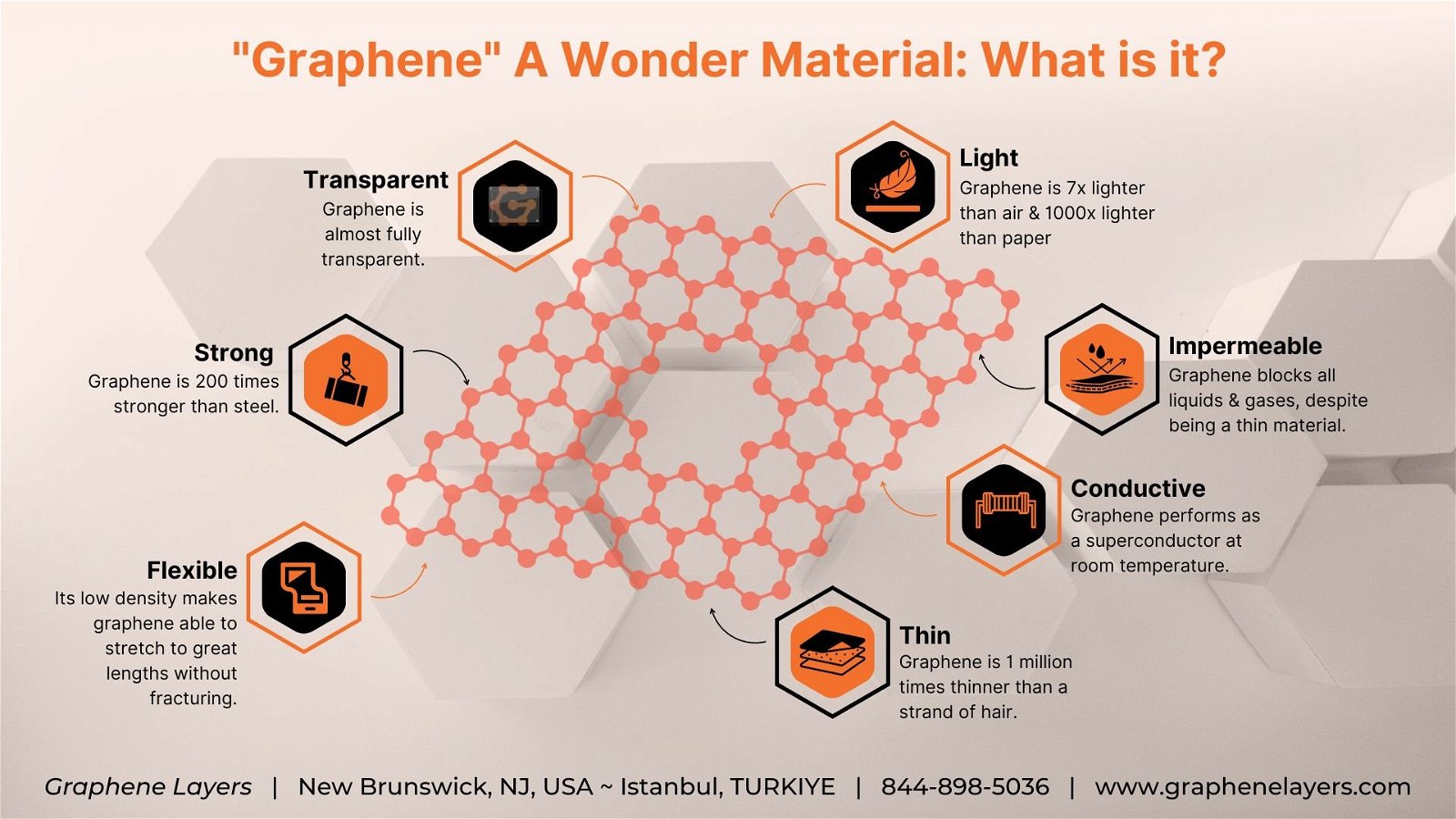
- Graphene is a single layer (monolayer) of pure carbon, tightly bound in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice. It is an allotrope of carbon.
- It is extracted from graphite. Graphite is arranged in a 3D crystalline manner, whereas, graphene is a 2D crystal, only an atom thick.
Properties
- Graphene is the thinnest (one atom thick) compound known.
- It is the lightest material known and the strongest compound discovered (between 100-300 times stronger than steel, and harder than diamond).
- It is an excellent conductor of electricity and has high thermal conductivity.
