Current Affairs January 04, 2024: VVPAT Machines, Green Cover Index, Polar Bears, Satellite-Based Internet Connectivity, Snow Leopard, Internationalization of Rupee
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
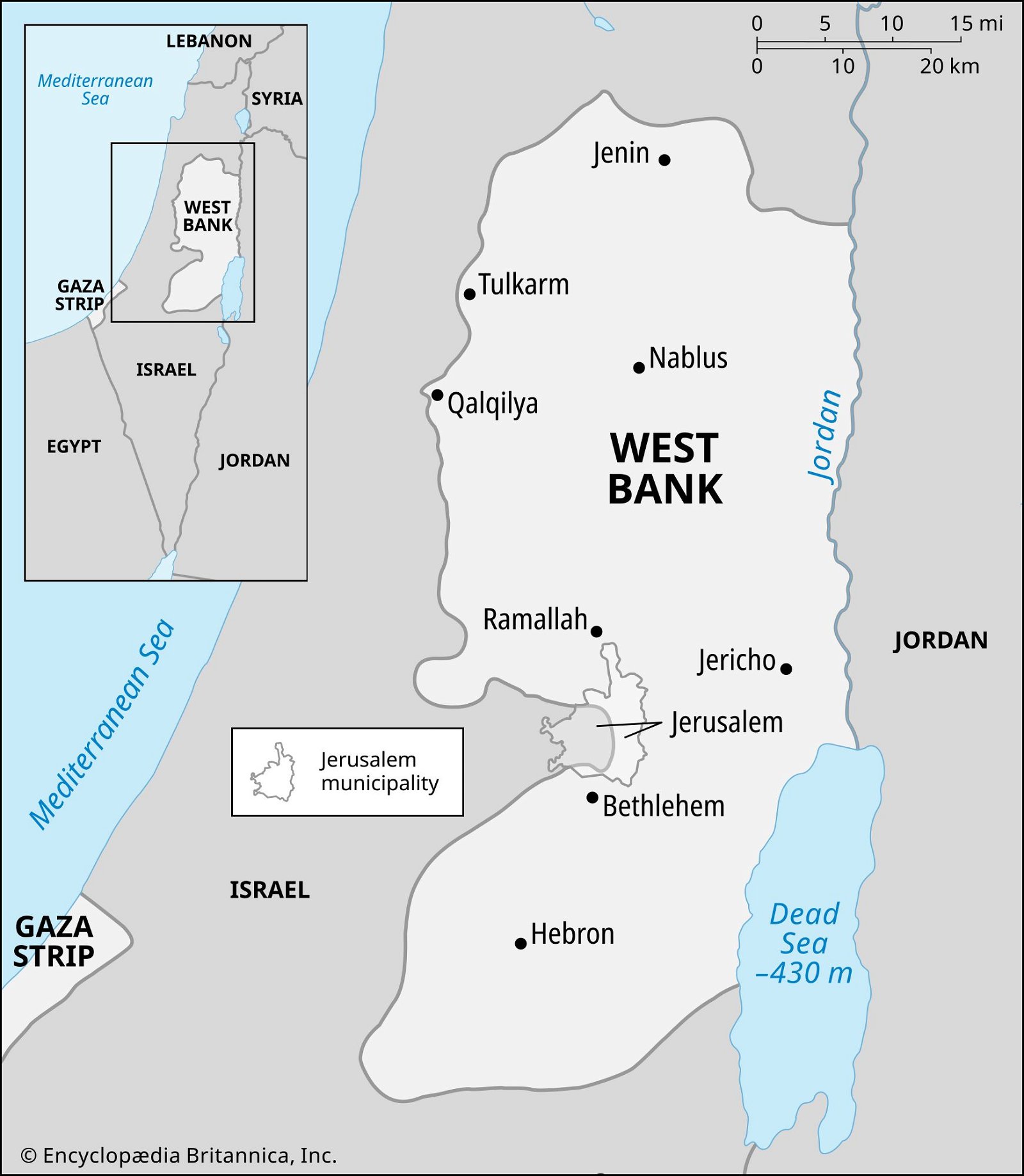
{GS2 – IR – Middle East} Death of Saleh al-Arouri
- Context (IE): Hamas leader Saleh al-Arouri was killed in an Israeli drone strike in Beirut, Lebanon.
