Current Affairs October 31, 2023: Minimum Export Price (MEP), Parliamentary Committees, Review Bombing, Muthuramalinga Thevar
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Geomorphology} Earthquakes Due to Cascade of Ruptures
- Context (TH): The interaction between the faultlines made the Turkey-Syria quakes more deadly.
- The earth’s crust consists of tectonic plates.
- Fault lines form where these plates interact, as they collide, pull apart. or slide past each other.
- When tectonic plates abruptly slip, they release pent-up pressure, causing earthquakes.
- The earthquakes in Turkey occurred along the East and North Anatolian Fault Lines.
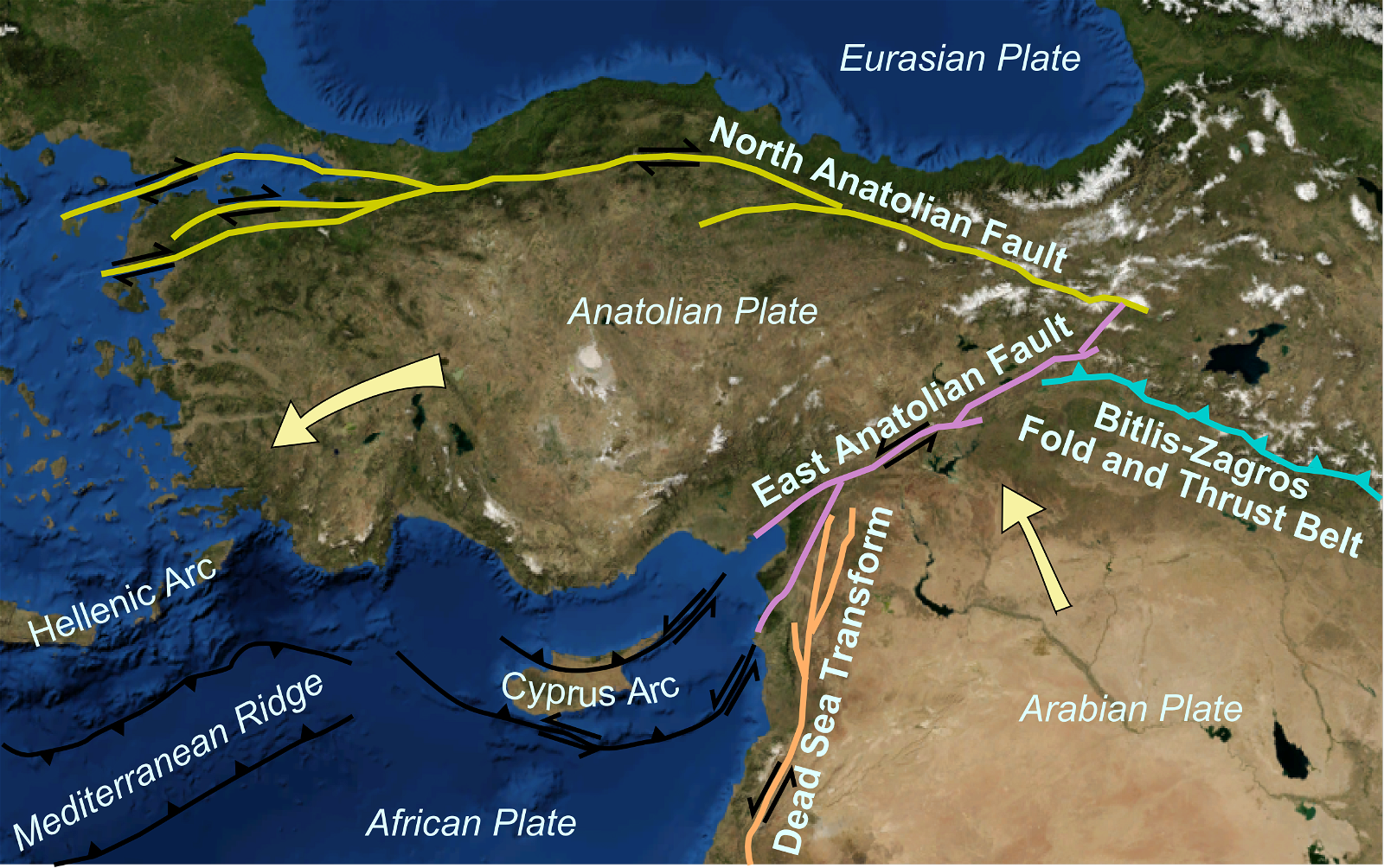
- Due to stress interaction of the East and North Anatolian Faults during the quakes, cascade of ruptures broke through fault bends and step-overs.
