
How to Study Geography GS UPSC IAS
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
The first basic step towards success in UPSC CSE is understanding the Syllabus followed by understanding the nature of questions. I have focused on these two aspects in this post.
Watch these videos
Prelims syllabus
- Indian and World Geography – Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and World
Mains Syllabus
- Salient features of world’s physical geography.
- Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian subcontinent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India).
- Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location – changes in critical geographical features (including water bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
Topic wise breakup of syllabus
Physical Geography
Geomorphology
- Earth’s Interior
- Tectonics
- Continental Drift
- Seefloor Spreading
- Plaeomagnetism
- Plate Tectonics
- Mountain Building [Orogeny]
- Physical Phenomena
- Earthquakes, Volcanoes, etc..
- Rocks
- Weathering & Erosion
- Erosional and depositional Landforms [No need to study in detail. Just 10-15 points under each heading]
- Fluvial landforms
- Glacial Landforms
- Marine Landforms
- Arid Landfroms
- Karst Landfroms
Climatology
- The Atmosphere
- Temperature Distribution
- Pressure systems and Wind systems
- Jet streams
- Airmasses
- Fronts
- Frontal Cyclones or Temperate Cyclones
- Humidity and Precipitation
- Geographical Phenomena
- Cyclones – Tropical and Temperate cyclones
- Climatic regions of the World
Oceanography
- Ocean relief
- Temperature Distribution
- Salinity
- Ocean Currents
- Tides
- Coral Bleeching
- Sea level change
- Marine pollution
- Laws related [United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea etc..]
Biogeography and Environmental Geography
- Soil Profile
- Soil degradation and conservation
- Biotic regions [Topic closely related to Climatic regions of the world]
- Deforestation and Conservation of forests.
- Changes in critical geographical features – flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
- Environmental Pollution [Coincides with ‘Conservation, Environmental pollution …..’ topic of GS 3]
Physical Geography of India
- Topics 1-9 [Introduction to Environment] from India A Comprehensive Geography By Khullar [Don’t read from page to page. Read only necessary Headings]
Economic Geography
- Resource distribution
- Marine resources
- Water resources
- Agricultural resources
- Land resources
- Mineral and Non-mineral resources
- Factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India). Mrunal.org articles
- For India Economic Geography
- Selective Headings from Kullar
- Ex: Water resources, Land utilization, Green Revolution, Mineral and Energy resources etc..
- Topics of GS 3 like Cropping Pattern, Irrigation Topics can be studied from Kullar.
Prelims Syllabus Analysis
Indian and World Geography – Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and World
Booklist
- Multiple books for each subject means too much burden on your pocket as well as brain.
- So less books, more revision, more practice tests is the key.
Analysis of books for Geography (GS) Prelims and Mains
| Contents form different books. | |||
| Physical Geography Paperback by Savindra Singh | Certificate Physical and Human Geography by Goh Cheng Leong | SPECTRUM GEOGRAPHY | |
Lithosphere (Geomorphology)
HYDROSPHERE (OCEANOGRAPHY)
ATMOPHERE (CLIMATOLOGY)
BIOSPHERE (BIOGEOGRAPHY) |
PART I
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
PART 2 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND VEGETATION
|
All the topics from the other two books present. | |
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of these books |
|||
| Physical Geography Paperback by Savindra Singh | Certificate Physical and Human Geography by Goh Cheng Leong | SPECTRUM GEOGRAPHY | |
| Analysis | |||
| Degree book. Good for optional.
Extensive coverage of PG |
Meant for civil services.
Good for GS and Optional
|
Meant for civil services.
Good for GS Good to understand the syllabus of Optional |
|
| All topics of Physical Geography present | Most important topic of PG – Plate tectonics, See floor spreading, Continental drift etc.. Missing | All topics of Physical Geography present | |
| Climatic regions not given enough empahasis | Climatic regions given great emphasis. | Climatic regions not explained properly | |
| Langunage: Ok for beginner.
600 page book with only PG Lot of repetition of sentences
|
Langunage: Ok for beginner.
