Current Affairs October 14, 2023: United Nations Security Council (UNSC), Dancing Frogs of Western Ghats, Large Ozone Hole Over Antarctica
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Geomorphology} Pontus Tectonic Plate
- Context (TWC | SA | LS): Remnants of the long-lost tectonic plate, the Pontus Plate, are discovered. This plate once underpinned the South China Sea and it is 1/4th of Pacific Ocean in size.

Tectonic Plates
- The earth’s lithosphere is broken into distinct plates floating on a ductile layer called asthenosphere (upper part of the mantle).
- Plates move horizontally over the asthenosphere as rigid units.
- The movement of these crustal plates (due to convection currents in the mantle) causes the formation of various landforms and is the principal cause of all earth movements.
How the Pontus Plate Got Subducted
- 120 million years ago, a vast ancient ocean called the Pontus Ocean existed between Eurasia and Australia, which had been tethered to Antarctica as part of the supercontinent Pangaea.
- As Pangaea broke apart, the Pontus plate underlying the Pontus Ocean was swallowed up slowly by insurgent plates carrying Borneo and the Philippines into their present-day positions.
For details on Plate Tectonics > PMF IAS Physical Geography
{GS2 – IR – UN} United Nations Security Council (UNSC)
- Context (TH): India called for the expansion of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) in both permanent and non-permanent categories of membership.
- India asserted that expansion is essential so that the developing countries and unrepresented regions find their due place at the UN.
- The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the UN and is considered the apex of the UN system.
- It is responsible for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- The UNSC is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions on member states.
UNSC Membership
- UNSC consists of fifteen members, and each member has one vote.
- Permanent Members: Five (China, France, Russia, UK, and US) (P5)
- Non-permanent members: Ten

