
Diseases Caused by Microorganisms
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Microbes or Microorganisms – Diseases Caused by Microorganisms – Diseases Caused By Bacteria, Viruses, Protozoans and Fungi.
Source: NCERT Science Textbooks Class 6-12, Wikipedia
Microbes or Microorganisms
- Microorganisms [microbes] include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, some algae, viruses, viroids and also prions that are proteinacious infectious agents. Viruses reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal.
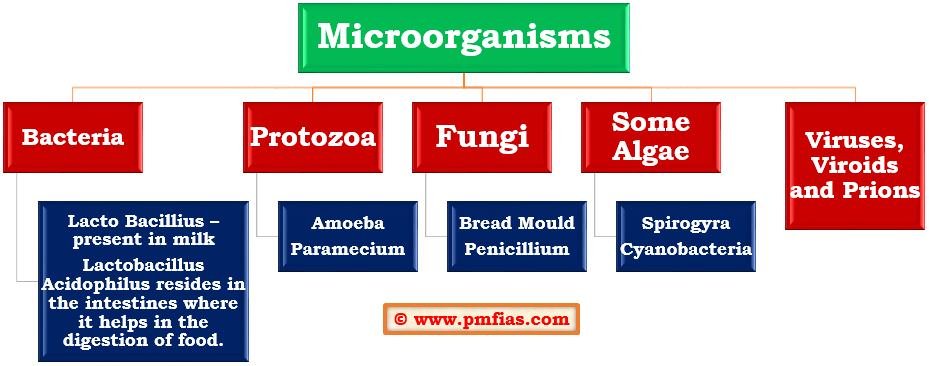
- Microorganisms may be single-celled like bacteria, some algae and protozoa, or multicellular, such as algae and fungi. They can survive under all types of environment, ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands.
- Microorganisms like amoeba can live alone, while fungi and bacteria may live in colonies.
Diseases Caused by Microorganisms
Disease |
Causative Agent |
Mode Of Transmission |
Type Of Organism Affected |
Details |
Diseases Caused By Bacteria |
||||
| Acne vulgaris (or simply acne or pimples)
|
Propionibacterium acnes | Direct contact/close contact | Humans/
Adolescents |
Skin disease that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with dead skin cells and oil from the skin.
Causes == Genetics + Excessive growth of the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes. |
| Anthrax
|
Bacillus anthraces | Contact with infected meat | Most animals including humans | Causes skin infections and Gastrointestinal (GI) infection that are fatal.
French scientist Louis Pasteur developed the first effective vaccine in 1881. |
| Cholera | Vibrio cholerae | Water/food | Humans | Effects small intestine. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and muscle cramps may also occur. Diarrhea can be so severe that it leads within hours to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. |
| Citrus Canker | Xanthomonas axonopodis | Air | Citrus fruit plants | Infection causes lesions on the leaves, stems, and fruit of citrus trees. |
| Diptheria
|
Corynebacterium diphtheriae | Air/direct contact | Humans | Symptoms: sore throat and fever. The neck may swell in part due to large lymph nodes. Complications may include myocarditis, inflammation of nerves, kidney problems, and bleeding problems due to low blood platelets. Myocarditis may result in an abnormal heart rate and inflammation of the nerves may result in paralysis. |
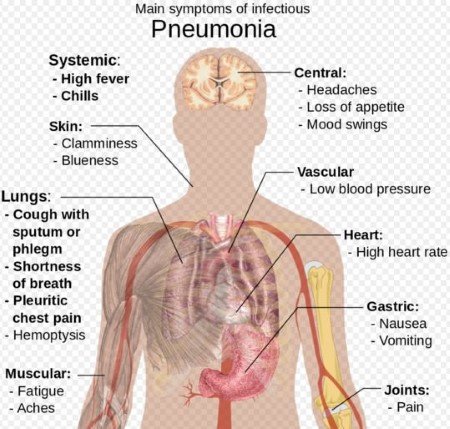
| Pneumonia
[caused by bacteria or viruses] |
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae | Air borne droplets of sneeze | Humans | Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli.
|
| Peptic ulcers | Helicobacter pylori | Humans | Ulcers in the lining of stomach and starting part of small intestine | |
| Plague | Yersinia pestis | Air/ direct contact | Humans | Unhygienic conditions is the main cause. [You know why Surat is one of the cleanest cities in India?]
The symptoms of plague depend on the concentrated areas of infection in each person: bubonic plague in lymph nodes, septicemic plague in blood vessels, pneumonic plague in lungs. |
| Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Air | Humans | Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections do not have symptoms, known as latent tuberculosis. About 10% of latent infections eventually progresses to active disease which, if left untreated, kills about half of those infected. The classic symptoms of active TB are a chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. |
| Typhoid | Salmonella typhi | Water | Humans | Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. |
Diseases Caused By Viruses |
||||
| AIDS | Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | Blood exchange | Humans and primates | Severely weakens immunity and makes way for a number of other pathogens. |
| Chicken Pox | varicella zoster virus (VZV) | Air/contact | Humans | Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease. The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters. Less severe than small pox. Almost eradicated after the invention of vaccination. |
| Small Pox | Variola major and Variola minor | Air/contact/water | Humans | One of the highly dreaded diseases that is highly contagious.
