
Copyright, Trademark, Geographical Indication (GI), Differences
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
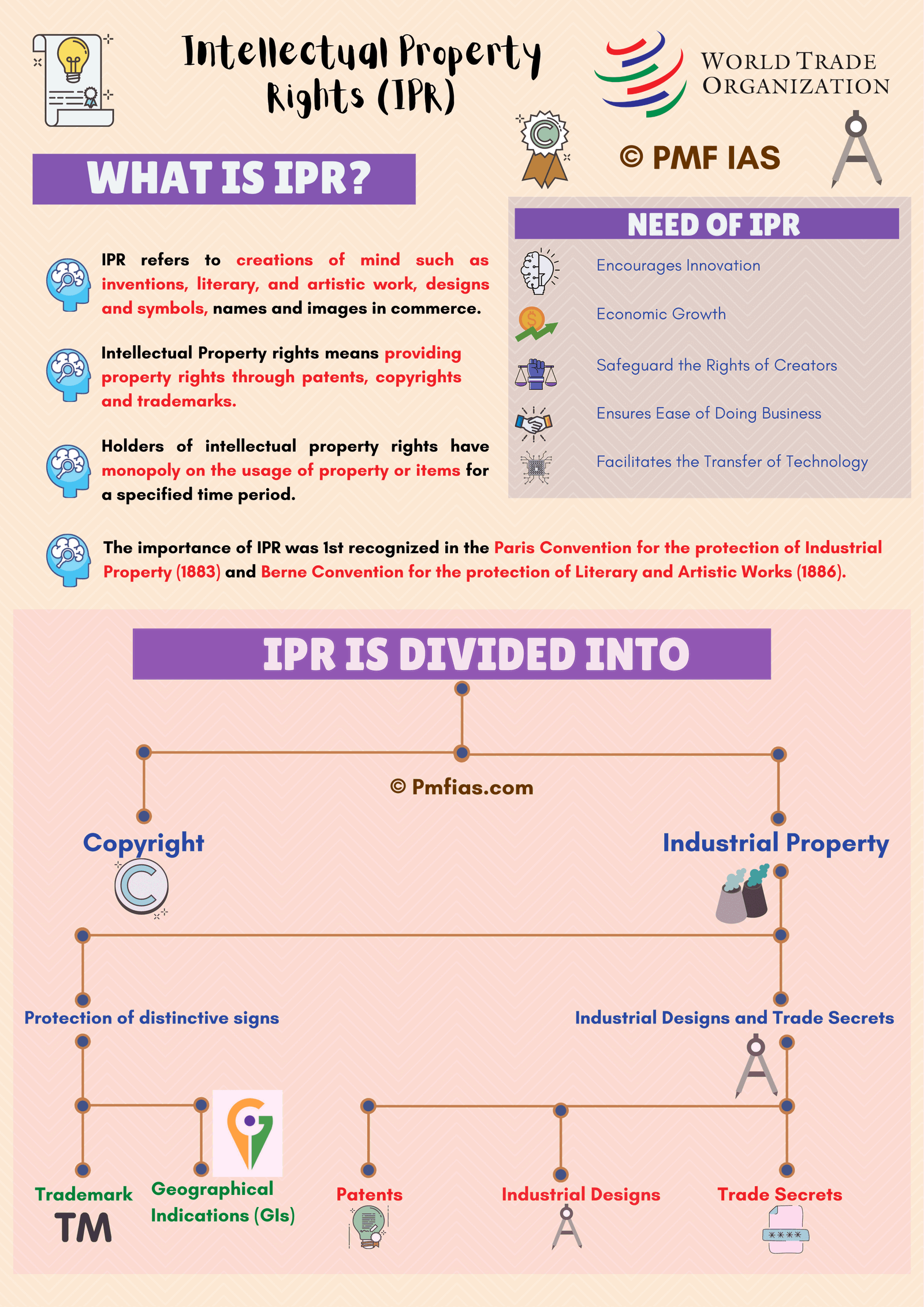
Copyright, Trademark & Geographical Indication (GI) are different types of Intellectual Property Rights.
