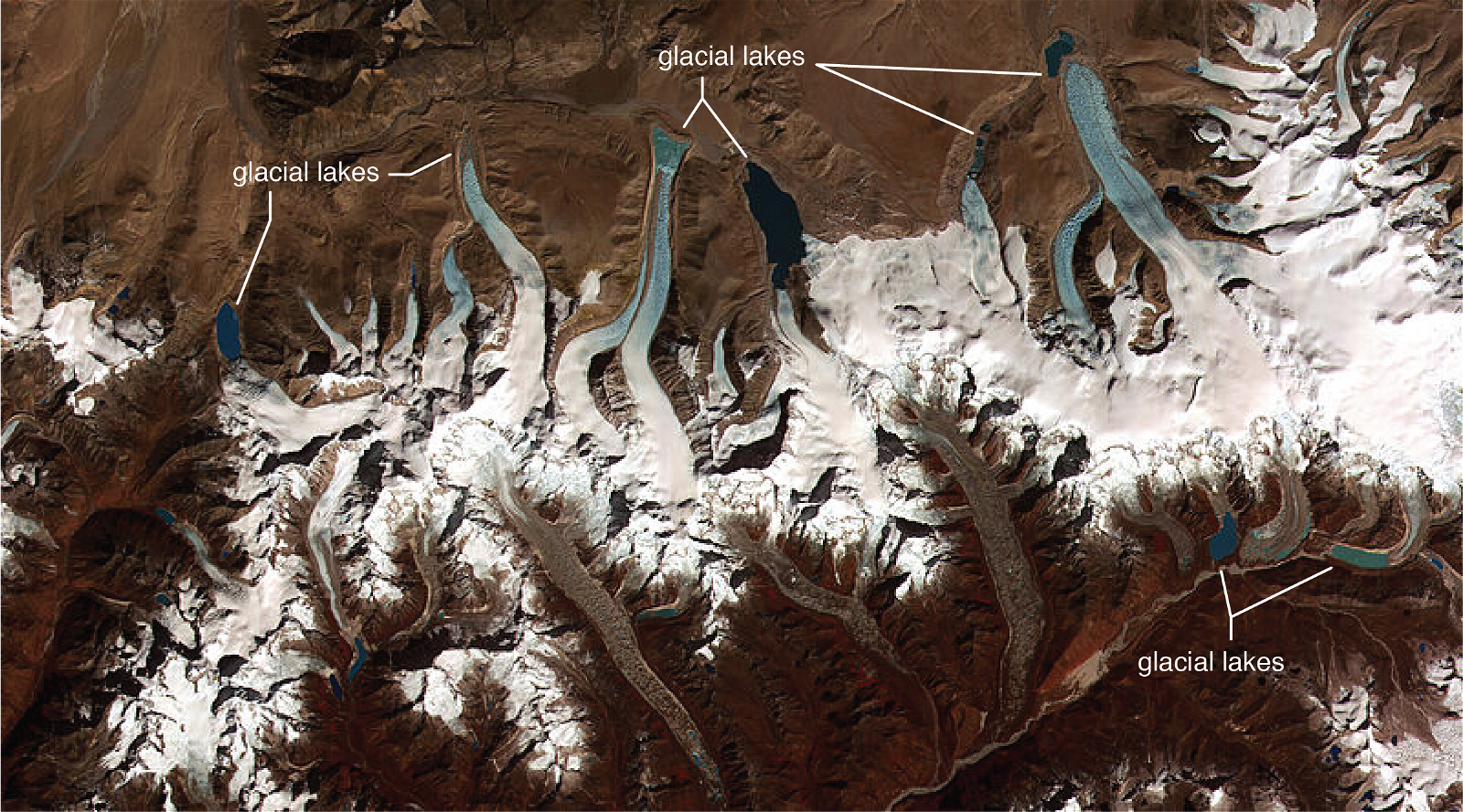
Circular Migration, Circular Migration in India
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Circular migration
- Context (TH): Circular migration is characterised by individuals moving between their country of origin and a destination country temporarily in response to employment opportunities.
- This phenomenon is predominantly observed among low-income groups seeking seasonal employment in various locations.
Evolution of Circular Migration
- Circular migration gained prominence in the 1960s and 1970s with the rise of globalisation.
- Improved transportation and communication, the expansion of social networks, and the growth of multinational corporations boosted the circular migration phenomenon.

Effect of Circular Migration on the Economy
- For a country of origin, circular migration can lead to the flow of remittances, boosting the domestic economy. However, it may also result in brain drain.
- For destination countries, circular migration can help fill low-income, low-skill job gaps. Yet, it can also lead to concerns and cultural conflicts among host populations.
Circular Migration in India
- In India, internal migration has historically followed circular patterns.
- The movement of rural populations to urban areas for employment in manufacturing, construction, and services sectors has been common.
- The uneven development post-liberalization has led to significant inter-state migration, with some states like West Bengal, Odisha, and Bihar witnessing high out-migration rates.
Challenges for Circular Migrants in India
- Circular migrants in India often face exploitation and work in unsafe conditions.
- Language barriers in destination states pose additional challenges.
- Migrants are at the mercy of middlemen or brokers and are subject to precarious, seasonal, and irregular employment.
- The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted their vulnerability as many migrants embarked on long journeys back to their hometowns during lockdowns.
Policy Recommendations to address the issue of Migrants
- Harmonize Labor Laws to provide equal protection to all workers.
- Social Security and Health Benefits to migrants, ensuring their well-being.
- Portability of State-Provided Benefits, especially food provided through PDS.
- Skill Development Programs to enhance their employability and income potential.
- Data Collection and Research on migration patterns to inform policy-making.
- Affordable Housing and basic amenities in urban areas
- Legal framework to Protect Migrant Rights
For more info on Migration: PMFIAS NCERT Human Geography Class 11-12 CH.3 Migration





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)