
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, Ramsar Site, Montreux Record
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 25, 2024 6:45 PM
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
- It is an international treaty for “the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands”.
- It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands.
- It is named after the city of Ramsar in Iran.
- The Convention was signed on 2nd of February 1971.
- The 2nd of February each year is World Wetlands Day.
- Number of parties to the convention (COP) is 171.
- At the centre of the Ramsar philosophy is the “wise use” of wetlands.
- Wise use: maintenance of ecological character within the context of sustainable development.
Need for Such Convention
- Wetlands are indispensable for the countless benefits or “ecosystem services” that they provide ranging from freshwater supply, food and building materials, and biodiversity, flood control, groundwater recharge, and climate change mitigation.
- 64% of the world’s wetlands have disappeared in the last century.
What is wetland
- The Convention uses a broad definition of wetlands.
- It includes all lakes and rivers, underground aquifers, swamps and marshes, wet grasslands, peatland, oases, estuaries, deltas and tidal flats, mangroves and other coastal areas, coral reefs, and all human-made sites such as fishponds, rice paddies, reservoirs and salt pans.
COP
- COP is the policy-making organ of the Convention which adopts decisions (Resolutions and Recommendations) to administer the work of the Convention.
- Every three years, representatives of the Contracting Parties meet as the Conference of the Contracting Parties (COP)
- COP13 took place in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, in 2018.
Under the Convention, the Contracting Parties commit to:
- Work towards the wise use of all their wetlands;
- Designate suitable wetlands for the List of Wetlands of International Importance (the “Ramsar List”) and ensure their effective management;
- Cooperate internationally on trans boundary wetlands, shared wetland systems and shared species.
Ramsar Site
- At the time of joining the Convention, each Contracting Party undertakes to designate at least one wetland site for inclusion in the List of Wetlands of International Importance.
- The inclusion of a “Ramsar Site” in the List embodies the government’s commitment to take the steps necessary to ensure that its ecological character is maintained.
- There are over 2,300 Ramsar Sites on the territories of 171 Ramsar Contracting Parties across the world.
- The countries with the most Sites are the United Kingdom with 175 and Mexico with 142.
- Bolivia has the largest area under Ramsar protection.
Transboundary Ramsar Sites
- Contracting Parties are designating their new and existing Ramsar Sites as Transboundary Ramsar Sites.
- These are ecologically coherent, shared wetlands extending across national borders, which are managed collaboratively.
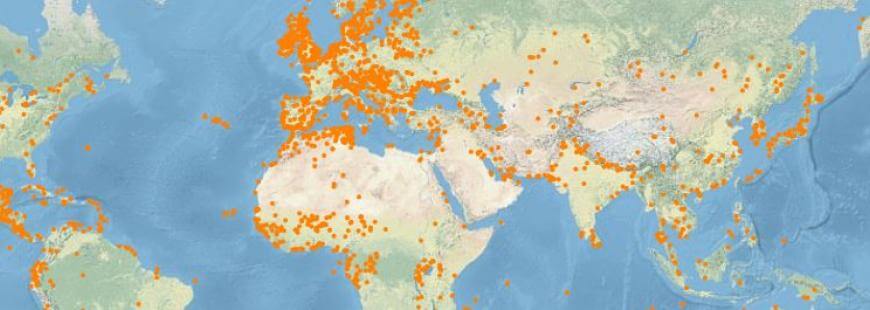
Global Distribution of Ramsar Sites (Source)
The Montreux Record
- The Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution or other human interference.
- It is maintained as part of the Ramsar List.
Q. If a wetland of international importance is brought under the ‘Montreux Record’, what does it imply?
- Changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring or are likely to occur in the wetland as a result of human interference.
- The country in which the wetland is located should enact a law to prohibit any human activity within five kilometres from the edge of the wetland
- The survival of the wetland depends on the cultural practices and traditions of certain communities living in its vicinity, and therefore the cultural diversity therein should not be destroyed
- It is given the status of ‘World Heritage Site’
Answer: a)
International Organization Partners
- The Ramsar Convention works closely with six organisations known as International Organization Partners (IOPs). These are:
- Birdlife International
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- International Water Management Institute (IWMI)
- Wetlands International
- WWF
- International Wildfowl & Wetlands Trust (WWT)
Other Partners
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD),
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS),
- World Heritage Convention (WHC) and
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).
- Project funding is done by various groups like multilateral development banks, bilateral donors, UN agencies such as UNEP, UNDP, Non-governmental organisations etc.
Criteria for Identification of Wetlands under Ramsar Convention
If a wetland
- contains a representative, rare, or unique example of a natural or near-natural wetland type.
- supports vulnerable, endangered, or critically endangered species; or threatened ecological communities.