- It is flexible, transparent, and has a large surface area.
Applications
- Electronics industry: It is used in applications ranging from miniaturised electronics to biomedical devices due to its thin composition and high conductivity.
- Biomedical industry: It can be used for targeted drug delivery, ‘smart’ implants, etc.
- Automobile industry: Graphene is highly inert and so can act as a corrosion barrier between oxygen and water diffusion.
- Potential alternative to lithium-ion batteries: It can be used to develop smaller, slimmer batteries with higher capacity, faster charging, and increased longevity than traditional batteries.
For details on Semiconductor >Semiconductor Manufacturing in India
{GS2 – IR – Middle East} Iran Blasts
- Context (IE): Two blasts struck the city of Kerman in Iran, leading to the deaths of at least 103 people.
- A crowd was present to mark four years since the 2020 US-ordered killing of General Soleimani.
- Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi blamed the Israeli government for the explosions.
 .
.
Qassem Soleimani
- Qassem Soleimani led the Quds Force of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- Soleimani was known to have participated in the 1979 Islamic Revolution, which led to the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty and the establishment of a theocratic state in Iran.
Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)
- The IRGC is a wing of the Iranian military and is believed to undertake foreign missions.
- It was designated as a Foreign Terrorist Organisation by the US in 2019.
- The US alleges it provides guidance, training, funding, and weapons to Shia militant partners and proxies in other Middle Eastern countries.
Recent situation in the Middle East
- Middle East peace is disrupted after the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict.
- Iran is seen as supporting Hamas, Hezbollah and Houthis (Yemen) in the Shia-Sunni conflict.
- Due to this equation, Iran finds itself at a proxy war with Israel and an anti-US stand.
- The recent death of Hamas leader, Saleh al-Arouri, and the Red Sea attacks by Houthis made the situation more tense in the region.
- Blasts in Iran are further expected to worsen the situation with expected retaliation.
{GS2 – MeitY – Initiatives} ERNET India
- Context(PIB): MeitY introduces ERNET India’s web portal, providing domain registration, DNS, and additional services for educational institutions.
ERNET India, or the Education and Research Network
- It is a not-for-profit scientific society operating under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It provides advanced networking and communication infrastructure to educational and research institutions nationwide.
- It serves as the exclusive domain registrar for educational and research institutions, managing domain names with extensions such as ‘ac. in,’ ‘edu. in,’ and ‘res.in.’
- ERNET India also helps with web accessibility, campus Wi-Fi, smart classrooms, and internet connections for schools and research centres.
{GS2 – MoE – Schemes} Prerana Programme
- Context (PIB): Ministry of Education launches PRERANA: An Experiential Learning program.
- The program will run from a Vernacular School, established in 1888, in Vadnagar, Gujarat.
- The curriculum of Prerana School is prepared by IIT Gandhi Nagar.
- Students can register through the portal forth where the registered applicants will go through a selection process, conducted at the School/block level, on designated ‘Prerana Utsav’ day.
- It is a week-long residential program for selected students of class IX to XII.
- A batch of 20 selected students (10 boys and 10 girls) will attend the program, every week from various parts of the country.
- The curriculum is rooted in nine value-based themes: Swabhiman and Vinay, Shaurya and Sahas, Parishram and Samarpan, Karuna and Sewa, Vividhta and Ekta, Satyanishtha and Shuchita, Navachar and Jigyasa, Shraddha aur Vishwas, and Swatantrata and Kartavya.
{GS2 – MoPNG – Initiatives} Open Acreage Licensing Policy (OALP)
- Context (PIB): The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas initiated the 9th bidding round under the Open Acreage Licensing Policy (OALP).
- OALP was launched in 2016 under Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP).
- Under the Open Acreage Licensing Policy, Companies can put in an Expression of Interest (EoI) for any area throughout the year but such interests are accumulated thrice in a year.
- The Government will examine the interest and if it is suitable for award, then the government will call for competitive bids after obtaining necessary environmental and other clearances.
- Successful implementation of OALP requires building of National Data Repository.
National Data Repository (NDR)
|
Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy
- Approved in 2016, it replaced the erstwhile New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP).
Main aspects of HELP
- Open Acreages: Freedom to investors for carving out blocks of their interest (OLAP).
- Single, uniform licensing system to cover all hydrocarbons (ie. Conventional and Unconventional hydrocarbons) under a single licensing framework, instead of the present system of issuing separate licenses for each kind of hydrocarbons.
