
Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam: January 02, 2021
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
[GS2 – Policy – MTA] Initiatives by TRIFED
PIB | PIB | Prelims + Mains | GS2 > Government policies for development
- Context: TRIFED is collaborating with different Ministries and Departments to jointly execute schemes and programmes for transforming tribal lives.
What is TRIFED?
- The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED) was established in 1987 under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984.
- It is a national-level apex organization functioning under the administrative control of Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MTA).
- Its basic mandate is to bring about socio-economic development of tribal people of the country.
- TRIFED works towards socio-economic development of tribal people by way of marketing development of the tribal products (such as ‘Minor Forest Produce (MFP)).
Recent Initiatives by TRIFED
GI Tagging for tribal Products
- TRIFED had taken up the cause of promotion of GI Tag products along with tribal products and transform them into a brand.
- TRIFED, along with the Ministry of Culture, has identified 8 heritage locations across the country, where GI specific Tribes India stores will be set up.
- Among these 8 heritage places, work is shortly expected to commence in
- Sarnath, Uttar Pradesh,
- Hampi, Karnataka,
- Golconda Fort, Telangana.
Development of Designer’s lab
- Designer’s lab is a place wherein select tribal artisans will give live demonstrations of their rich craft traditions.
- It has been planned to develop a designer’s lab at Lal Qila (Red Fort), Delhi, in close collaboration with the Ministry of Culture.
- Pochampally in Andhra Pradesh, famous for Ikat fabric, has been chosen to be the second venue for designer’s hub.
Aadi Mahotsav festival
- The Aadi Mahotsav festival is an initiative commenced by TRIFED in 2017.
- It aims to familiarize the people with the rich and diverse craft and culture and cuisine of tribal communities.
- This will be done in collaboration with the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) and India Post.
- The aim of this initiative is to create a brand for products from that region, increase awareness of the brand across the globe.
Marketing & Logistics intervention for promoting Tribal products of North – Eastern States
- This will be done in collaboration with the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) and India Post.
- The aim of this initiative is to create a brand for products from that region, increase awareness of the brand across the globe.
[GS1 – Social empowerment] Gender Gap in Farming
TH | Mains | GS1 > Role of Women; Social Empowerment | GS2 > Government policies for development
- Context: A forum for women farmer rights namely, Mahila Kisan Adhikaar Manch (MAKAAM), recently expressed their rising fears about the farm laws.
- They fear that their identity remains invisible in a male-dominated agricultural sector and the introduction of the bills could further deepen the divide.
- The new bills define a trade area outside the APMC mandi which is likely to bring in bigger private firms.
- MAKAAM fears that the newly developed ecosystem will incapacitate women mobility as the proximal market will lose its existence in this due course.
Women’s role and participation in farm activities
- Women have always been the backbone of a large majority of farming activity and yet they have not had the recognition they deserve due to gender inequality.
- In the Indian scenario, according to NSSO 68th round data, women constitute 63% of the workforce in agriculture while their share of operational landholding is a mere 12.8%.
- Traditionally, women have been involved in labour-intensive work like weeding, hand harvesting, pre-pack handling of various vegetables and rice production.
- However, the women farmers are deprived of farm basics like access to various resources like land, water, credit, technology, and training.
Major causes of the gender gap in the Indian agro-economy
Gender Discrimination in Land ownership
- Women are restricted in terms of access to land which comprises a major role in wealth creation and economic empowerment.
The longstanding patriarchal disconnect
- Lack of tenure security and accessibility to entitlements stand as a barrier in empowering female farmers.
- For example, under the aegis of Panchayati Raj Act (1993), in the proxy sarpanches or sarpanchpatis, the control is often vested with the husband of the elected woman representative.
- Such inclusions in State policy constrain women’s choices and prevent women from exercising their legal rights like exogamy (marrying outside one’s social group), property rights, etc.
- Patriarchy also leads to low level of female literary, male dominance in public & economic affairs, judicial and administrative actions at various levels.
Women and unpaid domestic responsibilities
- In most societies, gender roles are well defined.
- Chores like child-rearing, household tasks as well as rearing small livestock are undertaken by women and it does not add to any monetary benefit for themselves.
- This work burden limits the capacity of women to engage in income-generating activities.
Way forward
- It is crucial to adopt gender-specific interventions to enhance women’s role in agro-economy.
- Reforms need to be undertaken to ensure women farmers security, mobility, and access to local trade.
- An increased role and representation of women in local market committees will help reduce the gender gap.
