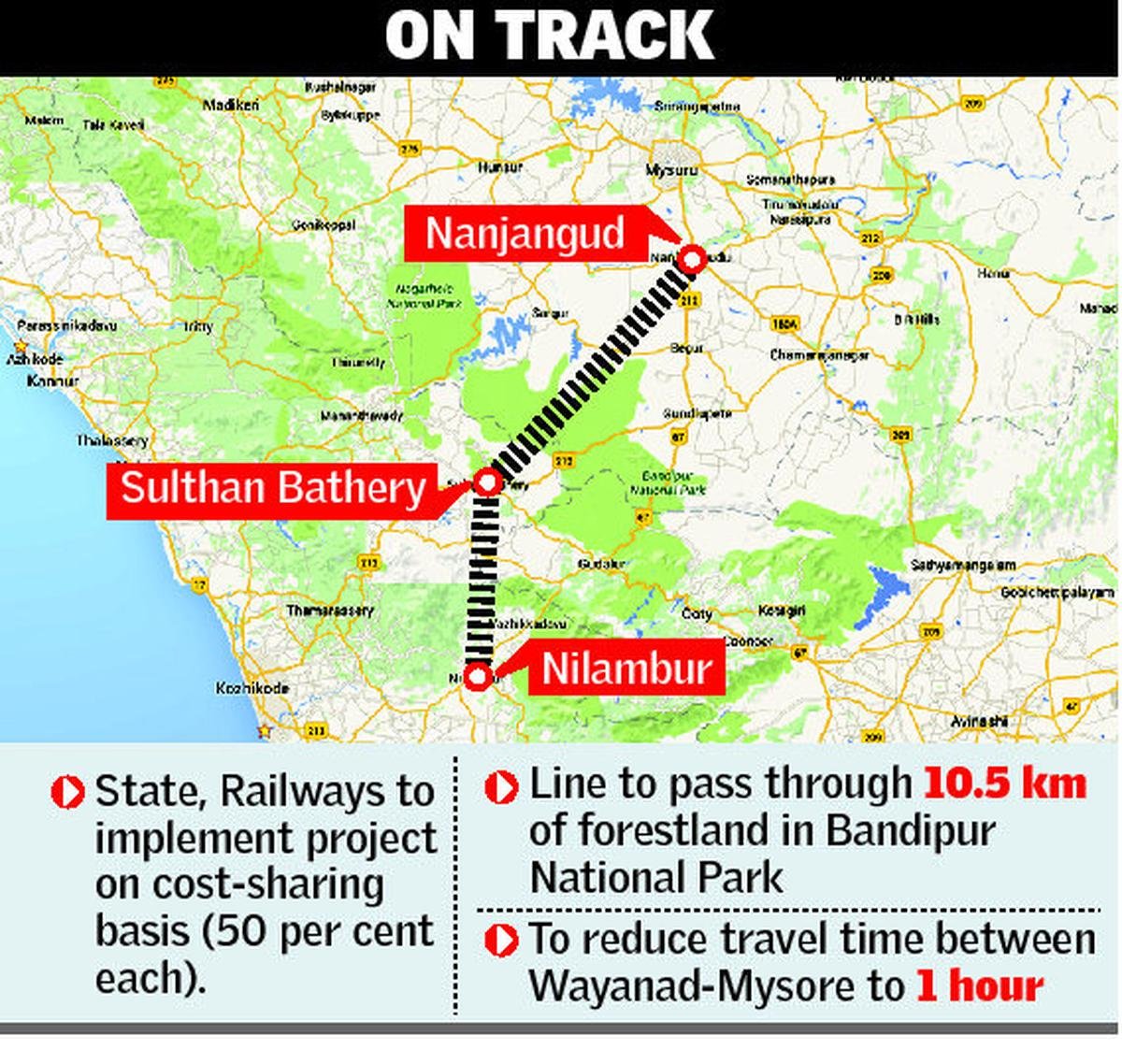
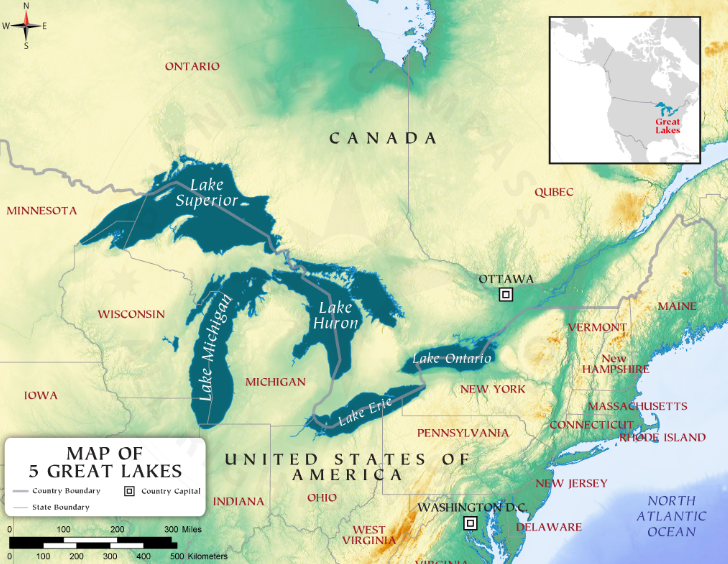
Semiconductor Manufacturing in India
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (LM): India is considering ₹10,000 crore revised scheme for local chip manufacturing.