- Each year, the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) elects five non-permanent members by a two-thirds majority for two years on a regional basis.
- A retiring member is not eligible for immediate re-election.
- The five permanent members have veto power — opposition from any of these five Countries blocks the resolution regardless of international support.
|
India and UNSC
- India is not a permanent member of the UNSC.
- In 2021, India was elected as a non-permanent member of the UNSC for the eighth time.
Benefits for non-permanent members
- Non-permanent members get monthly presidency of UNSC, and as a president, they could decide the matter to discuss in meetings.
- Non-permanent members can preside over several committees and working groups of UNSC.
Issues of UNSC
Troubling Role of P5 and its Veto
- Veto power makes P5 nations more equal than others, ignoring the collective will of 188 members.
- The veto system has become a tool to block the UN’s work and not encourage it.
- The recent conflicts in many states indicate the failure of the UNSC and the misuse of veto.
- During the Russia-Ukraine conflict, when Russia invaded a sovereign UN member-state, the UNSC proved powerless to respond because of a veto by Russia.
- Russia’s increasing resort to the veto has blocked resolutions on Ukraine, Syria, North Korea, etc.
Doesn’t Reflect the Present World Order
- The UNSC reflects the geopolitical realities of 1945 and not of today. Five countries are permanent members of the UNSC merely because they won a war 76 years ago.
- The world has changed, but not the UNSC. Lack of representation for Africa, South America and Asia is a major issue of UNSC (China is the only Asian P-5 member).
- Africa, with 55 member states, has no presentation in permanent membership.
- It is impossible to address the present problems if institutions do not reflect today’s world order.
- The lack of progress in reforms has “serious implications” for the relevance of the UN.
Obstacles to council reform
High procedural hurdles to amending the UN Charter
- Any amendment in the UN Charter requires:
- A two-thirds majority of the overall membership (129 of the 193 states in UNGA) with no opposition from permanent five members.
- To be ratified by two-thirds of the member states.
Divergent member state positions
- China is the only country among P5 opposing India’s entry into the UNSC. Support from other permanent members does not amount to anything since China can veto India’s candidacy.
|
Negotiating groups within UNGA are neutralising each other’s bid
L.69 Group
- It is a pre-reform group of developing countries.
- The group is seeking:
- An expansion of permanent and non-permanent membership to the UNSC
- Reform in the body’s working methods
- Better representation of developing country aspirations, including African countries and Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
G4 Group
- It comprises four countries: Brazil, India, Germany, and Japan.
- They support each other’s bids to become permanent members of the UNSC.
- They are demanding the reforms and representation of African countries in UNSC.
Coffee Club
- It is an informal group comprising 40 member states.
- It has been instrumental in holding back reforms to the UNSC.
- It opposes bigger regional powers from getting permanent seats in the UNSC.
- Italy and Spain are opposed to Germany’s bid.
- Pakistan is opposed to India’s bid.
Expansion of the Security Council
- Without structural changes, the UNSC’s performance and legitimacy will inevitably suffer.
- There is a need to strengthen and reform the UN by expanding permanent and non-permanent members of the UNSC.
- Inclusion of developing countries, including India and African countries, is essential to reflect contemporary realities.
|
United Nations
(All were established in 1945 when the UN was founded)
Specialized Agencies of the UN
UN System
|
{GS2 – Vulnerable Sections – Children} Child Marriage
- Context (DTE): Save the Children, an NGO, released the Global Girlhood Report 2023.
- It focuses on the impact of the climate crisis on the lives of Girl children across the globe.
Key Highlights
- Climate crisis impacts girls in various aspects, such as: food security, poverty, migration, safety, education and health.
- Globally, 9 million girls face extreme climate disaster risks and are forced into child marriage yearly.
- Around 2/3rd of child marriages occurs in regions with higher climate risks.
- Child marriage is used to help families facing financial struggles 7 food shortages during disasters.
- A 10% increase or decrease in rainfall is associated with a 1% increase in child marriage globally.
Recommendations
- Gender Equality: Make gender equality and protection from gender-based violence central priorities in climate action.
- Preparedness: Invest in anticipatory actions and systems that girls need to withstand climate shocks.
- Empower Girls: Support girls as decision-makers and promote autonomous feminist movements.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Invest in climate change adaptation, specifically focusing on children, especially girls, who are highly vulnerable to its impacts.
Initiatives by IndiaProhibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
Special Marriage Act 1954
Protection of children from sexual offences (POCSO) act 2012
|
{GS3 – Envi – Air Pollution} Large Ozone Hole Over Antarctica
- Context (IE): The European Space Agency Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite measurements have detected a giant ozone hole over Antarctica.
Ozone Layer
- Ozone layer is a layer of ozone gas (a trace gas) in the stratosphere (between 15 and 50 km).
- Almost 90% of ozone is in the stratosphere.
Benefit/Significance of Ozone Layer
- This layer absorbs Sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation and prevent them from reaching the Earth’s surface.
- Increase in penetration of UV rays leads to sunburns, skin cancer, cataracts, reduced crop yields etc.
Ozone Layer Depletion and Ozone Hole
- Ozone molecules are constantly formed and destroyed in the stratosphere.
- Without any intervention, the amount of ozone in the ozone layer should remain constant over time.
- But if more ozone molecules get destroyed than formed, then the earth’s ozone layer gradually thins and it is called ozone layer depletion.
- Ozone hole is an area where ozone levels drop below the historical threshold of 220 Dobson Units (DU is the measure of ozone concentrations).
- Causes of ozone depletion can be natural and anthropogenic.
Natural Causes of Ozone Hole
Solar Activity
- Solar radiation, including UV radiation, varies over an 11-year cycle known as the solar cycle.
- During periods of increased solar activity, more UV radiation reaches the Earth, which can lead to ozone depletion in the stratosphere.
- Solar flares and sunspots can produce UV radiation that can destroy ozone molecules.
Volcanic Eruptions
- Volcanic eruptions can release large amounts of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and water vapour.
- These substances can reach the stratosphere and cause ozone depletion by forming sulfate aerosols.
Stratospheric Winds
- Strong stratospheric winds can create a vortex and prevent its from mixing with surrounding air.
- Ozone holes are created since ozone within the vortex is isolated and not replenished.
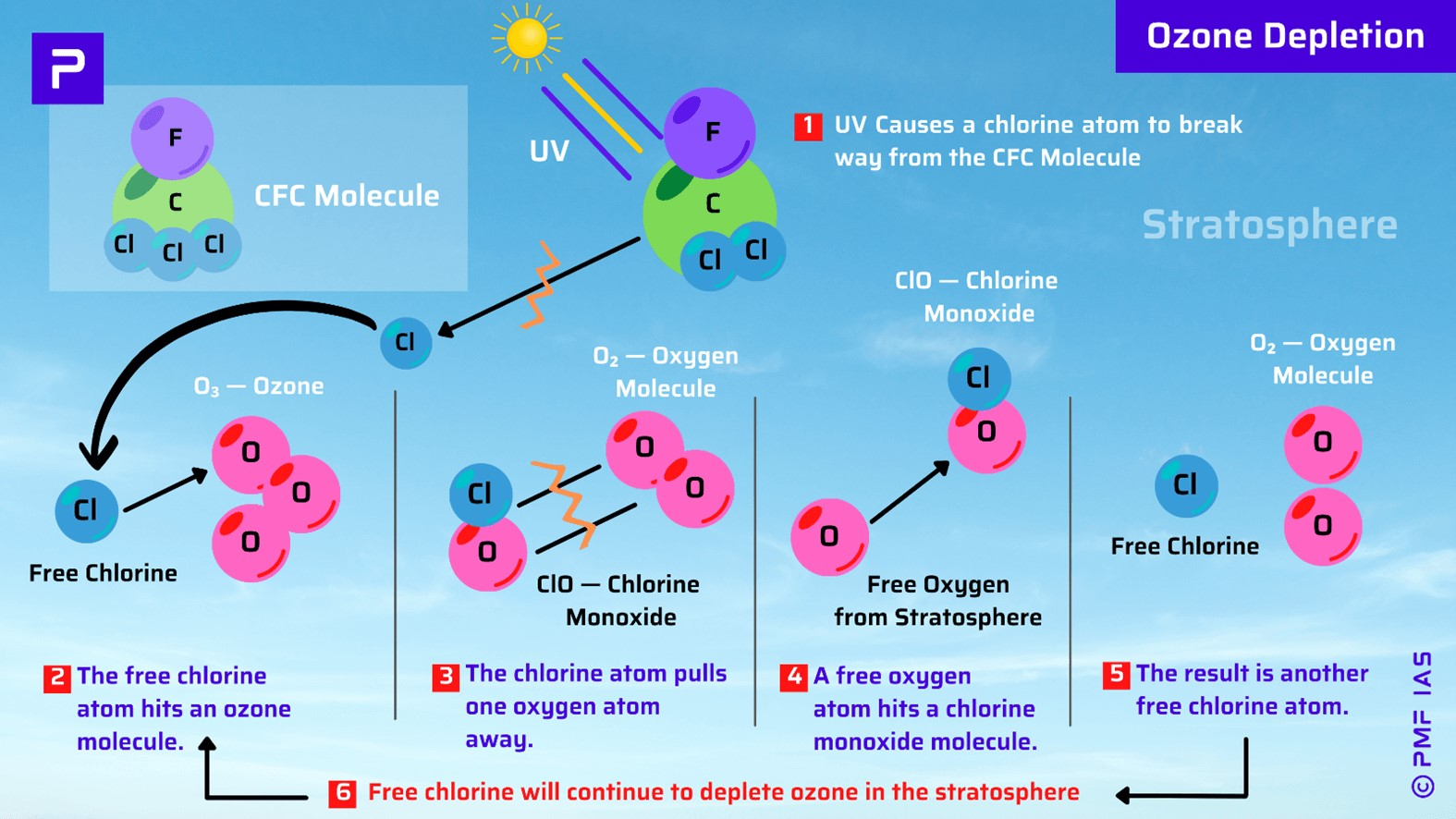
Anthropogenic Causes of Ozone Hole
Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS)
- ODS release chlorine and bromine atoms on exposure to UV rays.
- When chlorine and bromine atoms come in contact with ozone, they destroy the ozone molecules.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are the most abundant ODS.
- Nitrogenous compounds (NO2, NO, and N2O) also act as ODS.
| ODS | Sources |
| Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) | Refrigerators, Air-conditioners, Solvents, Dry-cleaning agents, etc. |
| Halons | Fire-extinguishers |
| Carbon tetrachloride | Solvents & Fire extinguishers |
| Methyl chloroform | Aerosols & Adhesives |
| Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) | Air-conditioners, Solvents & Fire extinguishers |
Unregulated Rocket Launches
- Rocket launches emit a variety of pollutants into the stratosphere, including nitrogen oxides, black carbon, and chlorine compounds. These react with ozone molecules and destroy them.
- Rockets also release water vapour into the stratosphere. Water vapour can influence the concentration and distribution of ODSs.
Annual Ozone Hole Over Antarctica
- The size of the ozone hole over Antarctica fluctuates each year, opening each year in August and closing again in November or December.
- Ozone hole opens up each year because of stratospheric winds.
- Each, stratospheric winds form a strong polar vortex over Antarctica.
- The winds in the polar vortex are isolated from the rest of the surrounding atmosphere.
- The cold temperatures inside polar vortex favour the formation of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs).
- PSCs provide surfaces for chemical reactions that release ODSs.
- In the spring, when the sunlight returns to Antarctica, the ODSs are released from the PSCs and begin to destroy ozone molecules.