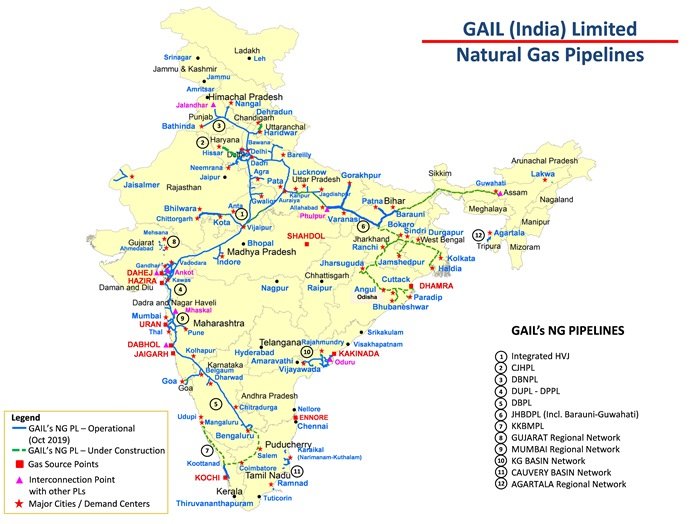
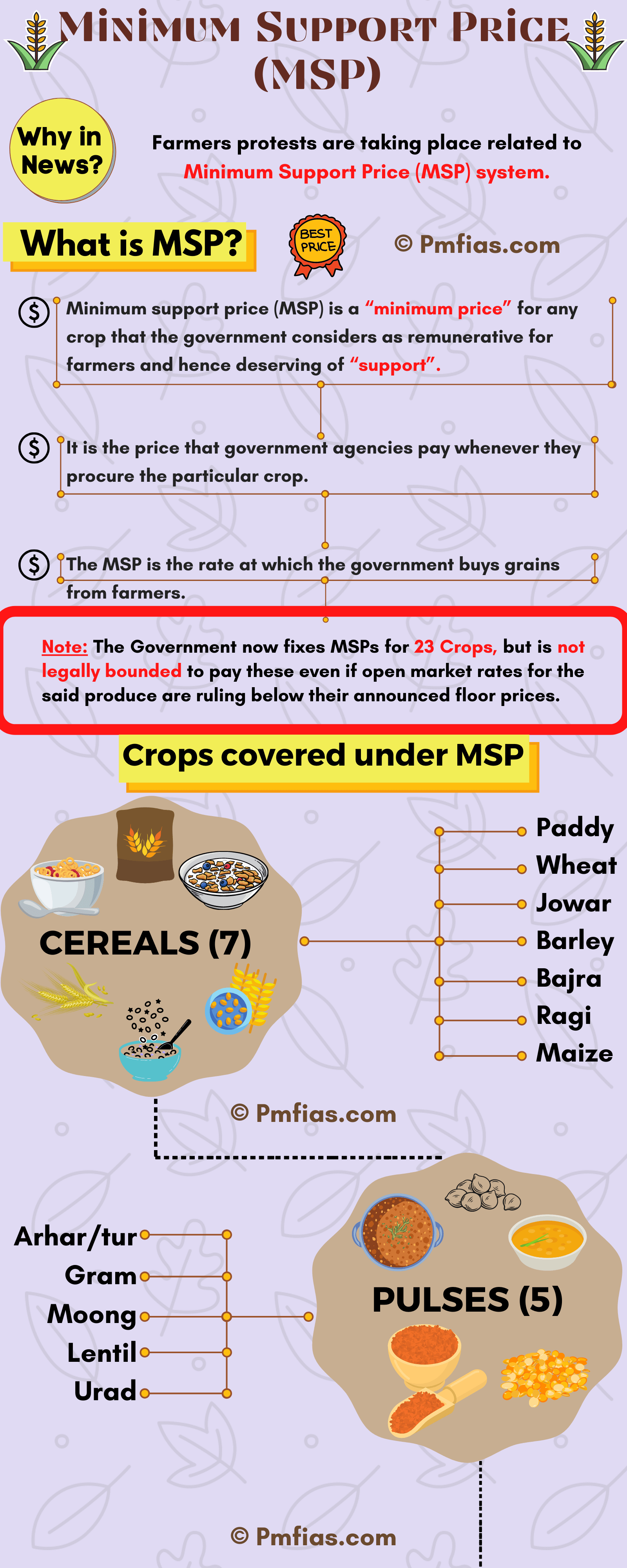
[GS3 – Infra] One nation one Gas Grid
PIB | Prelims + Mains | GS3 > Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
- Context: PM dedicated the Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline to the nation.
- The event marks an important milestone towards the creation of ‘One Nation One Gas Grid’.
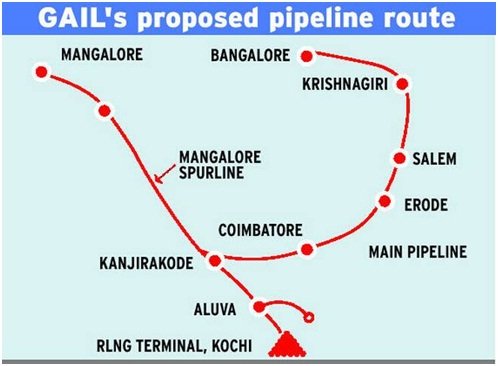
Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline
- The 450 km long gas pipeline will carry natural gas from Kochi (Kerala) to Mangaluru (Karnataka).