- This occurred because, during the quakes, both faults were heavily stressed. So, as they interacted, they exerted increasing stress on each other.
Fault Bends and Step-overs
Cascade of Ruptures
|
{GS1 – MIH – Personalities} Muthuramalinga Thevar
- Context (IE): Muthuramalinga Thevar was a politician and a leader of the Thevar community known for his contributions to the country’s freedom struggle.
- He was also known for his opposition to the implementation of the Criminal Tribes Act of 1920 and was instrumental in getting this discriminatory act abolished.
- Thevar was the secretary of the Harijan Sevak Sangh of Ramnad district (Tamil Nadu).
- He was a crusader against the practice of untouchability.
- In 1939, he led a congregation of Harijans into the Meenakshi Temple in Madurai.
|
Political Journey
- In 1936, Thevar joined the Congress party, which aimed to abolish the Criminal Tribes Act.
- He contested the election, became an MLA, and actively participated in trade unions.
- He later joined the All-India Forward Bloc and became the vice president in 1955.
Criminal Tribes Act 1871
|
{GS2 – MoD – Initiatives} Goa Maritime Conclave
- Context (TH | PIB): The Defense Minister emphasised the need for multinational cooperation to address maritime challenges in the Indian Ocean Region at the fourth Goa Maritime Conclave.
- Goa Maritime Conclave is an Indian Navy initiative that allows maritime security experts to share their knowledge and ideas. Delegates from twelve Indian Ocean nations attended the conclave.
- The theme for the fourth edition is ‘Maritime Security in the Indian Ocean Region: Converting Common Maritime Priorities into Collaborative Mitigating Frameworks.’
Objectives
- To promote collaborative mitigation frameworks in the IOR.
- To encourage cooperation to tackle shared maritime challenges effectively.
- To emphasise respecting international maritime laws, particularly the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- To advocate for a free, open, and rule-based maritime order.
{GS2 – MoHA – Laws} Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita 2023
- Context (TH): The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs delayed adopting a report on three bills that aim to replace existing criminal laws.
- Three bills replacing existing laws are:
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita Bill 2023: Replaces the Indian Penal Code 1860.
- Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita Bill 2023: Replaces the Criminal Procedure Code 1973.
- Bharatiya Sakhshya Bill 2023: Replaces the Indian Evidence Act of 1872.
The Objective of New Laws
- To protect the rights granted by the IC.
- To provide justice, and punishment will be used as a deterrent for crime.
Parliamentary Panel Consultations
1. Hindi Names of the Bills:
- The Hindi names of the Bills have caused disagreement.
- The panel’s report on the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita 2023 argues that since the Bill is in English, it complies with Article 348 of the IC, which mandates using English in legal documents.
2. Redrafting Provisions to Tackle Organized Crime:
- Section 109 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita 2023 defines an organised crime syndicate to include groups involved in various criminal activities.
- The panel is considering revising this provision to clarify its terms and scope.
3. Reconsidering the Criminalization of Adultery:
- Some members support reintroducing provisions criminalising adultery (Section 497 of the IPC) & non-consensual ‘unnatural sex’ (Section 377 of the IPC), which were removed in the new bills.
- The SC decriminalised adultery in a 2018 ruling, but concerns have been raised about safeguarding the institution of marriage.
Concerns Raised by Parliamentary Panel Members
- Avoid Rush for Short-Term Gains: Some members urged the panel to avoid rushing these Bills.
- Hurrying through the Bills was seen as undermining the essential process of “legislative scrutiny.”
- Need for Extensive Consultations: Members emphasized the necessity for thorough consultations with state governments and stakeholders.
- Exclusionary Hindi Nomenclature: Concerns were raised about the Hindi names of the Bills, which were seen as excluding a significant portion of the population.
- New Legislation vs. Amending Existing Codes: Some members believed that the Bills resembled existing laws and could have been amended rather than introducing new legislation.
Way Forward
- The panel should hold sittings across the country and listen to:
- Lawyers and activists on the details of the various sections.
- Members of the subordinate judiciary who work the law and procedure laid down in the codes.
