Galaxies: Spiral Galaxies & Elliptical Galaxies, Our Galaxy (The Milky Way)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 19, 2024 7:28 PM
- Galaxy is a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction. They are the major building blocks of the universe. The smallest galaxies contain about 100,000 stars, while the largest contains up to 3000 billion stars.

- From the billions of galaxies, two basic types have been identified: 1) Regular galaxies, & Irregular galaxies (1/10th of all galaxies. The stars are very old).
Regular Galaxies
|
Spiral Galaxies |
Elliptical Galaxies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dark matter
Why is it Called Dark Matter?
|
|
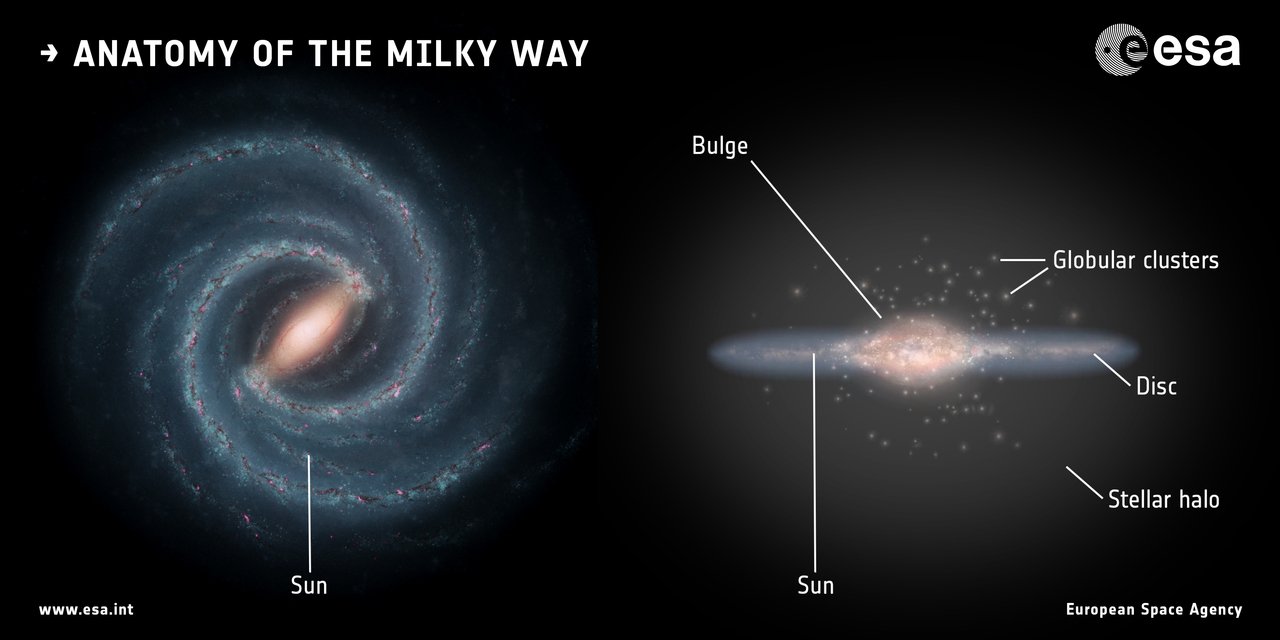
Our Galaxy (The Milky Way)
- The Milky Way galaxy hosts our solar system.
- It is shaped like a flat disc with a central bulge. Its diameter is between 1,50,000 and 2,00,000 light-years. In the nucleus, the thickness reaches 10,000 light years, whereas in the disc it is 500-2,000 light-years thick.
- A light year is a measure of distance and not of time. Light travels at a speed of 300,000 km/second. Considering this, the distances the light will travel in one year is taken to be one light year. The mean distance between the sun and the earth is 149,598,000 km. In terms of light years, it is 8.311 minutes.
- The Milky Way is estimated to contain 100-400 billion stars. The inner stars travel faster than those further out. A supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A* is at the centre. The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light years from the centre (about one-third from the centre) of the Milky Way.
- Stars like Sun are rare in the Milky Way galaxy, whereas substantially dimmer and cooler stars, known as red dwarfs, are common.
- The Sun completes one lap of the galaxy about every 220 million years. It revolves around the centre of the Milky Way with a speed of 285 km per second.
- Andromeda is the closest big galaxy to the Milky Way — being 2 million light years away.
Last updated on April 19, 2024 7:28 PM