
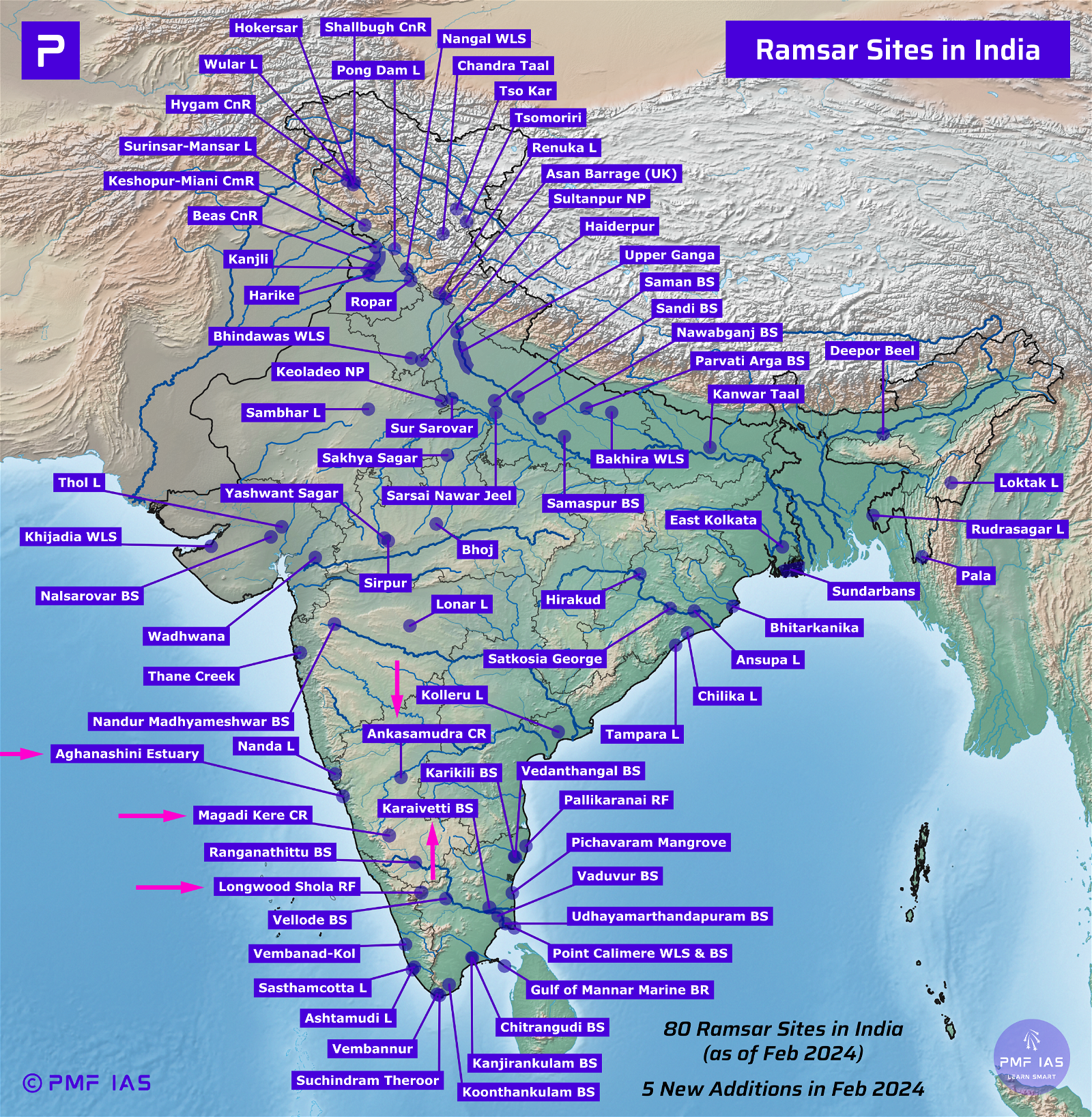
Ramsar Sites in India (80 Ramsar Sites in India)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Ramsar Sites in India
- As of February 2024, there are 80 Ramsar Sites in India (5 new additions in February 2024).
