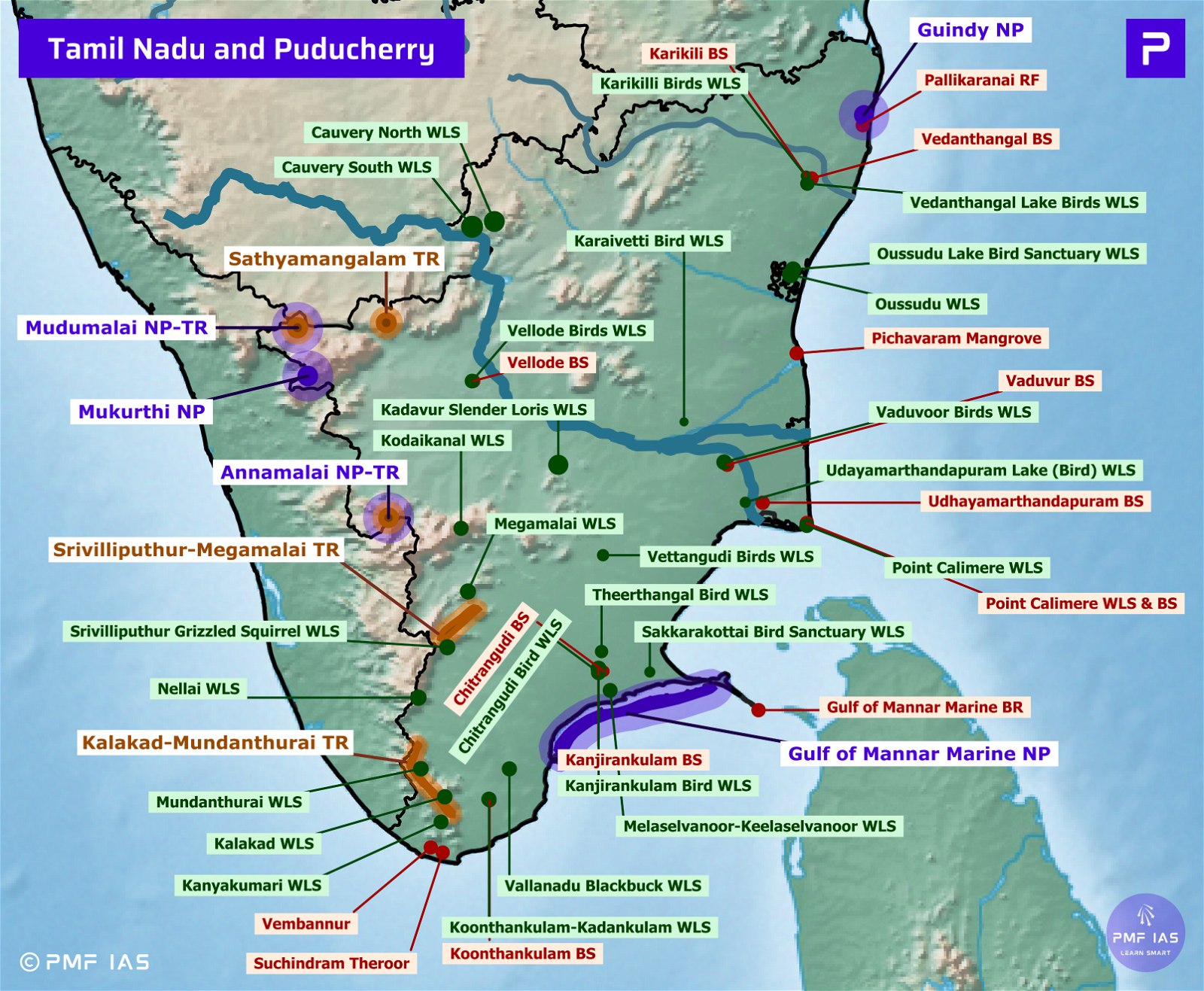
Assam National Parks, Tiger Reserves, Wildlife Sanctuaries & Ramsar Sites
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 26, 2024 7:22 PM
- Non-human Primates: golden langurs, Assamese macaques, rhesus macaque, slow loris, hoolock gibbons.
