Current Affairs January 15-16, 2024: Multidimensional Poverty in India, Global Ocean Heat Content, Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar, Himalayan Wolf, Indian Meteorological Department
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – IR – Maldives} Indian Troops in Maldives
- Context (IE): Maldives has asked India to withdraw all its military personnel from the island nation.
- Maldives and India have set up a high-level core group to negotiate the withdrawal of troops.
- Around 77 Indian military personnel are in the Maldives, as per official data.
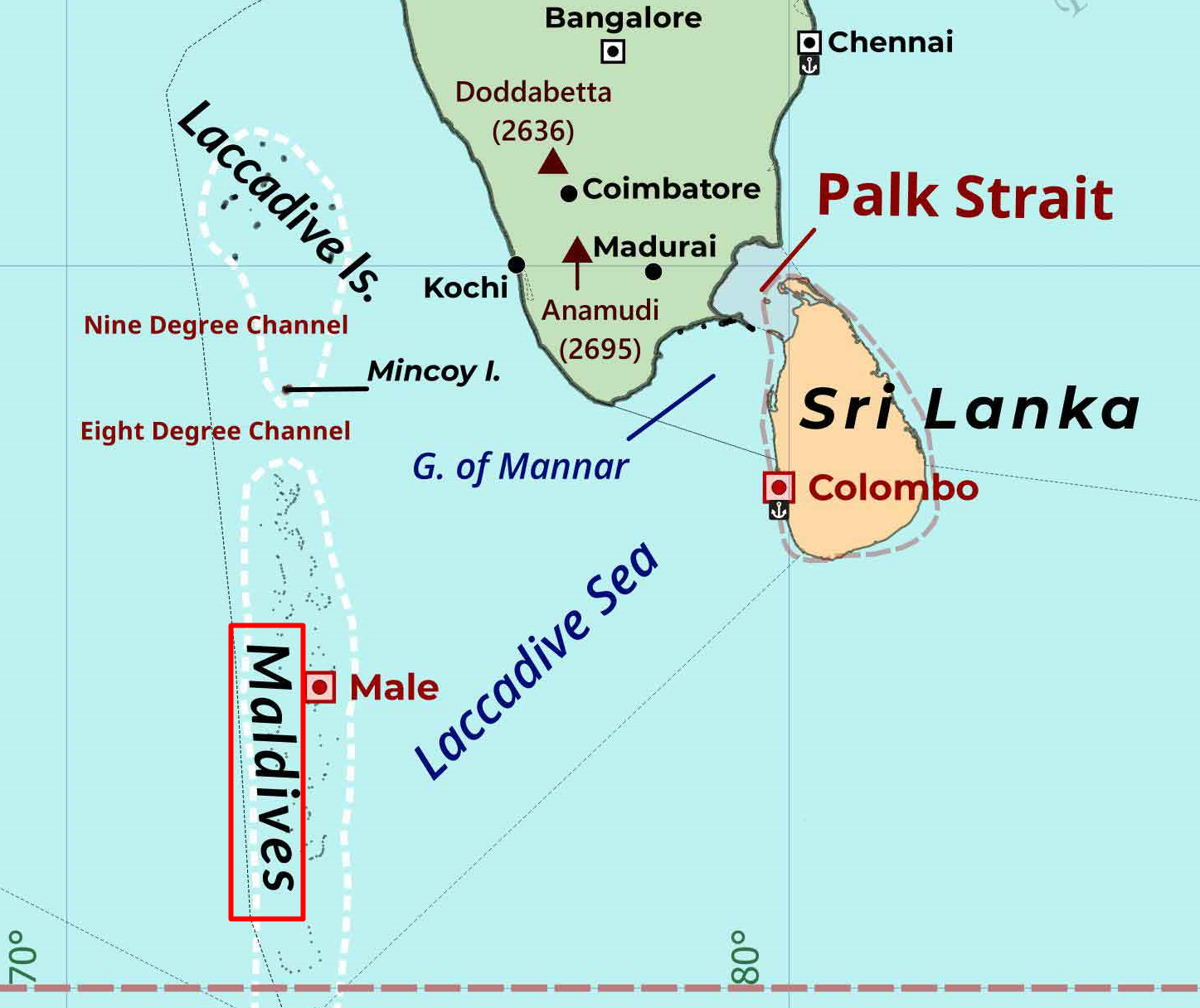
Why Indian troops in Maldives
- The Indian military saved the Maldivian President during Operation Cactus, thwarting a military coup.
