Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – April 02, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – MIH – Reorganization} Utkala Dibasa
- Context (IE): April 1 is celebrated as Utkala Dibasa.
- On this day in 1936, a separate Odisha state (then Orissa) was carved out from the erstwhile Bihar and Orissa Province, and the addition of Koraput and Ganjam districts of the Madras Presidency.
- It is one of two Indian states whose formation date predates Independence (the other is Bihar).
- Odisha is also the first state in the country to be consciously created on a linguistic basis.
Odisha in Modern History
- In 1568, the armies of the Bengal Sultanate conquered Odisha. Later, it was under Marathas.
- By 1760, the British had annexed Northern Circars, comprising the southern coast of Odisha, as a result of the Second Carnatic War. Later, it became part of the Madras Presidency.
- After the Marathas were defeated in the Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803), the northern and western districts of Odisha became part of the Bengal Presidency.
Movement for an Odia-speaking state
- In the 19th century, the movement for a separate Odia-speaking state emerged.
- Utkal Sabha was formed in 1882 for the same.
- In 1903, the still-active Utkal Sammilani was formed under the leadership of Madhusudan Das.
- Formation of Bihar and Orissa Province, 1912: The Bengal Presidency’s non-Bengali-speaking regions were finally carved out.
- Madhusudan Das also joined the legislature of the united Bihar and Orissa province and continued the statehood movement there.
- Separate Odia statehood demand came to prominence in the 1920s when the Indian National Congress adopted the reorganisation of provinces on a linguistic basis as a key part of its agenda.
- Orissa Province was finally created in 1936 with official reasons of administrative & political prudence.
- It was carved out from the existing Bihar & Orissa Province, Madras Province, and Central Province.
- However, 26 princely states, a part of the Eastern States Agency, continued to exist within Orissa Province’s borders until Independence.
|
{GS2 – Polity – IC – FRs} Right to Equality
- Context (TH): The rules of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA), 2019, were recently notified. This law has been challenged before the SC on the grounds that it violates Article 14 of the IC.
Article 14- Equality before law
- The State shall not deny any person equality before the law or equal protection of the laws within the territory of India.
- Article 14 rejects any discrimination based on caste, race, religion, place of birth or sex.
- This Article has a wide ambit and applicability to safeguard the rights of people residing in India.
This article is divided into two parts
- Equality before the Law: This part of the article indicates that all are to be treated equally in the eyes of the law.
- This is a negative concept as it implies the absence of any privilege in favour of any person. This is a substantive part of the article.
- Equal protection of the Laws: This part means that the same law will be applied to all people equally across society.
- This is a positive concept as it expects positive action from the state. This is a procedural part of Article 14.
Doctrine of Anti Arbitrariness
- The Supreme Court drastically increased the scope of Article 14 by including the executive discretion under its ambit.
E.P. Royappa v. State of Tamil Nadu, 1974
- Article 14 gives a guarantee against the arbitrary actions of the State.
- The Right to Equality is against arbitrariness. Since the executive and legislature are enemies, it is essential to protect the laws from the executive’s arbitrary actions.
S.G. Jaisinghani v. Union of India
- It is crucial to emphasise that the absence of arbitrary power is the first essential of the rule of law upon which our whole constitutional system is based.
- In a system governed by the rule of law, the executive authority’s discretion must be confined within clearly defined limits.
Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India
- A trinity exists between Article 14, Article 19 and Article 21 of the IC.
- Any law interfering with the personal liberty of a person must satisfy a triple test:
- It must prescribe a procedure;
- The procedure must withstand the test of one or more of the fundamental rights conferred under Article 19, which may be applicable in a given situation; and
- It must also be liable to be tested with reference to Article 14.
Natural Justice as a part of Article 14
- The principle of natural justice helps prevent miscarriage.
- These principles also check the arbitrary power of the state.
Manifest arbitrariness test
- It is a new test developed by the courts to regulate arbitrary executive actions.
- Unlike the reasonable classification test, it has no shape or form.