- Major Avifauna: Bengal florican, Greater adjutant, spot-billed pelican, lesser adjutant, white-winged wood duck, Baer’s pochard, greater spotted eagle, Sarus crane.
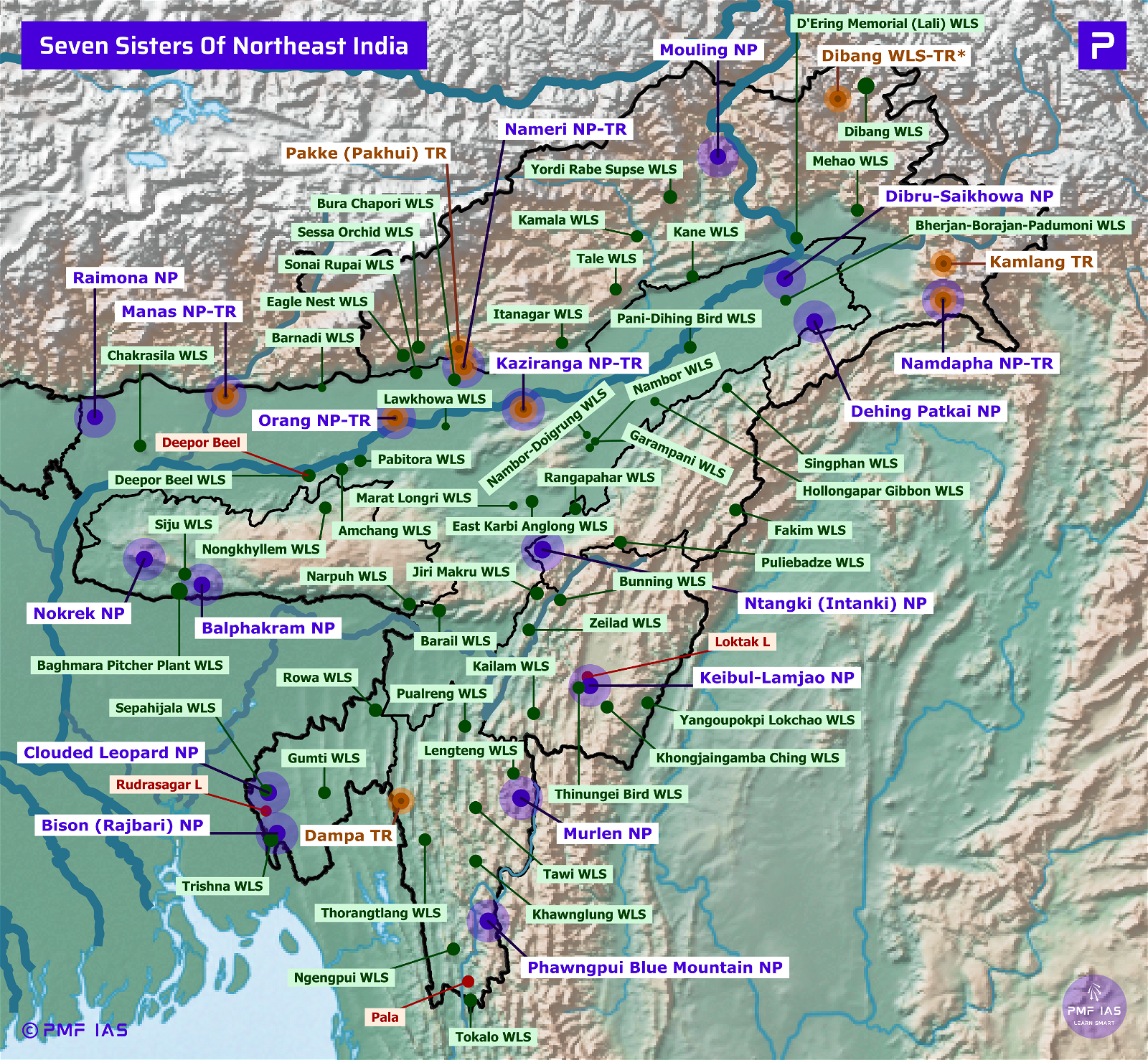
Dihing Patkai National Park, Wildlife Sanctuary, ER
- It is located in the foothills of Patkai Hills & Dihing River flows through it. Also called Jeypore Rainforest, it harbours the largest stretch of lowland rainforests in India.