- It is built by GAIL (India) Ltd.
- The total cost of the project was about Rs. 3000 crores.
- Laying of the pipeline necessitated it to cross water bodies at more than 100 locations.
- This was done through a special technique called Horizontal Directional Drilling method.

One Nation One Gas Grid
- Government is taking policy initiatives to increase the share of natural gas in India’s energy basket from 6 Percent to 15 Percent.
- Under One Nation One Gas Grid, all the willing rural households would be provided with cooking gas and electricity connection by 2022, that is by the 75th year of India’s independence.
Objectives
- Remove regional imbalance with regard to access for natural gas.
- Provide clean and green fuel throughout the country.
- Connect gas sources to major demand centres.
- Ensure the availability of gas to consumers in various sectors.
- Develop City Gas Distribution Networks in various cities for the supply of CNG and PNG.
- Synchronously connect all the regional grids.
Need for Grid
- India is the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases after the US and China
- The Grid would be helpful in meeting emission reduction targets that were signed at the Paris Agreement.
- Natural gas can be used as a transition fuel before completely switching to solar or clean energy.
- India aims to increase the share of Natural gas usage to 15% by 2030.
Natural Gas
- Natural gas consists of primarily methane and ethane. (LPG is a mixture of butane and propane)
- Propane, butane, pentane, and hexane are also present.
- Natural gas is formed during the process of formation of Petroleum.
- Hence, it is often found dissolved in oil or as a gas cap above the oil.
- Sometimes, the pressure of oil forces gases up to the surface.
- Such natural gas is known as associated gas or wet gas.
- Some reservoirs contain gas and no oil. This gas is termed non-associated gas or dry gas.
- Often natural gases contain substantial quantities of hydrogen sulphide or other organic sulphur compounds. In this case, the gas is known as “sour gas.”