- Shift to Revenue sharing model from profit sharing model/production sharing contract model (PSC).
- Marketing and Pricing Freedom: Only subject to a ceiling price limit.
|
Revenue Sharing Contracts Model
|
{GS2 – Social Sector – Health – Issues} Antibiotic Resistance
- Context (DTE|DTE ): Roche, a Swiss multinational healthcare company, has discovered a new class of antibiotics (Zosurabalpin) effective against gram-negative bacteria.
- Zosurabalpin exhibits strong activity against various species of Acinetobacter that cause pneumonia and sepsis, particularly Carbapenem-resistant A baumannii (CRAB).
- It is considered a significant development since no antibiotic has been introduced in the last 50 years against gram-negative bacteria.
About Gram-negative bacteria

Acinetobacter
- Acinetobacter belongs to the Gram-negative group of bacteria.
- These bacteria are ubiquitous in nature and can be found in soil, water, and various environments.
- it causes a variety of diseases, including lung infections (“pneumonia”), sepsis and blood, wound, or urinary tract infections.
Carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CRAB)
- An example of harmful Acinetobacter strain is CRAB.
- It has gained attention due to its ability to develop resistance to multiple antibiotics.
- CRAB is classified as a priority 1 (critical) pathogen by the WHO. Other drug-resistant forms of bacteria are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae.
- According to the 2019 report of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention on antibiotic resistance, CRAB was responsible for killing 700 people in 2017 and added about $281 million in healthcare costs.
Sepsis
- Sepsis is a life-threatening condition arising from the body’s overreactive response to an infection, leading it to injure its own tissues and organs.
- Bacterial infections cause most cases of sepsis. Sepsis can also result from other infections, including viral infections, such as COVID-19 or influenza, or fungal infections.
National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC)
Global Point Prevalence Survey (PPS)
|
{GS3 – Envi – Conservation} Hasdeo Arand
- Context (TOI): Tribal rights activists condemn large scale tree-felling in Hasdeo.
- Called as lungs of Chhattisgarh, Hasdeo Arand is a 1,70,000-hectare forest.
- The forest falls under Korba, Sujapur and Sarguja districts with a sizeable tribal population.
- The Hasdeo River, the largest tributary of Mahanadi River, flows through it.
- It is the largest unfragmented forest in Central India consisting of pristine Sal and teak forests.
- The forest is a catchment area of Hasdeo Bango Dam, which helps in the irrigation of around 3,00,000 hectares for crops.
- It is home to animals like sloth bears, elephants, bird species, and endangered butterfly species.
- The forests are ecologically sensitive and are part of the elephant corridor.
- The Aranya region is home to 22 coal mines.
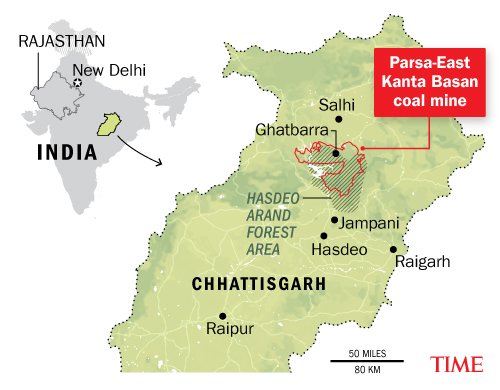
Protest Against Mining in Hasdeo
- In 2010, GoI designates Hasdeo Arand a “no-go” area for mining because of its rich forest cover.
- In 2011, the ‘No-Go’ policy circumvented. The Go, No-Go classification of forests was replaced and Parse East Kente Basab coal mine project was given a go ahead as part of Phase I.
- In 2022, Chhattisgarh government gave green light to Rajasthan Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam for coal mining as part of coal block’s Phase II.
- The tribal community has been protesting against the coal mining projects in the region to protect the ecologically sensitive region.
{GS3 – Envi – Species} Tigers
- Context(IE): Tiger’s comeback in Buxa National Park.
- Buxa reserve has corridor connectivity with the forests of Bhutan in the North & Manas Tiger Reserve in the East & with the Jaldapara National Park on the West.
Efforts taken to improve Tiger habitat
- Reduced human interference due to efforts taken to curb infiltration and trespassing.
- Increase in grassland coverage and creation of watering holes.
- Introduced 200 chital to increase the prey base.
- Introduction of “Tiger augmentation and monitoring project” in 2018.
What is Management Effectiveness Evaluation (MEE)?