- Indian military personnel train Maldivian troops in combat, surveillance, and rescue-aid operations.
- Helicopter operations, Dornier aircraft operations & associated maintenance and engineering works.
Apprehension and mistrust
- India-gifted Dhruv ALHs are seen as an attempt to increase India’s military presence.
- Previous Solih government’s perceived lack of transparency while dealing with India raised mistrust.
- The Maldivian police academy campus is seen as an attempt to settle more Indians in Maldives.
- Maldivian media also portrayed the UTF Harbour Project agreement at Uthuru Thilafalhu, a strategically located atoll near the capital Malé, as India’s military base project.
Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Dhruv
|

- Domestic politics & the pro-China government are the real reasons behind the withdrawal demand.
Historical Rollercoaster of Maldives’ foreign policy
- Maldivian culture, rooted in Buddhism, became a constitutionally Muslim nation after conversions.
- Maldives managed to maintain relative independence from European colonisation.
- It signed a Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation with the British in 1887.
- With internal political sovereignty, foreign affairs were surrendered to Britain.
- During the Second World War, the Maldives was a British naval base and continued as a British protectorate until its independence in 1965.
- Independent Maldives became a UN member in 1965.
- India was the first nation to launch a resident mission in Male in 1976.
- In 1978, the Indian International Airport Authority was awarded a tender to expand the Hulhule airport runway.
- Indo-Maldivian bilateral relationship was formalised by signing the Treaty of Friendship in 1981.
- Maldivian foreign policy under President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom took a lukewarm turn towards India despite India’s aid in preserving his regime during a coup attempt.
- Recognising China’s emergence as a global power with significant strategic interests in the Indian Ocean, President Gayoom visited China in 1984 and then again in 2006.
- Again, Indo-Maldivian ties improved with President Mohamed Nasheed coming to power in 2008 with campaign critical Sinocentric policies.
For details on India-Maldives relations, visit >India-Maldives Relations.
{GS2 – Social Sector – Poverty} Multidimensional Poverty in India
- Context (PIB): Findings of NITI Aayog’s ‘Multidimensional Poverty in India since 2005-06’ were recently revealed.
Findings of the Paper
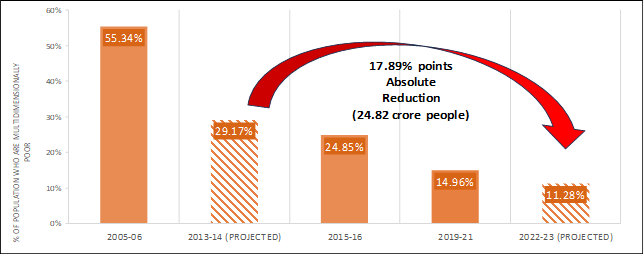
- India has registered a significant decline in Multidimensional Poverty in India (MPI) from 29.17% (2013-14) to 11.28% (2022-23).
- UP registered the largest decline in the number of poor escaping multidimensional poverty during the last nine years followed by Bihar, MP, and Rajasthan.
- The pace of decline in poverty headcount ratio using exponential method was much faster between 2015-16 to 2019-21 compared to period 2005-06 to 2015-16.
- All 12 indicators of MPI have recorded significant improvement.