- Coalbed methane is called ‘sweet gas’ because of its lack of hydrogen sulphide.
Oil + Gas ➔ Associated Gas or Wet Gas,
Only Gas ➔ Non-Associated Gas or Dry Gas,
Hydrogen Sulphide in gas ➔ Sour Gas,
Coalbed Methane ➔ Sweet Gas.
- On the market, natural gas is usually bought and sold not by volume but by calorific value.
Uses of Natural Gas
- Electric power generation.
- Many buses and commercial vehicles now operate on Compressed Natural Gas (CNG).
- Ammonia is manufactured using hydrogen derived from methane.
- Ammonia is used to produce chemicals such as nitric acid, urea, and a range of fertilizers.
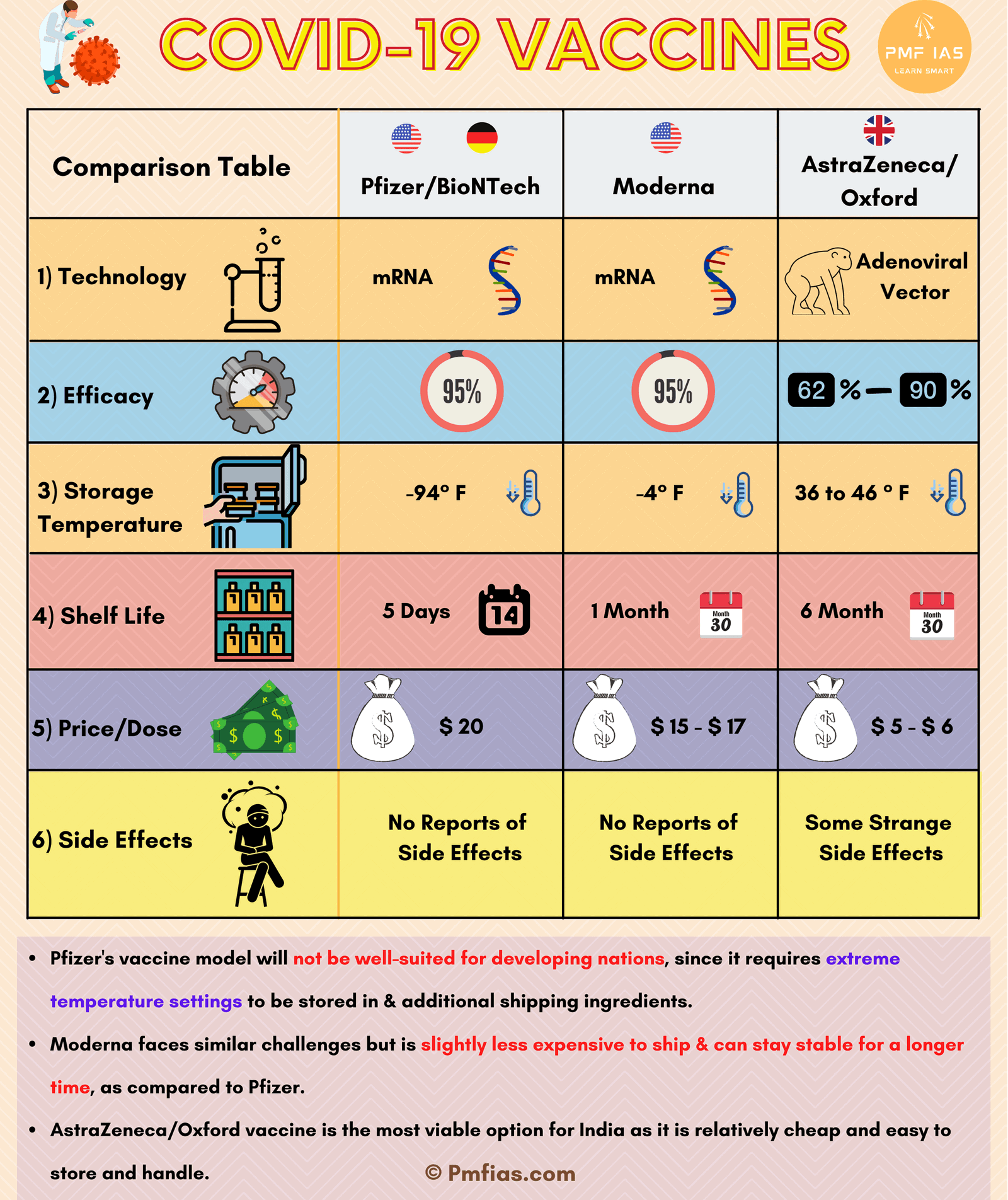
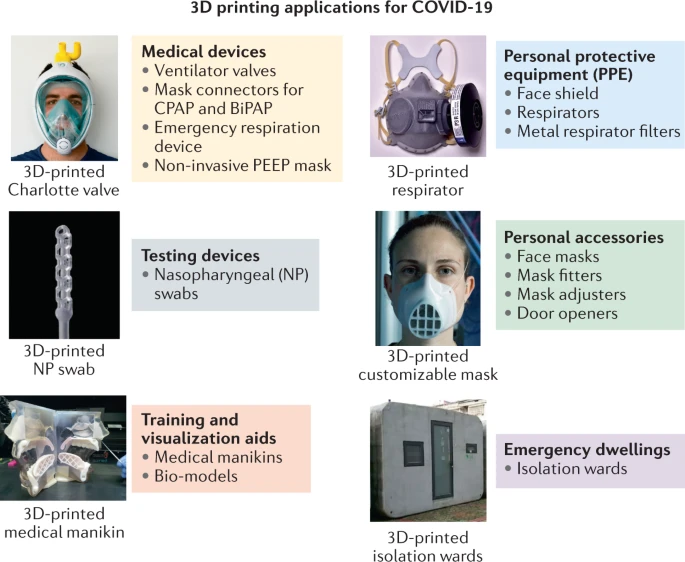
[GS3 – S&T – COVID] COVID-19 Vaccine in news
IE | Prelims + Mains | GS2 > Health
- Context: Drug Controller General of India has given the “restricted emergency use” approval to two vaccines i.e., Covishield & Covaxin against Covid-19.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Vaccines
- Vaccines prevent or mitigate infections.
- They are designed to induce a protective immune response in the body against the viruses.
- When vaccinated, the immune system of the body produces a specific response, consisting of specific T cells & specific antibodies that fight off the infection when exposed to the virus occurs at a later stage.
- More importantly, vaccination also leads to the induction of a specific immunological memory against the viruses represented in the vaccine.
- There are about a half-dozen basic types of vaccines, including killed viruses, weakened viruses, & parts of viruses, or viral proteins.
- A lot of trial & error is involved in making a vaccine. Hence it could take years to invent a vaccine.
- A new approach being taken by Moderna Pharmaceuticals is to copy genetic material from a virus & add it to artificial nanoparticles.
- This makes it possible to create a vaccine based purely on the genetic sequence rather than the virus itself.
