Black Carbon and its Impact on the Environment
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
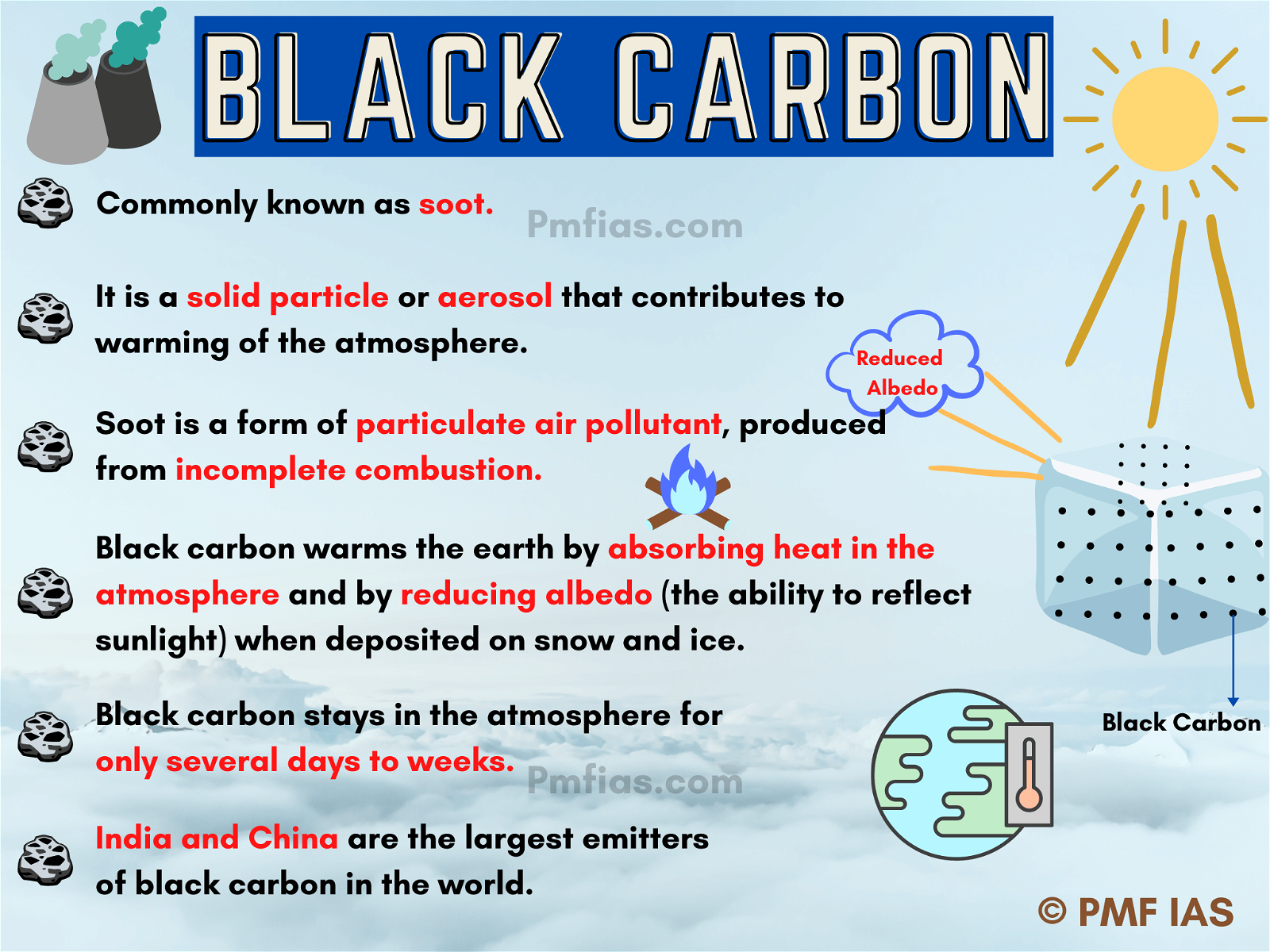
- Black carbon is a solid particle or aerosol (though not a gas) that contributes to warming of the atmosphere.
- Black carbon, commonly known as soot.
- Soot is a form of particulate air pollutant, produced from incomplete combustion.
- India and China are the largest emitters of black carbon in the world.
- The Indo-Gangetic plains will become the largest contributor of black carbon, with about 20 per cent from biofuels, 40 per cent from fossil fuels and about 40 per cent from biomass burning.
The Impact Black Carbon on the Environment
- Black carbon warms the earth by absorbing heat in the atmosphere and by reducing albedo (the ability to reflect sunlight) when deposited on snow and ice.
- BC is the strongest absorber of sunlight and heats the air directly.
- It emits infra-red radiation that increases the temperature.
- In addition, it darkens snowpack and glaciers through deposition and leads to melting of ice and snow (black carbon is contributing to the melting of Himalayan Glaciers).
- Regionally, BC disrupts cloudiness and monsoon rainfall.
- Black carbon stays in the atmosphere for only several days to weeks.
- Thus, the effects of BC on the atmospheric warming and glacier retreat disappear within months of reducing emissions.