Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam: January 07, 2021
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
[GS3 – Economy – Capital Market] Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs)
TH | Prelims | GS3 > Economy > Capital Market
- Context: SEBI proposed norms to facilitate new entrants to set up market infrastructure institutions (MIIs).
- Market infrastructure institutions (MIIs) are institutions like stock exchanges & depositories (banks/institutions that hold & assist trading of securities like bonds, equity shares, etc.).
Some of the Key proposals
- A resident promoter setting up an MII may hold up to 100% shareholding.
- It will be brought down to not more than (either 51% or 26%) in 10 years.
- Foreign individuals may acquire or hold up to 10% in an MII.
- Any person other than the promoter may acquire or hold less than 25% shareholding.
- At least 50% of ownership of the MII may be represented by individuals with experience of five years or more in the areas of capital markets or technology related to financial services.
Stock Exchange
- It is an organisation which facilitates buying & selling of shares of listed companies.
- Listed companies are those companies which are registered with the stock exchange.
- Only old shares are bought & sold because it is a secondary market. (IPO is done in a primary market)
- Shares are auctioned: demand & supply of shares are constructed on the bidding of people.
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) & National Stock Exchange (NSE) are the major stock exchanges in India.
- Primary market (new issues market): deals with new securities being issued for the first time (IPO).
- After IPO, the company’s shares are listed & traded in an open market (stock exchange).
- Secondary market (stock market or stock exchange): existing securities are bought & sold.
Securities & Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- It is an autonomous statutory regulator of the securities & commodity market in India.
- It was established in 1988 & given Statutory Powers through the SEBI Act, 1992.
- Headquarters: Mumbai; it has four other regional offices.
- SEBI is responsive to the needs of three groups, which constitute the market:
- issuers of securities (companies)
- investors
- market intermediaries (stock & commodity exchanges)
[GS3 – Economy – Exports] Duty Drawback Incentive
TH | Prelims + Mains | GS3 > Economy > LPG Reforms > Measures introduced to promote exports
- Context: CBI books six for duty drawback incentive fraud.
- They were booked for allegedly claiming duty drawback incentives without eligibility.
- Duty drawback (DBK) incentive schemes are issued by the Directorate of Drawback.
- Directorate of Drawback functions under Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC).
- DBK is the rebate (a partial refund) of any duty that is chargeable on imported (excisable) materials that are used to manufacture goods in India & then the finished goods are exported from India.
- Duty drawback is the sum of the following amounts:
- Customs duty (taxes on imported goods) that is paid on imported input goods. This includes Special Addition Duty (SAD — additional custom duty leviable on imported goods).
- Excise duty (taxes levied on the manufacture of goods within the country) that is paid on indigenous input goods
- Duty that is paid on packing material
- Input goods that are obtained without paying customs or excise duty are not eligible for DBK.
[GS3 – Economy – Taxes] Entertainment Tax – an indirect tax subsumed by GST
TH | GS3 > Economy > Taxes > Indirect Taxes > GST
- Context: More than 24 years! after a concert in Mumbai by Michael Jackson, Maharashtra cabinet retrospectively upheld the entertainment tax waiver granted for it.
- A consumer rights organisation had moved the HC in 1996 challenging the entertainment tax waiver.
- In 2011, the HC had ruled that the state government has a right to extend waiver under the state’s laws.
- The cabinet’s decision will allow the organiser to get back the profit deposited with the govt decades ago!
Entertainment tax
- Entertainment tax (amusement tax) is any tax levied on any form of commercial entertainment, such as movie tickets, exhibitions, circus, large festive celebrations, sport events, etc.
- The entertainment tax is an indirect tax, which is levied by the state government on the buyer.
- There is a demand to levy such a tax on online services like Netflix, Spotify, & others.
Laws that govern Entertainment tax
- Entertainment tax is different for different states as it falls under the purview of the state governments.
- Rules pertaining to entertainment tax are listed in the 7th Schedule, under Article 246 of the Constitution.
- The 7th Schedule under Article 246 deals with the division of power between the Union & the States.
- It demarcated the powers into 3 lists — Union List, State List, & the Concurrent List.
- In 2017, the entertainment tax was subsumed by Goods & Services Tax.
Impact of GST on Entertainment tax
- Prior to GST, municipal bodies had no share in entertainment taxes collected by states.
- 101st Constitution Amendment (introduced GST) permitted levy & collection of ET by local bodies.
- In the absence of a state law, it suggested that the State may compensate local bodies for the revenue loss & compensation may be made equal to 90% of the State GST collected on entertainment.
- Some states have made provisions that require local bodies to charge entertainment tax.
- In such states, entertainment tax is levied by local bodies over & above GST.
- Overall, GST has a mixed effect on the entertainment industry, depending on the states.
- For states where the entertainment tax was higher than GST rates, there is a shortfall in revenue & vice versa.
[GS3 – Envi – Conservation] Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres
TH | Prelims | GS3 > Conservation | Basics: Indian Vulture Crisis
- Context: To increase the availability of food for vultures in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR), the Forest Department is allowing dead cattle from a nearby cow shelter to be left for the scavengers.
