Habitat Rights of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): Baiga community, a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG), became the second PVTG to get habitat rights in Chhattisgarh, after the Kamar tribal group.
|
Habitat Rights
- Habitat rights recognition grants communities the right to their traditional territory, socio-cultural practices, livelihoods, ecological and traditional knowledge, and the protection of their natural and cultural heritage. (Habitat rights don’t grant ownership to property).
- Habitat rights are given to PVTGs under section 3(1) (e) of The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 or Forest Rights Act (FRA).
- According to FRA, “Habitat comprises the customary habitat and such other habitats in reserved forests and protected forests of primitive tribal groups and pre-agricultural communities and other forest dwelling Scheduled Tribes.”
How the Government Fixes a Habitat
- The procedure is based on guidelines from the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) in 2014.
- The tribal leaders are consulted about the extent of their culture, traditions, and occupation.
- The government corroborates it, and then a habitat is declared.
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) provides technical assistance to the administration to implement the habitat rights law.
- Four state-level departments, i.e., Forest, Revenue, Tribal, and Panchayati Raj, coordinate with the UNDP team to ascertain habitats.
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG)
- PVTG (previously known as a Primitive Tribal Group) is a sub-classification of Scheduled Tribes considered more vulnerable among the tribal groups.
- Dhebar Commission (or Tribal Panchsheel Committee) recommended the creation of Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs). Based on this, the Indian Government created PTGs in 1975.
- In 2006, PTGs were renamed as PVTGs.
- At present, there are 75 PVTGs out of 705 Scheduled Tribes.
- Odisha has the highest number of PVTGs.
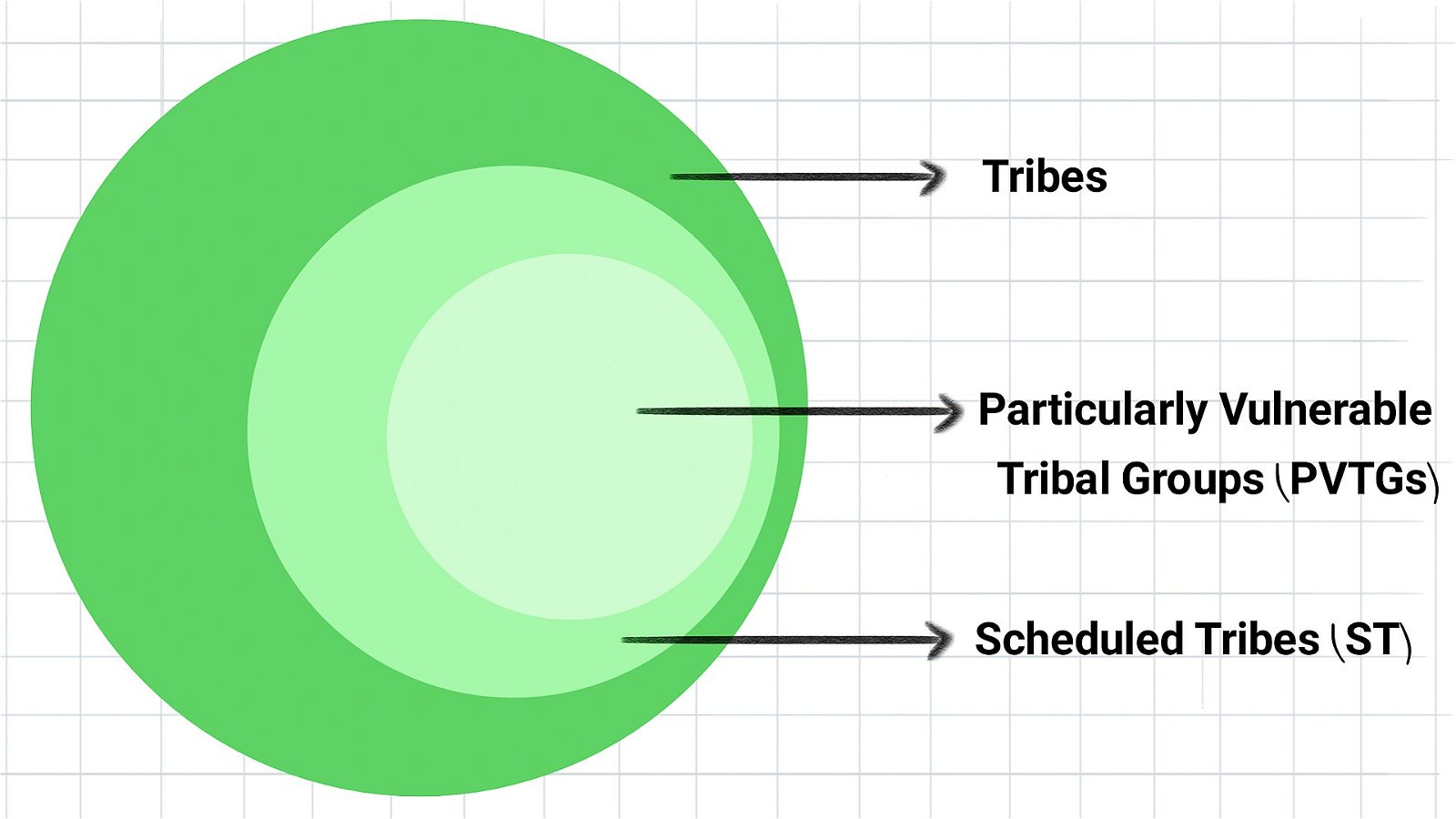
- Criteria followed for identification of PVTGs are:
- Pre-agricultural level of technology
- Low level of literacy
- Economic backwardness
- A declining or stagnant population
|
PVTGs with Habitat Rights
- Only three PVTGs have habitat rights.
- Bharia Tribe (Madhya Pradesh): 1st PVTG to get habitat right.
- Kamar Tribe (Chhattisgarh)
- Baiga Tribe (Chhattisgarh)
Benefits of Habitat Rights to PVTGs
- Protect traditional habitats from developmental activities: Habitat rights require consent and consultation of gram sabha for development activities. This provision helps protect traditional habitats from harmful activities like mining.
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)