Current Affairs February 20, 2024: BAPS Temple, Sudden reversal of Pollution cycle, National Council for Transgender Persons, National Film Awards, Revocation of GRAP Stage II, Satyendra Nath Bose & Quantum Physics, Northern Green Anaconda
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
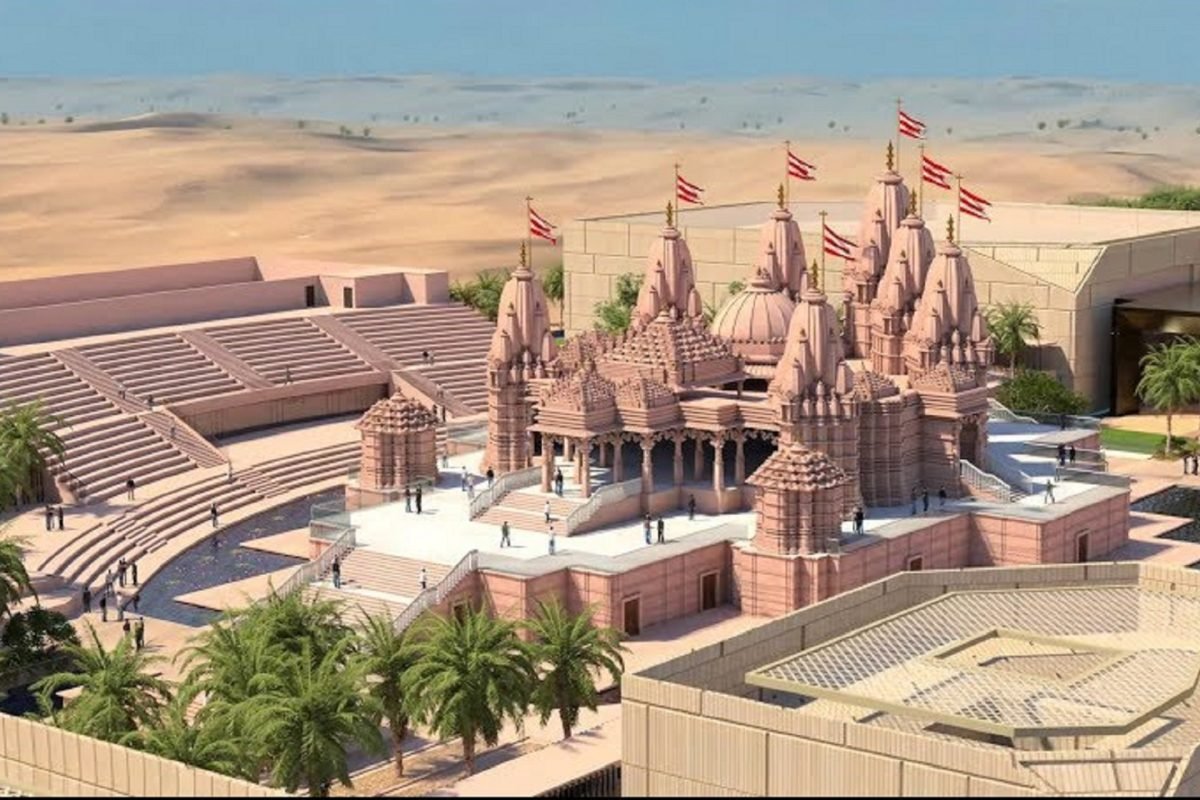
{GS1 – A&C – Architecture} BAPS Temple
- Context (IE): During a two-day visit to UAE, PM Narendra Modi inaugurated the BAPS Swaminarayan temple in Abu Dhabi.
- The BAPS temple is the first Hindu temple in the UAE.
- It is built at an estimated cost of Rs 700 crore.
- It is located in the Abu Mureikha area, about 50 km from the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque.
- The land for the temple complex has been built was gifted by Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan (President of the UAE) in 2015.
- It is Spread over 27 acres, and the temple complex is on 13.5 acres.
- It was first envisioned by Pramukh Swami Maharaj, spiritual leader of the BAPS Swaminarayan Sanstha, in 1997.

About BAPS
- BAPS stands for Bochasanwasi Akshar Purushottam Swaminarayan Sanstha (A Vaishnav sect of Hinduism), a Hindu denomination within the Swaminarayan Sampradaya.
- The organisation was founded in 1907 by Shastriji Maharaj.
