
The Universe, Big Bang Theory and The Evolution of The Universe
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 23, 2024 9:43 AM
- The Universe is all existing matter & space. It is incomprehensively large (beyond mental grasp). It consists of both physical (subatomic particles like electrons, protons to galactic super-clusters) and non-physical (light, gravitation, space etc.) components.
- The universe, at present, is said to possess about 100 billion galaxies, each comprising an average of 100 billion stars. In comparison, Milky Way Galaxy is believed to possess 100 billion to 400 billion stars. (1,000,000 = 1 Million = 10 Lakhs; 1,000,000,000 = 1 Billion = 100 Crore; 1,000,000,000,000 = 1 Trillion
Basic Terms
|
The Big Bang Theory
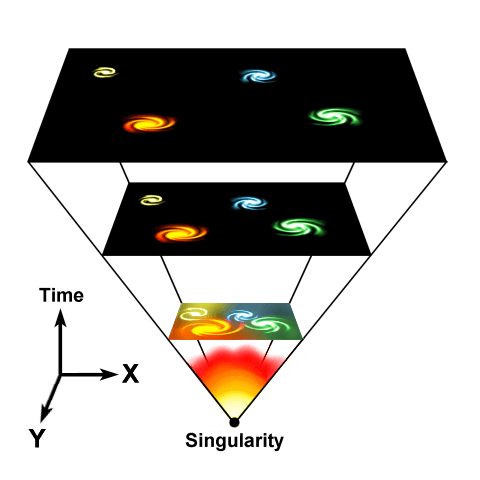
The Expanding Universe
- The Big Bang Theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe’s birth. It states that 13.8 billion years ago, all of space was contained in a single point of very high-density and high-temperature state from which the universe has been expanding in all directions ever since.
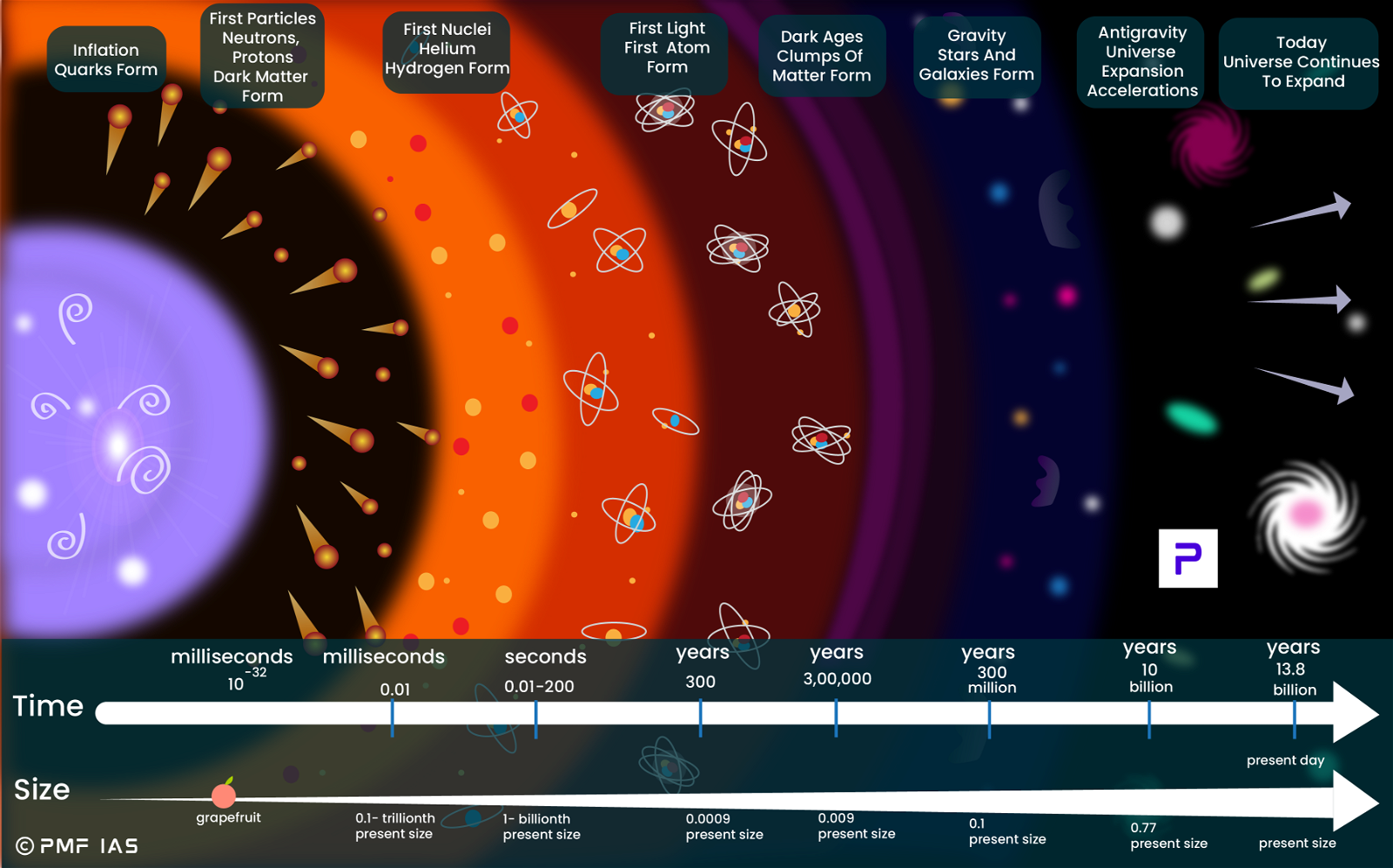
The Evolution of The Universe Since the Big Bang
|
Time |
T in °C |
Event |
| 10-43 Sec | 1032 | The cosmos goes through a superfast “inflation,” expanding from the size of an atom to that of a grapefruit in a tiny fraction of a second. |
| 10-32 Sec | 1027 | Post-inflation, the universe is a seething, hot soup of electrons, quarks, and other particles. |
| 10-6 Sec | 1013 | A cooling cosmos permits quarks to clump into protons & neutrons. |
| 3 min | 108 | Still too hot to form into atoms, charged electrons and protons prevent light from shining. |
| 3,00,000 years | 103 | Electrons combine with protons & neutrons to form atoms, mostly hydrogen & helium. Lithium & beryllium were formed in trace amounts. Light can finally shine. |
| 1 billion years | -200 | Gravity makes hydrogen and helium (primordial elements) coalesce to form the giant clouds that will become galaxies; smaller clumps of gas collapse to form the first stars. |
| 15 billion years | -270 | As galaxies cluster together under the influence of gravity, the first stars die and spew heavy elements into space: those will eventually turn into new stars and planets. |
