Patent, Patent vs. Trademark, Criteria for issuing Patents
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
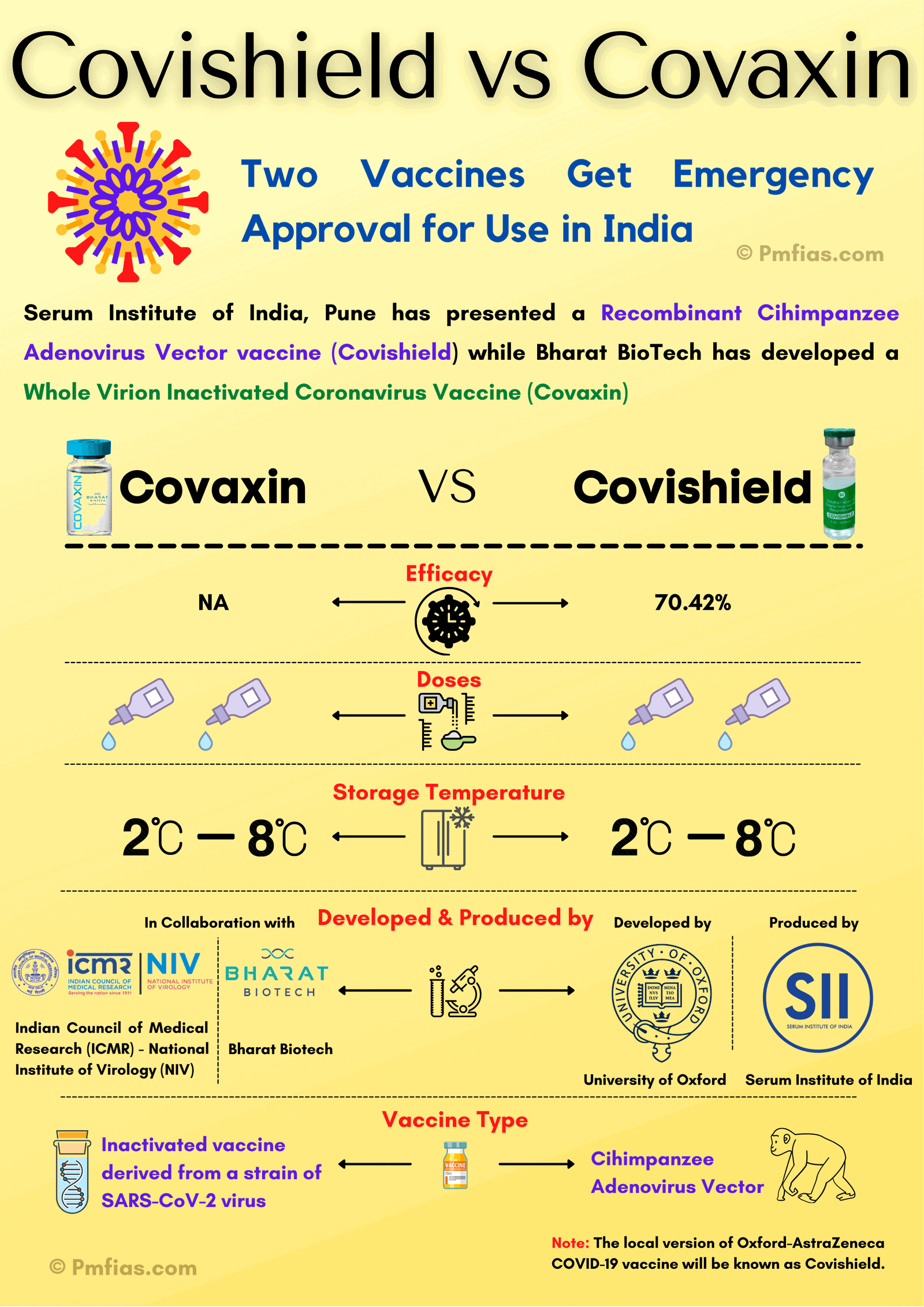
Patent
- A patent is an intellectual property right.
- A patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a new product or process that meets conditions of
- novelty,
- non-obviousness, &
- industrial use.
- A patent provides the owner with the right to decide how – or whether – the invention can be used by others.