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
Ramsar Site
Global Distribution of Ramsar Sites (Source) |
List of Ramsar Sites of India [80 Ramsar Sites in India as of May 2023]
- India has increased its tally of Ramsar sites (Wetlands of International Importance) to 80 from the existing 75 by designating five more wetlands as Ramsar sites.
- Ramsar Site certificates were given away to –
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
- Longwood Shola Reserve Forest, Tamil Nadu
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Karnataka
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve, Karnataka
- Aghanashini Estuary, Karnataka
| S.No. |
Ramsar Site |
State |
Designated Year |
Area (km2) |
| 1 |
Kolleru Lake |
Andhra Pradesh |
2002 |
901 |
| 2 |
Deepor Beel |
Assam |
2002 | 40 |
| 3 | Kanwar (Kabar) Taal | Bihar | 2020 | 26.2 |
| 4 | Nanda Lake | Goa | 2022 | 0.42 |
| 5 | Khijadia WLS | Gujarat | 2021 | 6 |
| 6 |
Nalsarovar BS |
Gujarat |
2012 | 123 |
| 7 | Thol Lake | Gujarat | 2021 | 6.99 |
| 8 | Wadhvana Wetland | Gujarat | 2021 | 10.38 |
| 9 | Bhindawas WLS | Haryana | 2021 | 4.11 |
| 10 |
Sultanpur NP |
Haryana |
2021 | 142.5 |
| 11 |
Chandra Taal |
Himachal Pradesh |
2005 | 0.49 |
| 12 |
Pong Dam Lake |
Himachal Pradesh |
2002 | 156.62 |
| 13 | Renuka Lake | Himachal Pradesh | 2005 | 0.2 |
| 14 |
Ranganathituu BS |
Karnataka |
2022 | 5.18 |
| 15 |
Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve |
Karnataka |
2024 | 0.5 |
| 16 |
Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve |
Karnataka |
2024 | 0.98 |
| 17 |
Aghanashini Estuary |
Karnataka |
2024 | 4.8 |
| 18 |
Ashtamudi Wetland |
Kerala |
2002 | 614 |
| 19 |
Sasthamkotta Lake |
Kerala |
2002 | 3.73 |
| 20 |
Vembanad-Kol Wetland (Longest Lake in India) |
Kerala |
1905 |
1512.5 |
| 21 | Bhoj Wetland | Madhya Pradesh | 2002 | 32 |
| 22 | Sakhya Sagar | Madhya Pradesh | 2022 | 2.48 |
| 23 | Sirpur wetland | Madhya Pradesh | 2022 | 1.61 |
| 24 | Yashwant Sagar | Madhya Pradesh | 2022 | 8.22 |
| 25 |
Lonar Lake (Impact Crater Lake) |
Maharashtra |
2020 | 4.27 |
| 26 |
Nandur Madhameshwar |
Maharashtra |
2019 | 14 |
| 27 |
Thane Creek |
Maharashtra |
2022 | 65.21 |
| 28 |
Loktak Lake |
Manipur |
1990 | 266 |
| 29 | Pala Wetland | Mizoram | 2021 | 18.5 |
| 30 | Ansupa Lake | Odisha | 2021 | 2.31 |
| 31 |
Bhitarkanika Mangroves |
Odisha |
2002 |
650 |
| 32 |
Chilika Lake (Oldest Ramsar Site in India) |
Odisha |
1981 |
1165 |
| 33 |
Hirakud Reservoir |
Odisha |
2021 | 654 |
| 34 |
Satkosia Gorge |
Odisha |
2021 | 981.97 |
| 35 | Tampara Lake | Odisha | 2021 | 3 |
| 36 |
Beas CnR |
Punjab |
2019 | 64 |
| 37 |
Harike Wetland |
Punjab |
1990 | 41 |
| 38 | Kanjli Wetland | Punjab | 2002 | 1.83 |
| 39 | Keshopur-Miani CmR | Punjab | 2019 | 34 |
| 40 |
Nangal WLS |
Punjab |
