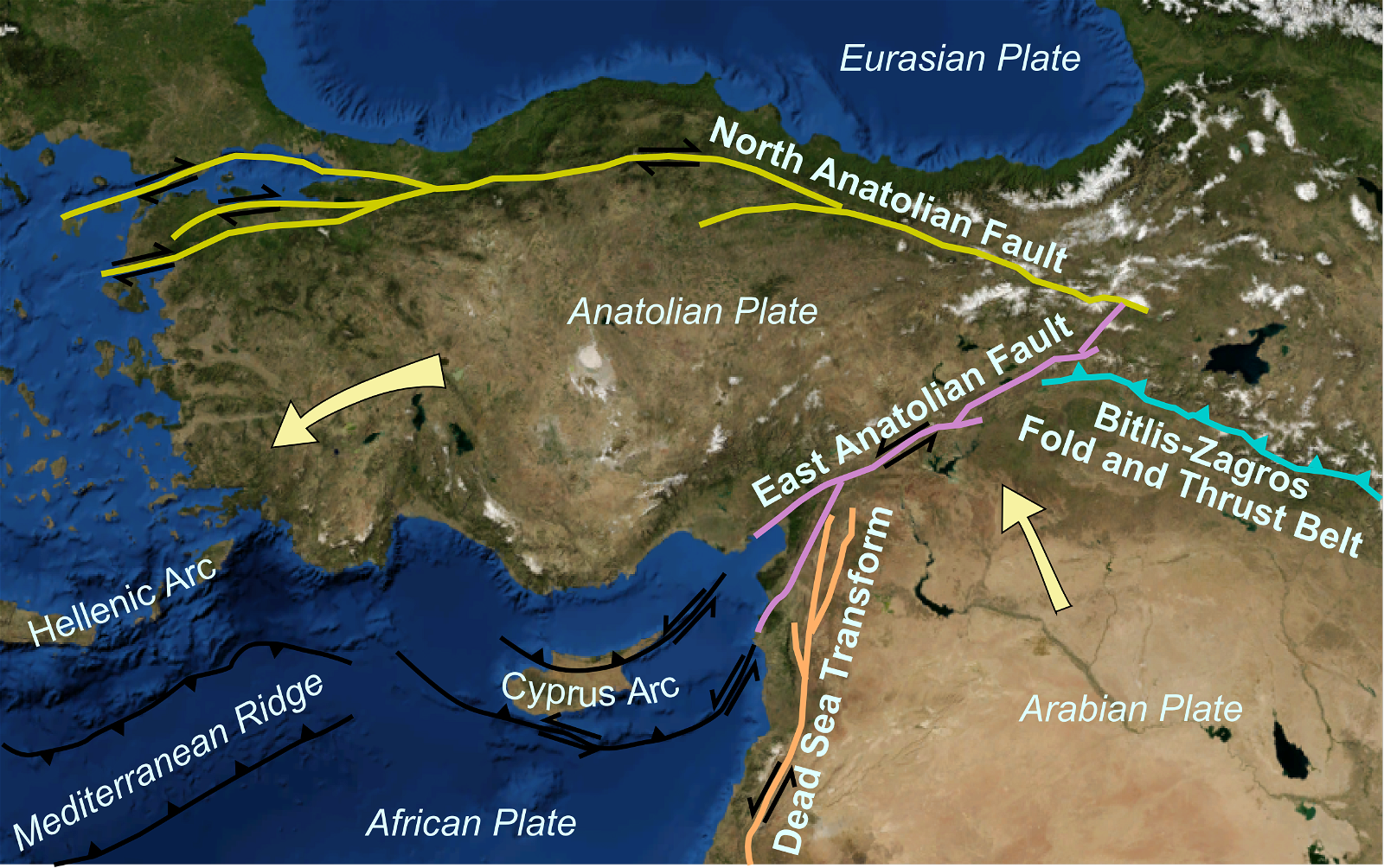
Microplastic in Clouds, Adverse Impact of Microplastics
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Microplastic in Clouds
- Context (WION): Microplastics have been found in cloud for first time.
- Concern: Microplastics can cause severe damage to climate and the human body if their presence in clouds is not contained through coordinated efforts.
Microplastics
- Microplastics are defined as plastics less than 5mm in diameter.
- There are two categories of microplastics.
- Primary microplastics: tiny particles designed for commercial use, like in cosmetics or textiles.
- Secondary microplastics: tiny particles that are a product of the breakdown of larger plastic items due to exposure to environmental factors such as the sun’s radiation or ocean waves.
- The problem with microplastics, like all plastics, is that they do not break down easily into more harmless particles. Instead, they find their way across the planet.
- An average human consumes at least 50,000 microplastic particles annually due to contamination of the food chain, potable water, and air.
- Microplastics contain a number of toxic chemicals which pose severe risks to human health. The biggest health risk associated is with the chemical Bisphenol A (BPA), which is used to harden plastic.
- BPA causes alterations in liver function, insulin resistance, fetus development in pregnant women, the reproductive system, and brain function.
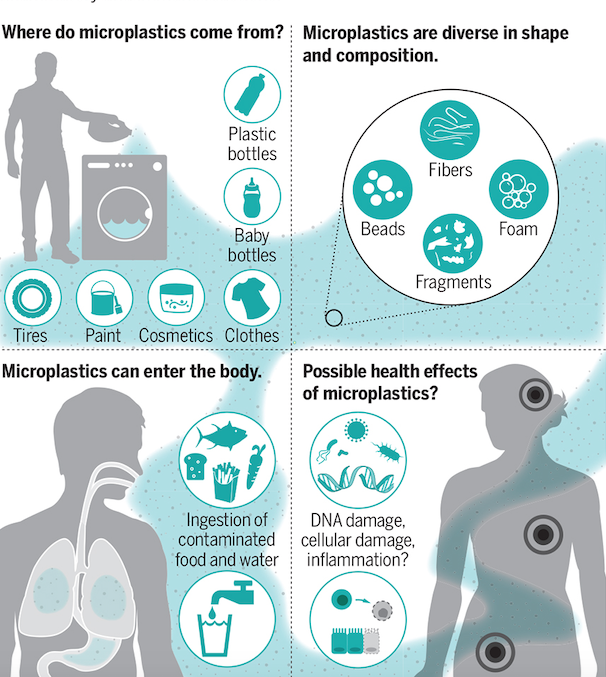
Sources of Microplastics
- Fragmentation of larger plastic items like bottles, bags, and packaging.
- Microbeads used in personal care products like exfoliating scrubs and toothpaste.
- Fibres released during the washing of synthetic textiles.
- Weathering and degradation of plastic debris in the environment.
Adverse Impact of Microplastics
- On Environment: The presence of microplastics disrupts the terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. They affect the soil health, water quality, nutrient cycling, and the organisms that inhabit these environments. These have cascading effects on the entire food web.
- On Aquatic Life: Microplastics are ingested by various marine organisms, ranging from zooplankton to fish, seabirds, and marine mammals. The ingestion can cause physical harm, such as blockage of digestive systems and internal injuries.
- Microplastics can accumulate in the tissues of organisms and transfer toxic chemicals associated with the plastic particles through the food chain.
- On Agriculture: Irrigation by microplactic contaminated water allowing these particles to enter food.
- On Human Health: Ingestion of microplastics by humans through water, food, and air can result in genetic modifications and several diseases. Microplastics are already detected in human blood.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)