Cause of This Year’s Ozone Hole Over Antarctica
- This year’s big ozone hole could be due to the volcanic eruptions at Hunga Tongain Tonga.
- The water vapour impacted the ozone layer through chemical reactions and changed its heating rate.
- The water vapour also contained other elements that can deplete ozone, like bromine and iodine.
Initiatives to Recover Ozone LayerVienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer
Montreal Protocol on on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer
Kigali Amendment to Montreal Protocol
|
For the detailed explanation on Ozone Depletion Mechanism, refer to PMF IAS Environment
{GS3 – Envi – Biodiversity} Dancing Frogs of Western Ghats
- Context (DTE | DH): Two genera of frogs endemic to the Western Ghats are among the most threatened amphibians globally, according to the 2nd Global Amphibian Assessment.
|
Micrixalus (Dancing Frogs)
- Micrixalus is a genus of frogs endemic to the Western Ghats.
- It is the most threatened amphibian genus in India, with 92% of its species threatened.
- It is the fifth most threatened amphibian genus globally.
- These frogs are called “dancing frogs” because they wave their feet to attract females during the breeding season. This act is called “foot flagging”.
- Habitat: They are found near perennial streams in the shola forests, wet evergreen forests, swamps, and secondary forests.
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, climate change, invasive species (mosquito fish), and chytrid fungus.

