Intermittency is Renewable Energy’s Major Issue but there are Solutions
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Intermittency
- Context (IE): Gravity is emerging as the best bet in solving renewable energy’s biggest problem, intermittency.
Intermittency in Renewable Energy
- Intermittency in renewable energy refers to the unpredictability and variability of energy production from sources like wind and solar, which depend on weather conditions and time of day.
- Types of intermittency
- Diurnal Intermittency
- Seasonal Intermittency
- Weather-Dependent Intermittency
- Intra-Hour Intermittency
- Spatial Intermittency
- Resource Availability Intermittency
- Random Intermittency (due to random events like equipment malfunctions)
Challenges from Intermittency in Renewable Energy
- Grid Reliability: Intermittent energy sources can cause sudden power fluctuations that disrupt grid stability, leading to blackouts or voltage issues.
- Matching Supply and Demand: Coordinating intermittent energy supply with fluctuating electricity demand is a significant challenge. It can result in overproduction or underproduction.
- Energy Storage Costs: Energy storage systems often mitigate intermittency. However, these systems can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- Grid Infrastructure: The existing grid infrastructure may not be well-suited to handle renewable energy sources’ variability and intermittent nature. Upgradation can be costly and time-consuming.
- Resource Variability: The variability of energy can make long-term energy planning challenging.
- Investment Uncertainty: Fluctuations in energy output can affect the return on investment and project profitability. This can make investors in renewable energy projects uncertain.
- Backup Generation: Backup sources like fossil fuels are sometimes necessary when renewable energy is scarce, which can impede efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
- Technological Challenge: Creating effective technologies to address intermittency, like advanced energy storage and smart grids, can be challenging regarding R&D and deployment.
Gravity-Based Storage: Solution to Intermittency
- Gravity-based energy storage uses the force of gravity to store energy.
- This is achieved by raising heavy objects to a high elevation when the electricity demand is low and generating electricity by lowering the heavy objects when the demand is high.
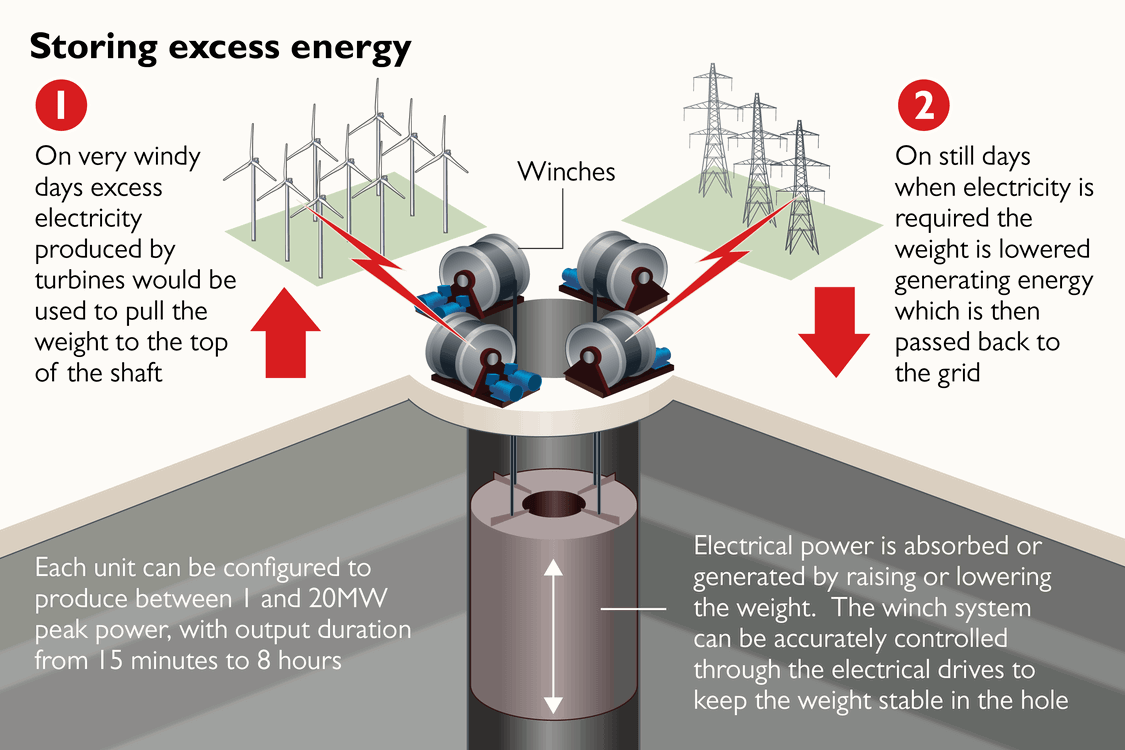
- There are a number of different gravity-based energy storage technologies, but they all work on the same basic principle.
- Example 1: Pumped hydro storage uses excess electricity to pump water uphill, then releases it downhill to generate electricity when needed.
- Example 2: Compressed air energy storage compresses air when there is excess electricity and then expands it to generate electricity when needed.
|
Benefits of Gravity-based Energy Storage
- High efficiency: These highly efficient storage systems recover most energy when discharged.
- Scalability: These storage systems can store large amounts of energy, making them ideal for intermittent renewable energy.
- Reliability: They are very reliable, with few moving parts and no emissions.
Challenges of Gravity-based Energy Storage
- Cost: These systems can be expensive to build because they require a lot of land and infrastructure.
- Land use: These systems require a lot of land, which can be challenging in areas where land is scarce.
- Response time: These systems can be slow to respond to changes in demand.
Intermittency Situation in India
- In India, grid managers face the challenge of sustaining a monthly addition of about 1,000 megawatts (1 GW) from renewables to the grid.
- Policy makers believe India needs to quickly develop energy storage options, as it is the world’s third largest producer of renewable energy, with ~40% of its electricity coming from non-fossil fuels.
- India’s green initiatives led to a 24% reduction in GDP emission intensity from 2005 to 2016, but they also posed challenges for a grid powered mainly by renewables.
- GoI is exploring two options: hydrogen and hybrid generation models blended with off-stream pumped storage.
- The Cabinet approved a policy for increasing green hydrogen production and its use as a fuel.
- The Power Ministry surveyed pumped hydro sites, and hydro PSUs are given targets for such schemes.
- They are considering opencast mines for potential pumped hydro sites.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)