Differences between Vaccine & Drugs
|
Vaccines |
Drugs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RNA Vaccine |
DNA Vaccine |
|
|
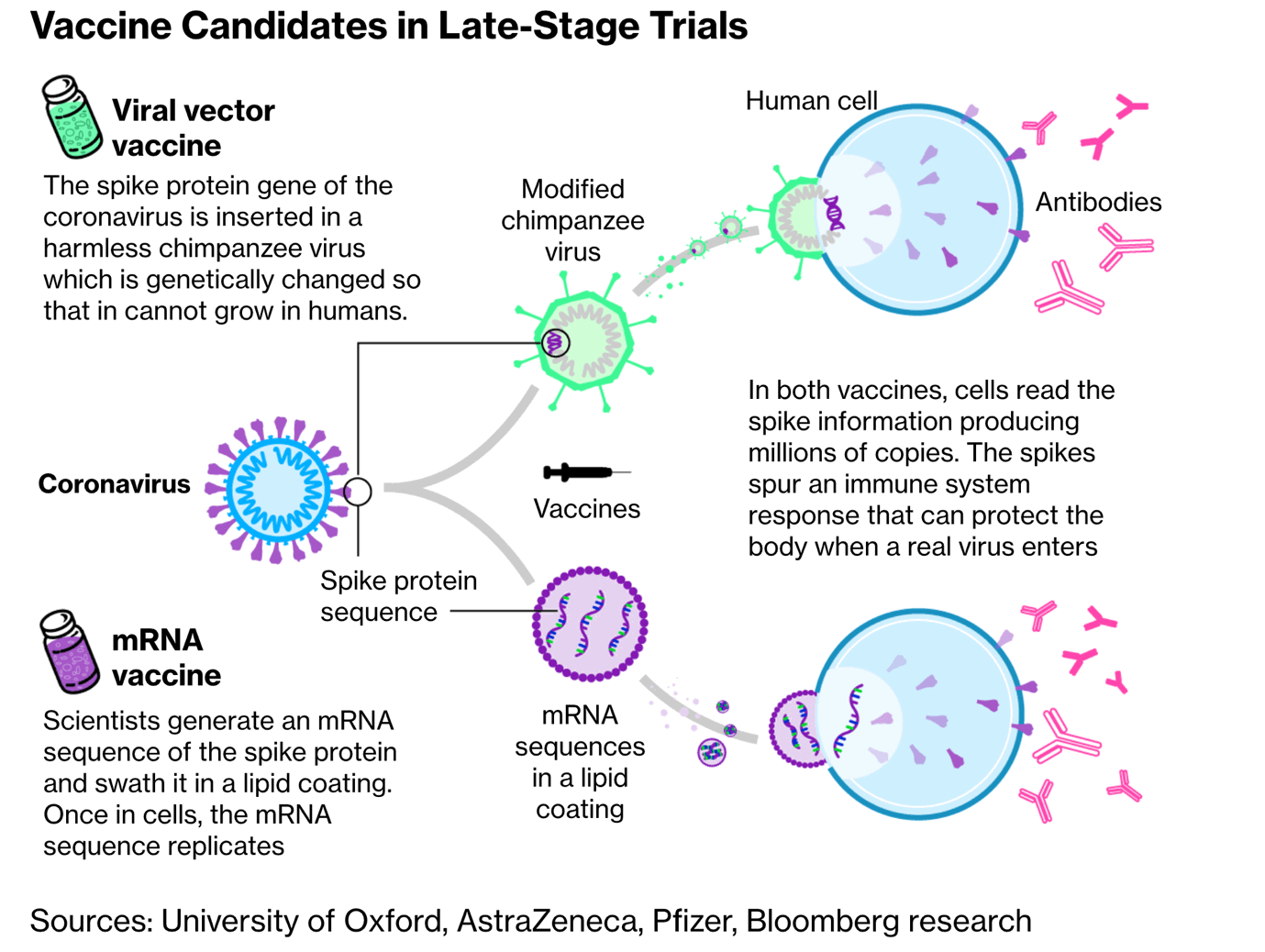
What is the mRNA vaccine?
- The genetic blueprint (or code) in living organisms is stored in a double-stranded molecule called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which makes proteins that are responsible for nearly every function in the human body.
- The conversion of DNA code into proteins requires a single-stranded molecule called the mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid).
- In an analogy with computers, one may think of the DNA as the hardware, the mRNA as the software & proteins as the applications.
- The mRNA-1273 is a piece of RNA that carries the code to make the COVID-19 virus Spike protein when introduced into cells.
- This protein present on the virus surface is critical for its entry into cells.
- Immunity (antibodies) to the Spike protein can block virus entry & its multiplication, & thus ameliorate the disease.
Covishield
- Developed by Oxford University in collaboration with AstraZeneca.
- India’s Serum Institute is their manufacturing and trial partner.
- Covishield vaccine has been developed by using a weakened version of the adenovirus.
- Adenovirus causes infections in chimpanzees and its genetic material is same as that of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
- Spike protein is the part of SARS-CoV-2 using which the virus enters a human body cell.
- Vaccine contains the genetic material of the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein.