- BAPS is a socio-spiritual Hindu faith with roots in the Vedas.
- Bhagwan Swaminarayan (1781-1830) revealed the faith in the late 18th century
- BAPS has a network of around 1,550 temples across the world.
- Notable Temples: It includes the Akshardham temples in New Delhi and Gandhinagar and Swaminarayan temples in London, Houston, Chicago, Atlanta, Toronto, Los Angeles, and Nairobi.
The architecture of the Temple

- It is Built in the traditional Nagara style with seven shikhars.
- The shikhara is adorned with depictions of deities such as Venkateshwara, Swaminarayan, Jagannath, and Ayyappa.
- The temple’s front panel depicts universal values, stories of harmony from different cultures, Hindu spiritual leaders and avatars.
- The temple has two central domes, the Dome of Harmony and the Dome of Peace, emphasising human coexistence through the carvings of earth, water, fire, air, and plants.
- A Wall of Harmony, one of the most enormous 3D-printed walls in the UAE, features a video showcasing critical milestones of the temple’s construction.
- No ferrous material (which is more vulnerable to corrosion) has been used in the temple.
- The external facade uses pink sandstone from Rajasthan, and the interior uses Italian marble.
- There are 96 bells and gaumukhs installed around the path leading to the temple.
- These 96 bells are a tribute to Pramukh Swami Maharaj’s 96 years of life.
- Nano tiles have been used, which will be comfortable for visitors to walk on even in the hot weather.
- There is a particular pillar called the ‘Pillar of Pillars’, which has around 1,400 small pillars carved into it.
- Buildings surrounding the temple are modern and monolithic, with their colour resembling dunes.
- Deities from all four corners of India have been featured in the temple.
- A ‘holy river’ surrounds it, for which waters from Ganga and Yamuna have been brought in.
- The river Saraswati has been depicted in the form of white light.
- A Varanasi-like ghat has been created where the ‘Ganga’ passes.
Significance of the Temple
- Represents cultural unity and cooperation.
- Symbolizes mutual respect and cooperation between India and UAE.
- Seven shikhara represent seven Emirates of UAE.
- A Wall of Harmony features a video showcasing critical milestones of the temple’s construction.
- The word ‘harmony’ has been written in 30 different ancient and modern languages.
- The temple was judged the Best Mechanical Project of the Year 2019 at the MEP Middle East Awards and the Best Interior Design Concept of the Year 2020.
- Value tales from Indian civilisation, Maya civilisation, Aztec civilisation, Egyptian civilisation, Arabic civilisation, European civilisation, Chinese civilisation and African civilisation have also been depicted.