2019 | 1 |
| 41 | Ropar Wetland | Punjab | 2002 | 13.65 |
| 42 |
Keoladeo National Park |
Rajasthan |
1981 |
28.73 |
| 43 |
Sambhar Lake |
Rajasthan |
1990 | 240 |
| 44 | Chitrangudi BS | Tamil Nadu | 2021 | 2.6 |
| 45 |
Gulf of Mannar Marine BR |
Tamil Nadu |
2022 | 526.72 |
| 46 | Kanjirankulam BS | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.96 |
| 47 | Karikili BS | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.584 |
| 48 | Koonthankulam BS | Tamil Nadu | 2021 | 0.72 |
| 49 | Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 12.475 |
| 50 |
Pichavaram Mangrove |
Tamil Nadu |
2022 | 14.786 |
| 51 | Point Calimere WLS & BS | Tamil Nadu | 2002 | 385 |
| 52 | Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.94 |
| 53 | Udhayamarthandapuram BS | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.44 |
| 54 | Vaduvur BS | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 1.12 |
| 55 | Vedanthangal BS | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.4 |
| 56 | Vellode BS | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.77 |
| 57 | Vembannur Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu | 2022 | 0.2 |
| 58 | Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu | 2024 | 4.5 |
| 59 | Longwood Shola Reserve Forest | Tamil Nadu | 2024 | 1.16 |
| 60 | Rudrasagar Lake | Tripura | 2005 | 2.4 |
| 61 |
Hokera Wetland |
UT of JK |
2005 | 13.75 |
| 62 | Hygam Wetland CnR | UT of JK | 2022 | 8.02 |
| 63 | Shallbugh Wetland CnR | UT of JK | 2022 | 16.75 |
| 64 | Surinsar-Mansar Lakes | UT of JK | 2005 | 3.5 |
| 65 |
Wular Lake |
UT of JK |
1990 | 189 |
| 66 |
Tso Kar (High Altitude Ramsar Site) |
UT of Ladakh |
2020 | 95.77 |
| 67 |
Tsomoriri (High Altitude Ramsar Site) |
UT of Ladakh |
2002 | 120 |
| 68 | Bakhira WLS | Uttar Pradesh | 2021 | 28.94 |
| 69 | Haiderpur Wetland | Uttar Pradesh | 2021 | 69 |
| 70 | Nawabganj BS | Uttar Pradesh | 2019 | 2 |
| 71 | Parvati Arga BS | Uttar Pradesh | 2019 | 7 |
| 72 | Saman BS | Uttar Pradesh | 2019 | 5 |
| 73 | Samaspur BS | Uttar Pradesh | 2019 | 8 |
| 74 | Sandi BS | Uttar Pradesh | 2019 | 3 |
| 75 | Sarsai Nawar Jheel | Uttar Pradesh | 2019 | 2 |
| 76 | Sur Sarovar (Keetham Lake) | Uttar Pradesh | 2020 | 4.31 |
| 77 | Upper Ganga River (Brijghat to Narora) | Uttar Pradesh | 2005 | 265.9 |
| 78 | Asan Barrage | Uttarakhand | 2020 | 4.44 |
| 79 | East Kolkata Wetlands | West Bengal | 2002 | 125 |
| 80 |
Sundarban Wetland (Largest Ramsar Site in India) |
West Bengal |
2019 |
4230 |
- BS: Bird Sanctuary | WLS: Wildlife Sanctuary | BR: Biosphere Reserve | CnR: Conservation Reserve | CmR: Community Reserve | IBA: Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (designated by Birdlife International)
- Most Indian Ramsar Sites lie on the Central Asian Flyway for migratory avian species.