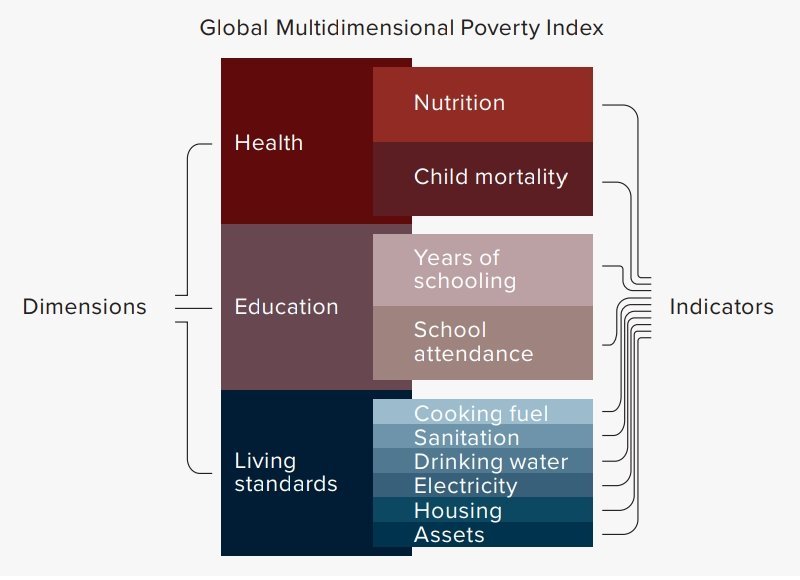
Multidimensional Poverty Index (Global MPI)
- Global MPI is a measure of multidimensional poverty covering 107 developing countries.
- It was first developed in 2010 by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) for UNDP’s Human Development Reports.
- Global MPI uses three dimensions and ten indicators.
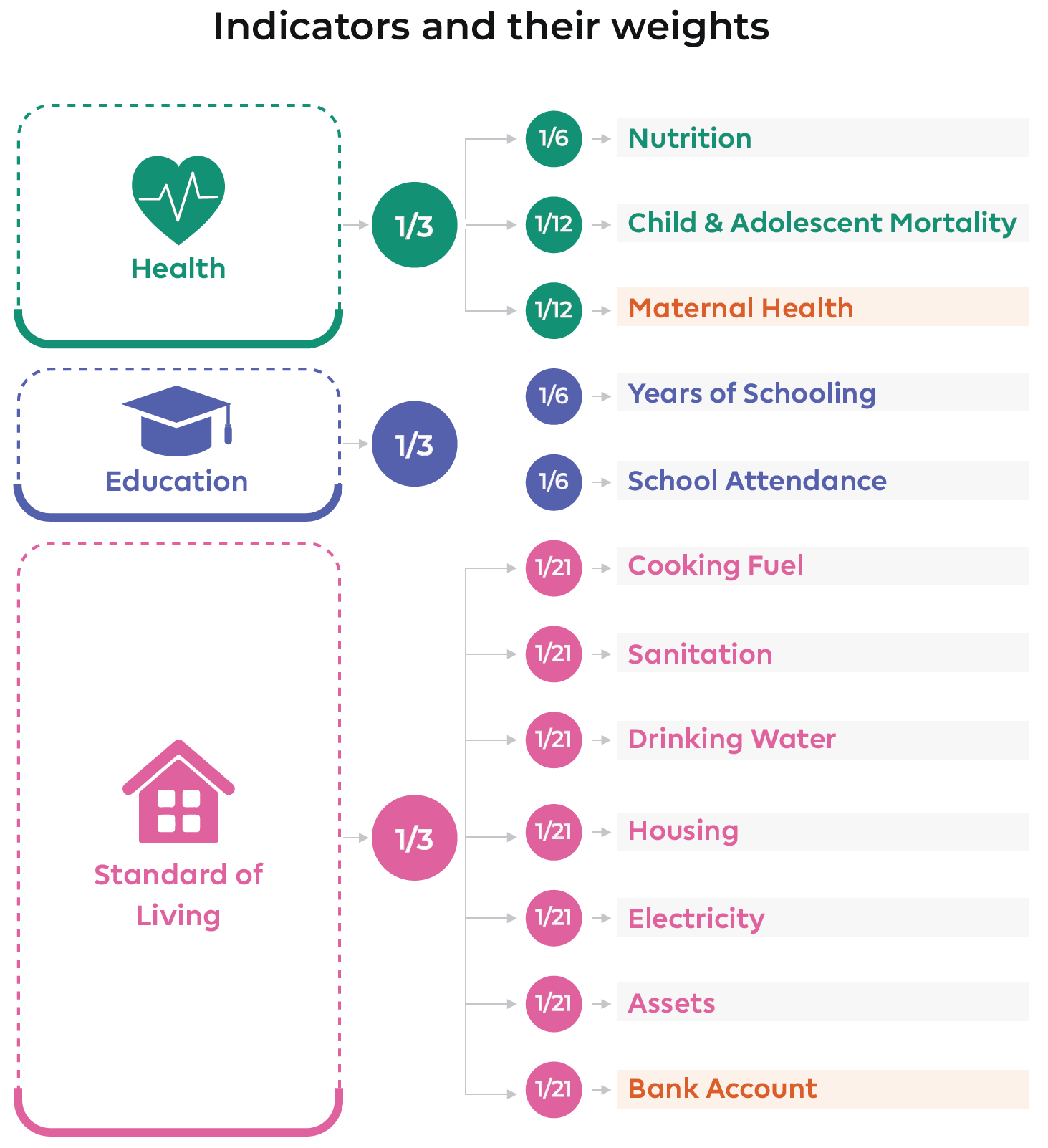
National Multidimensional Poverty Index (National MPI)
- It is published by NITI Aayog using the methodology in consonance with the global methodology.