-
A symbol of communal Harmony:
- A Muslim king donated land,
- The lead architect is a Catholic Christian,
- The project manager is a Sikh,
- The foundational designer is a Buddhist,
- The construction company is a Parsi group, and
- The director comes from the Jain tradition.
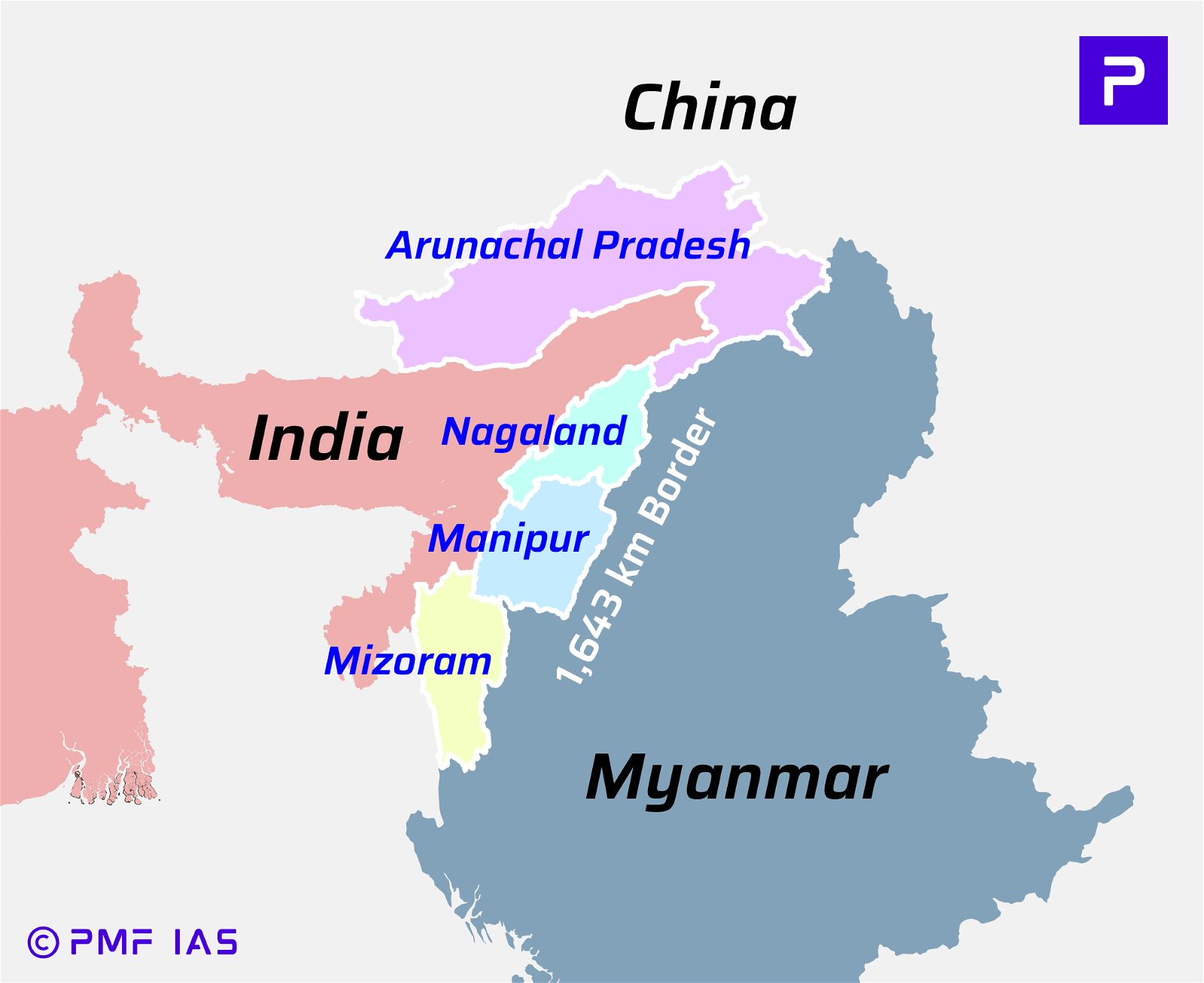
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Climatology} Sudden reversal of the pollution cycle
- Context (IE | DTE): In the winter of 2022-23, Delhi saw cleaner-than-usual air quality, while Mumbai’s air was more polluted than is usual for the coastal city. The PM 2.5 level in Mumbai increased significantly during the stubble-burning period.
- A new research paper concludes that this sudden flip-flop of the pollution cycle is linked to large-scale wind patterns associated with the triple dip La Nina.
- This change in wind patterns may have contributed to the intrusion of stubble-burning smoke from Punjab and Haryana into parts of peninsular India and Mumbai in the winter of 2022-23.
|
To know more about El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events – the El Nino and La Nina, visit >EL -NINO LA-NINA.
Geographical Reasons
- Change in wind direction:
- Winds blowing towards Delhi during this period are usually northwesterly, and they dump pollutants generated by stubble burning (Punjab and Haryana) in the NCR and the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- However, in November 2022, these winds were northerly, escaping most of the region in the NCR, including Delhi.
- Instead, these winds carried pollutants from stubble burning towards the west-south part of India, including Mumbai.
- Relatively high windspeed in the north and absence of cold day conditions:
- Air pollution in Delhi-NCR in the winter is linked to low temperature and low wind speed that keeps pollutants trapped close to the surface.
- However, Surface level winds from November 2022 to January 2023 were also relatively stronger in the north and slower in the southwest parts of the country compared to 2021-22.
- This, along with the absence of cold day conditions over northwest India till early January, may have prevented parts of the region from experiencing stagnation conditions that can prevent the dispersion of pollutants.
- Impact of La Nina:
- In the La Nina phase, winds over the equatorial Pacific Ocean are easterlies.
- Easterlies from the Pacific and northeasterlies from the Bay of Bengal appear to accelerate the northwesterly flow from north India and converge over the Indian peninsular region, mainly over northern parts of the west coast of India.
- Thus, it supports the transport of pollutants from North India towards Peninsular India.
