Virus, Difference Between Virus & Bacteria, DNA & RNA Viruses
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Virus, Difference Between Virus & Bacteria, DNA & RNA Viruses <===
- Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19 or 2019-nCoV)
- Immune System, T– Cells & Coronavirus, Cytokine storm
- Covid-19 Tests: RT-PCR, Rapid Antigen Test & Serological Test
- Proposed Vaccines, Treatments in the Context of COVID-19
- In the five-kingdom biological classification of Whittaker, there is no mention of acellular organisms like virus & viroid, & cellular organisms like lichens.
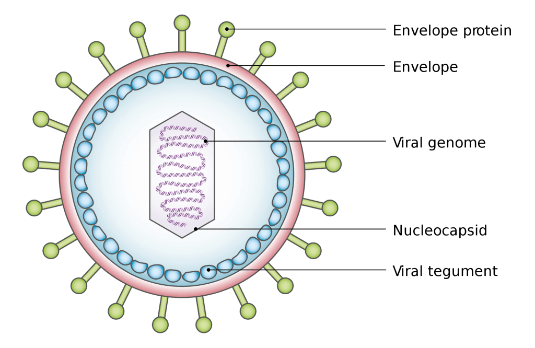
Viruses
- Viruses did not find a place in classification since they are not truly ‘living’, if we understand living as those organisms that have a cell structure.
- The viruses are non-cellular organisms that are characterized by having an inert crystalline structure outside the living cell.
- Viruses are obligate parasites. Once they infect a cell, they take over the machinery of the host cell to replicate themselves, killing the host.
- The name virus that means venom or poisonous fluid was given by Pasteur.
- In addition to proteins, viruses also contain genetic material, that could be either RNA or DNA.
- No virus contains both RNA & DNA.
- In general,
- viruses that infect plants have single-stranded RNA &
- viruses that infect animals have either single or double-stranded RNA or double-stranded DNA
- bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) are usually double-stranded DNA viruses.
- The protein coat called capsid made of small subunits called capsomeres protects the nucleic acid.
- These capsomeres are arranged in helical or polyhedral geometric forms.
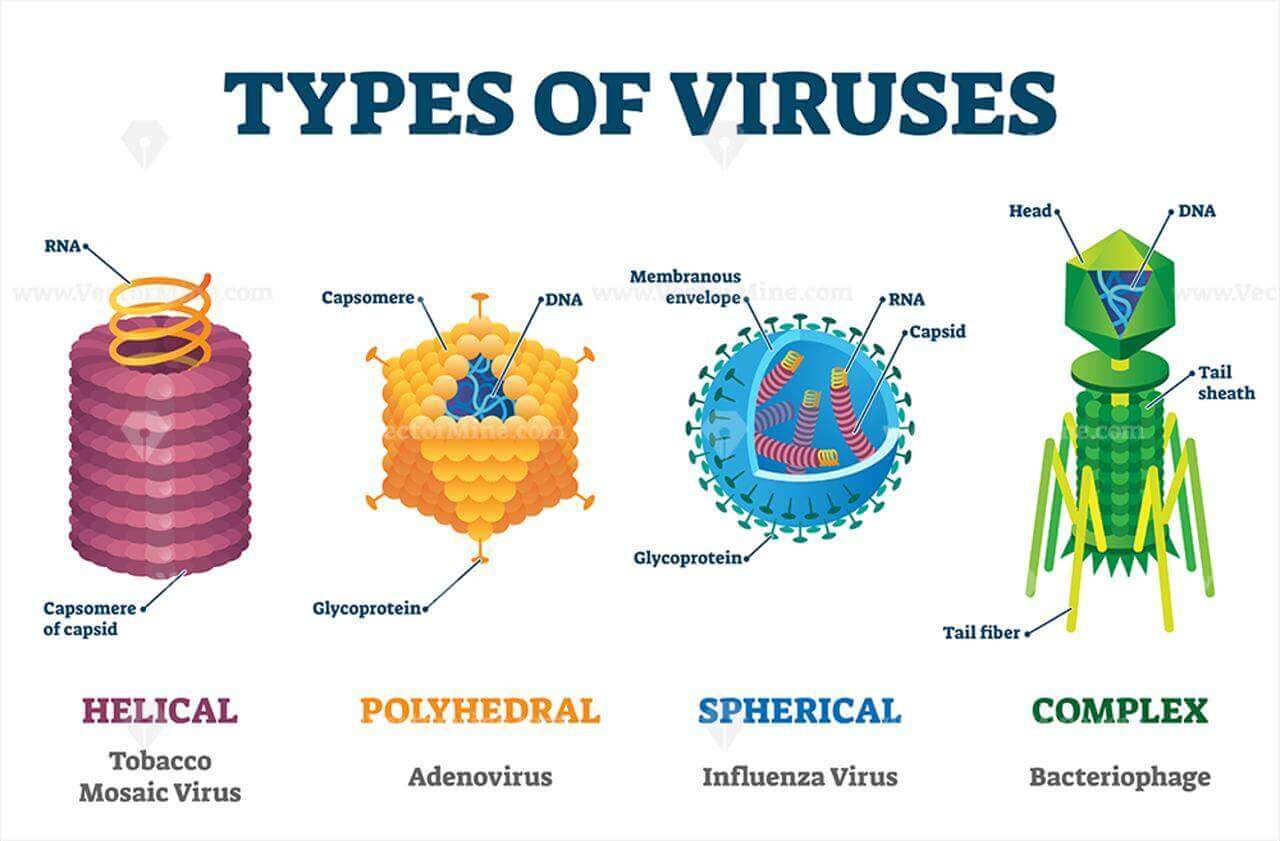
- Viruses cause diseases like mumps, smallpox, herpes & influenza. AIDS is also caused by a virus.