- Lebanon faces frequent Israeli invasions targeting Palestinian militants.

Saleh al-Arouri
- He joined Hamas in 1987.
- He was the founder of the West Bank headquarters of Hamas.
- He acted as a Hamas ambassador to Hezbollah — a Lebanese Islamic militant organisation backed by Iran.
- In 2015, the US designated Saleh al-Arouri a “Specially Designated Global Terrorist”.
- Analysts believe that the fighting between Israel and Hezbollah would escalate as Saleh al-Arouri was killed in the heart of Lebanon, which hosts the militant group.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Elections} Voter Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) Machines
- Context (IE): A plea has been filed in the Madras HC to count 100% of the VVPAT machine printout slips attached to the Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs).
- INDIA alliance has demanded that “Instead of the VVPAT slip falling in the box, it should be handed over to the voter who shall then place it in a separate ballot box after verifying his or her choice”.
About VVPATs
- VVPAT is an independent verification printer attached to EVMs.
- The use of VVPATs falls under Rule 49A of the Conduct of Elections Rules, 1961, which states that every EVM shall have a control unit and a balloting unit.
- When a vote is cast, a slip is printed on the VVPAT printer containing the serial number, name, and symbol of the candidate who voted.
- This remains visible to the voter through a transparent window for seven seconds. After that, this printed slip automatically gets cut and falls into a sealed drop box.
- According to ECI, EVMs and VVPATs are separate entities and are not connected to any network.
- These were first used in Nagaland’s bye-election for the Noksen Assembly seat in 2013.
- The 2019 Lok Sabha elections became the first general election to have 100% of EVMs attached to VVPATs.

Significance of VVPAT
- It allows voters to verify that their votes have been recorded accurately.
- If there is a need, these printouts can later be counted.
- VVPAT machines can be accessed by polling officers only.
- EVMs and VVPATs try to ensure the massive election process is in tune with the latest technological advancements.
- VVPATs add another layer of transparency and reliability to convince voters about the sanctity of EVMs.
- Its verification helps to eliminate chances of EVM manipulation.
- Electoral fraud and rigging can be checked.
- EVMs and VVPATs also quicken the election process as counting votes on EVMs takes much less time than counting paper ballots.
Challenges
-
Technical Malfunctions
- There have been instances of the machines malfunctioning, resulting in inaccurate printing or no printing.
-
Verification of Paper Trails
- Another challenge is verifying the paper trails generated by the VVPAT machines.
-
Voter Confidence
- The lack of transparency and accountability on the part of the EC has led to questions about the fairness and accuracy of the elections.
- The SC in Dr. Subramanian Swamy v ECI (2013) held that VVPAT is an “indispensable requirement of free and fair elections”.
EC on VVPAT
- EC told the SC that verification of 20,600 VVPATs (Five randomly selected polling stations per Assembly seat) had been conducted.
- Not a single case of transfer of vote meant for candidate ‘A’ to candidate ‘B’ has been detected.
- Differences in the count, if any, have always been traceable to human errors like non-deletion of mock poll votes from the control unit of the EVM or the VVPAT.
- EC received 25 complaints out of the 118 crore voters who cast their votes. It said all these complaints were found to be false.
- The EC said 100% verification was a “regressive thought and tantamount to going back to the days of manual voting using ballot system”.
- Manual counting of all VVPAT slips would take time and introduce the potential for human error.
{GS3 – Envi – Initiative} Green Cover Index
- Context (PIB): The Green Cover Index was launched for a comprehensive pan-India estimation of green cover over the national highway network.
- It will be estimated by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC-ISRO) and NHAI.
|
- It will be an annual assessment.
- The index findings will facilitate the comparison and ranking of various National Highways for timely and periodic intervention.
- The green cover would be estimated for every 1 km length of the National Highways.