- The Court has said that what is “without adequate determining policy or principle” is manifestly arbitrary.
- Legislation becomes manifestly arbitrary when it is unfair, unreasonable, discriminatory, not transparent, biased, or based on favouritism or nepotism.
- When something is done by the legislature that is excessive and disproportionate, such legislation would be manifestly arbitrary.
- Therefore, arbitrariness, in the sense of manifest arbitrariness, would apply to negate legislation as well under Article 14.
Doctrine of Reasonable Classification
- Article 14 promotes the idea that reasonable classification is not only allowed but also necessary for societal progress, preventing improper discrimination and ensuring equitable treatment.
- Article 14 does not mandate that law be general or universally applicable but recognises the need for tailored laws catering to specific classes.
- It refers to the lawful and justifiable categorisation of individuals or groups based on intelligible differentia that distinguish them from others.
- Unequals and Equals: It acknowledges that individuals in different situations or positions may warrant different treatment.
- It ensures that equals are treated equally while allowing for reasonable distinctions.
- Legitimate Control Policies: These permit the enactment of laws tailored to specific locations and legitimate control policies in the state’s interest and safety and security.
- Avoidance of Class Legislation: The doctrine prohibits class legislation that arbitrarily selects a large group of persons without reasonable justification for differential treatment.
- Reasonable classification helps the State make laws for the welfare of different sections of society and provide equitable treatment to everyone.
Classification Test
- The classification test is a tool that the Court employs to decide what state action would violate equality.
- The classification test is a judicial import from the U.S. dating back to 1950.
Indra Sawhney v UOI, 1993
- “The Court interpreted the relation between Article 14 and Article 16.
- Article 16(1) is a facet of Article 14. Just as Article 14 permits reasonable classification, so does Article 16(1).
- A classification may involve the reservation of seats or vacancies.
- Articles 14 and 16 aim to achieve equality and equality of opportunity, and Clause (4) of Article 16 achieves the same objective.
- Both provisions have to be harmonised, keeping in mind that both restate the principle of equality enshrined in Article 14.
Essentials of Classification Test
- Intelligible Differentia: A valid classification must be based on intelligible differentia that differentiates the grouped individuals from those excluded.
- Rational Nexus: The differentia must have a rational nexus with the objective the legislation seeks to achieve.
- Legitimate Purpose: It should serve a legitimate legislative purpose, such as addressing social inequalities, without violating fundamental rights.
- Fairness and Non-Arbitrariness: The classification should be fair and not arbitrary. It ensures that individuals are treated differently for valid reasons and not based on whims or prejudices.
- Judicial Review: The doctrine is subject to judicial review, wherein courts assess the reasonableness and constitutionality of classifications to prevent unfairness or arbitrariness.
Role played by the doctrine of reasonable classification in Administrative Law
- It plays an important role in the administrative laws in the following ways:
Guide the interpretation of statutes.
- It guides the formation of statutes so that their interpretation does not give rise to any irrational or ludicrous conclusion.
- The legislators and the judges use this doctrine as their guiding principle for enacting or interpreting laws.
- It helps them deliver fair justice to the people without any arbitrariness.
Testing the legitimacy of the law
- It determines the legitimacy of any bill or law that is introduced or enacted by the Government.
- This doctrine determines the rationality of that bill or law.
- It clarifies whether the law is justifiable or not, which in turn reduces problems and increases acceptability.
Provide a standard for judicial review
- This doctrine is also helpful in providing a standard for judicial review.
- The judicial review nullifies any administrative action that seems irrational or arbitrary.
- Some discretionary powers have been granted to the administration, but those are also subject to judicial review.
{GS3 – Envi – Species} Germany legalises Cannabis
- Context (TH): Germany became the largest EU nation to legalise recreational use of Cannabis.
- Adults over 18 are now allowed to carry 25 gms. dried cannabis & cultivate up to three marijuana plants.
- The ban will continue for those under 18s and within 100 metres of schools, kindergartens, and playgrounds.