Nyctibatrachidae (Night Frogs)
- Nyctibatrachidae is a genus of frogs endemic to the Western Ghats.
- It is the second most threatened amphibian genus in India, with 84% of its species threatened.
- These frogs are called “night frogs” because of their nocturnal nature and dark colour.
- Habitat: They occur near streams in hilly evergreen forests.
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and chytrid fungus.

Ecological Significance of Amphibians (GS 1, Geo, BG)
- Amphibians, including frogs, toads, salamanders, and newts, play a vital ecological role.
Indicator Species
- Amphibians are sensitive to environmental changes, including pollution and habitat degradation.
- Their population health and distribution are critical indicators of ecosystem health.
- A decline in amphibian populations signals broader ecological issues.
Food Chain
- Amphibians are both predators and prey in many ecosystems.
- They help control insect populations by eating mosquitoes and agricultural pests.
- At the same time, they serve as a food source for a wide range of animals, including birds and snakes.
- Amphibian population changes can trigger trophic cascades, affecting species across the food chain.
|
Nutrient Cycling
- Amphibians’ consumption and excretion impact nutrient distribution.
- By doing so, they affect plant and aquatic communities.
Wetland Ecosystem Engineers
- Many amphibians depend on wetland ecosystems, where their actions can have cascading effects.
- They influence water quality, vegetation growth, and the composition of other species in wetlands.
Seed Dispersal
- Some amphibians, particularly tree frogs, are involved in seed dispersal.
- They aid in plant diversity and forest regeneration.
Disease Regulation
- Amphibians can help control disease vectors. For example, they consume insects that can carry diseases like malaria and Zika virus.
{GS3 – Envi – Invasive Species} Gambusia: A Solution Turned into a Problem
- Context (DTE): Andhra releases millions of Gambusia fish to fight mosquito-borne diseases.
Gambusia Fish
- Gambusia (or mosquitofish) are freshwater fish native to North America.
- It is an omnivore that eats small organisms, including mosquito larvae, insects, and algae.