North Westerly
|
To know more about Trade winds – Easterlies and Westerlies, visit > Trade winds
{GS2 – MoST – Initiatives} Indian National Young Academy of Science (INYAS)
- Context (PIB): The Indian National Young Academy of Science (INYAS) recently held its 9th Annual General Body Meeting.
- It is the first and only recognised academy for young scientists in India.
- It was founded by the Indian National Science Academy (INSA) council in December 2014.
- INYAS aims to create a vibrant community of young scientists who contribute to scientific advancements, policy formulation, and public engagement.
- It fosters interdisciplinary research, mentorship, and advocacy for science and technology.
- Membership Eligibility:
- Applicants should hold a PhD degree in any discipline of pure and applied sciences and engineering or an M.S. /M.D. in medical sciences.
- They must be less than 40 years of age as of December 31, 2023.
- Activities:
- Saransh: Three Minute Thesis Competition: INYAS organises this competition to encourage concise and impactful scientific communication.
- SciPADReC (Science Policy, Advisory, and Diplomacy Centre): INYAS actively engages in science diplomacy discussions.
- International Sci-Art Image Competition: A creative initiative that combines science and art.
- National Competition for Research Excellence Awards: Recognizing outstanding research contributions.
|
{GS2 – MoSJE – Schemes} National Council for Transgender Persons (NCTP)
- Context (PIB): The National Council for Transgender Persons (NCTP) convened its pivotal meeting at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre (DAIC).
- The agenda was to confront the challenges faced by transgender people, encompassing issues concerning Education, Life with dignity, Health support, Opportunities for livelihood, and Skill enhancement.
- Specific concerns raised included the necessity for unisex toilets, the establishment of shelter homes, the distribution of Ayushman Cards, and the provision of GarimaGreh.
National Council for Transgender Persons (NCTP)
- It is the statutory body primarily concerned with advising the government on all policy matters affecting transgender and intersex persons, as well as individuals with diverse GIESC (gender identity/expression and sex characteristics) identities.
- It was established in 2020 under the provisions of the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019.
- The Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment leads the council.
- It includes four representatives from the transgender community and one from the intersex community, each representing different regions (north, south, east, west, and northeast).
- Several Joint Secretary-level ex-officio members from various governmental ministries also serve on the council, along with five expert members from non-governmental organisations.
National Portal for Transgender Persons
- It is an initiative by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- The portal serves as a centralised platform to address the needs and rights of transgender individuals.
- Components:
- TG Certificate & ID Cards
- GarimaGreh (Shelter Homes)
- Skill Training
- Medical Support
- Recognition & Appreciation
GarimaGreh
The SMILE scheme
|
{GS2 – MoIB – Initiatives} Changes to the National Film Awards
- Context (IE): The Ministry of Information & Broadcasting (I&B) has made significant changes to the National Film Awards.
Indira Gandhi Award for Best Debut Film of a Director
- This award was previously associated with former PM Indira Gandhi and will now be known as the “Best Debut Film of a Director”.
- The connection between Indira Gandhi and this award dates back to the 28th National Film Awards in 1980.
Nargis Dutt Award for Best Feature Film on National Integration
- This award, previously named after the legendary actor Nargis Dutt, has been rechristened as the “Best Feature Film Promoting National, Social, and Environmental Values”.
- Nargis Dutt’s name became synonymous with the National Film Awards during the 13th edition in 1965, where she was honoured for the best feature film category.
Other Changes
- The Dadasaheb Phalke Award, recognising lifetime contributions to cinema, now carries a prize of Rs 15 lakh (increased from Rs 10 lakh).
- The Swarn Kamal and Rajat Kamal awards have also seen an increase in prize money to Rs 3 lakh and Rs 2 lakh, respectively.
- The awards for “Best Animation Film” and “Best Special Effects” have been combined into a new category called “Best AVGC (animation, visual effects, gaming, and comics) Film”.
- Changes have also been made in the non-feature film category, including the introduction of a new award for the “Best Script”.
- The award for the “Best Feature Film” in each language specified in Schedule VIII of the Constitution has been renamed as the “Best (name of the language) Feature Film”.
- These modifications aim to streamline and enhance the recognition of excellence in Indian cinema.
Why was there a need to change these awards?
- Relevance and Sensitivity: Renaming these awards allows the focus to shift from individual personalities to the artistic achievements of filmmakers and their contributions to cinema.
- Inclusivity and Representation: The new names emphasise the essence of the awards without being tied to specific individuals.
