Molecule, Ion, Molecules of Elements & Compounds, Atomicity
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Molecule
- A molecule is a group of atoms that are chemically bonded together (held together by attractive forces).
- A molecule can be defined as the smallest particle of an element (e.g., O2) or a compound (e.g., H2O) that is capable of independent existence and shows all the properties of that substance.
- Atoms of the same element (e.g., O2) or of different elements (e.g., H2O) can join together to form molecules.
- Law of conservation of mass: Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Law of constant proportions: Many compounds are composed of two or more elements and each such compound has the same elements in the same proportions, irrespective of where the compound came from.
- In a compound such as water, the ratio of the mass of hydrogen to the mass of oxygen is always 1:8.
- Thus, if 9 g of water is decomposed, 1 g of hydrogen and 8 g of oxygen are always obtained.
- Law of constant proportions is also known as the law of definite proportions (in a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass).
Source | Credits | Picture Credits: NCERT General Science
Molecules of Elements and Compounds
Molecules of elements
- The molecules of an element are constituted by the same type of atoms. E.g., O2
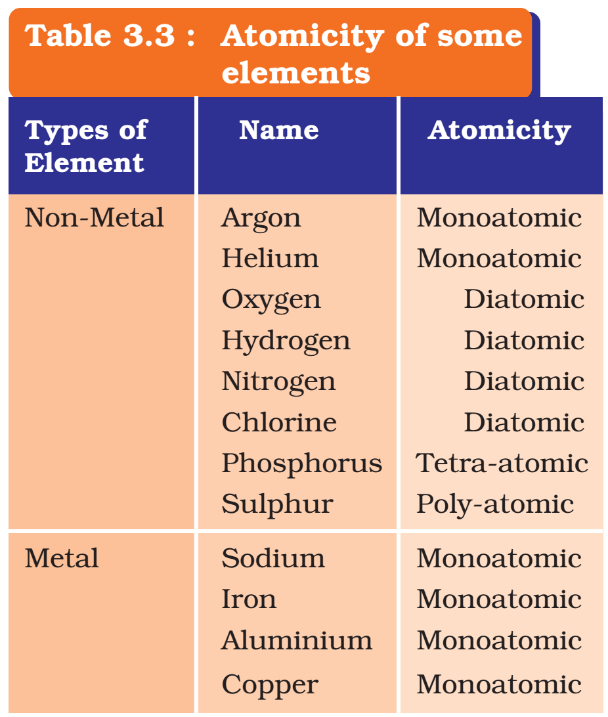
- Molecules of many elements, such as Argon (Ar), Helium (He) etc. are made up of only one atom of that element. But this is not the case with most of the non-metals.
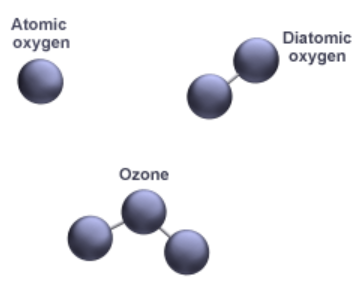
- E.g. a molecule of oxygen consists of two atoms of oxygen and hence it is known as a diatomic molecule.
- If 3 atoms of oxygen unite into a molecule, instead of the usual 2, we get ozone (O3).
- The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity.
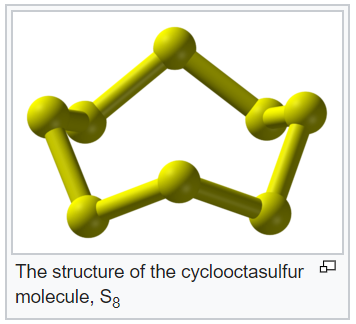
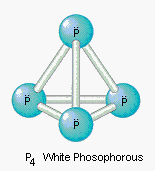
- Molecules of metals and some other elements, such as carbon, do not have a simple structure but consist of a very large and indefinite number of atoms bonded together.
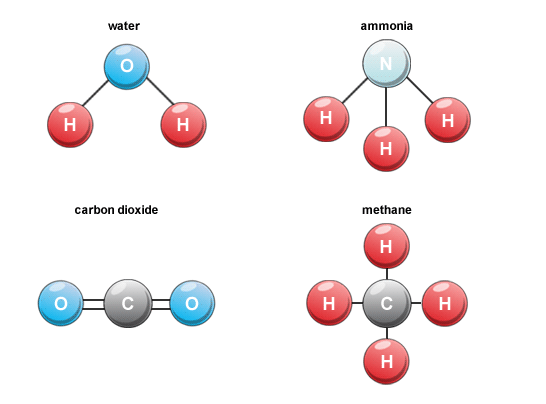
Molecules of compounds
- Atoms of different elements join together in definite proportions to form molecules of compounds. E.g. H2O, CO2, etc.
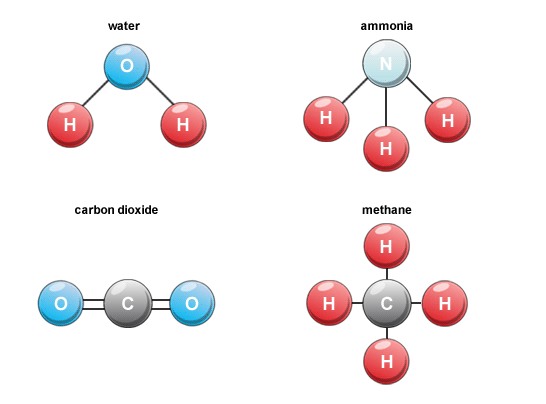
- Molecule is the general term used to describe any atoms that are connected by chemical bonds.