Almost eradicated after the invention of vaccination. |
| Chikungunya | Chikungunya virus | Aedes mosquitoes, such as A. aegypti and A. albopictus | Causes severe joint pains. Animal reservoirs of the virus include monkeys, birds, cattle, and rodents. This is in contrast to dengue, for which primates are the only hosts | |
| Cold, influenza (flu) and most coughs | Rhino viruses | Air borne droplets of sneeze | Humans | Summer are hostile for the virus. Most common during winter months. |
| Dengue fever | Flavivirus | Female Aedes mosquito | Humans | high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash.
In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into the life-threatening dengue hemorrhagic fever, resulting in bleeding, low levels of blood platelets and blood plasma leakage, or into dengue shock syndrome, where dangerously low blood pressure occurs. |
| Ebola | Ebola virus | Animal to man | Humans and Some Animals | Ebola infection shows a sudden onset of the disease resulting initially in flu-like symptoms: fever, chills and malaise.
As the disease progresses, it results in multi-system involvements indicated by the person experiencing lethargy, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and headache.
|
| Foot and Mouth Disease | Picornavirus[genus Aphthovirus] | Close-contact animal-to-animal spread | Animals | Serious problem to animal farming in India. |
| Hepatitis B | hepatitis B virus (HBV) | Blood Exchange, STD [Sexually transmitted disease] | Humans | Affects the liver. Acute as well as chronic. |
| Measles | measles virus | Air | Humans | Complications occur in about 30% and may include diarrhea, blindness, inflammation of the brain, and pneumonia among others. |
| Polio or Poliomyelitis
|
Poliovirus | Water/faecal-mouth | Humans | Weak muscles leading to deformations. |
| Zika | Zika virus
|
Aedes mosquitoes, such as A. aegypti and A. albopictus | Humans | 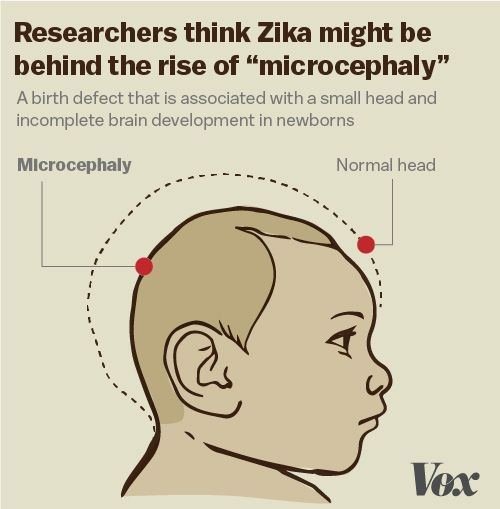 |
Diseases Caused By Protozoans |
||||
| Amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery) | Entamoeba histolytica | Contaminated Water/food | Humans | Symptoms may include abdominal pain, mild diarrhoea, bloody diarrhea or severe colitis with tissue death and perforation. This last complication may cause peritonitis. People affected may develop anemia due to loss of blood. |
| Dysentery | Leishmania | |||
| Kala-Azar or Visceral leishmaniasis | Leishmania genus | Sandflies | Humans | This disease is the second-largest parasitic killer in the world (after malaria).
The parasite migrates to the internal organs such as the liver, spleen (hence “visceral”), and bone marrow, and, if left untreated, will almost always result in the death of the host. Signs and symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and substantial swelling of the liver and spleen. |
| Malaria | Different species of Plasmodium (P. vivax, P. malaria and P. falciparum) | Female Anopheles mosquito | Humans | Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases it can cause yellow skin, seizures, coma, or death. |
| Sleeping Sickness | Trypanosoma | Infected tsetse fly | Humans | Initially, in the first stage of the disease, there are fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains. This begins one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness and trouble sleeping. |
| Yellow Vein Mosaic of Okra [Ladies finger] | Bhendi yellow vein mosaic virus | Insect | Okra plant | Okra are dwarfed, malformed. |
Diseases Caused By Fungi |
||||
| Ringworms | Fungi belonging to the genera Micr Trichophyton and Epidermophyton | Skin-skin contact | Humans | The fungi that cause parasitic infection, collectively dermatophytes, feed on keratin, the material found in the outer layer of skin, hair, and nails. |
| Rust of wheat | Puccinia rust fungus | Air/seeds | Wheat and other crops | Wheat leaf rust is a fungal disease that affects wheat, barley and rye stems, leaves and grains. In temperate zones it is destructive on winter wheat because the pathogen. overwinters. Infections can lead up to 20% yield loss exacerbated by dying leaves which fertilize the fungus. |










But cyanobacteria is NOT an algae… it is a prokaryote, it the oldest living bacteria. NOT an algae. please update your information