- The panel should hold wide consultation with all stakeholders.
Parliamentary Committees
Standing Committees
Departmentally Related Standing Committees (DRSCs)
Ad hoc Committees
Need for Parliamentary Committees
|
{GS2 – Polity – IC – FRs} Right to Freedom of Expression vs. Review Bombing
- Context (TH): Malayalam director approached the Kerala High Court seeking a gag on social media and YouTube reviews following a film’s release to protect it from review bombing.
- It is being claimed that review bombing threatens the industry’s financial stability.
Review Bombing
- Review bombing is the act of posting numerous negative reviews, often coordinated, to harm the reputation of a product, service, or content.
- Mainly linked to media and entertainment, review bombing extends to other areas like online marketplaces, apps, and businesses.
- It can be done for various reasons, such as:
- Protest or grievance
- Promote competitors’ product
- Personal vendettas
- Social or political motivations
Freedom of Expression
- Freedom of expression is a fundamental right guaranteed by Article 19(1)(a) of Indian Constitution.
- It states that all citizens have the right to freedom of speech and expression, subject to certain reasonable restrictions.
Key Elements of Freedom of Expression
- It is solely available to a citizen of India, not to a foreign national.
- It includes the right to express one’s views and opinions about any issue.
- It includes the right to express in any medium, such as by words, writing, printing, etc.
- This right is not absolute; GoI can impose reasonable restrictions in cases which involve:
- Sovereignty and integrity of India
- Security of the state
- Friendly relations with foreign nations
- Public order, decency and morality
- Contempt of court
- Defamation and incitement to an offence.
Reasons Why Review Bombing Should be Protected as Part of Freedom of Expression
- To hold businesses and creators accountable
- To raise consumer awareness
- To hold as a protest against powerful businesses and creators
Reasons Why Restrictions on Review Bombing is Not Violation of Freedom of Expression
- It can misled consumers seeking accurate information.
- It can unfairly harm the reputation and livelihood of creators, businesses, or developers.
- Coordinated review bombing can suppress the genuine opinions of users.
- It is susceptible to manipulation by trolls, competitors, or individuals with malicious intent.
- Prolonged and widespread review bombing can erode trust in online review systems.
- Review bombers often escape accountability, making addressing this practice’s misuse difficult.
Way Forward
- There is a grey area between review bombing and freedom of expression.
- If review bombing is motivated by genuine reasons, it can be a form of freedom of expression.
- But if review bombing is motivated by malicious intent, it misuses freedom of expression.
- So, the interests of creators, businesses, etc., should be protected from review bombing but not at the cost of freedom of expression. So, a proper regulatory body is the need of the hour.
{GS3 – Envi – Plastic Pollution} Plastic Pellets
- Context (DTE): Plastic pellets are washing up on the beaches of Maharashtra.
- Plastic pellets (or nurdles) are tiny 1-5 mm beads made by petrochemical companies.
- They act as raw materials for the plastic industry to manufacture products.
- They can be made from polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride.
- Sources of plastic pellet pollution: Leak from various sources, including production facilities, transportation, storage, and recycling activities. (They are not the result of littering by citizens.)
- Challenge: Cleaning up pellets is tougher than regular beach clean-up due to their small size.

Chronic and Acute Pellet Spills: Reason Behind Marine Plastic Pellet Pollution
- Plastic pellets are transported from one country to another through the marine route.
- Major exporters of plastic pellets are the US, Saudi Arabia, and South Korea.
- India is the sixth-largest importer of plastic pellets. Majority of plastic pellets are imported into India from West Asian countries like the UAE, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia.
- Plastic pellets were found in marine waters near the shipping route of plastic pellets.
- The primary shipping route between Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and China is via the Indian Ocean.
|

{GS3 – IE – Banking} Term Deposit
- Context (TH): The RBI has increased the minimum amount for offering non-callable/without premature withdrawal option term deposits (TDs) from fifteen lakh to one crore.
- This means that all domestic term deposits accepted from individuals for one crore and below shall have premature-withdrawal-facility.
- These instructions will also be applicable for:
- Non-Resident (External) Rupee (NRE) Deposit
- Ordinary Non-Resident (NRO) Deposits
- Banks are also permitted to offer differential rates on interest on TDs based on the non-callability of deposits (i.e., non-availability of premature withdrawal option) in addition to the tenor and size.