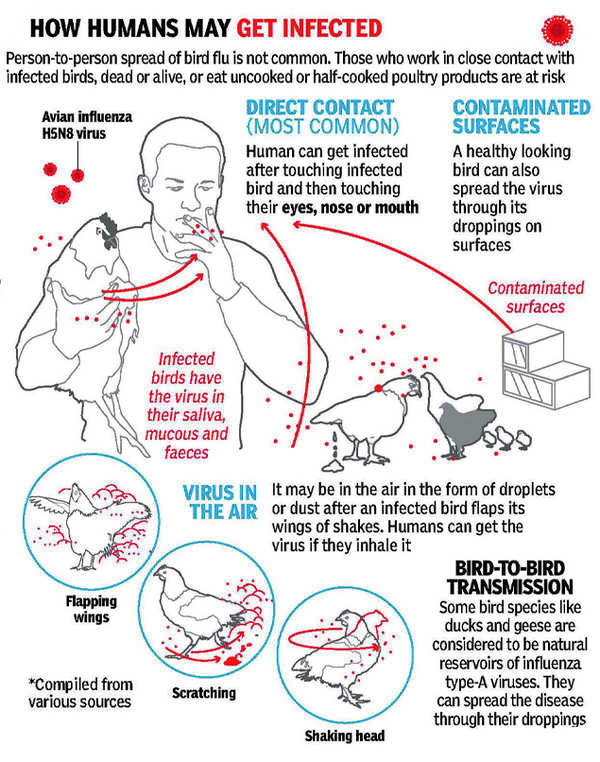
{GS3 – Envi – Species} Polar Bears | Avian Influenza
- Context (DTE): The first case of the death of a Polar bear due to Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) has been reported from the Arctic region.
Polar Bears
- Polar bears are the largest carnivorous land mammals on Earth.
- They are the only bear species to be considered marine mammals as they spend most of their lives on the sea ice of the Arctic Ocean for their food and habitat.
Physical Characteristics
- The bear’s outer layer of fur is hollow and reflects light, giving the fur a white colour that helps the bear remain camouflaged.
- The skin under the polar bear’s fur is black; this is evident only on the nose.
- Polar bears also have a thick layer of fat below the surface of the skin, which acts as insulation on the body to trap heat.
Distribution
- Most polar bears occur north of the Arctic Circle to the North Pole. There are some populations south of the Arctic Circle in the Hudson Bay of Manitoba, Canada.
- Polar bears live in Alaska, Canada, Russia, Greenland, and some northern islands owned by Norway, such as Svalbard.
- They are not found in the Antarctica region.
Diet
- They primarily feed on ringed seals and bearded seals.
Ecological significance
- The polar bear is the apex predator within its range and is a keystone species for the Arctic.
- They keep the population of Seals in check, thus maintaining the food chain and ecosystem health.
Other features
- They are solitary animals except when mating when a female raising her cubs forms a family group, or when many bears are attracted to a food source like a beached whale.
- Considered talented swimmers, polar bears can sustain a pace of six miles per hour by paddling with their front paws.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable (VU)
- CITES: Appendix II

Avian Influenza (H5N1)
- Avian influenza, or bird flu, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects birds.
- The H5N1 avian influenza virus was first detected in 1996 in China (‘H’ and ‘N’ stand for hemagglutinin & neuraminidase, the proteins on the virus’s surface that regulate entry and exit in host cells).
- These viruses (Type A) occur naturally among wild aquatic birds worldwide and can infect domestic poultry and other bird and animal species.
- Migrating waterfowl, most notably wild ducks, are the natural carriers of bird flu viruses.
- Strains of avian influenza viruses can generally be classified into two categories:
- Low pathogenicity avian influenza (LPAI) that typically causes little or no clinical signs;
- High pathogenicity avian influenza (HPAI) can cause severe clinical signs and possible high mortality rates.
- Transmission to humans: Most virus strains do not infect humans, but two contagious strains, H7N9 and H5N1, have caused serious medical complications in humans.
- The virus spreads to humans through close contact with live or dead infected birds.
- Human to human spread of avian influenza A viruses is rarely reported.
- Symptoms in people can range from mild upper respiratory tract infection (fever and cough) to severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (difficulty breathing), shock, and even death.
{GS3 – Envi – Species} Snow Leopard
- Context (TH): Snow Leopard has been declared the National Symbol of Kyrgyzstan.
- Snow leopard (or Ghost of the Mountains) is a keystone and indicator species of high-altitude habitat. It is a flagship species for the high-altitude Himalayan ecosystem.
- It is the 7th largest cat species in the world.
- Distribution: It is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. In India, it occurs in the Himalayan region.

- Habitat: Alpine and subalpine zones.
- Indian states/UTs with largest snow leopard population: 1st Ladakh > 2nd HP > 3rd Uttarakhand.