- Like the global MPI, India’s national MPI has three equally weighted dimensions – Health, Education, and Standard of living – represented by twelve indicators.
- The national MPI model retains the ten indicators of the global MPI model.
- It also adds two indicators, viz., Maternal Health and Bank Accounts, in line with national priorities.
Initiatives undertaken to reduce Multi-dimensional poverty in India
- Initiatives like Poshan Abhiyan and Anemia Mukt Bharat have significantly enhanced access to healthcare facilities, leading to a substantial decrease in deprivation.
- The Targeted Public Distribution System (National Food Security Act), Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana provides conncessional food grains to rural and urban populations.
- Clean cooking fuel distribution through Ujjwala Yojana.
- Improved electricity coverage via Saubhagya.
- Transformative campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Jal Jeevan Mission.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and PM Awas Yojana have played pivotal roles in financial inclusion and providing safe housing for the underprivileged.
For details on Poverty topic >Poverty in India.
{GS3 – Envi – CC Impacts} Global Ocean Heat Content
- Context (DTE): In 2023, global ocean heat content doubled or tripled since the late 1980s.
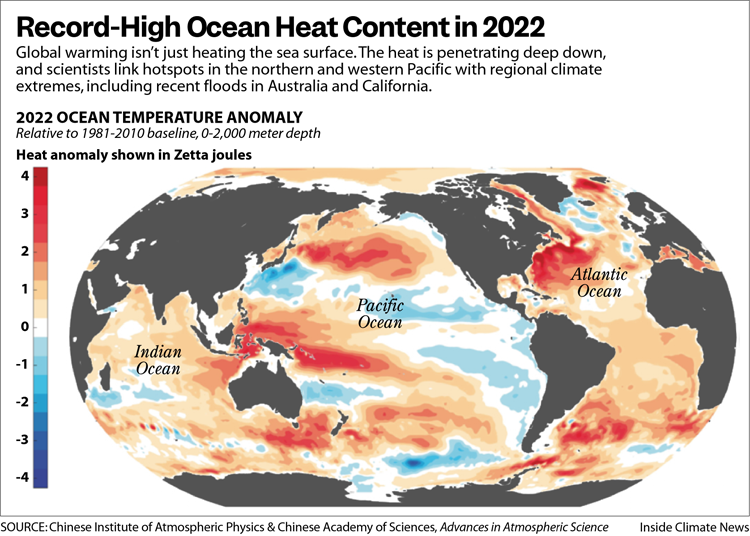
Key Findings
- The amount of heat stored in the upper 2,000 metres of the global ocean or the ocean heat content reached 286 Zetajoules (ZJ) in 2023 relative to the 1981–2010 average.
- The 2023 estimate represents around 4.6 billion Hiroshima nuclear bombs.
- Warming in much of the Atlantic, North Pacific, Western Pacific and Southern oceans is occurring at a faster rate than the global average.