- After vaccination, the surface spike protein is produced, priming the immune system to attack the SARS-CoV-2 virus if it later infects the body.
- Covishield will cost around Rs 400-450.
- Efficiency of Covishield has been pegged at over 70 per cent.
- Covishield is two-dose Covid-19 vaccines.
- Require to be kept at 2-8 degree Celsius.
Covaxin
- Covaxin is India’s first indigenous vaccine against Covid-19.
- Developed by Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research and National Institute of Virology, Pune.
- Covaxin is an inactivated vaccine.
- An inactivated vaccine is one which is developed by inactivating the live microbe that cause the disease.
- This destroys the pathogen’s ability to replicate but keeps it intact so that the immune system can still recognise it and produce an immune response.
- Cost: Rs 100-200.
- No efficacy rate has been made public.
- Covaxin is two-dose Covid-19 vaccines.
- Require to be kept at 2-8 degree Celsius

Moderna & Pfizer Vaccine
- The Moderna and Pfizer vaccines use the same technology, based on messenger RNA, or mRNA.
- Such vaccines make use of the messenger RNA molecules that tell the body’s cells what proteins to build.
- The mRNA, is coded to tell the cells to recreate the spike protein of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes Covid-19.
- It is the spike protein which appears as spikes on the surface of the coronavirus.
- Spike Protein initiates the process of infection.
- Spike Protein allows the virus to penetrate cells, after which it goes on to replicate.
- A coronavirus vaccine based on mRNA, once injected into the body, will instruct the body’s cells to create copies of the spike protein.
- In turn, this is expected to prompt the immune cells to create antibodies to fight it.
- These antibodies will remain in the blood and fight the real virus if and when it infects the human body.
Sputnik-V
- This vaccine has been developed by Moscow’s Gamaleya Institute.
- The vaccine is based on the DNA of a SARS-CoV-2 type adenovirus, a common cold virus.
- In this vaccine, adenovirus is used as a tool to deliver genes or vaccine antigens to the target host tissue.
- The vaccine uses the weakened virus to deliver small parts of a pathogen & stimulate an immune response.
- The vaccine is administered in two doses & consists of two types of a human adenovirus, each carrying an S-antigen of the new coronavirus, which enter human cells & produce an immune response.
ZyCoV–D
- DNA Vaccine ZyCoV-D by Zydus Cadila is approved for Phase III clinical trials.
- ZyCoV-D is a plasmid DNA vaccine, under the Vaccine Discovery Programme supported by the Department of Biotechnology under the National Biopharma Mission.
- Plasmids are circular deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) vectors that can be used as vaccines.
- Scientists insert the virus genetic material into plasmids that they have obtained from bacteria.
- The plasmid is then inserted into the body and this triggers an immune response.
- Vaccine can remain stable even at 30 degree Celsius for about three months.
- This can be a major factor when planning nation-wide vaccine distribution as it would have minimal cold chain requirements when it reaches the hinterland.
National Biopharma Mission
- The National Biopharma Mission (NBM) is an industry-Academia Collaborative Mission for accelerating biopharmaceutical development in the country.
- Under this Mission the Government has launched Innovate in India (i3) programme to create an enabling ecosystem to promote entrepreneurship and indigenous manufacturing in the sector.
- The mission will be implemented by Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The mission was approved in 2017 at a cost of Rs 1500 crore and is 50% co-funded by World Bank loan.
- The mission is focused on the following 4 verticals:
- Development of product leads for Vaccines, Biosimilars and Medical Devices.
- Upgradation of shared infrastructure facilities and establishing them as centres of product discovery/discovery validations and manufacturing.
- Develop human capital by providing specific trainings to address the critical skills gap among the nascent biotech companies across the product development value chain.
- Technology Transfer Offices to help enhance industry academia inter-linkages.
Co-WIN
- The Union Health Ministry has developed a digital platform application Co-WIN.
- It is developed for real-time monitoring of Covid-19 vaccine delivery, recording data & to enable people to get themselves registered for vaccination.
What are the challenges faced by India in delivering the vaccine?
- The main challenge is to work with a new vaccine and provide it across age groups.
- Current vaccination program which focuses primarily on pregnant women and children.
- There are issues related to financial and human resources.
- Skill manpower to handle vaccination is lacking.
- Storage issue related to cold chain infrastructure
- Some vaccines, such as the ones made using mRNA technology need to be stored in extremely cold temperatures, (-70 degree Celsius) which cannot be made available in every region.
- Most facilities in India are said to be equipped to operate at a maximum of -40 degree Celsius.
A most important challenge is Vaccine hesitancy
- According to WHO Vaccine hesitancy is the delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccines despite the availability of vaccination services.
- It is complex and context-specific varying across time, place and vaccine.
- It is one of 10 threats to global health.
