National IPR Policy, Intellectual Property Rights Issues
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
National IPR Policy, 2016
- The Policy aims to push IPRs as a marketable financial asset, promote innovation & entrepreneurship, while protecting public interest.
- The plan will be reviewed every five years in consultation with stakeholders.
- To have strong & effective IPR laws, steps would be taken — including review of existing IP laws — to update & improve them or to remove anomalies & inconsistencies.
- The policy is entirely compliant with the WTO’s agreement on TRIPS.
- Department of industrial policy & promotion (DIPP) is the nodal agency for all IPR issues.
- The policy retains the provisions on Compulsory Licensing (CL) as well as preventing ever-greening of drug patents (Section 3(d) of India’s Patents Act).
- Under Indian Patents Act, a CL can be issued for a drug if the medicine is deemed unaffordable, among other conditions, & the government grants permission to qualified generic drug makers to manufacture it.
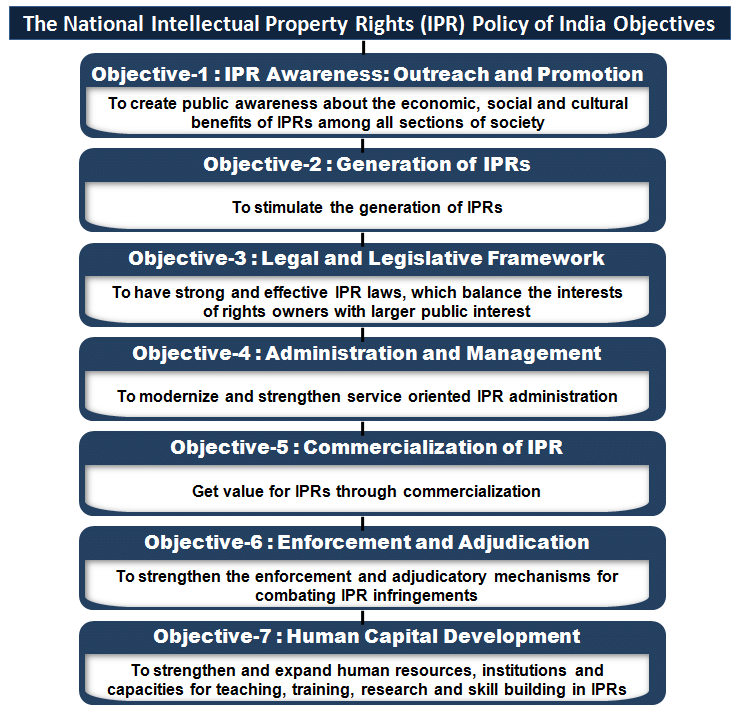
Objectives under the policy are
Intellectual Property Rights Issues: The Five Major Challenges Faced
- There are many IPR issues that one faces while getting IP rights in India. The issues are as follows:
Patent Evergreening Prevention
- One of the most important intellectual property rights issues challenges is the prevention of the evergreening of the patents for multinational companies.
- Evergreening is strategy for extending the term of granted patent which is about to expire without increasing therapeutic efficacy in order to retain royalties.
- As we know, the companies cannot evergreen their patents simply by making minor changes.
- So, section 3(d) in the Indian Patent Act (IPA) possess as one of the biggest issues with regards to IPR.
- This act bars the grant of patents to new forms of substances.
- This has discouraged investments from western countries.
Subsidies & IPR Issues
- A major form of subsidies includes food subsidy, fertilizer subsidy, education subsidy, etc.
- For the complete implementation of TRIPS agreements, one needs to reduce or eliminate these subsidies.
- Thus, GOI needs to create a balance between providing subsidies & providing IP rights in India.
The Product Patents Process
- A product patent protects a product.
- It offers high protection to the original inventor to reduce the competition for the same product.
- Whereas a process patent protects the process through which one manufactures the product & not the product.
- It reduces the element of monopoly in the market.
- As India is a part of the TRIPS agreement, the agreement requires all its members to shift their patent regime from process to product patent.
- This remains a challenge for India, as process patent would be more helpful to a country like India.
- This is since India is a developing country & ordinary people are struggling with basic necessities like food.
Protecting traditional knowledge
- Traditional knowledge, especially in the field of medicine, is like a gold mine.
- GOI is bound to protect traditional knowledge by not allowing MNC’s to get patents on traditional culture.
- Above all, the government has created a Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) to prevent the patenting of traditional knowledge.
- So, this is one of the intellectual property rights issues in India.
Compulsory Licensing & Drug Price Control Order
- One of the most important intellectual property rights issues that the government needs to address is the use of compulsory licensing.
- Compulsory licenses are authorizations given to a third-party by the Government to make, use or sell a particular patented product without the need of the permission of the patent owner.
- The provisions regarding compulsory licenses are given in the Indian Patents Act, 1970 & in the TRIPS (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) Agreement.
- It is a relaxation available to the developing countries under the TRIPS agreement, something which organizations misuse sometimes.
- Moreover, under section 84 of the IPA, a company can acquire a compulsory license for “private commercial use” under certain circumstances.
- With the Drug Price Control Order, the company needs to justify the price of the drug with regards to investments.
- If someone plays foul, then the government has the right to intervene.
- Multinationals are asking the government to revoke this provision.
- However, the government is not ceding the demands to protect the interest of the masses.
Some other issues
- Trademark Violations: India has very high level of trademark counterfeiting against which the authorities in India do not take proper actions.
- Enforcement of IPR regulations is quite weak in the country because of two important reasons
- India is key exporter of counterfeit fake products such as foodstuffs, textiles, shoes, electronics etc
- Judicial delays in IPR disputes
- India maintains high custom duties on IP intensive products as advocated by western countries impacting the investment (US puts India into priority watch list i.e., special 301 report).