- CO2 concentration in the atmosphere in 2023 was more than 50% above the preindustrial level.
- The Salinity Contrast index (difference between the salinity averaged over high and low-salinity regions) reached 7.2 mg per kg in 2023, the fourth-highest value since 1958.
What is Ocean Heat Content?
- Ocean heat content (OHC) is the amount of heat energy stored by the oceans.
- It is calculated by measuring the ocean’s temperature at different locations and depths, and then integrating the areal density of ocean heat over the entire ocean.
- OHC is measured in joules, a unit of energy, and compared against the 1971–2000 average, which is set at zero for reference.
Significance of Ocean Heat Content
- Changes in OHC influence ocean currents and weather patterns. E.g, the heat stored deep in the ocean can influence the strength, duration, and frequency of tropical cyclones.
- Indicator of climate change and is used to quantify the rate of global warming as over 90% of the extra heat trapped by humanity’s GHG emissions is stored in the oceans
- Sea level rise: The expansion of seawater as it warms (thermal expansion) contributes to sea level rise. The increase in OHC accounts for 30–40% of global sea-level rise from 1900 to 2020.
- Climate stabilization: The ocean’s ability to store and release heat over long periods gives it a central role in stabilizing Earth’s climate system.
- Marine ecosystems: High OHC can disrupt marine ecosystems, bleach coral, and contribute to extreme weather events such as hurricanes.
{GS3 – IE – Institutions} World Economic Forum Annual Meeting
- Context (IE): The World Economic Forum (WEF) will hold its Annual Meeting in Davos, Switzerland.
- Davos brings together participants, including paying members and selected invitees comprising investors, business leaders, political leaders, economists, celebrities, journalists, etc.
About WEF
- German professor Klaus Schwab founded the WEF in 1971.
- It was initially known as the European Management Forum.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- It introduced the concept of “stakeholder capitalism”.
|
- Partnering corporations (generally >$5 billion annual turnover) fund WEF.
- Bretton Woods fixed exchange rate mechanism and the Arab-Israeli War in 1973 led to the expansion of the focus of the Annual Meeting from management to economic and social issues.
Diplomatic Endeavours of WEF Annual Meet
- The European Management Forum was the first non-governmental institution to initiate a partnership with China’s economic development commissions in 1979.
- North and South Korea held their first ministerial-level meetings in Davos.
- German Unification was discussed between the East German PM and the chancellor.
- In 1992, South African President de Klerk met Nelson Mandela and Zulu prince Mangosuthu Buthelezi at the Annual Meeting, their first joint appearance outside South Africa
- The idea of the foundation of G20 also originated from the WEF meeting.
Reports Published by WEF
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Global Gender Gap Report
- Energy Transition Index
- Global IT Report
- Global Travel and Tourism Report.
{GS3 – IE – Securities} Initial Public Offering
- Context (IE): India has seen an IPO boom recently.
- An IPO is when an unlisted company raises funds by offering shares to the public or new investors.
- Following the IPO, the company is listed on the stock exchange.
|
- The company has to file its offer document with the market regulator, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Sebi), before releasing an IPO. This document is called the Red Herring document.
|
- If an IPO is an Offer for sale (OFS) by promoters or existing investors, then the money goes to them. E.g, in the case of LIC, the issue was an OFS by the government, and the proceeds went to the GoI
- The per-share price of the public issue is fixed by the issuer in consultation with the merchant banker based on the company’s valuation.
- SEBI has no role in price fixation.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
|
Eligibility for IPO release
- Net tangible assets of at least Rs 3 crore,
- Net worth of Rs 1 crore in each of the preceding three full years,
- Minimum average pre-tax profit of Rs 15 crore in at least three immediately preceding five years.
Categories of investors in IPO
- “Qualified institutional buyers” is a category of investors that includes foreign portfolio investors (FPIs), mutual funds, commercial banks, insurance companies, pension funds, etc.
- Retail investors invest up to Rs 2 lakh in an issue.
- High-net-worth individuals (HNI) are retail investors investing above Rs 2 lakh.