Statewise Number and Area of Ramsar Sites
|
Rank |
State |
No. of Ramsar Sites |
Rank |
State |
Area Under Ramsar Sites (km2) |
|
|
1 |
Tamil Nadu |
16 |
1 |
West Bengal |
4355 |
|
|
2 |
Uttar Pradesh |
10 |
2 |
Odisha |
3456 |
|
|
3 |
Odisha |
6 |
3 |
Kerala |
2130 |
|
|
4 |
Punjab |
6 |
4 |
Tamil Nadu |
956 |
|
|
5 |
UT of JK |
5 |
5 |
Andhra Pradesh |
901 |
|
| 6 | Gujarat | 4 | 6 | Uttar Pradesh | 395 | |
| 7 | Madhya Pradesh | 4 | 7 | Rajasthan | 269 | |
| 8 | Karnataka | 4 | 8 | Manipur | 266 | |
| 9 | Kerala | 3 | 9 | UT of JK | 231 | |
| 10 | Himachal Pradesh | 3 | 10 | UT of Ladakh | 216 | |
| 11 | Maharashtra | 3 | 11 | Himachal Pradesh | 157 | |
| 12 | West Bengal | 2 | 12 | Punjab | 156 | |
| 13 | Rajasthan | 2 | 13 | Haryana | 147 | |
| 14 | UT of Ladakh | 2 | 14 | Gujarat | 146 | |
| 15 | Haryana | 2 | 15 | Maharashtra | 84 | |
| 16 | Andhra Pradesh | 1 | 16 | Madhya Pradesh | 44 | |
| 17 | Manipur | 1 | 17 | Assam | 40 | |
| 18 | Assam | 1 | 18 | Bihar | 26 | |
| 19 | Bihar | 1 | 19 | Mizoram | 19 | |
| 20 | Mizoram | 1 | 20 | Karnataka | 11.7 | |
| 21 | Uttarakhand | 1 | 21 | Uttarakhand | 4.4 | |
| 22 | Tripura | 1 | 22 | Tripura | 2.4 | |
| 23 | Goa | 1 | 23 | Goa | 0.42 | |
|
80 Ramsar Sites (as of Feb 2024) |
~14,000 km2 (as of Apr 2023) |
|||||
Largest, Smallest and Oldest Ramsar Sites in India
|
Largest Ramsar Sites in India |
|||
|
Ramsar Site |
State |
Area (km2) |
|
|
1 |
Sundarban Wetland |
West Bengal |
4230 |
|
2 |
Vembanad-Kol Wetland |
Kerala |
1512.5 |
|
3 |
Chilika Lake |
Odisha |
1165 |
|
4 |
Satkosia Gorge |
Odisha |
981.97 |
|
5 |
Kolleru Lake |
Andhra Pradesh |
901 |
|
Smallest Ramsar Sites in India |
|||
| 1 | Renuka Lake | Himachal Pradesh | 0.2 |
| 2 | Vembannur Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu | 0.2 |
| 3 | Vedanthangal BS | Tamil Nadu | 0.4 |
| 4 | Nanda Lake | Goa | 0.42 |
| 5 | Udhayamarthandapuram BS | Tamil Nadu | 0.44 |
|
Oldest Ramsar Sites in India |
|||
|
1 |
Chilka Lake – 1981 |
||
|
2 |
Keoladeo Ghana NP – 1981 |
||
Description of Ramsar Sites in India
- India has increased its tally of Ramsar sites (Wetlands of International Importance) to 80 from the existing 75 by designating five more wetlands as Ramsar sites.