- In plants, the symptoms can be mosaic formation, leaf rolling & curling, yellowing & vein clearing, dwarfing & stunted growth.
Viroids
- Viroids are infectious agents that are smaller than viruses.
- A viroid is a free RNA, it lacks the protein coat that is found in viruses, hence the name viroid.
- The RNA of the viroid was of low molecular weight.
- Viroids cause potato spindle tuber disease.
|
Virus |
Viroid |
|
It is a nucleoprotein particle. |
It is an RNA Particle. |
|
Nucleic Acid can be DNA or RNA. |
Viroid is formed of only RNA. |
|
A protein covering of coat is present. |
A protein coat is absent. |
|
Virus has a larger size. |
Viroid has a smaller size. |
|
Virus infects all types of organisms. |
Viroid infects only plants. |
Difference Between Virus & Bacteria
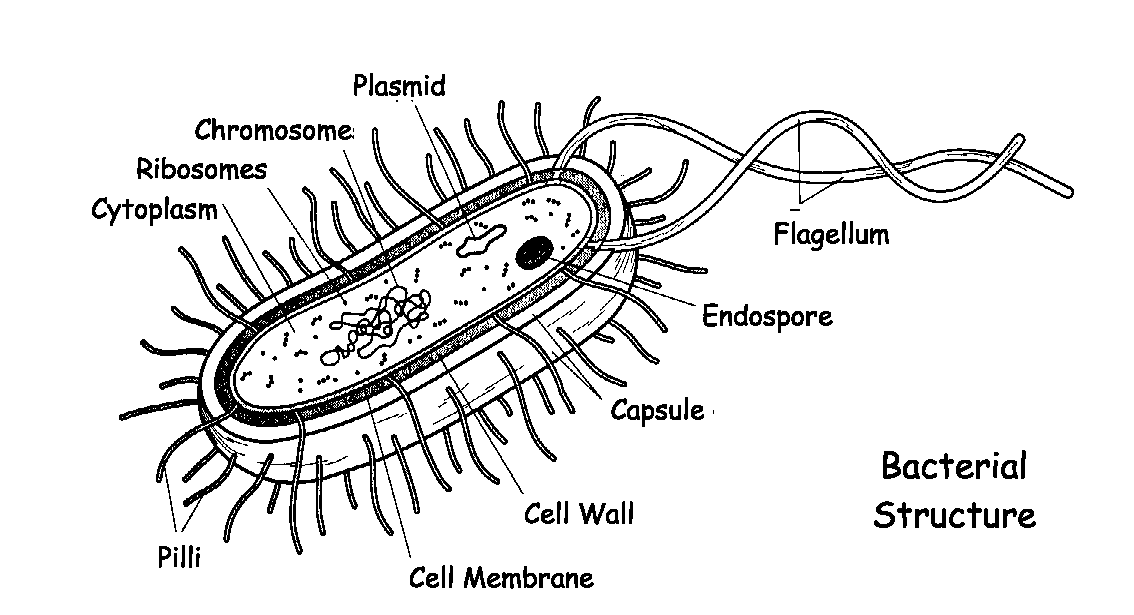
- Bacteria are single-cell, living organisms that can survive without a host.
- They can live on surfaces, in soil, in water, & in the air.
- You can kill them by messing with their ability to do cellular respiration or their ability to grow.
- Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections because antibiotics kill bacteria.
- Hence Antibiotics are useless against viruses.
- There are some antiviral drugs that help protect you from a viral infection.
- Antivirals either make it harder for the virus to get into the cell or they prevent the virus from reproducing once they are inside of your cells.
- Most bacteria reproduce by simply dividing into two.
- Bacteria can cause diseases such as pneumonia & food poisoning.