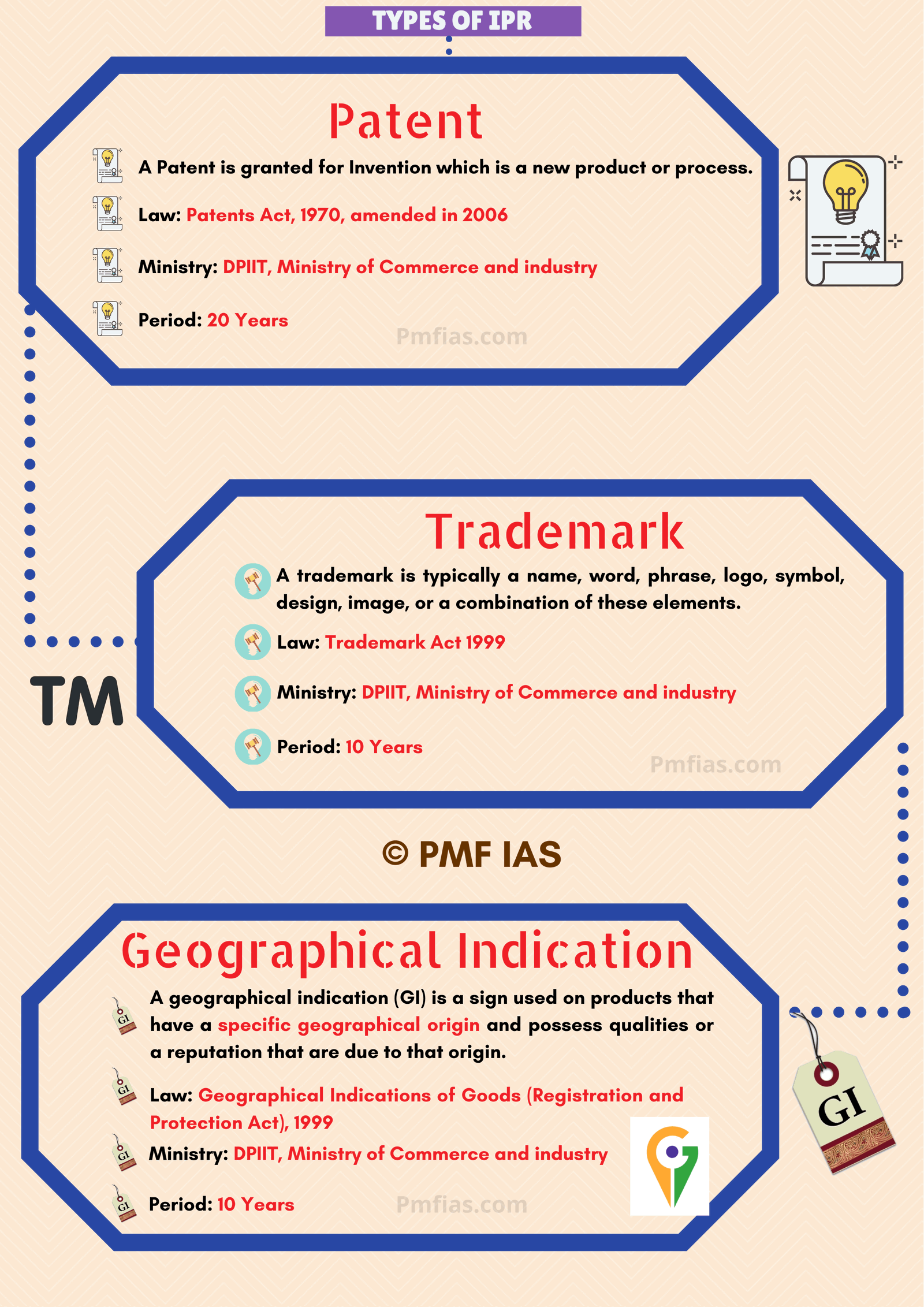
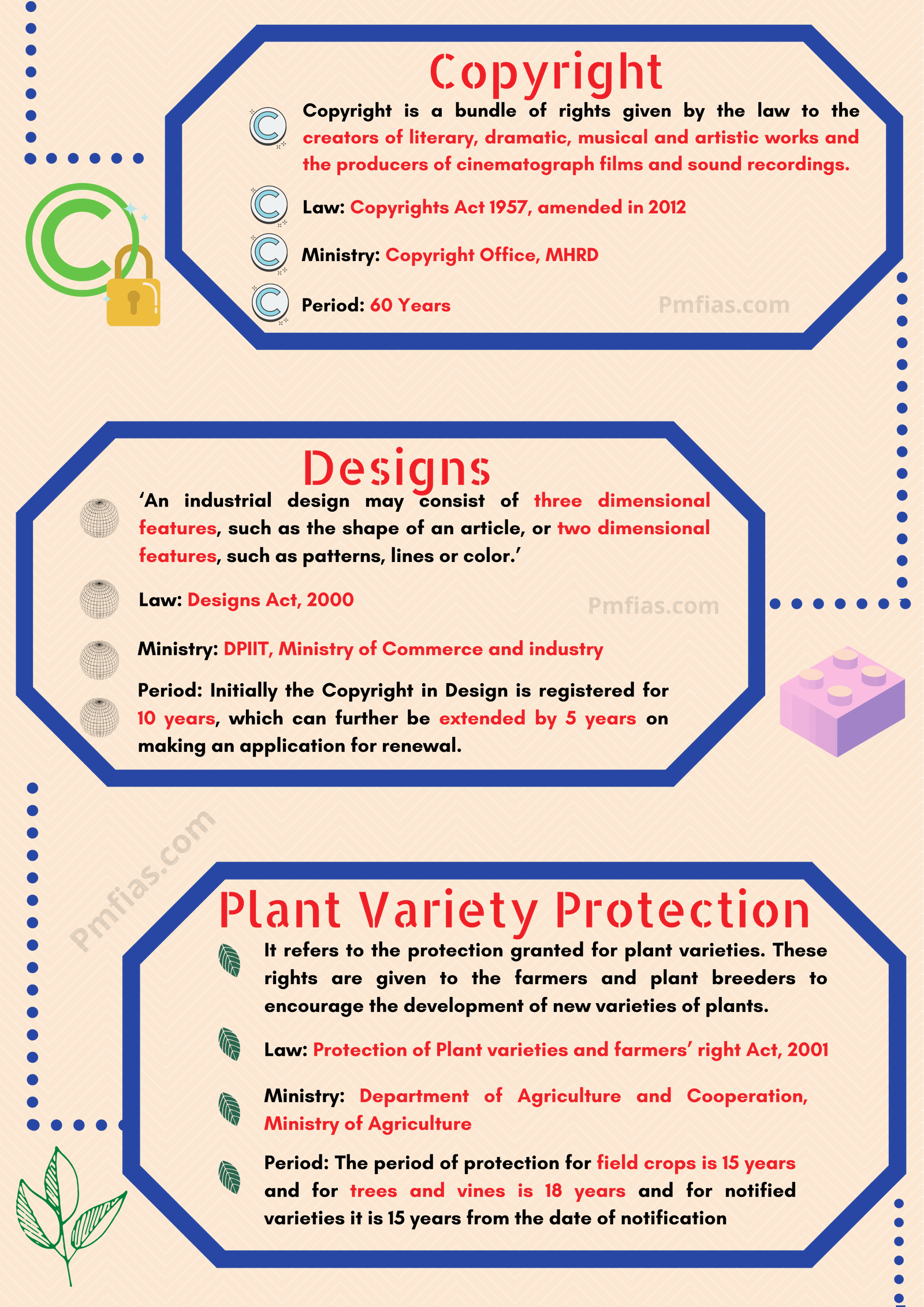
Copyright
- Copyright is a legal term used to describe the rights that creators have over their literary & artistic works.
- Works covered by copyright range from books, music, paintings, sculpture & films, to computer programs, databases, advertisements, maps & technical drawings.
- Copyrights in India are governed by “The Copyright Act, 1957”.
Trademark
- A trademark is a sign capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one enterprise from those of other enterprises.
- Trademarks date back to ancient times when artisans used to put their signature or “mark” on their products.
- Trademarks in India are governed by Trade Marks Act 1999 which was amended in 2010.
Geographical Indications
- A GI tag is a legal recognition given primarily to an agricultural, natural or a manufactured product (handicrafts & industrial goods) originating from a definite geographical territory.
- GI tag conveys an assurance of quality & distinctiveness of a product, which is essentially attributable to the place of its origin.
- Most commonly, a geographical indication includes the name of the place of origin of the goods.
- Once the GI protection is granted, no other producer can misuse the name to market similar products.
- It also provides comfort to customers about the authenticity of that product.
- Geographical Indicators in India are governed by “The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection) Act, 1999”.
What is the difference between a Geographical Indication (GI) & a Trademark?
- A trademark is a sign/word/phrase used by an entity to distinguish its goods & services from those of others.
- A geographical indication tells consumers that a product is produced in a certain place & has certain characteristics that are due to that place of production.
- A trademark gives the entity the right to prevent others from using the trademark.
- On the other hand, GI may be used by all producers who make their products in the place designated by a geographical indication.













Kindly look into it. I found some random Telegram Channel sharing Paid PDFs of PMF IAS in free..
https://t.me/RobinhoodGPSC/1080
please check adjacent posts also