- In a bid to save endangered species of vultures from extinction, the National Board for Wildlife has approved a new plan that proposes setting up Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres in some States.
- A captive breeding centre would come up in the buffer zone of Mudumalai Tiger Reserve.
- Critically endangered Oriential White-backed Vultures, Indian white-rumped vulture & long-billed vulture are found here.
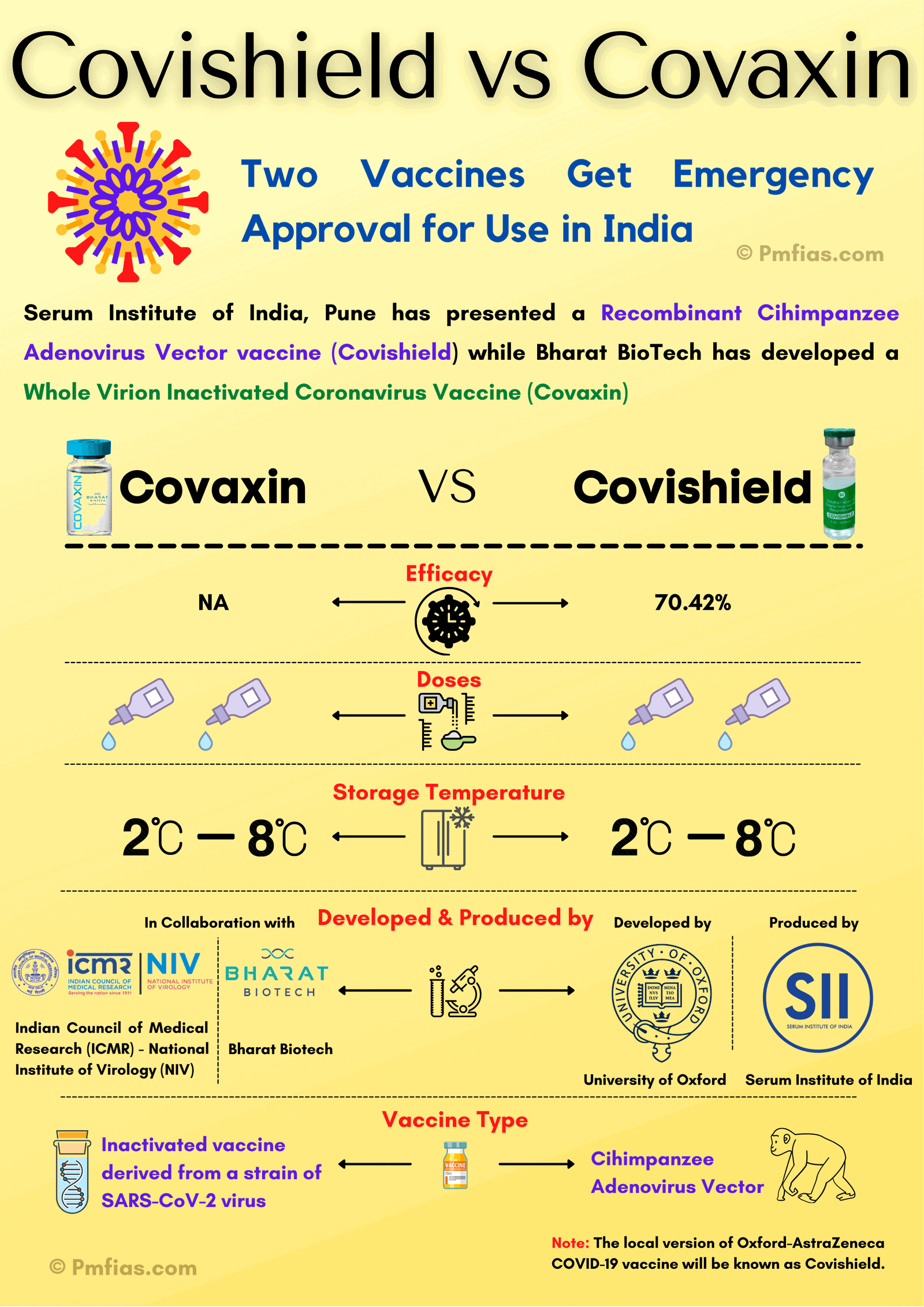
[GS3 – S&T – COVID] Covishield vs Covaxin
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
[GS3 – S&T – Diseases] Avian influenza (H5N8) – Bird Flu
TH | Prelims | GS2 > issues related to Health
- Context: Avian influenza (H5N8) has been confirmed among ducks in Kottayam.
- Bird flu/Avian influenza (H5N8) is a highly contagious viral disease affecting several species of food-producing birds (chickens, turkeys, quails, guinea fowl, etc.) as well as pet birds & wild birds.
- While it can prove lethal for birds, the H5N8 strain of avian influenza has a lower likelihood of spreading to humans as compared to H5N1.
- Human infections are primarily acquired through direct contact with infected poultry.