- The Digboi Oil Refinery (the oldest refinery of Asia) and Lido Coal Mines are located near the park.
- It has the highest concentration of the White Winged Wood Duck (EN), the state bird of Assam.
- Vegetation: Assam Valley tropical wet evergreen forest (rainforest with distinct four layers).
- Major Fauna: Elephant, tiger, leopard, clouded leopard, golden cat, fishing cat, marble cat, hog deer, sloth bear.
- Major Avifauna: Oriental darter, lesser adjutant, greater spotted eagle, hornbills, hill myna.
- Threats: Coal mining, oil extraction, tea gardens, village settlements, deforestation.
Dibru-Saikhowa National Park, Biosphere Reserve
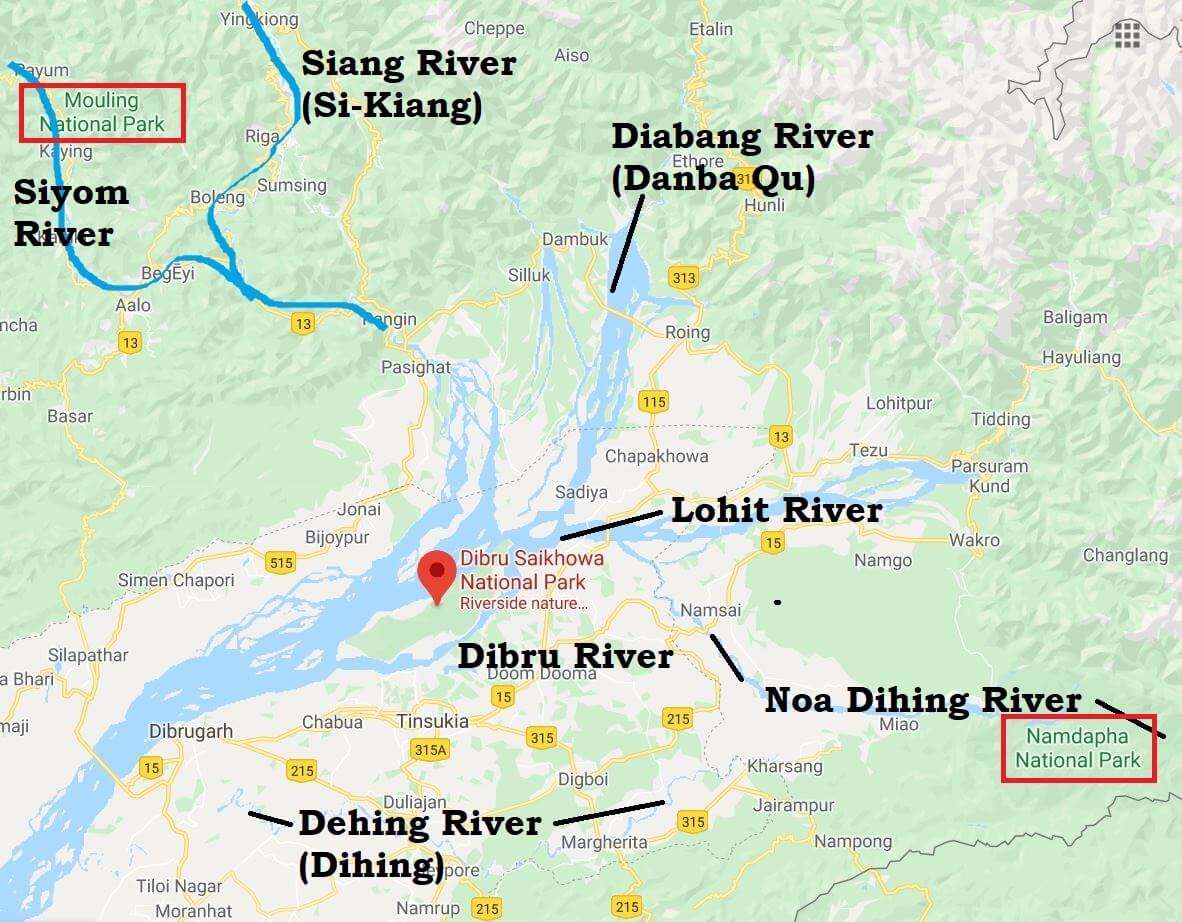
- It is bounded by the Brahmaputra and Lohit Rivers in the north and Dibru River in the south.
