[CA 17-08-2016] DDUGJYojana | Balochistan| Nubra Valley | Radiocarbon date | Banking Governance
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Current Affairs August 17, 2016 – Topics gathered from PIB and The Hindu.
Nubra Valley
Prelims – India – Location Based Questions
- An ancient camping site dating 9,000 BC has been discovered by ASI (Ministry of Culture).
- The site lies on the way to Saser La pass from Nubra Valley.
High resolution map of JK: http://goo.gl/XNsRyG
- The valley is formed by Shyok River and the Nubra or Siachan River.
- The Shyok river is a tributary of the Indus river.
- The valley separates the Ladakh and Karakoram Ranges.
- The average altitude of the valley is 3048 metres above the sea level.
- Khardung La pass connects the valley with the Leh town.
- Siachen Glacier lies to the north of the valley.
- The Sasser Pass and the Karakoram Pass connect Nubra with Uyghur (Xinjiang) region of China.


Picture Credits: Wikipedia
Which of the following statements are true?
- Nubra Valley lies in the Ladakh region of J&K.
- Sasser and Karakoram passes lie across the Karakoram range.
- Nubra Valley lies between Ladakh and Karakoram ranges.
- Nubra valley is formed by Nubra and Indus rivers.
Options:
- All
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
J&K divisions: https://goo.gl/LJFk83
Answer: c) 1, 2 and 3 only Nubra valley is formed by Nubra and Shyok rivers.
Radiocarbon date
Prelims – General Science
- It is the technique used to determine the age of an object containing organic material.
- Radiocarbon dating is also known as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating.
Basics
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Mass Number: The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom’s mass number.
- Isotope: Isotopes are atoms of an element with different mass number (atoms having same number of protons but different number of neutrons)(Isotopes).

Picture Credits: Wikipedia
- Radioactivity: Nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiation (Mass is converted to energy – Einstein’s E = mc2).
- Half-life: the period of time after which half of a given sample will have decayed.
Underlying principle
- Radiocarbon (14C or carbon-14) is a weak radioactive isotope of carbon.
- It is constantly created in the atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen.
- 14C is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis.
- Animals acquire 14C by eating the plants.
- When the animal or plant dies, the amount of 14C begins to decrease as it undergoes radioactive decay or radioactivity.
- The age of the material can be calculated by the amount of 14C left.
- The older a sample is, the less 14C is to be detected (because the half-life of 14C which is about 5,730 years).
Example:-
Let’s say human body in general contains 1 gram of 14C.
A human fossil unearthed in Siberia has 0.25 gram of 14C.
So the age of the fossil is 11,460 years.
[1 gram become 0.5 gram in 5730 years. 0.5 gram becomes 0.25 gram in another 5730 years. So age = 5730 + 5730 years.]
- The oldest dates that can be reliably measured by radiocarbon dating are around 50,000 years ago.
Which of the following statements are true?
- Radiocarbon dating is used to determine the age of organic material only.
- Radiocarbon is an isotope of carbon with mass number 12.
- Half-life of a radioactive atom is the period of time after which half of a given sample will have decayed.
- Radiocarbon dating can be used to determine the age of fossils that are millions of years old.
Options:
- 1 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
Answer: c) 3 only
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana
GS3 – Infrastructure – Energy
- Launched in July 2015.
- Under the scheme, government plans to spend 76,000 crore rupees for rural electrification.
- The scheme replaced/subsumed Rajiv Gandhi Grameen Vidyutikaran Yojana (RGGVY).
Official Objectives
- Continuous power supply to rural India (round the clock power to rural households and adequate power to agricultural consumers).
- Feeder separation (separate lines for rural households & agricultural purposes).
- Strengthening of sub-transmission & distribution infrastructure.
- Metering at all levels in rural areas – prevents chori of power – improves the financial health of the distribution companies.
Unofficial Objectives
- In India, electricity for agricultural purposes is highly subsidized. This leads to inefficient use of power. By feeder separation the power supply to agricultural purposes can be regulated (Households will have 24*7 power supply and pump sets will get power for 6-9 hours only).
- Agricultural pump-sets consume hell lot of power and hence load shedding becomes necessary in villages. By feeder separation, the households will now not have to bear the brunt of frequent load shedding.