- The minimum age to invest in stocks and hold a demat account is 18 years.
|
{Prelims – Awards} Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar
- Context (PIB): GoI invited individuals or teams for nominations to “Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar“.
- Nominations can be submitted through the Ministry of Home Affairs Award Portal.
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) coordinates the awards.
- Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar will be announced on National Technology Day (May 11, 2024).
- The Award Ceremony for all categories is on National Space Day (August 23, 2024).
Rastriya Vigyan Puraskar
- The award recognises the outstanding contributions of researchers, technologists, and innovators in various fields of science and technology.
- It aims to recognize lifetime achievements and distinguished contributions and encourage young scientists and exceptional teams in various science and technology domains.
Award Categories
- Vigyan Ratna (VR): Maximum of 3 awards for lifetime achievements.
- Vigyan Shri (VS): Maximum of 25 awards for distinguished contributions.
- Vigyan Yuva: Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award: Maximum of 25 awards for young scientists.
- Vigyan Team (VT) award: Maximum of 3 awards for exceptional team contributions.
Domains for Recognition
- Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is given in 13 domains: Physics, Chemistry, Biological Sciences, Mathematics & Computer Science, Earth Science, Medicine, Engineering Sciences, Agricultural Science, Environmental Science, Technology & Innovation, Atomic Energy, Space Science and Technology, and Others.
Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
National Technology Day
National Space Day
|
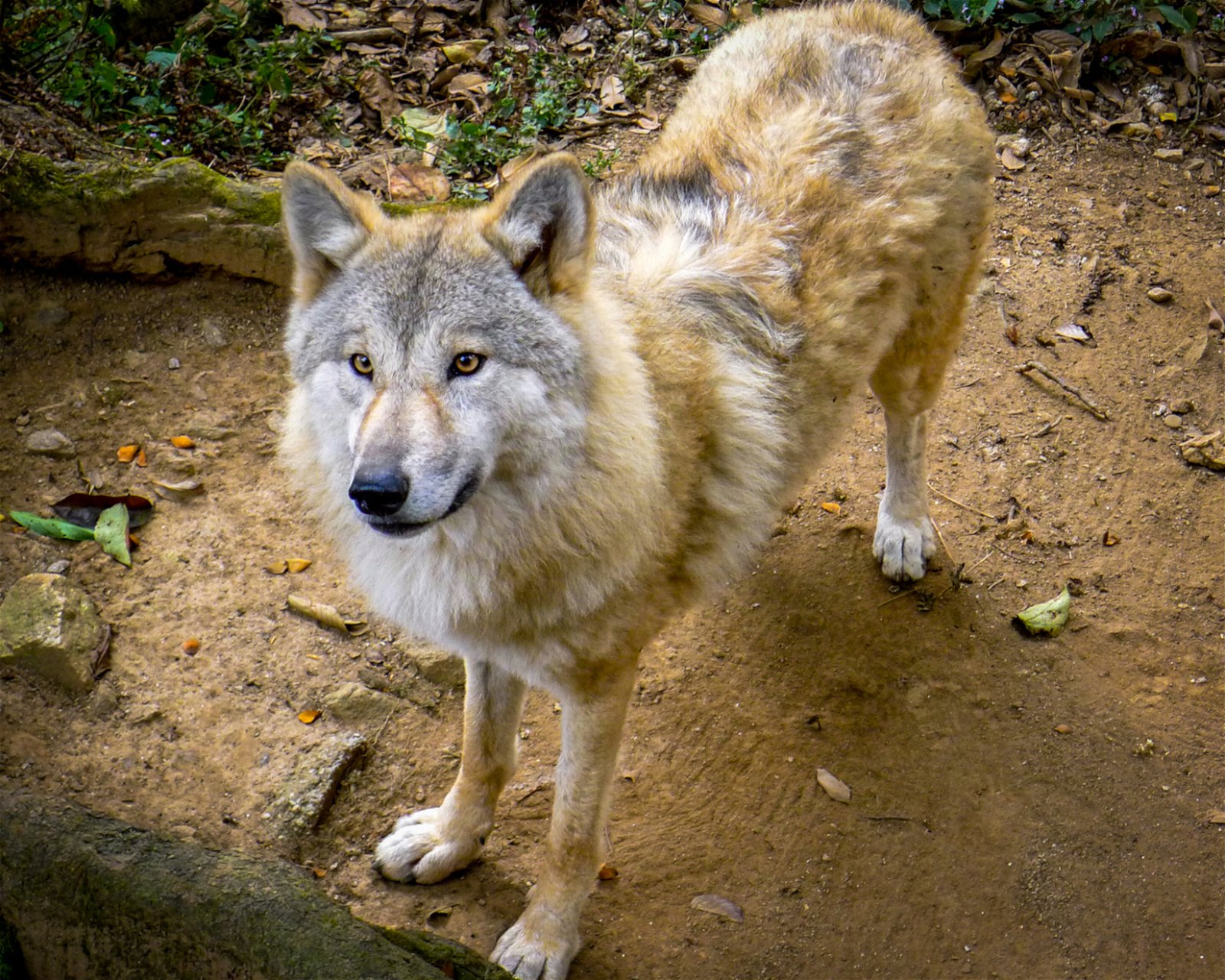
{Prelims – Envi – Species} Himalayan Wolf (Canis lupus chanco)
- The Himalayan Wolf is a prominent lupine predator found across the Himalayas.