What is a Semiconductor?
- It is a material, composed of Silicon, Germanium etc., that fits between a conductor (full conductivity) and an insulator (no conductivity), designed to manage and control the flow of current in electronic devices and equipment.
- Global major producers: Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, USA, and China.
- Semiconductors Market in India: $25 billion; projected to reach $80 billion by 2028.
Significance of domestic manufacturing of semiconductors
- Technological Sovereignty: For e.g. concentrating chip production in a few countries can lead to a ‘Malaccan Dilemma’ kind of crisis for India.
- Key to net zero carbon emissions target: Semiconductor chips are key components in green technologies like EVs, solar panels, turbines, LEDs, etc.
- Insulation from Global Supply Chain Shocks: The concentration of chip manufacturing in a few countries makes India vulnerable to global shocks like the US-China trade war, the COVID-19 pandemic, etc.
- Positive spillover effect in the health sector (AI/ML Tools performing complex surgeries), Space sector (Satellite, Launch Vehicles, Deep space probes), etc.
- National security: by reducing dependence on imported semiconductors, safeguarding critical infrastructure, defense systems, and sensitive data from vulnerabilities.
- Essential component for advanced technologies like AI, Quantum computing, Blockchain applications, 5G, IoT, Self-driven vehicles, Drones, etc.
- Stable forex reserves: It will help India boost export earnings by tapping the global market and save huge Forex, thus narrowing the trade deficit.
|
Challenges in making India a Semiconductor hub
- Highly capital-intensive: The manufacturer has to maintain a large volume production facility to support volume orders, which will result in very high investment in the beginning.
- High maintenance and infra dependency: Requirement of high-quality supply of pure water, uninterrupted electricity, etc.
- Lack of highly skilled labor and technology
- Scarcity of raw materials: From a value-chain perspective, its production needs silicon, Germanium and Gallium arsenide, and Silicon carbide which are not available in India and needs to be imported.
- Adverse effect on environment: Use of toxic materials in the fabrication process such as arsenic, antimony, and phosphorous, along with high global warming potential fluorinated compounds.
Way Forward
- Making available sustainable logistics and infrastructure required for a modern Fabrication plant, with swift transportation, uninterrupted electricity, etc.
- Industry and academia collaboration: Promotion of a start-up culture among faculty and students in higher educational institutes through initial capital and mentoring. For eg. Semiconductor Startup Incubation and Acceleration Program (SSIAP) at IIT Hyderabad.
- ‘Friend Shoring’ for a secure supply of inputs (For eg. QUAD, South Korea, Taiwan, etc).
- Strategic framework covering the entire chip-making value chain i.e. design centers, testing facilities, packaging, etc. Legislative backing to policy on lines of USA and EU Chips Act.
- Other Measures: Facilitative tax & IPR regime, Industrial clusters, funding across the value chain, etc.
GoI Initiatives for semiconductor manufacturing
- Production Linked Incentive scheme (PLI)
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme to train high-quality engineers.
- Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (M-SIPS) for Semiconductors.
- Digital RISC-V (DIR-V) program for the production of microprocessors.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)