- Streamlining and Clarity: Simplifying award names makes it easier for audiences, filmmakers, and industry professionals to understand their purpose.
- The introduction of the “Best AVGC Film” category combines animation, visual effects, gaming, and comics, streamlining recognition for these creative fields.
- Financial Recognition: Enhancing the monetary value of awards encourages excellence and dedication in filmmaking.
- Adapting to Industry Changes: New categories and criteria reflect the changing landscape of Indian cinema.
- The addition of the “Best Script” award in the non-feature film category recognises the importance of storytelling.
{GS3 – Envi – Air Pollution} Revocation of GRAP Stage II
- Context (PIB): The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) has decided to revoke Stage II of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) in the entire National Capital Region (NCR).
- Delhi’s average Air Quality Index (AQI) was recorded at 231, which is about 70 AQI points below the threshold for invoking Stage-II actions (Delhi AQI 301-400) under GRAP.
- Although Stage-II restrictions are lifted, all actions outlined under Stage-I of GRAP will continue to be enforced.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- GRAP is a set of emergency measures aimed at mitigating air pollution in the Delhi National Capital Region (NCR) that come into effect once the air quality index (AQI) reaches a certain threshold.
- It was initially proposed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in 2016 and was first notified by the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change in 2017.
- Implementing Agency: Since 2021, the GRAP is enforced by the CAQM.
- The GRAP considers multiple pollutants, including ozone, sulfur dioxide, and oxides of nitrogen, not just PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations.
- State governments in the NCR may restrict BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel four-wheelers under Stage 3 (severe category).
- Construction activities on linear public projects are banned under the ‘severe+’ category.
- Data sources for AQI and meteorological forecasts include the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
Thresholds and Stages
- Stage-I: Activated when the AQI is in the ‘poor’ category (201 to 300).
- Stage-II, Stage-III, and Stage-IV: Activated three days ahead of the AQI reaching the ‘very poor’ (301 to 400), ‘severe’ (401 to 450), and ‘severe+’ (above 450) categories, respectively.
To know more about AQI, refer to CA-24-September-2023
{GS3 – Envi – CC} HP Environment friendly Schemes
- Context (DTE): The Himachal Pradesh (HP) budget for the year 2024-25 has introduced initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable development and supporting farmers.
Mukhya Mantri Harit Vikas Chhattravriti Yojana (CM Green Development Scholarship Scheme)
- Postgraduate science and engineering graduates will receive two-year scholarships to conduct research on climate change and environmental conservation in two villages within each assembly.
- The goal is to address climate threats and foster sustainable practices.
- This initiative not only supports higher education but also promotes practical solutions for environmental challenges.
- The collaboration with the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change and the German development agency GIZ enhances knowledge exchange and expertise.
Rajiv Gandhi Natural Farming Startup Scheme
- It has been introduced with a focus on chemical-free farming.
- ten farmers from each panchayat will be encouraged to adopt natural farming practices.
- Existing farmers engaged in agriculture will receive priority.
- Those who participate and grow chemical-free grains (eliminating chemicals from wheat and maize) will receive a maximum of 20 quintals of grain per family at the minimum support price (MSP).
|
- Additionally, the state will purchase naturally grown wheat at Rs 40 per kilogram and maize at Rs 30 per kilogram, the highest rates in the entire country.
{GS3 – S&T – Tech} Fintech – UPI
- Context (TH): The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Communications and Information Technology is worried about foreign-owned fintech apps (Walmart-backed PhonePe and Google Pay) dominating India.
- They suggest promoting local players to address this concern.
|
Significance of UPI
- Minimal Impact of Fraud
- The fraud-to-sales ratio (representing fraudulent transactions compared to the total) has remained at around 0.0015% over the years despite the increased volume of transactions in the last five years.
- According to McKinsey’s Global Payments Report (September 2023), the advantages of instant payments are,
- Helps in eliminating the hidden costs associated with managing cash transactions.
- Has induced a shift in consumer behaviour, enhancing security and digital commerce access.
Committee’s recommendations
- Need for effective regulation of digital payment apps due to the increasing use of digital platforms for payments in India.
- Promoting local players because regulatory bodies like the RBI and the NPCI would find it more feasible to control local apps compared to foreign apps operating in multiple jurisdictions.
|
Way forward
- A balanced mix (Local fintech players + Foreign fintechs) should be allowed to evolve, varying across areas like payments, lending, wealth management, and insurance.