Big Crunch (The Death of The Universe)
- At some point, the universe would reach a maximum size & begin collapsing. The universe would become denser & hotter again, ending in a state like that in which it started — a single point of very high density.
Accelerating Expansion of The Universe & Dark Energy
- It is the observation that the expansion of the universe is such that the velocity at which a galaxy is moving away from the observer is continuously increasing with time (Hubble’s law). It implies that the universe will get increasingly colder as matter spreads across space.
- The accelerated expansion of the universe is thought to have begun since the universe entered its dark-energy-dominated era — roughly 5 billion years ago.
- Dark energy is an unknown form of energy that is hypothesised to permeate (spread throughout) all of space, tending to accelerate the universe’s expansion
Last updated on April 23, 2024 9:43 AM













How can I download this ? these parts are not available in download section….
In S&T setion compilation of Science PDF are available.This topic is along with other topcs is covered in those pdfs
Yes this part is not available in the notes section.
Good
How can I download this ? these parts are not available in download section….
Is these notes are enough for preliminary paper?
Plz!tell me sir! Coz I didn’t understand bookish language any more!! It’s very boring..
Sir, how can Supernova explosions be taken as the evidence of Expansion of Universe?
answer is 1&2 correct. 3&4 are not related to expansion.
yes the correct options are 1,2,4 but that option isnt given.. so “now should we choose none of the above or option a 1,2”?
Is the content available on the website is same in the printed book as well ?
Occurrence of type la supernovae is not an evidence for expansion of universe.
Wikipedia says “ Unlike the other types of supernovae, Type Ia supernovae generally occur in all types of galaxies, including ellipticals.”
Observation of that phenomenon gave evidence to it. not the event itself.
Sir , I’m not getting this content in Hindi…so please help me