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, climate change, unregulated tourism, and competition with livestock.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Vulnerable | CITES: Appendix I | WPA,1972: Schedule I

{GS3 – IE – Industry} MoU between QCI and KVIC
- Context (PIB): The MoU between the Quality Council of India (QCI) and the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) was signed recently.
- The QCI will ensure the quality of ‘New Khadi of New India’ products to promote it as a ‘global brand’.
- QCI will assist the KVIC in training, productivity enhancement and marketability.
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
- KVIC is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament.
- In April 1957, it took over the work of the former All India Khadi and Village Industries Board.
Objectives of the KVIC
- Social objective: Providing employment.
- Economic objective: Producing saleable articles.
- Create self-reliance amongst low-income people and build a strong rural community spirit.
{GS3 – IE – MSME} Year end Recap of MoMSME
- Context (PIB): A year-end recap of the Ministry of MSME (MoMSME) schemes was presented.
Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
- PMEGP was launched in 2008 and works under the Ministry of MSME.
- PMEGP credit-linked subsidy scheme for providing employment opportunities by establishing micro-enterprises in the non-farm sector.
- The maximum project cost admissible for setting up a new enterprise is Rs. 50 lakhs in the manufacturing sector and Rs. 20 lakhs in the service sector.
- Geo-tagging of the PMEGP units and 2-day Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP) training are other features of PMEGP.
MSME Champions
- It aims to modernise processes, reduce waste, sharpen business competitiveness, and facilitate the National and Global reach and excellence of MSME clusters and entrepreneurs.
Components of MSME Champions
- MSME-Sustainable (ZED): It creates awareness amongst MSMEs about Zero Defect Zero Effect (ZED) practices and incentivises them for ZED Certification.
- MSME-Competitive (LEAN): It will train entrepreneurs to improve the efficiency of production processes with maximum resource utilisation to make them globally competitive and LEAN-certified.
- MSME-Innovative: It will help MSMEs with innovation in incubation, design intervention and protecting IPR.
CHAMPIONS 2.0 Portal
- It was launched in 2023 as an upgraded version of the “CHAMPIONS” portal.
- The portal will enhance user-friendliness and grievance resolution turn-around time to promote e-governance.
Contribution by MSME Technology Centres in the Space and Defence Sector
- Central Tool Room & Training Centre (CTTC), Bhubaneswar, manufactured and supplied precision components for the ‘Chandrayaan-3’ and ‘Aditya L1’ missions.
- The Institute for Design of Electrical Measuring Instruments (IDEMI), Mumbai, has manufactured and supplied a guiding device used in the assembly of the Chandrayaan-3.
- MSME technical institutions are also undertaking indigenisation of defence components.
{GS3 – IE – RBI} Internationalization of Rupee
- Context (IE): India recently made payment in Indian Rupees to UAE for crude oil imports.
- Internationalisation of Rupee involves increasing the use of the rupee in cross-border transactions.
- It involves promoting the rupee for import and export trade and other current account transactions, followed by its use in capital account transactions.
- It requires:
- Further opening up of the currency settlement,
- Strong currency swap and forex market,
- Full convertibility of the currency on the capital account and
- Cross-border transfer of funds without any restrictions.
|
|
Initiatives towards Internationalisation of Rupee
- Trade Settlement in Indian Rupee with countries like Nepal, Bhutan, Iran etc.
- ‘International Settlement of Trade in Indian Rupee’ through special VOSTRO accounts.
- Currency Swap Agreement with SAARC, UAE, BRICS, etc.
- Issue of Masala Bonds.
|
Advantages of Rupee Internationalisation
- Reduces the cost of doing business, enables better business growth, and improves the chances for Indian businesses to grow globally.
- Reduces the need for holding foreign exchange reserves.
- Make India less vulnerable to external shocks.
- Improves bargaining power of Indian businesses.
- Help in circumventing sanctions. E.g. Sanctions on Russia and Iran.
- Results in quick settlement of transactions.
Challenges Associated
- It may increase volatility in the rupee’s exchange rate in the initial stages.
- It may accentuate an external shock, given the open channel of the flow of funds into and out of the country and from one currency to another.
- The rupee is not fully convertible. Foreign traders face limitations and require government approvals when converting large sums of rupees into foreign currencies, making the process less attractive.
Way Forward
Short-term measures
- Allow non-residents to open rupee accounts. The ability to open accounts outside the country of the currency is a foundational element of the internationalisation of a currency.