Gambusia Fish as Mosquito Control Strategy
The reasons due to which gambusia are used as biocontrol to lower mosquito populations are:
- Mosquito Larvae Predation: They are voracious feeders that primarily feed on mosquito larvae.
- Environmental Friendly: They are environmentally friendly mosquito control agents, unlike chemical pesticides that can harm non-target species and the environment.
- Self-Sustaining Control Method: Once introduced, they establish a self-sustaining population, effectively controlling mosquito larvae without continuous human intervention.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to the ongoing costs of chemical mosquito control methods, using Gambusia fish is often a cost-effective long-term solution.
|
Gambusia Fish as Invasive Species
- In many places where Gampusia has been introduced, they have become invasive species.
- The IUCN has declared Gambusia as one of the 100 worst invasive alien species in the world.
|
WHO Guidelines on Introduction of Gambusia for Mosquito Control
- WHO supported Gambusia as an effective mosquito control method in man-made breeding habitats, like swimming pools and garden ponds, without access to the natural environment.
- It warned against releasing Gambusia into the natural environment due to their invasiveness.
|
{GS3 – IE – Industry} Classification of Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs)
- Context (HBL): RITES Limited, a PSU under the Ministry of Railways involved in transport consultancy and the engineering sector, was recently granted Navratna status.
- The Department of Public Enterprises under the Ministry of Heavy Industries & Public Enterprises grant Ratna status in three categories:
- Maharatna Companies (13 companies)
- Navratna Companies
- Mini Ratna Companies
Maharatna companies
- Maharatna companies are CPSEs that have achieved the highest recognition and autonomy.
- As of 2023, there are 13 Maharatna companies in India which are:
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL)
- Coal India Limited (CIL)
- Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL)
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL)
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL)
- National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC)
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC)
- Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL)
- Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL)
- Rural Electrification Corporation Limited (RECL)
- Power Finance Corporation (PFC)
- Oil India Limited (OIL)
Eligibility Criteria
- Listed on the Indian stock exchange as per SEBI regulation.
- Net profit over Rs. 5,000 crores in the last three years.
- Annual turnover of Rs. 25,000 crore or net worth of Rs. 15,000 crore for three years.
- Global presence through international operations.
Benefits
- Greater openness and financial autonomy.
- Autonomy in hiring and firing employees.
- Freedom to invest in new projects.
Navratna
- Navratna companies are CPSEs with a certain degree of autonomy to compete globally.
Eligibility Criteria
- PSU should be
- A Miniratna-I, Schedule ‘A’ company.
- ‘Excellent’ or ‘very good’ rating under the MoU system in three of the last five years.
- It must have a composite score of 60 in six performance indicators.
Benefits
- Navratna PSUs have been granted financial independence to invest up to Rs 1,000 crore without seeking approval from the Union government.
Miniratna
- Miniratnas are CPSEs that have made profits in the last three years and have positive net worth.
- Benefits: Miniratnas can enter joint ventures set by subsidiary companies and overseas offices but with certain conditions.
Memorandum of Understanding for PSU
|
{GS3 – S&T – IT} CORS Network
- Context (PIB I TOI): Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) Network is a National Survey network of Real Time Kinematic (RTK) base stations that broadcast corrections in position of the survery drones/rovers, usually over an internet connection.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) base stations
- Real Time Kinematic (RTK) is a differential Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS; like GPS, NaIC) technique with high positioning performance near a base station.
- The technique is based on the transmission of corrections from the base station to the rover/drone so that the errors that drive the stand-alone positioning cancel out.

Capabilities of CORS Network
- It is capable of precise Location-based services, which can provide centimetre-level positioning services in real-time through real-time kinematics with an accuracy of +/- 3cm.
- The Survey of India will set up more than 1,000 CORS stations across India.
- The CORS network is available 24 /7 throughout the year.
Survey of India
|

Significance of CORS Network
- Precision Farming: It can enhance crop yield by precise field location and elevation data for efficient irrigation and soil monitoring.
- Disaster Management: It provides real-time water level data for flood prediction and swift response.
- Geological Studies: CORS is vital for tectonic plate tracking, aiding early earthquake warnings.
- Surveying and Mapping: CORS can improve the implementation of the Swamitva scheme, i.e. land surveying accuracy, and simplify title verification.
- Meteorology: CORS data enhances weather forecasts, weather event prediction and mitigation.
- Navigation: CORS supports precise maritime navigation, enhancing sea travel safety.
- Scientific Research: CORS data tracks environmental changes, glacier movements, and sea level rise for climate research.
{Prelims – PIN India – PAN – RS} Kanwar Lake
- Context (DTE): Kanwar Lake is neglected and on the brink of drying up.
- Kanwar Lake, known as Kabartal Jheel, is Asia’s largest freshwater oxbow lake and the only Ramsar site in Bihar.
- It’s a residual oxbow lake formed due to the meandering of the Gandak River, a tributary of the Ganga, covering most of the Indo-Gangetic plains in northern Bihar.
- The wetland is an important stopover along the Central Asian Flyway, with 58 migratory waterbirds using it for rest and refuelling.
- The significant threats to the site include water management activities such as drainage, water abstraction, damming, and canalisation.

For more info on the Ramsar convention: Ramsar Convention on Wetlands PMFIAS





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)