Non-callable deposits
|
{GS3 – IE – Exports} Minimum Export Price for Controlling Inflation
- Context (PIB | IE | IE): GoI is increasing the minimum export price (MEP) on agri products like wheat, rice, and onion to ensure domestic availability.
Minimum Export Price (MEP)
- MEP is a trade policy tool governments use to set a floor price for certain exportable commodities.
- Objectives of implementing MEP may include:
- Food Security: To maintain affordable access to essential food items.
- Price Stability: To prevent export-driven domestic price spikes.
- Revenue Generation: To generate income from exports.
- Market Control: To maintain control over the export of strategic or sensitive products.
Recent MEPs Imposed by GoI on Agri Products
|
Agri Product |
Minimum Export Price (MEP) |
| Basmati Rice | $1,200/tonne |
| Onion | $800/tonne |
Reasons Why MEPs Imposed by GoI on Agri Products
- To ensure domestic availability and curb food inflation.
- Competitive populism: A political strategy in which different political parties or leaders compete to offer populist policies to gain the electorate’s support.
Implication of MEPs Imposed by GoI on Agri Products
- Losing export markets: E.g., India may lose its basmati export market to Pakistan.
- Reduced export competitiveness: It will lead to a reduction in export volumes.
- Trade disputes: Other countries may see MEPs as trade barriers.
- Market distortions: Lower exports discourage farmers from producing certain crops, affecting the country’s crop selection and cropping patterns.
- Implicit tax on farmers: It may hurt farmers who rely on exports for their income.
- Complexity and administrative burden: It may require additional resources to monitor and enforce.
- It leads to smuggling and other illegal activities
- Negatively impacts the food security of some countries
Minimum Export Price (MEP) for Rice
- GoI is restricting rice export to ensure adequate availability of rice in the domestic market.
- Recent restrictions by GoI on rice exports:
- MEP of $1,200/tonne on basmati rice
- Ban on the export of non-basmati white rice
- Ban on the export of broken rice: To ensure adequate availability for domestic livestock industry consumption and ethanol production.
- Export duty of 20% on rice in the husk (paddy or rough), husked (brown rice), and semi-milled or wholly-milled rice
- Export duty of 20% on parboiled rice.
- Limitation: Selective export controls, such as those on rice, can be bypassed through misclassification. For example, white non-basmati rice is exported under heads of parboiled and basmati rice.
|
Issues with MEP for rice
- MEP was set only for basmati and excluded other premium-quality Indian rice.
- The MEP set for basmati was too high ($1,200/tonne).
Other Premium Quality Indian Rice Varieties
|
Solution: Uniform MEP
- Include other premium varieties: Other premium rice varieties not sold through PDS will also be insulated from trade policy vagaries like MEP.
{Prelims – In News} Operation Chakra II
- Context (TH): The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has launched Operation Chakra-II to fight against cyber-enabled financial crimes.
- For this, CBI has partnered with Microsoft, Amazon, and national and international agencies.
- The CBI is working with the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) of the USA, the Cyber Crime Directorate and IFCACC of INTERPOL, the National Crime Agency (NCA) in the UK, the Singapore Police Force and the BKA of Germany to notify further leads.
{Prelims – S&T – AI} Digital Twins
- Context (IE): Building of ‘Digital Twins’ of Indian cities is being suggested to solve the urban crisis.
- A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object, process, service, or environment.
- It is a real-time simulation of the object or system.
- It can be used to predict physical objects’ performance and identify potential problems to optimize its operation.
- Digital twins are created using sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
Digital Twins of Cities
- Digital twins of cities replicate urban areas, using data on roads, power, streetlights, water, sewage, and storm drains.
- Benefits of digital twins of cities are:
- Improve urban planning: E.g., traffic flow, air quality, and energy consumption.
- Efficient infrastructure management
- Reduced environmental impact
- Enhanced public services: E.g., healthcare, education, and transportation
- Disaster preparedness
{Prelims – Species In News} Candolleomyces Albosquamosus
- Context (TH): Researchers identified a new mushroom species from the Western Ghats.
- The new species sports a honey-yellow cap and a white stem.
- Habitat: It is found in dead logs or bamboo culms in the natural forest.

Mushrooms
- Mushrooms are the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting bodies of a fungus.
- They are typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source.
- Mushrooms can be edible, medicinal, toxic, and psychedelic (also called magic mushrooms).
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)