- Ramsar Site certificates were given away to:
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
- Longwood Shola Reserve Forest, Tamil Nadu
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Karnataka
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve, Karnataka
- Aghanashini Estuary, Karnataka
|
Ramsar Site |
Description |
|
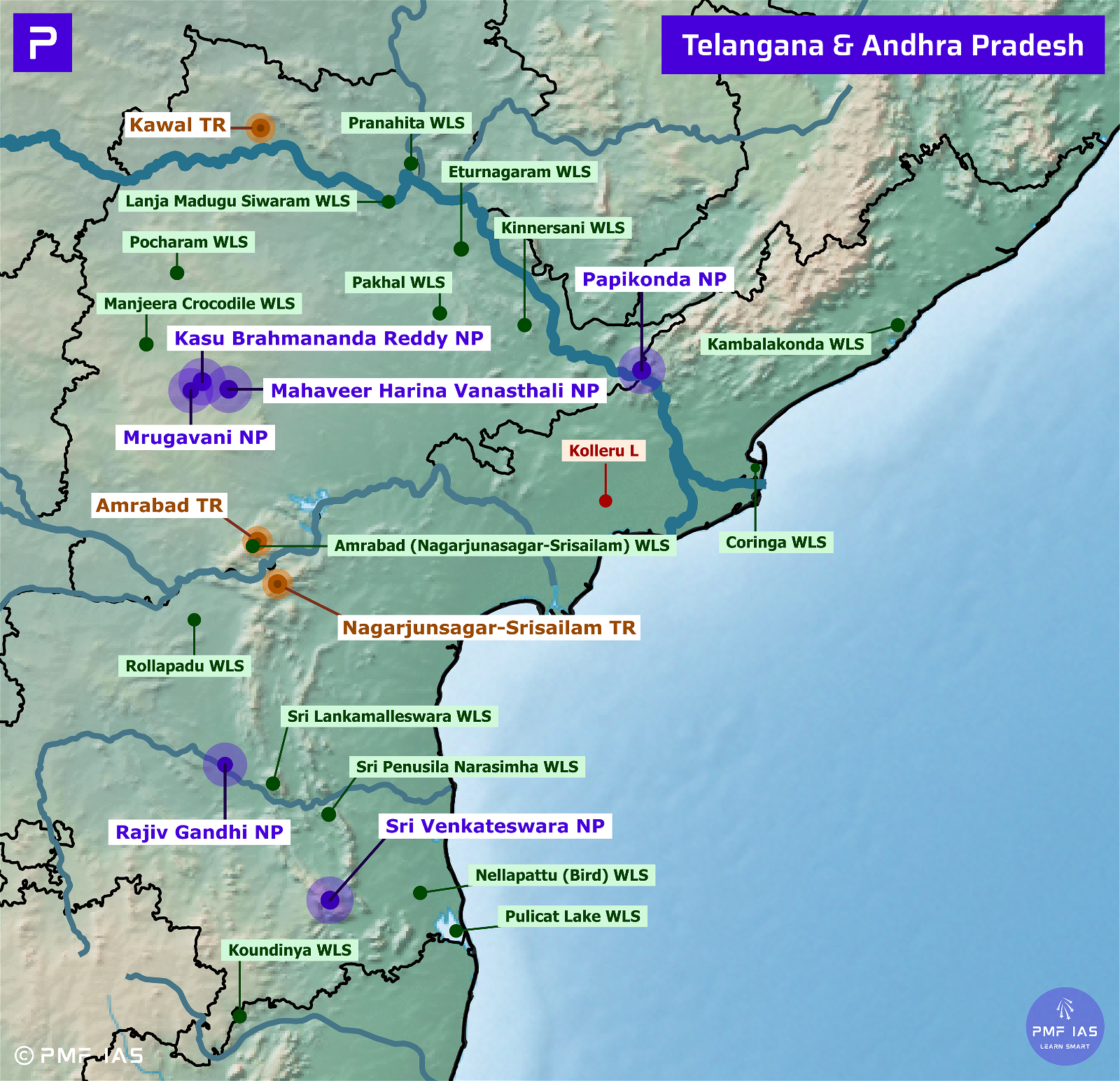
Andhra Pradesh (1) |
||
|
Kolleru Lake |
|
|
Assam (1) |
||
|
Deepor Beel |
|
|
Bihar (1) |
||
| Kanwar Taal or Kabar Taal Lake |
|
|
Goa (1) |
||
| Nanda Lake |
|
|
Gujarat (4) |
||
| Khijadia WLS |
|
|
| Nalsarovar BS |
|
|
| Thol Lake |
|
|
| Wadhvana Wetland |
|
|
Haryana (2) |
||
| Bhindawas WLS |
|
|
| Sultanpur NP |
|
|
Himachal Pradesh (3) |
||
| Chandra Taal |
|
|
| Pong Dam Lake |
|
|
| Renuka Lake |
|
|
Karnataka (4) |
||
| Aghanashini Estuary |
|
|
| Ankasamudra Bird CnR |
|
|
| Magadi Kere CnR |
|
|
| Ranganathituu BS (IBA) |
|
|
Kerala (3) |
||
| Ashtamudi Wetland |
|
|
| Sasthamkotta Lake |
|
|
| Vembanad-Kol Wetland |
|
|
Madhya Pradesh (4) |
||
| Bhoj Wetland |
|
|
| Sakhya Sagar |
|
|
| Sirpur wetland |
|
|
| Yashwant Sagar |
|
|
Maharashtra (3) |
||
| Lonar Lake |
|
|
| Nandur Madhameshwar |
|
|
| Thane Creek
(Flamingo Sanctuary and IBA) |
|
|
Manipur (1) |
||
| Loktak Lake |
|
|
Mizoram (1) |
||
| Pala Wetland |
|
|
Odisha (6) |
||
| Ansupa Lake |
|
|
| Bhitarkanika Mangroves |
|
|
| Chilika Lake |
|
|
| Hirakud
Reservoir |
|
|
| Satkosia Gorge |
|
|
| Tampara Lake |
|
|
Punjab (6) |
||
| Beas CnR |
|
|
| Harike Wetland |
|
|
| Kanjli Wetland |
|
|
| Keshopur-Miani CmR |
|
|
| Nangal WLS |
|
|
| Ropar Wetland |
|
|
Rajasthan (2) |
||
| Keoladeo National Park |
|
|
| Sambhar Lake |
|
|
Tamil Nadu (16) |
||
| Chitrangudi BS |
|
|
| Gulf of Mannar Marine BR |
|
|
| Kanjirankulam BS |
|
|
| Karaivetti BS |
|
|
| Karikili BS |
|