- It is famous for Feral horses (descendants of horses who bolted out of stables set up by the British Army in and around Tinsukia during World War II).
- Vegetation: Wet evergreen and semi-evergreen, deciduous, littoral and swamp forests.
- Major Fauna: Bengal tiger, Indian leopard, clouded leopard, sloth bear, dhole, Gangetic dolphin, Asian elephant, wild boar, sambar, hog deer, barking deer.
Kaziranga Tiger Reserve, National Park
- It lies in the Eastern Himalayan biodiversity hotspot and the Brahmaputra River flows through the park.
- This park which hosts 2/3rd of the world’s one-horned rhinoceroses, is a World Heritage Site. It is recognized as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International.
- Vegetation: Alluvial grasslands and savanna woodlands, and tropical moist deciduous and semi-evergreen forests.
- Major Flora: Spear grass, elephant grass, common reed, cotton tree, and elephant apple.
- Major Fauna: One-Horned rhinoceros (VU), Royal Bengal Tiger, Asian elephant, wild water buffalo (EN) and swamp deer are collectively known as the ‘Big Five’ of Kaziranga. Other important fauna: fishing cat, small Indian civets, sloth bear, Chinese pangolin, Indian pangolins.
- Threats: Floods and encroachment by people.
Manas Biosphere Reserve, National Park, Tiger Reserve, ER
- It is a UNESCO Natural World Heritage site located on the Himalayan Foothills. It is contiguous with the Royal Manas National Park (Bhutan). Manas river (a tributary of Brahmaputra) passes through the heart of the National Park.
- The bhabar-terai region with riverine succession makes it one of the richest areas of biodiversity.
- Vegetation: Semi-evergreen forests, moist and dry deciduous forests, savanna woodland, and grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Hispid hare, pygmy hog, wild water buffalo (EN), rhinoceros (reintroduced in 2007), elephants, sambar, Chinese pangolin, clouded leopards.
- Major Avifauna: It has the world’s largest population of the endangered Bengal florican. Other major bird species include great hornbills, pelicans, eagles, and herons.
Nameri Tiger Reserve, National Park
- It is located in the foothills of theEastern Himalayas & Kameng River flows along its southern boundary. Its northern boundary is shared with the Pakke Tiger Reserve. It has two core areas: Nameri National Park & Sonai-Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Major Flora: Ajar, hollock, nahor and orchids.
- Major Fauna: Tiger, leopard, sambar, dhole, gaur, clouded leopard (VU), barking deer, marbled cat, Himalayan black bear, capped langur, Indian giant squirrel.
- Major Avifauna: White-winged wood duck.
- Threats: Logging, human-elephant conflict, poaching.
Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, Tiger Reserve
- It lies on the bank of the Brahmaputra River. Pachnoi River, Belsiri River and Dhanshiri River border the park.
- The park, formed of alluvial flood plains, is an integral part of the Indo-Burma hotspot of biodiversity.
- Vegetation: Moist deciduous forest, swamp forest, wet alluvial and savannah grassland.
- Major Fauna: Indian rhinoceros (VU), pygmy hog (EN), Asian elephant, wild water buffalo (EN), Bengal tiger, hog deer, Gangetic dolphin (EN), Indian pangolin (EN).