- When pump-sets and homes are connected to the same line, the chances of equipment failure is high. Feeder separation will prevent this problem as well.
- Rich and the Middle class tackle load shedding by using invertors which are highly inefficient (60-70% efficiency only). So inverters are defeating the very purpose of load shedding. By 24*7 power supply to households, the menace of investors can be tackled.
- Feeder separation makes it easy to detect and prevent power theft. It prevents the misuse of ‘free power’ provided for agricultural purposes.
Benefits
- Modernization of villages and financial services: Improvement in Health, Education, Banking (ATM) services.
- Self-employment and micro-entrepreneurship: Small and household enterprises shall grow.
- Digital India: Improvement in accessibility to radio, telephone, television, internet and mobile etc.
- Effective governance: Epanchayat, e-seva, e-billing: Accessibility of electricity to schools, panchayats, hospitals and police stations etc.
“100% rural electrification can be a game changer in India’s development model.” Evaluate this statement. [200 words]
Answer should include:
- Schemes and government initiatives related to rural electrification.
- % of people living in Villages. Expected Changes in Village population in the next 20 years.
- “Villages are the backbone of India.” M.K. Gandhi
- Lack of employment in villages and Distress Migration.
- Benefits as mentioned above. [Add more points if you have any]
WAPCOS
GS 2 – Indian and Neighborhood, International Relations
- Water and Power Consultancy Services (India) Limited.
- WAPCOS Limited is a “Mini Ratna-I” Public Sector Enterprise.
- It functions under the aegis of the Union Ministry of Water Resource, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation.
- It provides services in Water Resources, Power & Infrastructure sectors in India & Abroad.
- Its notable achievement has been the successful construction of Salma dam in Afghanistan.
- The Company succeeded in securing new business in many African countries.
Why invest abroad?
- WAPCOS and similar companies (ONGC Videsh) strengthen bilateral relations.
- They create a goodwill for India by providing jobs to locals and by aiding long term development of the region.
- Soft power: Afghanistan is a gateway to energy surplus Central Asia. Helping Afghanistan will help India in the long run.
- China has investments in most parts of Africa. These investments help China to secure raw materials for its industries. India wants to catch up with China and gain a strong foothold in the African countries. Hence it keeps making these foreign investments.
Military = Hard power.
Investments, aid etc. = Soft power.
Gender issues
General Topic
- Sexism: prejudice, stereotyping, or discrimination, typically against women, on the basis of sex.
- Male privilege: Concept used to examine the social, economic, and political advantages or rights that are made available to men solely on the basis of their sex.
Recent developments in India-China relations
- Chinese is advancing with its CPEC – China Pakistan Economic Corridor in PoK under its One Belt, One Road (OBOR) initiative.
- China blocked the move to list Masood Azhar, the Jaish-e-Mohammad leader, as a terrorist at the United Nations.
- China prevented India’s entry into the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- Pakistan has continues to be a low-cost and effective proxy of China against India.
- China is shielding Pakistan from international pressures consequent upon its use of cross-border terrorism as an instrument of state policy against India.
- Beijing has cautioned that India should avoid getting “entangled” in the South China Sea issue.
- India, to balance economic and military asymmetry with China, might side with the US in the South China sea issue.
- India can encourage anti-Pakistan militants in Balochistan, this would adversely affect the utility of Gwadar port, another key link in the OBOR.
Recent developments in India-Pak relations
- Pakistan and its administrative establishment provokes India by constantly referring to the recent violence and human rights violation in Kashmir. [Those who use the facade of human rights to sponsor barbaric terrorism are hypocrites of the worst kind. M.J.Akbar]
- PM Modi hits back at Pak by referring to human rights violations by Pak in Balochistan and POK.
- Pakistan has proposed a bilateral agreement with India over a mutual ban on non-testing of atomic weapons.
- Such a ban will ease the entry of the two countries into the elite Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- Interesting comment by M.J. Akbar: We are a nation which believes in faith equality and not in faith supremacy.
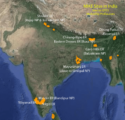
Balochistan
- Balochistan is Pakistan’s largest but least developed province.
- Similar to Kashmir’s, the roots of the conflict go back to Independence.
- After the formation of Pakistan in 1947, the rulers of the Khanate of Kalat, a princely state under the British and part of today’s Balochistan, refused to join the new nation.