- supports populations of plant and/or animal species important for maintaining the biological diversity of a particular biogeographic region.
- supports plant and/or animal species at a critical stage in their life cycles or provides refuge during adverse conditions.
- regularly supports 20,000 or more water birds.
- regularly supports 1% of the individuals in a population of one species or subspecies of water birds.
- supports a significant proportion of indigenous fish subspecies.
- is an important source of food for fishes, spawning ground, nursery and/or migration path.
- is an important source of food and water resource, increased possibilities for recreation and eco-tourism, etc.
Ramsar Sites in India
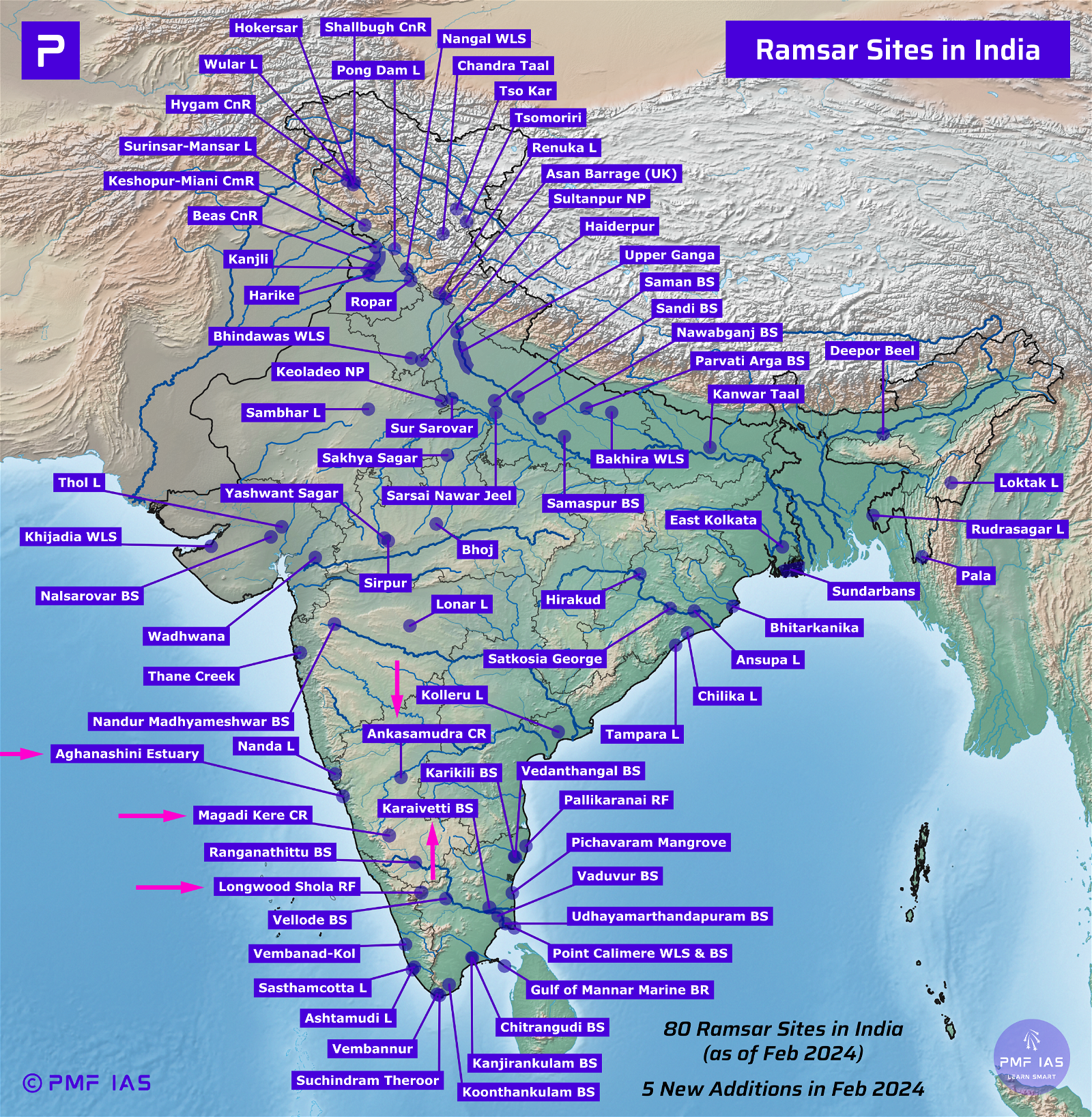
Last updated on April 25, 2024 6:45 PM







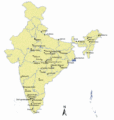






Ramsar sites is not updated as to date pls look on it team its 75 now
i am looking for current affairs compilations of , environment, science tech, and agriculture cant find anywhere on your website, please help in this regard.