- Avian influenza virus subtypes include A(H5N1), A(H7N9), & A(H9N2) A(H5N8)
Government Response
- Directions have been given to enforce culling of sick birds as per the 2015 National Avian Influenza Plan.
- The plan is prepared & revised by Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying (not MoEF).
- The plan provides guidance to state govts in prevention, control, & containment of avian influenza.
- Fishing will be banned in the affected region.
Influenza (Flu) in Humans
|
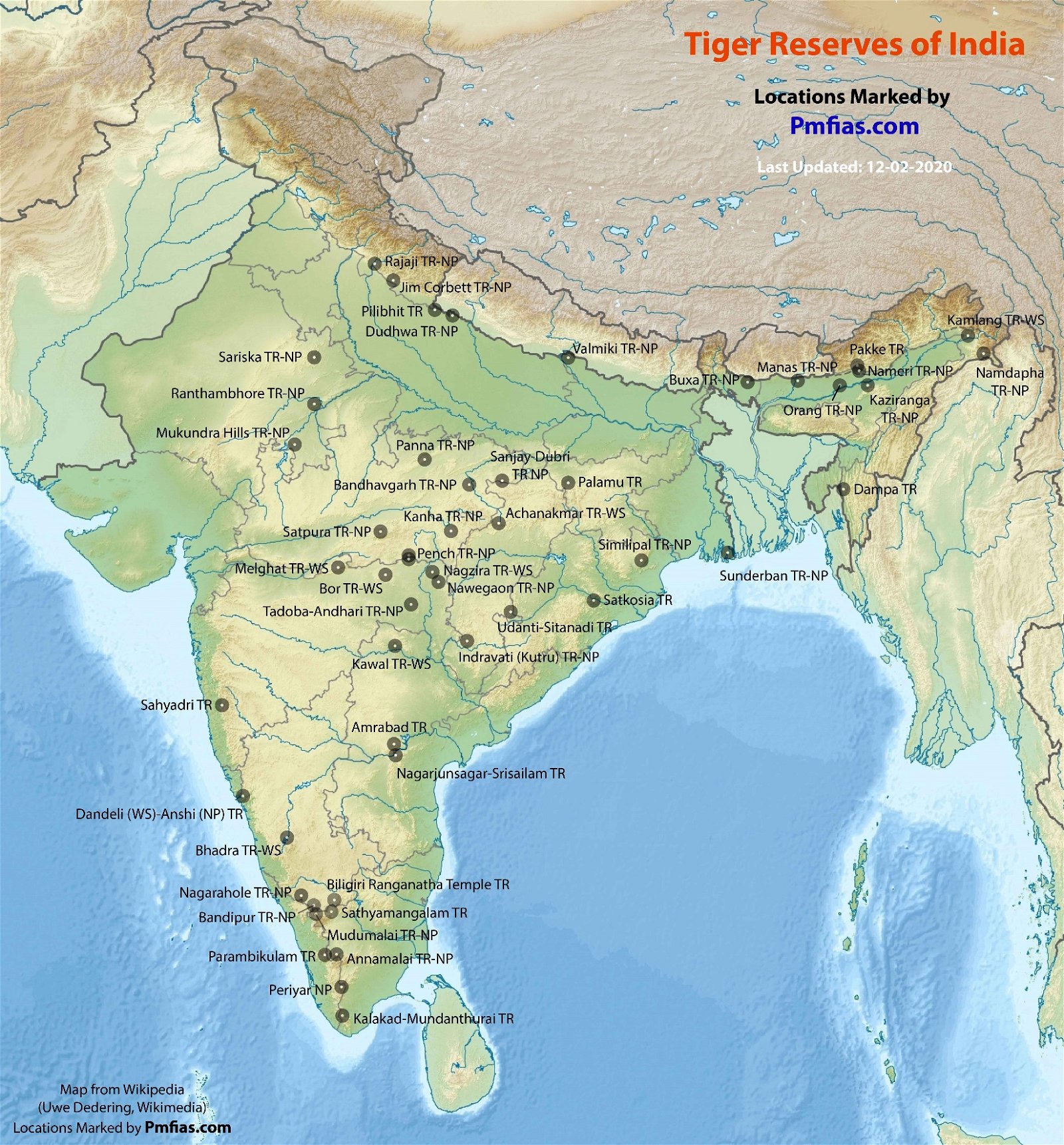
[Prelims – Envi Mapping – TR] Mudumalai Tiger Reserve
TH | Prelims | Mapping > Tiger Reserves
- It lies on the north-western side of the Nilgiri Hills (Blue Mountains), in Nilgiri District.
- It shares its boundaries with the states of Karnataka & Kerala.
- Vegetation: tropical moist deciduous, tropical dry deciduous forest, tropical dry thorn forests are in the east.
- Major Fauna: Indian elephant, Bengal tiger, gaur, golden jackal, bonnet macaque, sambar deer, Indian muntjac, Indian giant squirrel, red giant flying squirrel, etc.
- Major Avian Fauna: Indian white-rumped vulture (CR) & Indian Vulture (CR).
- Threats: Tourism & invasive species such as lantana.