- It is thought to be the ancestor of the domestic dog.
- They are genetically distinct from grey wolves.
Habitat
- They can be found living in Ladakh in the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, and the mountains of Central Asia predominantly above 4,000 m (13,000 ft) in elevation.
- Living at such high altitudes, these wolves have genetically adapted themselves to live in low oxygen (hypoxic) conditions.
- They generally avoid dense forests and deep snow zones.
Physical description
- Himalayan wolves are light tan in color and have grey shades on their body.
- Some wolves of this species have white or black shades around the face or along the chest.
- It is larger than the Indian and common European wolves.
Diet
- This carnivore preys upon larger mammals to rodents, birds or even crabs etc.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable | CITES: Appendix I | WPA, 1972: Schedule I
- Threats: Habitat modification, illegal hunting, etc.

{Prelims – In News} Hydroxychloroquine
- Context (IE): Administration of hydroxychloroquine to COVID-19 patients during the pandemic resulted in an increased deaths.
Hydroxychloroquine
- It is a drug used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis & lupus.
- It is also used for the prevention of malaria & its treatment. It is a derivative of the antimalarial drug chloroquine.
- Administered in COVID-19 cases, it suppresses the cytokine storm by lowering immune reactions.
{Prelims – In News} Indian Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Context (PIB): The Indian Meteorological Department completed 150 years of its establishment.
- The IMD was established in 1875.
- It is India’s National Meteorological Service and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It is one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- Headquarters: New Delhi (Initially at Shimla, later at Poona and finally shifted to New Delhi).
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Science.
- Headed by: Director General of Meteorology.
- There are six Regional Meteorological Centres located in Chennai, Guwahati, Kolkata, Mumbai, Nagpur, and New Delhi, each under a Deputy Director General.
Functions
- To provide meteorological information for weather-sensitive activities like agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, offshore oil explorations, etc.
- To provide the meteorological statistics needed for activities such as oil exploration, agriculture, water resource management, industry, and other nation-building projects.
- To issue warnings about dangerous weather conditions that can destroy both life and property, such as tropical cyclones, dust storms, heavy rain, snow, cold and heat waves etc.
Initiatives launched
National Framework of Climate Services (NFCS)
- Objective: To reduce losses from climate hazards and extreme weather events.
- It would strengthen the production and delivery of science-based climate monitoring and prediction services for agriculture, health, energy, disaster, etc.
Panchayat Mausam Sewa Portal
- It provides information on all weather parameters such as severe weather warnings, maximum and minimum temperatures, humidity, wind speed, etc.
- The information will be provided in Hindi, English, and 12 regional languages to all panchayat heads and panchayat secretaries.
- It will help in reducing crop loss and input cost and better planning of agricultural activities.
Mausam App
- It provides weather-related services like current weather, forecast of every hour to 7 days, Rainfall, Humidity, Sunrise/Sunset, Rain, Lightning & Cyclone Alert, Aviation & Agro-Meteorological advisories.