- However, not all bacteria are bad. In fact, some friendly types actually help protect us from the disease.
|
Virus |
Bacteria |
|
They are very Small |
They are larger in size as compared to virus |
|
Non-Cellular |
Single-Celled |
|
Have no metabolism of their own |
Have metabolism of their own |
|
Take no food by any method |
Take food by absorption |
|
Do not grow & do not divide |
Grow in size & divide to produce more bacteria (by Cell-Division) |
|
Command the host cell to produce virus |
They can reproduce by their own |
|
Can be crystallised |
Cannot be crystallised |
|
All produce diseases in man, animals & plants |
Some are harmless, some useful & some are disease-causing |
|
Contains only genetic material & protective coating |
Contains various cells subunits or organelles such as cytoplasm & cell wall which all perform specific functions |
|
They have simpler DNA (if their genetic material is DNA) |
They have more complex DNA |
|
Multiply faster than bacteria |
Multiply slower than Viruses |
|
They are Non-Living |
They are living |
|
Vaccines prevent the spread & antiviral medicines help to slow reproduction but cannot stop it completely |
They can be treated with Antibiotics |
| Example– Common Cold, Flu & Sore Throat | Example– Strep Throat, Tuberculosis, Whooping Cough |
|
|
|
Difference Between DNA & RNA Viruses
- A virus can self-replicate inside a host cell.
- The infected cells may produce thousands of new copies of the original virus at an extraordinary rate.
- The genetic material of a virus can be either DNA or RNA.
- The viruses that contain DNA as their genetic material are called the DNA viruses.
- RNA viruses, on the other hand, contain RNA as their genetic material.
- DNA viruses are mostly double-stranded while RNA viruses are single-stranded.
- RNA mutation rate is higher than the DNA mutation rate.
- DNA replication takes place in the nucleus while RNA replication takes place in the cytoplasm.
- DNA viruses are stable while RNA viruses are unstable.
- Antigens: A substance which the body recognizes as alien & which induces an immune response.
- Antibodies: A blood protein produced by the body in response to & counteracting an antigen.
Difference between DNA vs RNA
|
DNA |
RNA |
|
Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
Ribonucleic Acid |
|
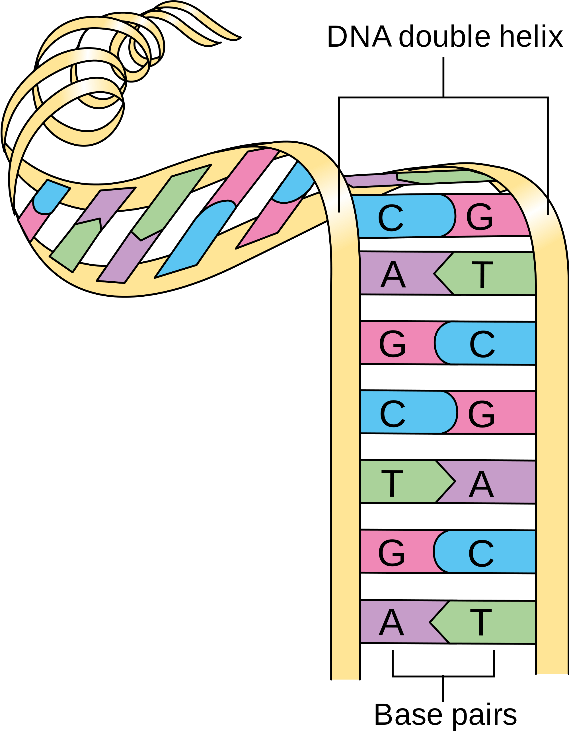
Double-Stranded |
Single Stranded |
|
Deoxyribose Sugar |
Ribose Sugar |
|
Self Replicate |
Can’t Self-Replicate It is synthesized from DNA when required |
|
Occurs inside the nucleus & of cell & some cell organelles (mitochondria) but in plants, it is present in mitochondria & plant cell |
It is found in the cytoplasm of the cell but very little is found inside the nucleus. |
|
DNA is the genetic material in all living organisms |
RNA is the genetic material in some viruses |
|
Long Polymer Chain |
Shorter Polymer Chain |
|
Life of DNA is longer |
Its life is short |
|
DNA occurs only in one form in any organism |
3 types of RNA are present in an organism: – mRNA, rRNA, tRNA |
|
DNA is functional in the transmission of genetic information It forms as a media for long-term storage |
RNA is functional is the transmission of the genetic code that is necessary for the protein creation from the nucleus to the ribosome |
|
Bases present are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, & Thymine |
Bases present are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine & Uracil |
|
|
|
Difference between Gene & Genome
|
Gene |
|
|
A gene is a part of DNA Molecule. |
The genome is total DNA in a cell. |
|
The hereditary element of genetic information. |
All set of nuclear DNAs. |
|
Encodes protein synthesis. |
Encodes both proteins & regulatory elements for protein synthesis. |
|
Length is about a few hundreds of bases. |
Length of the genome of a higher organism is about billion base pairs. |
|
A higher organism has about thousands of genes. |
Each organism has only one genome. |
|
Variations of the gene named alleles can be naturally selected. |
Horizontal gene transfer & duplication cause large variations in the genome. |