- Non-human Primates: Rhesus macaque
- Threats: Illegal occupation by immigrants, poaching, and wide river channels.
Raimona National Park
- It is located along the Himalayan foothills together with Buxa Tiger Reserve of West Bengal and Phipsoo Wildlife Sanctuary and Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park of Bhutan.
- It is bounded by the Sankosh River on the west, the Saralbhanga River on the east, the Indo-Bhutan border on the north and Ripu RF on the south.
- Vegetation: Moist deciduous and semi-evergreen forest.
- Major Fauna: Asian elephant, Bengal tiger, clouded leopard (VU), Indian gaur, wild water buffalo, chital, hornbill.
- Non-human Primates: Golden langur (EN) (endemic to the region; named as the mascot of Bodoland region).
- Major Avifauna: White-bellied heron, Oriental darter, lesser adjutant, Bengal florican, hill myna.
Wildlife Sanctuaries of Assam
Barak Bhuban Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is a proposed Wildlife Sanctuary in Assam’s Barak Valley (between the Barak River and the Sonai River).
-
Major Fauna: Slow loris, rhesus macaque, pig-tailed macaque, stump-tailed macaque, Assamese macaque, capped langur, hoolock gibbon.
Barnadi Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated on the Himalayan foothills bordering Bhutan.
-
Burachapari Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated on the south bank of the Brahmaputra River.
-
Chakrasila Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated on the north bank of the Brahmaputra River.
Deepor Beel Wildlife Sanctuary (Ramsar Site)
- It is a permanent freshwater lake in a former channel of the Brahmaputra river.
-
It is a few kilometres to the left of Guwahati, whereas Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary is around 35 km to the right.
Dihing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated on the Assam-Arunachal border. The Dihing River originates in the Patkai Bum Hills (Arunachal Pradesh & Myanmar border) and flows through this Wildlife Sanctuary.
-
It was recently upgraded to a National Park.
Garampani Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located adjacent to Nambor Wildlife Sanctuary.
-
It contains hot water spring and waterfalls.
Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary
-
It contains India’s only apes – the hoolock gibbons (EN), and North-eastern India’s only nocturnal primate – the Bengal slow loris (VU). Threats: Tea gardens.
Lawkhowa Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated between Kaziranga National Park and Orang National Park.
-
Marat Longri Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located a few kilometres from Diphu, Karbi Anglong.
-
It is an important component of Dhansiri-Lungding ER.
Nambor Wildlife Sanctuary
-
It is located on the periphery of the Mikir Hills (Karbi Anglong Plateau).
Nambor-Doigrung WLS
- It is located in the Golaghat district in Assam.
-
The sanctuary along with Garampani Wildlife Sanctuary, Nambor Wildlife Sanctuary are part of the Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong ER.
Pabitora Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is about 30 km to the east of Guwahati.
-
Pobitora (Mini Kaziranga) has exceeded its rhino-bearing capacity. Under the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020) several rhinos were Translocated from Pobitora and re-introduced into the Manas National Park.
Pani-Dihing Wildlife Sanctuary (BS)
-
It is to the north-east of Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary.
Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary
-
It is located to the west of Pakke Tiger Reserve (Arunachal Pradesh) and Nameri National Park (Assam).
Others
- Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary: Located on the fringe of Guwahati (between Guwahati & Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary).
- Barail Wildlife Sanctuary: Barail Range of Assam.
- East Karbi Anglong Wildlife Sanctuary: Near Diphu, East Karbi Anglong district.
Ramsar Sites of Assam (1)
Deepor Beel
- It is a permanent freshwater lake in a former channel of Brahmaputra. It is a few kilometres to the left of Guwahati, whereas Pobitora WLS is ~35 km to the right.
- Threats: over-fishing, hunting, pollution from pesticides, and infestation by water hyacinth.
- Endangered Avifauna: Grey Pelican or Spot-billed pelican (VU), Lesser Adjutant Stork (VU), Greater Adjutant Stork (EN), Baer’s Pochard (CR).
Last updated on April 26, 2024 7:22 PM