- MEE is a tool used by governments and international bodies to understand how well National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries are being managed.
- There are 30 Headline Indicators developed under six elements of the MEE framework.
- The ratings are assigned in four categories, as
- Poor up to 40%
- Fair: 41 to 59%.
- Good: 60 to 74%.
- Very Good: 75% and above.

IUCN Framework for evaluating Protected Area Management Effectiveness
What was the need of this tool?
- India has a network of 903 protected areas.
- India also has 70% of the global tiger population 70% of Asiatic lions and more than 60% of leopard’s global population.
- Hence, to assess the efficacy of protected areas, an evaluation of management effectiveness is required.
{GS3 – IE – Banking} Bitcoin Ponzi Scheme
- Context (IE): The Enforcement Directorate (ED) has arrested a Delhi resident concerning a Bitcoin-based Ponzi scheme.
- In this case, bitcoins were invested instead of money. This case also questioned crypto exchanges as they converted bitcoins to Indian currency without any accounting trail.
Ponzi schemes
- Ponzi schemes are fraudulent investment schemes promising high rates of return without much risk to investors.
- Fraudulent schemes run by Charles Ponzi in the US in 1882 led to the popular term ” Ponzi Scheme”.
- It works like a multi-level pyramid scheme.
- A Ponzi scheme pays existing investors with funds collected from new investors.
- As the flow of fresh investments runs out, the scheme falls apart.
- However, multi-level marketing itself is not illegal in India if a product is being sold.
- However, direct marketing companies cannot promote pyramid or money circulation schemes.

Provisions related to Ponzi Schemes in India
- Non-clear jurisdiction of regulatory bodies on Ponzi schemes led to their popularity.
- Prize Chit and Money Circulation (Banning) Act, 1978, bans Ponzi schemes in India.
- It empowers state governments to enforce the law.
- The Enforcement Directorate under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 also investigates similar cases.
- The Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act 2019 has been enacted to prevent fraudulent schemes.
{GS3 – Infra – Initiatives} Indus Water Treaty | Ratle Hydro Electric (HE) Project
- Context (PIB): Ratle Hydro Electric Power Corporation Limited (RHPCL) signed a power purchase agreement (PPA) with Rajasthan for forty years.
|
- The “Run of River” Ratle HE project is on River Chenab in Kishtwar (Jammu & Kashmir).
- With a generation capacity of 850 MW, it also has a gravity dam.
- Pakistan alleged in 2013 that the Project breached the Indus Water Treaty, but the World Bank approved the Project.
Indus Water Treaty (IWT)
- India and Pakistan signed the IWT in September 1960.
- The World Bank is also a signatory to the pact.
- The treaty provides for river water sharing mechanisms and information exchange between the two sides on the use of the water of the Indus River system.
- Western Rivers (Chenab, Jhelum, Indus) are allocated to Pakistan, while Eastern Rivers (Sutlej, Beas, Ravi) are allocated to India for unrestricted use.
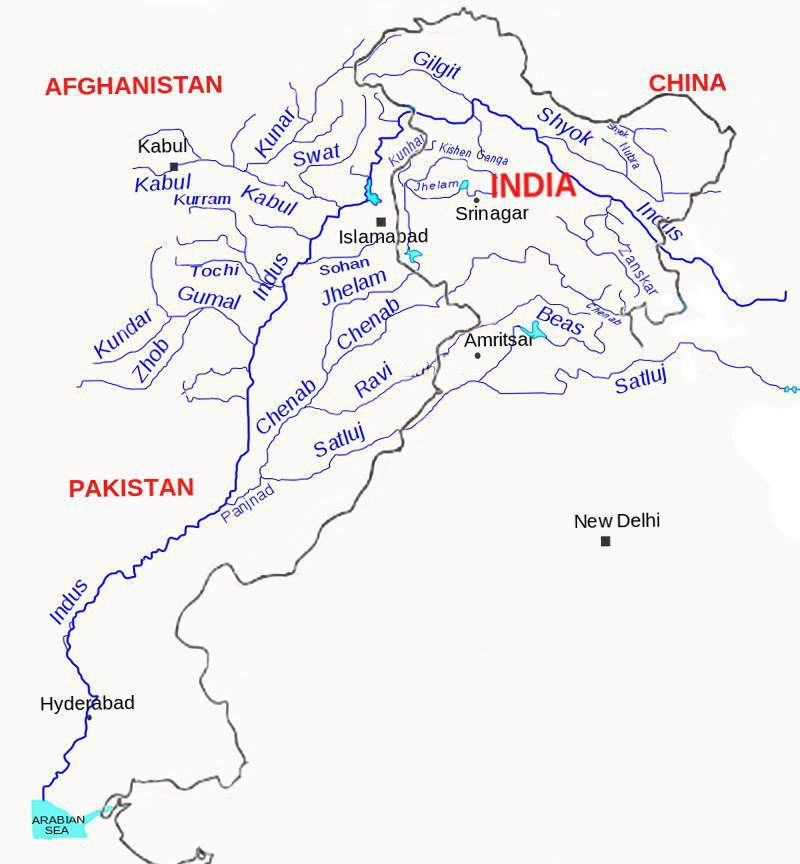
- India is left with 20% water rights, while Pakistan enjoys 80% water usage rights.