Mausamgram
- available through the Mausam App, it allows the public to view observations, forecasts, & warnings for their location through a map or search function using place names, pincodes, or coordinates.
Decision Support System (Weather Analysis and Forecast Enabling System (WAFES))
- It serves as a visualization platform to analyze meteorological observations and prediction models, aiding decision-making for severe weather phenomena and their socio-economic impact.
- It provides real-time information for various sectors such as Urban, Power, Hydrology, Health, Energy, Agriculture, Transport, and Tourism under the “UPHHEATT” initiative (for the cause of welfare).
{Prelims – In News} Operation Amrith
- Context (TH): Kerala launched Operation Amrith to prevent the overuse of antibiotics.
- It aims to detect Over-the-counter (OTC) sales of antibiotics by conducting surprise raids in retail and medical shops.
Other steps taken by Kerala to prevent Antibiotic overuse
- India’s first state to develop an AMR action plan in 2018.
- First state in India to establish block-level AMR Committees in all blocks in 2023.
- For surveillance, launched the Kerala Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (KARS-NET).
- For proper disposal of unused antibiotics, it has developed the Programme on Removal of Unused Drugs (PROUD).
{Prelims – PIN India} Vadnagar
- Context (TH): An excavation was led by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) found evidence of a cultural continuity in Vadnagar (Gujarat).
- Recent unpublished radiocarbon dates indicate its potential age around 1400 BCE. This timeframe aligns with the late phase of the post-urban Harappan period.
- Evidence from the archaeological excavation makes it as the oldest living city within a single fortification uncovered in India.
- The findings also suggest that the existence of the “Dark Age” is probably a myth.
Findings from new archaeological excavation at Vadnagar
- Multireligious: Vadnagar housed a diverse population practicing Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, Islam.
- Multicultural: Archaeological excavations revealed seven cultural stages– Mauryan, Indo-Greek, Indo-Scythian, Hindu-Solankis, Sultanate-Mughal, and Gaekwad-British colonial rule.
- Evidence of cultural continuity: Evidence points to a settlement dating back to 800 BCE, contemporary with late-Vedic or pre-Buddhist Mahajanapadas.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Excavated artifacts include pottery, copper, gold, silver, iron objects, and intricately designed bangles.
- Indo-Greek Influence includes coin moulds from the Indo-Greek rule, featuring the Greek king Appollodatus.
- Climate Influences such as rainfall or droughts, influenced the rise and fall of kingdoms and recurrent invasions by Central Asian warriors over 3,000 years.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} Indo-Thai CORPAT
- Context (PIB): The maiden Bilateral Maritime Exercise between the Indian Navy (IN) and Royal Thai Navy (RTN) was conducted recently along with Indo-Thai CORPAT.
- Indigenously built Indian Naval ships Kulish and IN LCU 56 participated in the exercise.
- The Indo-Thai Bilateral Exercise is being named as ‘Ex-Ayutthaya’. It symbolises the significance of two of the oldest cities Ayodhya in India and Ayutthaya in Thailand.
|
{Prelims – Sci – Bio – Diseases} Cervical cancer
- Context (IE): The government is set to roll out a human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination campaign for girls in the 9-14 age group.
Cervical Cancer
- Cervical cancer starts in the cervix and is caused by Human Papilloma Virus (HPV).
- HPV is a sexually transmitted infection.
- Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women.
- It occurs mainly in women over age 30.
- It is a preventable and curable disease (if detected early and managed effectively).
- HPV vaccine can prevent cervical cancer if given before girls or women are exposed to the virus.
| Cervix: It connects the vagina (birth canal) to the upper part of the uterus (womb). |
Cervavac
- It is India’s first indigenously developed Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus (qHPV) vaccine against cervical cancer.
- qHPV vaccine: It protects from 4 types of HPV, which cause 80% of cervical cancer.
- Cervavac will be administered to girls between 9 and 14 years to prevent cervical cancer.
Significance
- Globally, India contributes the largest share of cervical cancer cases.
- It is also the second most common cancer in Indian women.
National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI)
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)