- Pakistan sent troops in March 1948 to annex the territory.
- The then ruler of Kalat, later signed a treaty of accession.
- Some groups continued to fight, triggering the first conflict between Balochis and the Pakistani Army.
- After the 1948 rebellion was put down, crisis erupted in 1958.
- In 1962-63 and 1973-77, Baloch nationalists mounted violent campaigns for independence.
- Tensions started building up after General Pervez Musharraf seized power in 1999.
- When the military started building new cantonments in Balochistan, radical nationalist factions saw it as a bid by the Army to tighten control over the region.
- The fifth wave of insurgency that broke out in this context is still on.
- The province has several separatist groups, the strongest being the Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA).
- BLA is designated as a terrorist group by Pakistan and the U.K.
- Islamabad alleges that India has been backing the BLA.
- Every time there is unrest in the region, the Army uses brute force to retain order (same).
Strategic and Economic Importance of Balochistan
- Gwadar port (important strategic point of Makran coast and String of Pearls) is a part of Balochistan.
- Major part of CPEC [China Pakistan Economic Corridor] runs through Balochistan.
- CPEC is a $46 billion project linking the Gwadar port with the city of Kashgar, a trading hub in the western Chinese region of Xinjiang.
- The Iran-Pakistan gas pipeline is planned to run through Balochistan.
Recent developments related to China
- A tribunal constituted under the provisions of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) awarded a negative arbitration against China over its claim to the South China Sea.
- US deployed THAAD anti-missile defence system in South Korea.
Giant panda
Prelims – Environment.

- Conservation status: Endangered.
- Habitat: Central China. Major diet is bamboo.
- Threats: Farming, deforestation, and other development.
- Giant panda is different from Red Panda (endangered). Red panda is found in eastern Himalayas and south-eastern China.
Draft Ganga Act to draw from Highways Act
- Water Resources Ministry is the nodal agency in charge of implementing the Rs. 20,000-crore National Clean Ganga Mission by 2022.
- So far it has spent only around Rs. 320 crore, despite Rs. 2,000 crore being sanctioned.
- This was partly due to a lack of consensus between the Ganga States and the center.
Solution
- Center aims to make Ganga Act similar to National Highways Act were Center’s decision is final in case of disputes.
- The National Highways Authority of India Act empowers the Central government to have complete power over roads, bridges designated as a part of “national highways.”
Mr. Rajan’s Suggestions on Banking Governance
BBB should appoint top executives at state-owned banks
- The task of appointing top executives and non-official directors in public sector banks should be left to the Bank Board Bureau (BBB).
- At present, the Centre appoints the chief executive, executive directors and other board members.
- Rajan’s suggestion is in line with the proposals of the P.J. Nayak committee set up by the RBI to look into the issue of governance in Indian banks.
About BBB
- The Centre set up the BBB in February 2016 under the chairmanship of former Comptroller and Auditor General of India Vinod Rai.
- At present, BBB is involved in the short-listing and selection process of public sector bank executives. The final appointments are made by the government.
Some other suggestions
- Recruit people with expertise in risk management and IT, cyber security etc. in the middle management that have been thinned out by retirements.
- Persuading courts to allow some campus hire, making bank entrance exams much less onerous.
- Freedom to hire locally, and pay wages commensurate with the local labour market.
- Rewards like Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) that give all employees a stake in the future of the bank.
- Pay better to the top level management to attract talent through lateral entry.
- Central bank and the government should reduce the differences in regulatory treatment between
- public sector banks and private sector banks, and
- between banks and other financial institutions, to encourage competition among them.
What are the administrative challenges that the public sector banks in India are facing? Suggest improvements.
Challenges
- Political interference in functioning and appointments.
- Loan waiver schemes that put more pressure on public sector banks.
- Inefficient top level managements. [Less pay = less talent]
- No clear legislation to govern lateral entry.
- Redundant hire and fire system. Slow reforms [Socialist and trade union mess]
Improvements
- Improvements that Mr. Rajan sir mentioned.
How to make animal rearing more productive
GS 3 – Economies of Animal Rearing
- Development of database of animal diseases.
- Creating awareness on the benefits of the vaccination in livestock.
- Rearing productive livestock with the help of veterinary sciences.
Understanding economies of animal rearing is important to achieve the national mandate of food and nutritional security.