- India can also utilise western rivers for agricultural usage and “run of river” projects.
- A Permanent Indus Commission was also constituted as a dispute resolution body with an annual meeting requirement.
- Unresolved disputes are referred to the World Bank-appointed Neutral Expert.
Chenab River
- The Chenab originates near the Bara Lacha Pass in the Lahul-Spiti part of the Zanskar Range.
- Two small streams on opposite sides of the pass, namely Chandra and Bhaga, join to form Chenab.
Hydroelectric Power
Run of the River Project
|
Other HE Projects on the Indus Basin
Kishanganga HE Project
- It is a run-of-the-river project in Bandipora (Jammu and Kashmir).
- It requires diverting water from the Kishanganga River through the tunnel to a power plant.
- Pakistan objected to it, arguing it would impact water flow in the Kishanganga River (Neelum in Pakistan).
- India won in The Hague’s Permanent Court of Arbitration (CoA) in 2013.
Kiru HE Project
- It has a 624 MW installed capacity, proposed on river Chenab (Kishtwar district).
Pakal Dul HE Project
- It is a reservoir-based scheme proposed on river Marusudar (right bank tributary of river Chenab) in Kishtwar (Jammu & Kashmir).
Dulhasti Power Station
- It is run-of-the-river with an installed capacity of 390 MW to harness the hydropower potential of river Chenab (Kishtwar district).
Salal Power Station
- It is a run-of-the-river scheme with an installed capacity of 690 MW to harness the hydropower potential of the Chenab River in the Reasi district of Jammu and Kashmir.
{GS3 – Infra – Initiatives} Kuppa Pumped Hydro Project
- Context (PIB): Govt. of Gujarat to invest Rs. 4,000 crores in proposed 750 MW Kuppa Pumped Hydro Storage Project.
- NHPC and the Government of Gujarat plan to develop and utilise pumped hydro storage projects as an effective solution for energy storage.
- This project will help achieve the national objective of clean and green energy, i.e. attaining 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 and a “Net Zero” target by 2070.
NHPC (National Hydroelectric Power Corporation)
- NHPC Limited is India’s leading hydropower company with a total installed capacity of 7,097.2 MW of renewable energy.
- Established in 1975, Headquartered in Faridabad, Haryana.
- Hydroelectric power the company has expanded its objects to include other sources of energy like Solar, Geothermal, Tidal, Wind etc.
- At present, NHPC is a Mini Ratna Category-I Enterprise of the Central Government.
Criteria for granting Maharatna status to CPSEs
Criteria for granting Navratna status to CPSEs
6 Performance Indicators Criteria for granting Miniratna status to CPSEsMiniratna Category-I status
Miniratna Category-II status
Department of Public Enterprises, Ministry of Finance |
{GS3 – IS – Cyber Security} Cybercrimes
- Context (TH): In 2023, Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS) frauds accounted for 11% of cyber-financial frauds originating in India, as per the Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C).
- The central government’s cybercrime portal (cybercrime.gov.in) and the 1930 helpline received 1,310,329 complaints about cyber-related financial frauds. This included AePS frauds where biometrics were cloned.
- The scams involve cloning people’s Aadhaar-linked biometrics. This is done by using silicon fingerprints and unauthorised biometric devices.