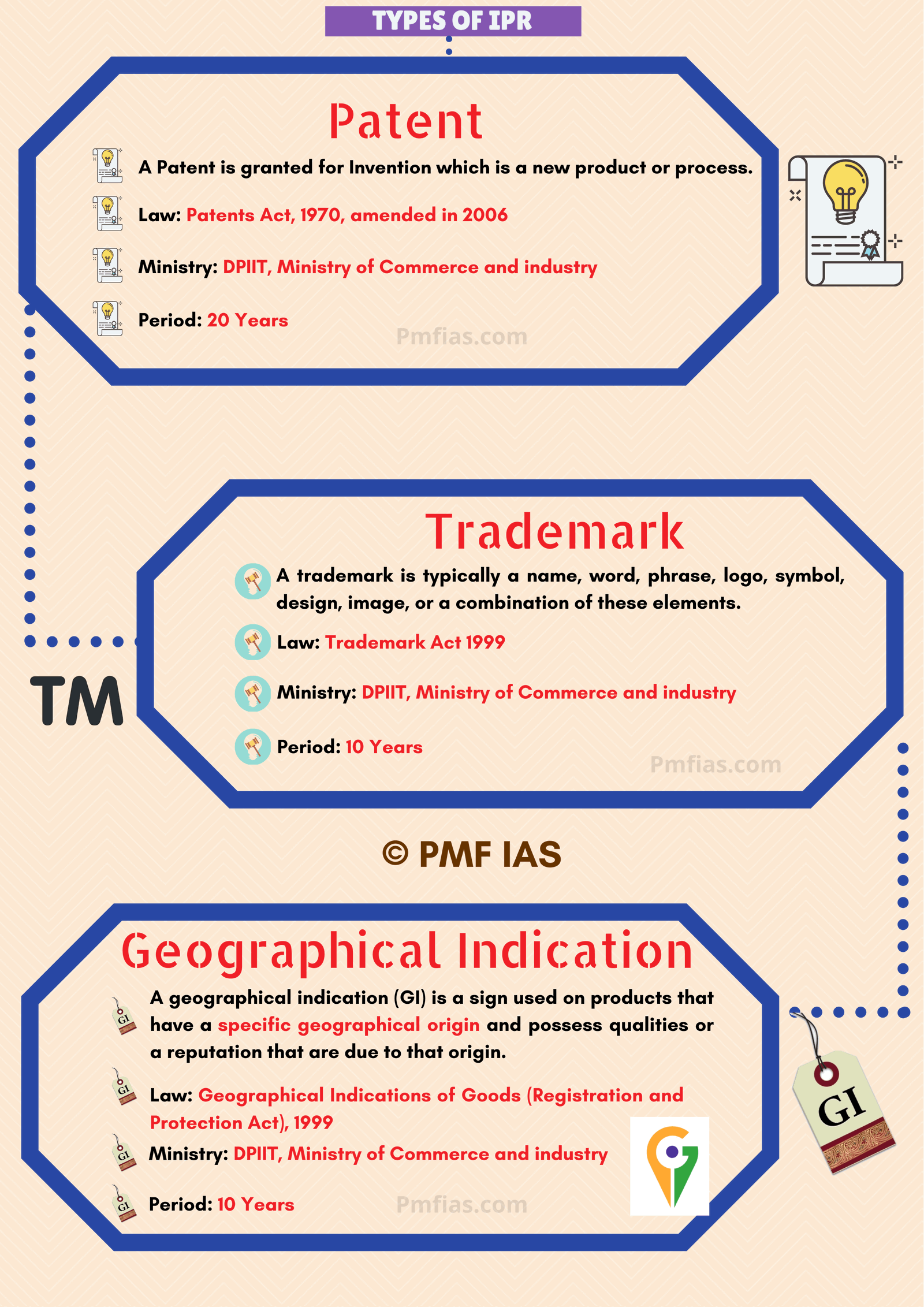
Criteria for issuing Patents in India
- Novelty: it should be new (not published earlier + no prior Public Knowledge/ Public Use in India)
- Non obviousness: It must involve an inventive step (technical advanced in comparison to existing knowledge + non‐obvious to a person skilled in the relevant field of technology)
- Industrial use: It should be capable of Industrial application
- Patents in India are governed by “The patent Act 1970” which was amended in 2005 to make it compliant with TRIPS.
What cannot be patented?
- Frivolous Invention: Invention that harms public order/Morality/ health of animals, plants & humans
- Methods of agriculture or horticulture
- Traditional Knowledge
- Computer Program
- Inventions related to Atomic Energy
- Plants & Animals
- Mere discovery of scientific principle
Patent (Amendment) Rules, 2020
- The central government has published an amended Patent (Amendment) Rules, 2020.
- The new rules have amended the format of a disclosure statement that patentees & licensees are required to annually submit to the Patent Office.
- The format contains disclosing the extent to which they have commercially worked or made the patented inventions available to the public in the country.
- The disclosure is to be made in the Form 27 format as prescribed under the Patent Rules, 2003.
- The patentees & licensees as well as the Patent Office have blatantly disregarded this statutory requirement.
- There has been significant pressure from MNCs & the U.S. to do away with this requirement.
Criticism of Patent (Amendment) Rules, 2020
- The amendment has significantly weakened the requirement of submitting information in the disclosure.
- This could hamper the effectiveness of India’s compulsory licensing regime which depends on full disclosure of patent working information.
- This in turn could hinder access to vital inventions including life-saving medicines.