- Local fintech players have a natural advantage in understanding the Indian customer, ecosystem, and market infrastructure.
- Foreign fintechs excel in new technologies and global connectivity.
To know more about the parliamentary standing committee, visit > parliamentary committee
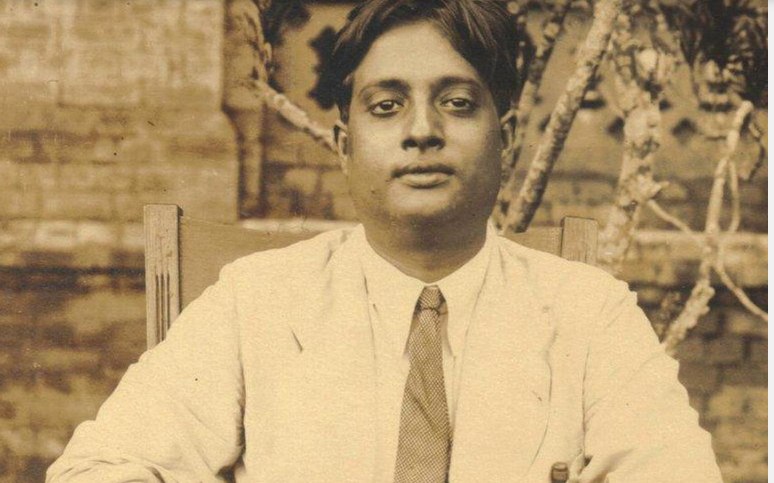
{GS3 – S&T – Tech} Satyendra Nath Bose & Quantum Physics
- Context (TH): This year marks 100 years of Satyendra Nath Bose’s discovery.
- He was an Indian physicist specialising in mathematical physics.
- He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, providing the foundation for Bose-Einstein statistics and the theory of the Bose-Einstein condensate.
Early life
- Bose was born in Calcutta (now Kolkata) in 1894.
- After completing his schooling, he joined Presidency College to study physics.
- After a few years, he was appointed as a faculty in the newly founded Rajabazar Science College.
- Later, he joined the Dhaka University as a lecturer.
Significant contribution
- Bose & Saha (his friend) published the first English translation of Einstein’s papers on general relativity.
- Saha was one of the first people to start finding applications of the developing quantum theory to molecular physics.
-
Developed the foundation for Bose-Einstein statistics:
- Bose read Planck’s papers on the distribution of energy in blackbody radiation to teach this material to his class.
- It was while teaching quantum theory in Dacca that he first noticed a logical problem in all known derivations of the Planck law of blackbody radiation.
- In 1924, Saha stayed with Bose in Dhaka and pointed out the 1923 papers of Wolfgang Pauli, Einstein and Paul Ehrenfest and their relation to Einstein’s 1917 paper.
- This led him to develop Bose statistics – a new method to count states of indistinguishable particles and applied it to his derivation of Planck’s radiation law.
- He discovered the correct set of equations to use to work out the behaviour of collections of photons (particles of light).
- Bose Discoveries (along with Einstein)
- Define the two classes of subatomic particles: fermions and bosons.
- Discovered Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC)
Numerous Nobel Prizes were awarded for research related to the concepts of the boson and the Bose-Einstein Condensate. Bose was never awarded a Nobel Prize.
{Prelims – Envi – Species} Northern Green Anaconda
- Context (DTE): Research has unveiled the existence of two genetically distinct species within the Anaconda family.
- The two distinct species are- the southern green anaconda (Eunectes murinus) and the newly identified northern green anaconda (Eunectes Nakajima).
- Despite their similar appearances, these species exhibit a staggering 5.5% genetic difference, indicative of their evolutionary divergence nearly 10 million years ago.
- It is the largest, heaviest, and second-longest snake (after the reticulated python) in the world.
- Characteristics:
- Size and Adaptations: Their nostrils and eyes positioned atop their heads enable breathing and vision while submerged.
- Physical Description: Olive-colored with large black spots blend seamlessly into lush Amazonian habitats.
- Habitat and Prey: Green anacondas predominantly inhabit South America’s Amazon and Orinoco basins, preying on a diverse range of animals, including capybaras, caimans, and deer.
- Predatory Behavior: Utilizes their large, flexible jaws, anacondas immobilise and consume prey without venom, relying on suffocation and swallowing techniques.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Least Concern | CITES: Appendix II





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)