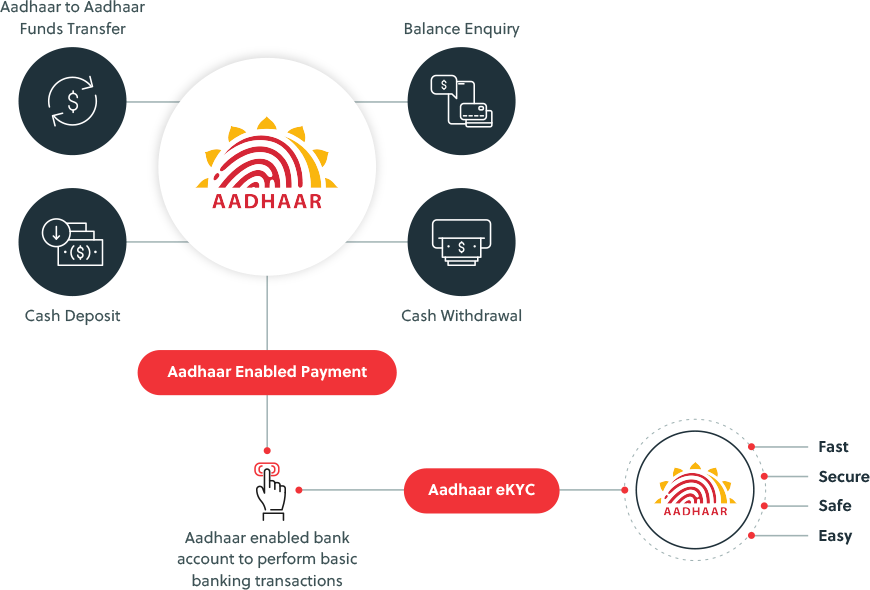
What is AePS?
- AePS, or Aadhaar-enabled Payment System, is a financial service in India that allows customers to carry out banking transactions using only the bank name, Aadhaar number, and fingerprint.
- It eliminates the requirement for OTPs and the necessity to input bank account information and other financial details.
Types of Services Available under AEPS
Issues related to Aadhaar in India
- Privacy Issues: Concerns about the potential misuse of Aadhaar data. For example, leak in biometric information.
- Authentication Errors: leading to the exclusion of individuals from essential services.
- Centralisation of personal data makes it a potential target for cyber-attacks.
- Excessive Government Surveillance: Due to the extensive use of Aadhaar in public and private transactions.
- Concerns about the involvement of foreign entities in Aadhaar-related projects and potential risks associated with international data sharing.
About Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C)
|
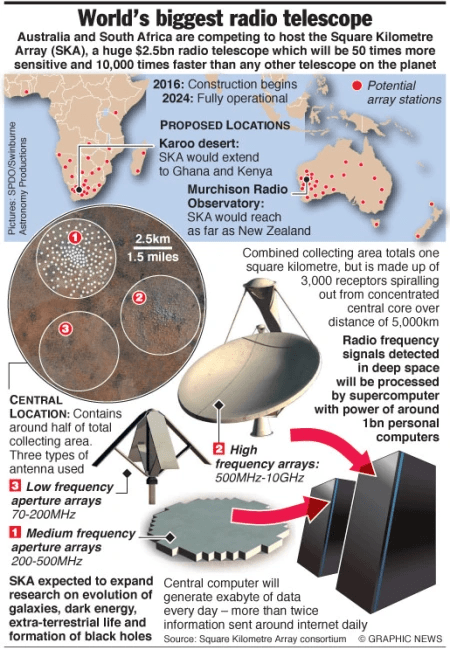
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO)
- Context (IE): Union Cabinet approves Rs 1250 Cr for India’s participation in the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO).
- SKAO is an international project to build the world’s largest radio telescope, with eventually over a square kilometre (one million square metres) of collecting area.
- Headquarters: United Kingdom.
- It is an array of antennas located in South Africa and Australia.
- Objective: Answer key questions in modern astrophysics and cosmology like studying the universe‘s history, understanding how galaxies evolve, deciphering the nature of dark matter, etc.
- Member countries: Australia, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, The Netherlands and the UK.
- India joined in 2012 as an Associate Member. In 2022, the National Centre for Radio Astronomy, Pune, and SKAO signed cooperation agreements.
- India is participating through the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The SKAO will comprise a network of high and low-frequency radio telescopes:
- SKA-Low in Australia,
- SKA-Mid in South Africa.
| Radio telescopes, unlike optical telescopes, can detect invisible gas and therefore can reveal areas of space that may be obstructed by cosmic dust. |

Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT)
- It is the world’s largest and most sensitive radio telescope array for low frequencies.
- Location: Khodad, 80 km north of Pune, Maharashtra.
- It detects radio waves from celestial bodies with wavelengths of about one meter.
- It is operated by the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), which is part of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in Mumbai.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)