Reasons for vaccine Hesitancy
- Misinformation related to:
- Religious factor: Vaccines contains microbes & animal products which is forbidden in religious customs.
- Vaccine derived poliovirus: For instance, Oral Polio Vaccines (OPV) contains weakened but live poliovirus, which have caused polio disease earlier.
- Social media: Misinformation spread through social media stirring fear in the minds of people by falsely blaming vaccines for unrelated diseases.
- Accessibility: Vaccines are often not available within the reach of communities causing inconvenience to peoples, thus avoiding vaccination.
[GS3 – S&T – Tech] 3D Printing
PIB | Prelims + Mains | GS3 > Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nanotechnology
- Context: PM mentioned 3D printing in his speech.
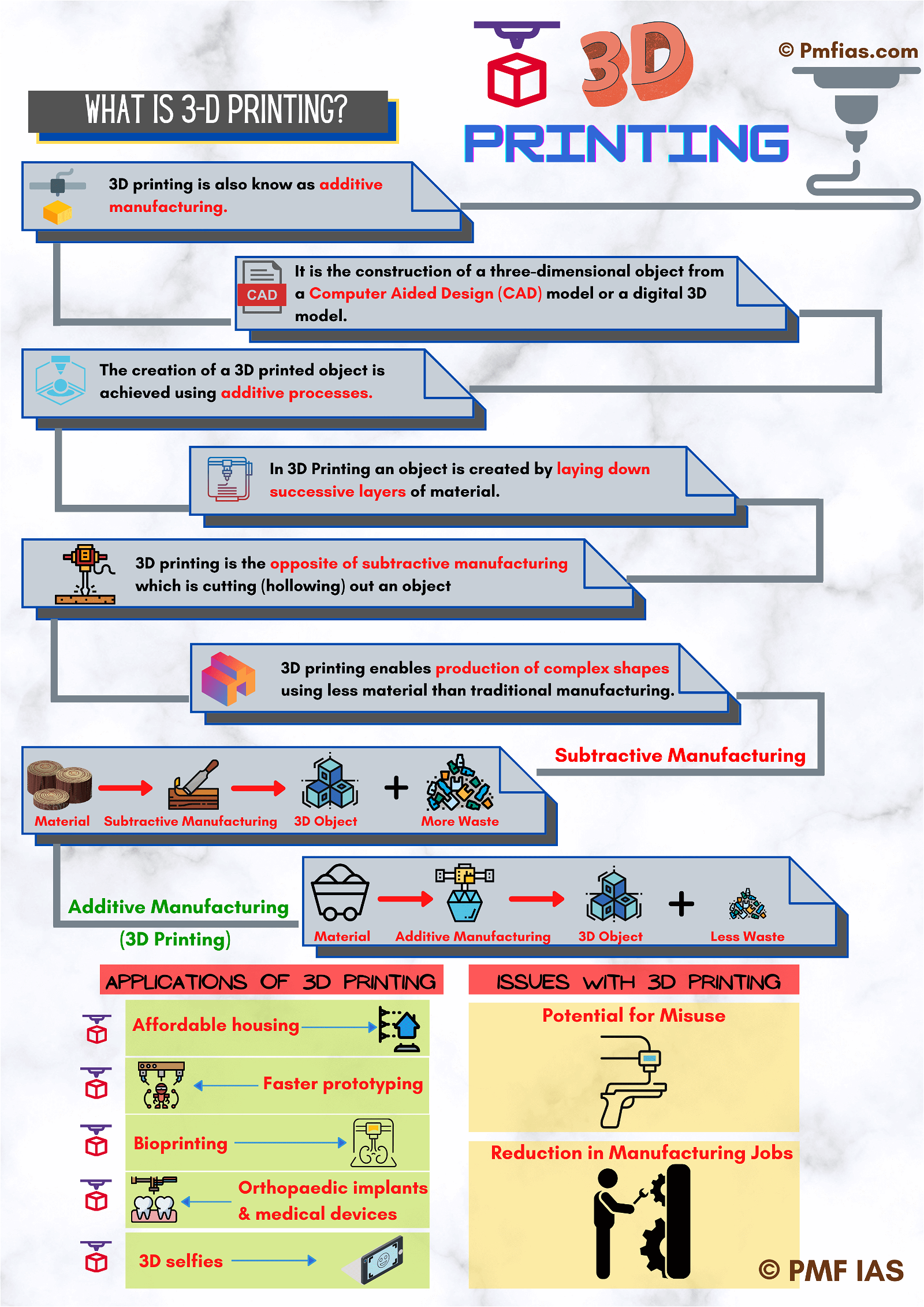
- 3D printing (additive manufacturing), is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model or a digital 3D model.