- Earlier, Malta and Luxembourg legalised recreational use in 2021 and 2023, respectively.
Cannabis/Hemp
- Species: Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis.
- It is an annual, dioecious, flowering herb. Also referred to as “Marijuana”, a Mexican term.
- Hashish is an unpollinated female plant of Cannabis. Cannabis oil (hashish oil) is obtained by solvent extraction of the crude plant material or of the resin.
- Main Chemical components: Cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
- CBD: Provides relief to chronic pain without causing psychoactive side effects.
- THC: Psychoactive components of Marijuana.
|
Status in India
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) prohibits the sale and production of cannabis resin and flowers. Still, the use of leaves and seeds of the cannabis plant is permitted (due to negligible THC concentration).
- Cannabis farming is legalised in Uttarakhand and some districts of Gujarat, MP, & UP.
- Himachal Pradesh government is also considering the legalisation of Cannabis cultivation.
UN Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs 1961
|
{GS3 – Envi – Species} Indian laurel tree (Terminalia tomentosa)
- Context (TH): The indigenous knowledge of the Konda Reddi tribe (PVTG) about the Indian laurel tree has proven resourceful.

- Indian Laurel tree is found in Papikonda National Park (Alluri Sitharama Raju district of Andhra Pradesh).
- Unique quality: During parched summers, it stores water that has a strong smell and tastes sour, an amazing adaptation.
- Species of Terminalia are native to southern and southeast Asia in India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam.
- Habitat: Dry and moist deciduous forests up to 1000 m.
Uses
- Timber: Wood (furniture, musical instruments, etc.).
- Leaves: Food for Antheraea paphia (silkworms), which produce the Tassar silk (Tussah).
- Bark: Medicinal use against diarrhoea and extraction of Oxalic acid.
- Fruit: Yields pyrogallol and catechol to dye and tan leather.
|
For more details about Konda Reddi tribe, visit > Konda Reddi tribe.
{GS3 – IE – RBI} 90 years of RBI
- Context (PIB): The Prime Minister addressed the opening ceremony of RBI@90, marking 90 years of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- The Prime Minister also released a commemorative coin to celebrate this milestone, as RBI commenced its operations on April 1, 1935.
Establishment of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Enactment of the RBI Act: In 1934, the British government passed the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- Formation of RBI: The RBI was formally established in Calcutta (now Kolkata) on April 1, 1935.
- Basis of Establishment: on the recommendations of the Royal Commission on Indian Currency & Finance in 1926. This commission is also known as the Hilton Young Commission.
- The RBI’s concept was based on the strategies formulated by Dr Ambedkar in his book The Problem of the Rupee–Its Origin and Its Solution.
- Nationalised in 1949; before this, private stakeholders held the bank.
- The First Governor of RBI was Sir Osborne Smith.
- The first Indian Governor of RBI was C D Deshmukh.
Functions of RBI
| Functions | Description |
| Issuer of Currency Notes |
|
| Banker to other Banks |
|
| Banker to the Government |
|
| Foreign Exchange Management |
|
| Credit control |
|
| Supervisory Function |
|
| Promotional Functions of RBI |
|
{GS3 – IE – Securities} Front-running
- Context (ET): SEBI has barred two individuals from the securities market for three years and fined them over Rs 77 lakh for their involvement in front-running.
- SEBI had found that the offenders had access to advanced information about impending trades of a significant client.
- Following that, they executed trades in the NSE equity segment and NSE equity derivative segment to make profits.
- This is violative of PFUTP (Prohibition of Fraudulent and Unfair Trade Practices) rules.
- The fine amount will be credited to the Investor Protection and Education Fund (IPEF).
What is Front-running?
- Front-running, also known as forward-trading or tailgating, is an illegal practice in the stock market.
- It involves trading based on advanced information before it’s available to clients.
- It can happen when traders know their firm plans to buy several shares of a particular stock and buy shares from the same stock on their own.
Investor Protection and Education Fund (IPEF)
- Established under the provision of the Companies Act, 2013.
