Pygmy Hog (Porcula salvinia/Sus salvanius)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Pygmy Hogs Reintroduced in Assam
- Context (TH | IE): Eighteen captive-bred pygmy hogs are released in Assam’s Manas National Park, their historical habitat, under the Pygmy Hog Conservation Programme (PHCP).
Pygmy Hog (Porcula salvinia/Sus salvanius)
- Pygmy Hog is the world’s smallest wild pig.
- It is one of the indicator species of grassland habitats.
- It lives in sociable family groups of up to 20, led by a matriarch.
- Pygmy hog-sucking Louse is a critically endangered parasite that feeds only on Pygmy Hogs.
- Distribution: This rare pig species is found only in Manas Wildlife Sanctuary, Assam. Earlier, it was located across north India, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Habitat: It lives in dense, tall riverine grasslands.
- Threats: Habitat loss and hunting.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: EN | CITES: Appendix I | WPA: Schedule I

Pygmy Hog Conservation Programme (PHCP)
- PHCP was launched in 1996 by the Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust along with the MoEF, the IUCN, and local NGOs, EcoSystems India & Aaranyak.
- It maintains a captive population and reintroduces hogs in protected areas of Assam.
Why the Conservation of Pygmy Hogs is Crucial to India’s Wildlife Protection Goals
- Pygmy hogs are an indicator species.
- Pygmy hogs only live in the wet high grasslands at the foothills of the Himalayas.
- It is also the habitat for other rarities such as the one-horned rhinoceros, hog deer, Eastern barasingha, tiger, water buffalo, lesser florican and the hispid hare.
- So, if pygmy hogs are not around, it means something is seriously wrong with the habitat, which, in turn, would endanger the fate of the other animals.
|
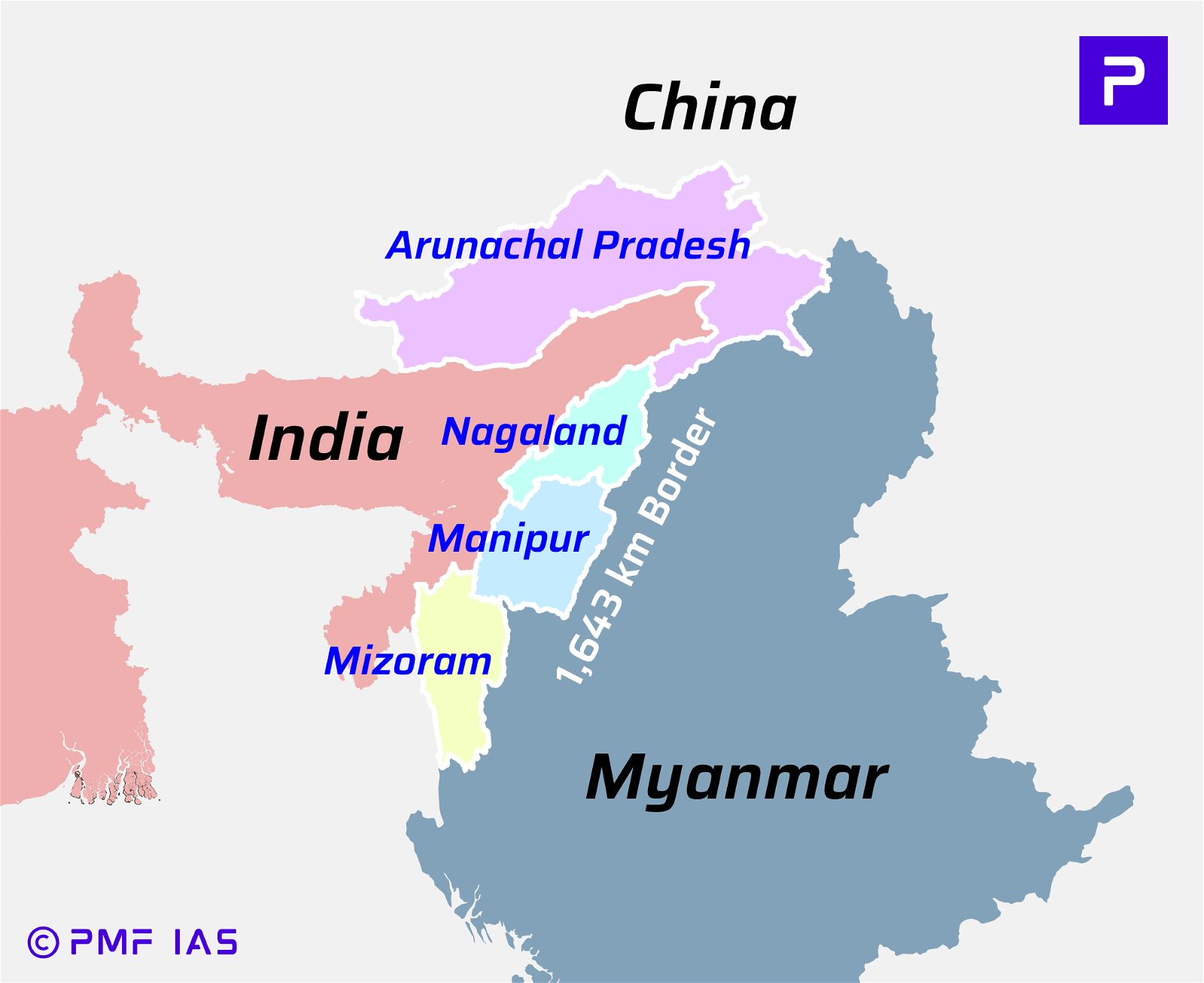
Manas National Park and Tiger Reserve
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)