|
| Koonthankulam BS (IBA) |
|
|
| Longwood Shola RF |
|
|
| Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest |
|
|
| Pichavaram Mangrove |
|
|
| Point Calimere WLS & BS |
|
|
| Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex |
|
|
| Udhayamarthandapuram BS |
|
|
| Vaduvur BS |
|
|
| Vedanthangal BS (IBA) |
|
|
| Vellode BS |
|
|
| Vembannur Wetland
Complex |
|
|
Tripura (1) |
||
| Rudrasagar Lake |
|
|
UT of JK (5) |
||
| Hokera Wetland |
|
|
| Hygam Wetland CnR (IBA) |
|
|
| Shallbugh Wetland CnR |
|
|
| Surinsar-Mansar Lakes |
|
|
|
Wular Lake |
|
|
UT of Ladakh (2) |
||
| Tso Kar
(IBA) |
|
|
| Tsomoriri |
|
|
Uttar Pradesh (10) |
||
| Bakhira WLS |
|
|
| Haiderpur Wetland |
|
|
| Nawabganj BS |
|
|
| Parvati Arga BS |
|
|
| Saman BS |
|
|
| Samaspur BS |
|
|
| Sandi BS |
|
|
| Sarsai Nawar Jheel
(IBA) |
|
|
| Sur Sarovar
(Keetham Lake) |
|
|
| Upper Ganga River |
|
|
Uttarakhand (1) |
||
| Asan Barrage
(Asan CnR) |
|
|
West Bengal (2) |
||
| East Kolkata
Wetlands |
|
|
|
Sundarban Wetland |
|
|













Please update all your materials sir/maam.
As of 25th dec 2020, there are 42 Ramsar sites in india
Updated
Please update there are now 46 ramsar sites in india
Worst maps. totally unclear and very vague. either put a political map and mention wetlands or put a river map with wetlands. cant able to find the state border properly and too many rivers and wetland names.
please change the map.
Nice work pmfIAS….nice + clear maps with good detail.
Very comprehensive and easy to understand along with rivers
great work!! much needed!
Lok tak lake area is much more of aulad,both are fresh water lake,then how wular is biggest fresh water lake in india,as you mention,plz tell.
Please update the site list.
Pls update the 75 sites asap.Thanks
update all 75 sites please!!!!
List is getting biggerr every year! :O