200 pages only
|
Language: tough for beginner. NCERT basics must before reading this book.
1000 pages All topics including Indian and Economic geography present. |
|
| Only PG
No Indian Geo, Economic Geo. Must buy Kullar for Indian Geo |
Only PG
No Indian Geo, Economic Geo. Must buy Kullar for Indian Geo |
Indian Geo present (But not explained in detail)
Kullar is better for Indian Geo. Economic geo present (not given in enough detail. Should supplement with mrunal.org and internet) |
|
| Good for Prelims and Mains. But only PG | Good for Prelims
Bad for Mains |
Good for Prelims and Mains | |
| The book is not revised as of 2014-15 | The book is not revised as of 2014-15 | The book is revised every year | |
| India A Comprehensive Geography By Khullar | |||
|
|||
Also view analysis by mrunal.org
http://mrunal.org/2014/09/answerkey-csat-2014-geography.html
http://mrunal.org/2014/04/mains-answerkey-gs1-geography-2013-part-13-analysis-booklist-mains-2014-contiental-drift-hot-deserts-western-ghat-deltas-sample-answers-explaination.html
Personally I would recommend
-
NCERT [must for basics]
-
For Physical Geography: Spectrum’s Geography [Amazon and Flipkart], [Syllabus oriented topics only][]
-
For climatic regions only: Certificate Physical and Human Geography [Amazon and Flipkart] (only last 50-60 pages of the book).
-
For Indian Geography: If you buy Spectrum, you can look at Indian Geography topics and decide whether to buy INDIA A COMPREHENSIVE GEOGRAPHY by KHULLAR or not.
-
For Economic Geography: org Notes by Mrunal and my own notes which I will be posting in few days
In simple words
-
Buy Spectrum’s Geography only, complete relevant topics first and then decide whether to buy other books
Mains Syllabus Analysis
Physical Geography
Salient features of world’s physical geography.
Booklist
- NCERT [New is better] and must
- Spectrum’s Geography [Amazon andFlipkart],[Syllabus oriented topics only]Reference books
Or
- Physical geography by Savindra Singh [Amazon and Flipkart] [Syllabus oriented topics only]
Or
For Indian Geography
Economic Geography
Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian subcontinent);
factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India)
Booklist
I have compiled notes and I will be posting them on My blog http://www.pmfias.com/
Important Geophysical phenomena
Physical Geography
- Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc.,
A combination of Physical geography, Climatology (Climate Change)
- geographical features and their location – changes in critical geographical features (including water bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
Booklist
- Same as for Physical geography
- Current affairs play a major part here
Topicwise questions from 2013 and 2014 Mains Papers
- Some questions fall under multiple headings
Physical Geography of the World
- What do you understand by the theory of continental drift? Discuss the prominent evidences in its support.
Physical Geography of India
- There is no formation of deltas by rivers of the Western Ghat. Why?
- Bring out the causes for more frequent landslides in the Himalayas than in Western Ghats
Physical Geography – Climatology
- Tropical cyclones are largely confined to South China Sea, Bay of Bengal and Gulf of Mexico. Why?
- What do you understand by the phenomenon of temperature inversion in meteorology? How does it affect the weather and the habitants of the place?
Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian subcontinent);
- Account for the change in the spatial pattern of the Iron and Steel industry in the world.
- Critically evaluate the various resources of the oceans which can be harnessed to meet the resource crisis in the world.
- How does India see its place in the economic space of rising natural resource rich Africa?
- With growing scarcity of fossil fuels, the atomic energy is gaining more and more significance in India. Discuss the availability of raw material required for the generation of atomic energy in India and in the world.
- It is said the India has substantial reserves of shale oil and gas, which can feed the needs of country for quarter century. However, tapping of the resources doesn’t appear to be high on the agenda. Discuss critically the availability and issues involved.
factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India)
- Why did the Green Revolution in India virtually by-pass the eastern region despite fertile soil and good availability of water?