-
Legal Framework:
- Amounts credited to IEPF are maintained under the Consolidated Fund of India (Art 266 of IC).
- Administered by the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- Sources of Funds: Various amounts, such as dividends, application money, matured deposits, etc., that remain unpaid or unclaimed for seven years must be transferred to the IEPF.
-
Utilization:
- Used for promoting investor awareness and protecting investor interests.
- Funds may be utilised to distribute disgorged amounts among eligible applicants who have suffered losses due to wrongful actions by any person, in accordance with court orders.
|
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Ozone discovery in Callisto (Jupiter’s moon)
- Context (TH): An international team of scientists, including from India, has discovered strong evidence indicating the presence of ozone on Jupiter’s moon Callisto.
- The study focused on the chemical evolution of SO2 astrochemical ice under ultraviolet irradiation, aiming to understand the formation of ozone.
- By analysing UV absorption spectra of irradiated ice samples, the researchers identified a distinct signature indicating the presence of ozone.
Significance of Ozone for Human Life
- Not all sunlight is beneficial; ultraviolet radiation, particularly UV-B and UV-C, can harm organisms.
- UV-B (290-320 nanometres) and UV-C (100-280 nanometres) can damage DNA, cause mutations, and increase the risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Ultraviolet light also inhibits plant growth and harms various organisms.
- The ozone layer in the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs UV-B and UV-C radiation.
- Ozone, made of three oxygen atoms, forms a shield in the lower part of the stratosphere (15-35 km above ground).
- Without the ozone layer, higher levels of UV radiation would make the planet uninhabitable for many species and disrupt ecosystems.
Significance of this research
- Ozone is crucial for shielding life from harmful UV radiation on Earth, highlighting its importance for habitability.
- Its detection on Callisto suggests the presence of oxygen, essential for the formation of complex molecules required for life.
- The discovery of ozone on Callisto raises questions about the moon’s potential habitability and extends to other icy moons in the Solar System.
- Insights from this research could inform our understanding of habitable conditions beyond Earth.
|
{Prelims – Envi – Species} Nellore Cattle
- Context (MC): The world’s most expensive cow, an Indian breed (Nelore cow), was sold for $4.3 million at auction in Brazil.
- The sale of the cow, named Viatina-19 FIV Mara Imóveis, highlights the importance of superior genetic qualities in the livestock industry.
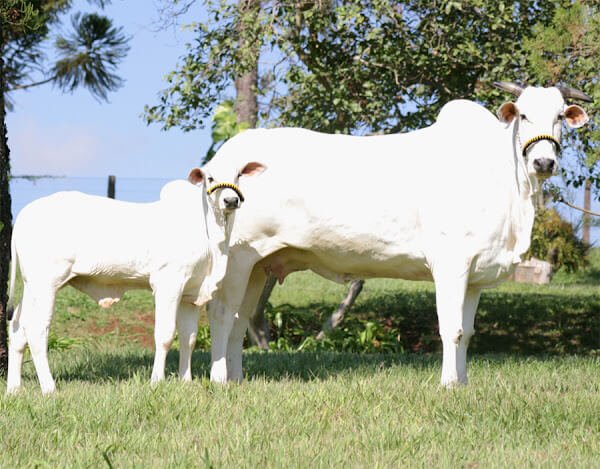

- Nellore Cattle are named after the Nellore district in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is known for its lustrous white coat and iconic hump.
- These cattle are descendants of the robust and adaptable Ongole cattle of India.
- Significance: Its ability to thrive in hot temperatures, thrive on poor-quality forage, have an efficient metabolism, and resist parasitic infections have made it highly sought after by cattle ranchers.
- Nellore cattle are primarily reared for their high-quality beef.
- Its genetic material holds the promise of producing offspring with enhanced traits.
- Nellore cows make up 80 per cent of Brazil’s bovine population. Nellore breed thrives in Brazil due to its resilience and adaptability to harsh climates.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)