- Step up measures for including Indian Government Bonds (IGBs) in global bond indices.
- Rationalize the FPI regime to facilitate foreign investments into the Indian debt markets (both government and corporate).
Medium-term measures
- Review withholding tax for masala bonds issuances.
- Expand the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system for settling international transactions.
- Include the rupee in the Continuous Linked Settlement (CLS) system.
Long-term measures
- Include the rupee in the Special Drawing Rights (SDR) basket.
- Use bilateral and multilateral payment and settlement mechanisms, such as Asian Clearing Union (ACU), to internationalize the rupee.
{GS3 – IE – Skill} Skills on Wheels
- Context (PIB): The “Skills on Wheels” programme was launched recently.
- The National Skill Development Corporation and IndusInd Bank will implement the programme.
- Over five years, it will train 60000 rural youths to take industry-relevant skill training to improve their theoretical and practical knowledge.
- It is a customised bus with retrofitted tools to promote the ‘Skill India Mission’.
National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)
- It is a not-for-profit public limited company incorporated in 2008.
- The Ministry of Finance set it up as a Public Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- The GoI, through the MSDE (Ministry for Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship), holds 49% of the share capital of NSDC.
- The private sector holds 51% of the share capital.
- It aims to promote skill development by creating for-profit vocational institutions.
{GS3 – Infra – Initiatives} GRID-INDIA
- Context (PIB): 7th Grid-India Day was celebrated recently.
- GRID-INDIA was separated from POWERGRID in 2017 as a Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE) under the Ministry of Power.
- GRID-INDIA is entrusted with the crucial responsibility of ensuring the integrated operation of the electricity grid in a reliable, efficient, and secure manner.
{GS3 – S&T – Bodies} Postponement of Indian Science Congress (ISC)
- Context (IE): The Department of Science and Technology (DST) withdrew from the funding and organisation of the 109th ISC on allegations of irregularities.
- The 109th edition of the ISC was initially meant to be hosted by Lucknow University (LU) on the theme ‘The Global Perspective on Science and Technology for a Sustainable Future’.
Indian Science Congress (ISC)
- The Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA) organises annual national-level ISC with support from DST.
- It sees participation from institutions funded by the DST, Department of Space, Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The Prime Minister always inaugurates the ISC.
- Except for the two years following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022), the Indian Science Congress has been held every year since 1914.
- The 108th edition of the Congress was held in Nagpur from January 3-7, 2023.
Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA)
|
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Satellite-Based Internet Connectivity
- Context (IE): SpaceX launches first ‘direct-to-cell’ Starlink satellites.
- Satellite based internet connectivity refers to the use of artificial satellites positioned in space to facilitate communication over long distances.
Working Mechanism
- Satellite communication works by using satellites to relay signals between two points on Earth.
- The satellites are placed in orbit around the Earth, and they act as a mediator between the two points.
- When a signal is sent from one point to the satellite, the satellite amplifies the signal and retransmits it to the other point.

Benefits
- Global coverage: Satellites can provide coverage to remote and under served areas where terrestrial infrastructure is limited or non-existent.
- Scalability: Satellite networks can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate increasing user demand, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Security: Satellite communication can be more secure than terrestrial communication, as it is less susceptible to interception.
- Reliable communication: Independence from terrestrial infrastructure enables seamless communication in challenging terrains making them more resilient to disasters or physical communication.
- Low Latency makes satellite communication more suitable for applications that require real-time interaction, e.g. high-frequency trading, and teleconferencing.
Challenges associated with space satellite communication
- High cost involved for deployment, operation, and launching satellites into space, building ground station infrastructure, and associated maintenance expenses.
- Risk of Debris: Satellite communication requires a network of satellites for internet coverage raising the problem of space debris and their collision (Kessler Syndrome) hindering space exploration.
- Signal Interference: Weather conditions like storms and other atmospheric disturbances can degrade the quality and reliability leading to disruptions, reduced data rates, or signal loss.
- Latency: Transmitting signals from Earth to satellites in space and back results in a noticeable delay in communication making it problematic for real-time applications.
- Limited bandwidth: They can only transmit a limited amount of data at a time posing problem for applications that require high bandwidth, e.g. streaming video or online gaming.
- Coverage gaps: Physical features like mountains, tall buildings, etc can obstruct the requirement of a clear line of sight path leading to signal attenuation.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)