- A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements.
- All compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
- E.g. Hydrogen gas (H2) is a molecule, but not a compound because it is made of only one element.
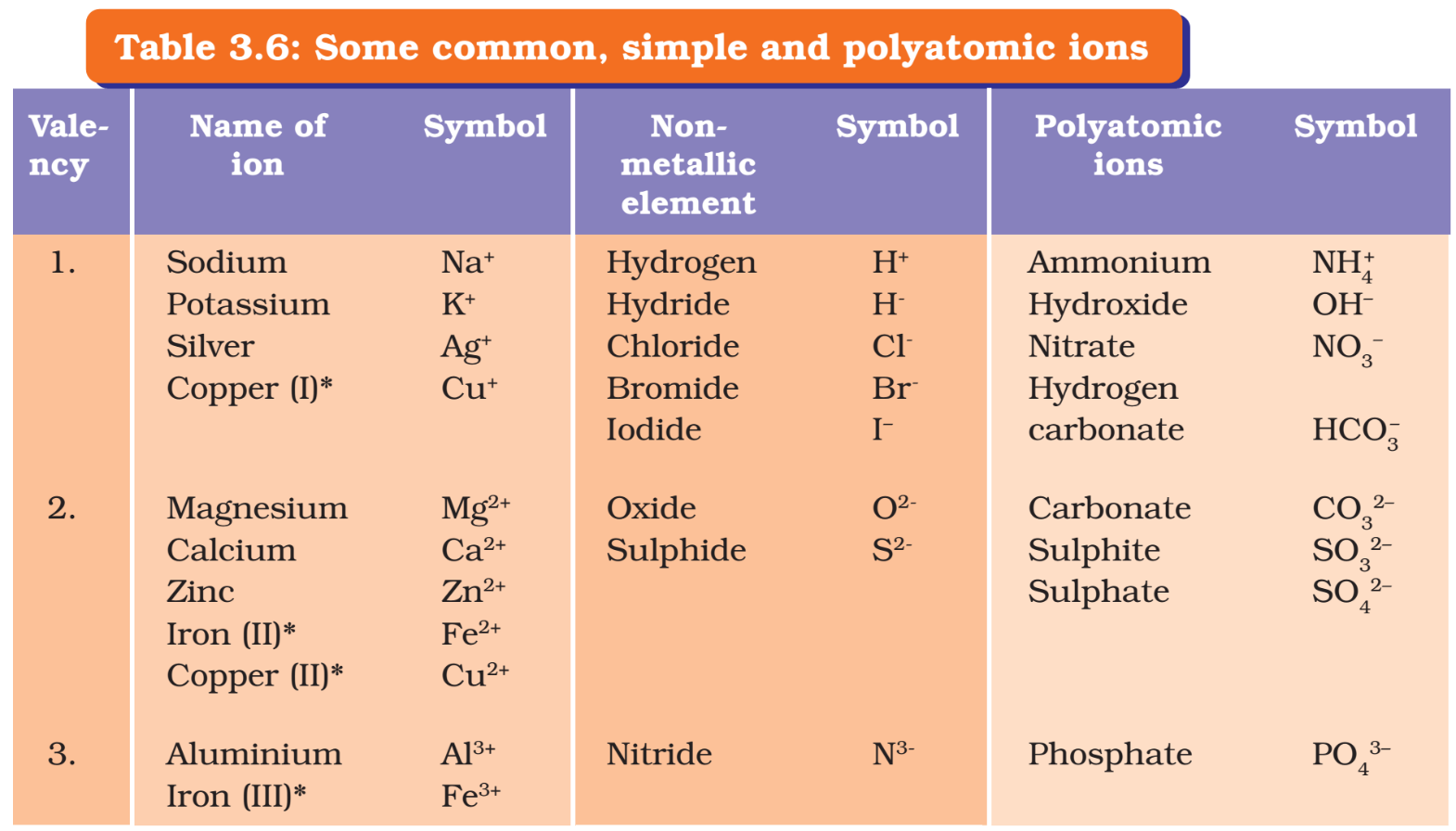
What is an Ion?
- Compounds composed of metals and non-metals contain charged species known as ions.
- An ion is a charged particle and can be negatively or positively charged.
- A negatively charged ion is called an ‘anion’ and the positively charged ion, a ‘cation’.
- E.g., The constituent particles of sodium chloride (NaCl) are positively charged sodium ions (na+) and negatively charged chloride ions (cl–).
- Ions mainly consist of a single charged atom or a group of atoms that have a net charge on them.
- A group of atoms carrying a charge is known as a polyatomic ion.
Summary
- Law of Conservation of Mass: During a chemical reaction, the sum of the masses of the reactants and products remains unchanged.
- Law of Definite Proportions: In a pure chemical compound, elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass.
- An atom is the smallest particle of the element that can exist independently and retain all its chemical properties.
- A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound capable of independent existence under ordinary conditions. It shows all the properties of the substance.
- A chemical formula of a compound shows its constituent elements and the number of atoms of each combining element.
- Clusters of atoms that act as an ion are called polyatomic ions. They carry a fixed charge on them.
Source | Credits | Picture Credits: NCERT General Science