- Do you agree that there is a growing trend of opening new sugar mills in the Southern states of India? Discuss with justification
- Analyze the factors for highly decentralized cotton textile industry in India
Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc.,
- Tropical cyclones are largely confined to South China Sea, Bay of Bengal and Gulf of Mexico. Why?
- The recent cyclone on the east coast of India was called “Phailin”. How are the tropical cyclones named across the world?
geographical features and their location
- Explain the formation of thousands of islands in Indonesian and Philippines archipelagos.
- Why are the world’s fold mountain systems located along the margins of continents? Bring out the association between the global distribution of Fold Mountains and the earthquakes and volcanoes.
- Major hot deserts in northern hemisphere are located between 20-30 degree north and on the western side of the continents. Why?
changes in critical geographical features (including water bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
- Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree?
- Bring out the relationship between the shrinking Himalayan glaciers and the symptoms of climate change in the Indian sub-continent.
- Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world.






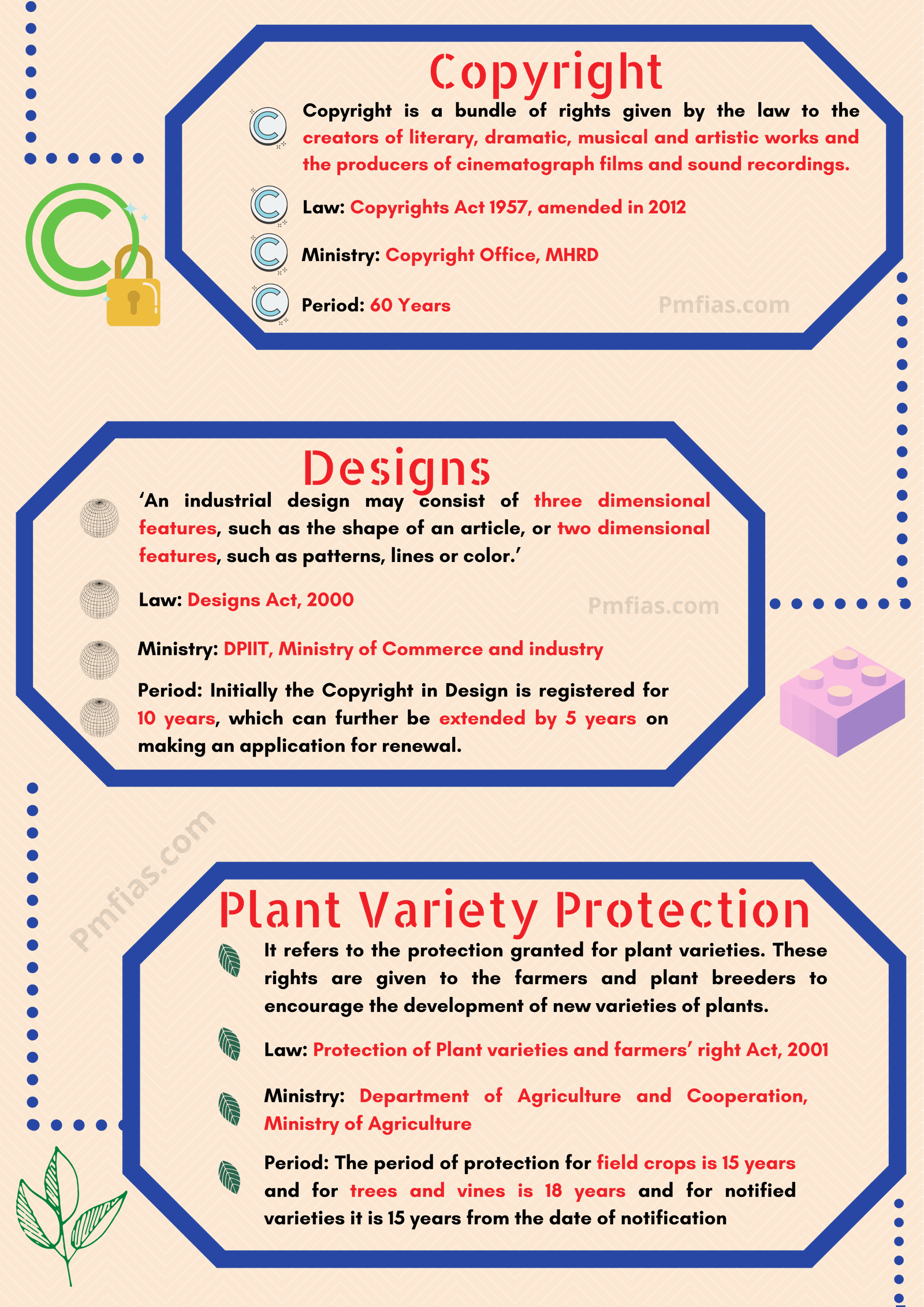
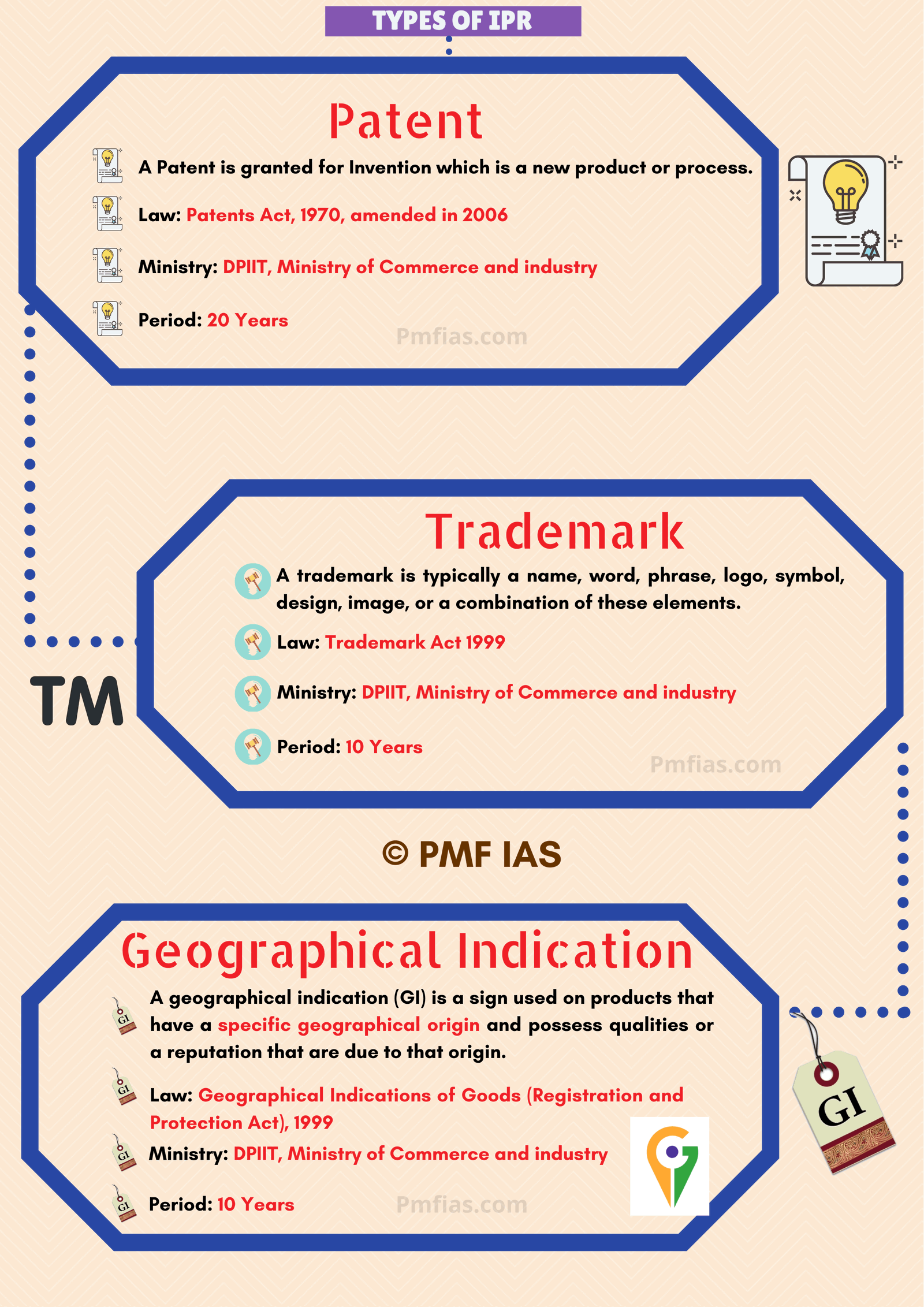



Your’e God from heaven……..Thank you thanx a lot
can you please explain about cyclone roanu from point of view of questions for civil services,pre and mains.