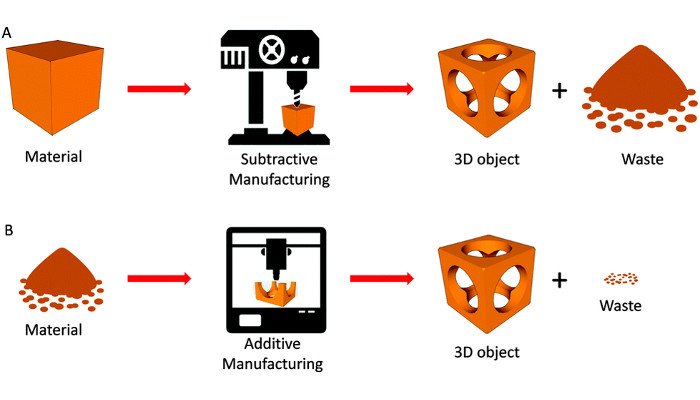
- The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes.
- In an additive process, an object is created by laying down successive layers of material.
- Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced cross-section of the object.
- 3D printing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing which is cutting (hollowing) out an object.
- 3D printing enables production of complex shapes using less material than traditional manufacturing.
Source & Credits | Source & Credits
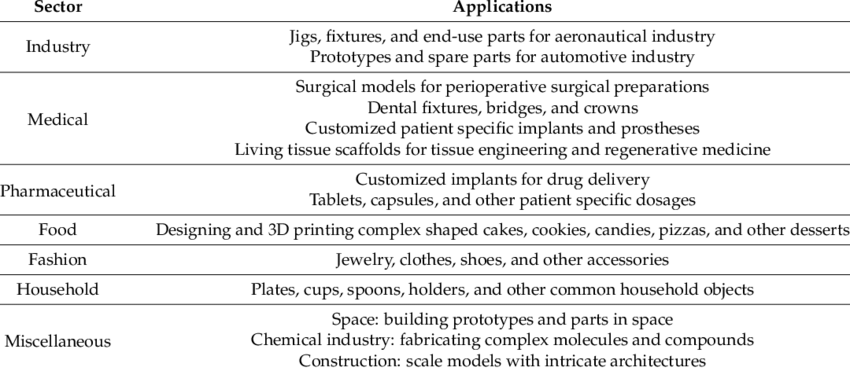
Envisaged time and money-saving applications of 3D printing
- Affordable housing: 3D printing will slash time and cost of construction required, by a significant amount.
- Faster prototyping of ideas and designs in jewellery, automobile and construction industries.
- Bioprinting: Biomaterials such as cells and growth factors are combined to create tissue-like structures imitating their natural counterparts.
- Orthopaedic implants and medical devices: Due to 3D printing’s capabilities for creating porous surfaces, these types of implants more easily integrate with the patient’s own natural bones.
- 3D selfies: generates 3D selfie models from 2D pictures of customers.
Pros of 3D Printing
- Flexible Design: more complex designs can be produced than traditional manufacturing processes.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing can manufacture parts within hours.
- Print on Demand: print on demand reduces the space to stock inventory. This saves space and costs.
- Strong and Lightweight Parts: particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
- Better properties: parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength, or water repellence.
- Minimising Waste: as 3D printing is an additive process it cuts on waste generation.
- Cost-Effective: as a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated.
- Advanced Healthcare: 3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys, and hearts.
Issues with 3D printing
- Potential for misuse: 3D printing can be used to manufacture parts of guns and weapons if a 3D CAD model for the part is available.
- Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs since most of the production is automated and done by printers.
- Limited Materials: the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is since not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing.
- Lack of Economies of scale: 3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost-effective to produce.
India & 3D Printing
- Asia leads the world in 3D printing with China, Japan & South Korea being the major players.
- But globally, the US remains the leader, with more than 35 per cent market share.
- In India, the market for 3D printers is still at a nascent stage.
- However, it offers huge growth opportunities in the coming years.
- Considering the benefits associated with 3D printing, various industries in India have already started using or are ready to use 3D printing technology.
Challenges Associated
Lack of domestic manufacturers:
- At present, India primarily imports 3D printers from countries such as China, the US and Germany.
- Only if materials could be engineered and locally produced, the cost could come down drastically.
The high cost of imports:
- The technologies are extremely capital intensive and so are the materials
- Everything (material & technology) is imported from developed countries.
Investment issues:
- A lot of design participants/entities (especially small scale & medium scale) still do not believe in prototyping as an investment but see it as a costly expenditure.
Awareness:
- A lack of in-depth knowledge about this 3D printing technology makes companies who opt for prototyping, finally either doing away with it entirely or finding another alternative
- This largely reduces the reach of 3D printing.













Great initiative, several key areas are covered from exam point of view. But current affairs are updated only till then 2nd of Jan. Sir kindly post current affairs on a daily basis.