Did you read these two posts?
http://www.pmfias.com/tropical-cyclones-favorable-conditions-tropical-cyclone-formation/
http://www.pmfias.com/storm-surge-cyclones-over-arabian-sea-bay-of-bengal-naming-of-cyclones-cyclones-during-south-west-monsoon-season/
What will the name of next cyclone in Indian Ocean: http://i0.wp.com/www.pmfias.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/naming-of-cyclones-indian-ocean.jpg
Was it a category 1 cyclone (Roanu has a maximum sustained wind speed of 100 km/h)? http://i2.wp.com/www.pmfias.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/Categories-of-Tropical-Cyclones-destruction.jpg
Path of Tropical Cyclones (Roanu had a more regular path)
These cyclones start with a westward movement, but turn northwards around 20° latitude. They turn further north-eastwards around 25° latitude, and then eastwards around 30° latitude. They then lose energy and subside.
Tropical cyclones follow a parabolic path, their axis being parallel to the isobars.
Coriolis force or earth’s rotation, easterly and westerly winds influence the path of a tropical cyclone.
Tropical cyclones die at 30° latitude because of cool ocean waters and increasing wind shear due to westerlies.
Why there are very few Tropical Cyclones during southwest monsoon season?
The southwest monsoon is characterized by the presence of strong westerly winds in the lower troposphere (below 5 km) and very strong easterly winds in the upper troposphere (above 9 km). This results in large vertical wind shear. Strong vertical wind shear inhibits cyclone development.
Also the potential zone for the development of cyclones shifts to North Bay of Bengal during southwest monsoon season.
During this season, the low pressure system upto the intensity of depressions form along the monsoon trough (ITCZ), which extends from northwest India to the north Bay of Bengal.
The Depression forming over this area crosses Orissa – West Bengal coast in a day or two. These systems have shorter oceanic stay (they make landfall very quickly) which is also one of the reasons for their non-intensification into intense cyclones.
Annual frequency of Cyclones over the Indian Seas
The average annual frequency of tropical cyclones in the north Indian Ocean (Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea) is about 5 (about 5-6 % of the Global annual average) and about 80 cyclones form around the globe in a year.
The frequency is more in the Bay of Bengal than in the Arabian Sea, the ratio being 4:1.
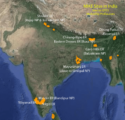
States Vulnerable to Cyclones (map given in post)
Hello Sir,
Thank you very much for the help.
I felt geography is very tough after your videos, notes and few other youtube videos. I can really say I’m good now. Sir I have NCERT and GC leong books. For physical and Indian Geography your notes is sufficient or should I purchase the mentioned books.
Im beginner and aspirant of 2019. My optional is Sociology.
So if you can guide me on this. Thats great.
Thank you very much sir
“For physical and Indian Geography your notes is sufficient or should I purchase the mentioned books”
My notes + Indidustrial Locational factors by Mrunal.org + Regular current affairs should be more than enough for GS.
HII SIR ‘
I am just beginner for this upsc preparation i dont know where to start for geography for GS ….is ur notes for geography and keep revising that or else i want to read all the standard books , please guide me from mains perspective for gs sir .
i have doubt on how to read ur pmfias notes for geography?