Current Affairs July 19, 2023: Universal Immunization Program, UN Refugee Convention of UNHRC, BIMSTEC, Land Records DILRMP
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Health – 2023/07/19} Universal Immunisation Program (UIP)
- Context (IE I HT): India records 93% DPT3 coverage in 2022 (an all-time high was 91% in 2019).
- Universal Immunisation Program (UIP) was introduced in 1985 and was integrated into Child Survival & Safe Motherhood Program in 1992.
- It became a part of the National Reproductive and Child Health Programme in 1997.
- Ministry of Health provides free vaccines to infants/children/pregnant women against 12 vaccine-preventable diseases through UIP.
- UIP has been a crucial component of the National Rural Health Mission since its inception in 2005.
Immunization
|
Vaccines provided under UIP
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Vaccine
- It is given to infants to protect them from tubercular meningitis and disseminated TB.
- BCG vaccine is given at birth or as early as possible before one year.
Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV)
- It protects children from poliomyelitis.
- OPV is given at birth, called zero dose and three doses are given at 6, 10 and 14 weeks.
- A booster dose is given at 16-24 months of age.
Hepatitis B (Hep B) Vaccine
- It protects from Hepatitis B virus infection.
- It is given at birth or as early as possible, within 24 hours.
- Subsequently, three doses are given at 6, 10 and 14 weeks in combination with DPT and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) as a pentavalent vaccine.
Pentavalent Vaccine
|
Rotavirus Vaccine (RV)
- It gives protection to infants and children against rotavirus diarrhoea.
- It is given in select states.
- Three doses of vaccine are given at 6, 10, and 14 weeks of age.
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV)
- It protects infants/ children against disease caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- It is given in select states.
- The vaccine is given in two primary doses at 6 and 14 weeks, followed by a booster dose at 9 months.
Fractional Inactivated Poliomyelitis Vaccine (fIPV)
- It is used to boost the protection against poliomyelitis (polio).
- Two fractional doses of IVP are given intradermally at 6 and 14 weeks of age.
Measles, Rubella (MR) vaccine
- In a few states, a combined vaccine is given to protect against Measles and Rubella infection.
- First dose is given at 9 completed months, and second dose is given at 16-24 months.
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine (JE)
- It gives protection against Japanese Encephalitis.
- JE vaccine is given in select districts endemic for JE.
- First dose is given at 9 completed months and second dose at 16-24 months of age.
DPT Booster
- DPT is a combined vaccine; it protects children from Diphtheria, Tetanus and Pertussis.
- DPT first booster is given at 16-24 months of age, and DPT second booster is given at 5-6 years of age.
Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine (TT)
- TT is used to protect against tetanus.
- It is given at 10 years and 15 years of age.
- Pregnant women-TT-1 is given early in pregnancy; and TT-2 is given 4 weeks after TT-1.
| Vaccine | Disease | Type |
| BCG vaccine | Tuberculosis | Nationally |
| DPT vaccine | Diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), tetanus | Nationally |
| Hepatitis B vaccine | Hepatitis B | Nationally |
| Hib vaccine | Meningitis, pneumonia, and other infections caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b | Nationally |
| PCV vaccine | Pneumonia, meningitis, and other infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae | Nationally |
| Rotavirus vaccine | Rotavirus diarrhoea | Sub-nationally |
| IPV vaccine | Polio | Nationally |
| MR vaccine | Measles and rubella | Nationally |
| Japanese encephalitis vaccine | Japanese encephalitis | Sub-nationally |
| Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine | Pneumococcal Pneumonia | Sub-nationally |
| Td vaccine | Tetanus and diphtheria | Nationally |
|
Mission Indradhanush
- Mission Indradhanush is a health mission launched in 2014 to accelerate full immunisation coverage for all children under the age of TWO and pregnant women in India.
- The government has identified 201 high-priority districts across 28 states where the concentration of children who are only partially or never immunised is the highest.
Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI)
- IMI was launched in 2019. It is a nationwide program implemented in all 28 states and 8 UTs of India.
- IMI has four phases. The first phase was launched in December 2019, the second in March 2020, the third in July 2021, and the fourth in August 2022.
- IMI has been very successful in increasing full immunisation coverage in India.
{GS2 – International Institutions – 2023/07/19} UN Refugee Convention of UNHRC
- Context (Reuters): UK’s Illegal Migration Bill has become an act.
- It will deter illegal migration to the country – primarily via small boats crossing the English Channel.
- It will prevent most people from claiming asylum in Britain without permission.
- It will deport asylum seekers to their country of origin or a so-called safe country like Rwanda.
- So far, the UK has paid (bribed) the Rwandan government £140m for the scheme.
- Previously, a plan to remove refugees to Rwanda was declared illegal by the U.K. Court of Appeal.
- The UN has criticised the bill for the violation of refugee rights.
1951 Refugee Convention of UNHRC and its 1967 Protocol
- It is related to the Principle of Non-Refoulement, which asserts that refugees should not be forced to return to a country where they face serious threats to their life or freedom.
- The 1951 convention was initially limited to Europe, but the 1967 protocol removed this limitation.
- India is not a signatory of the 1951 UN Convention or the 1967 Protocol.
- UNHCR stated that Non-Refoulement is considered part of customary international law and binding on all states whether they have signed the Refugee Convention or not.
Customary International Law
|
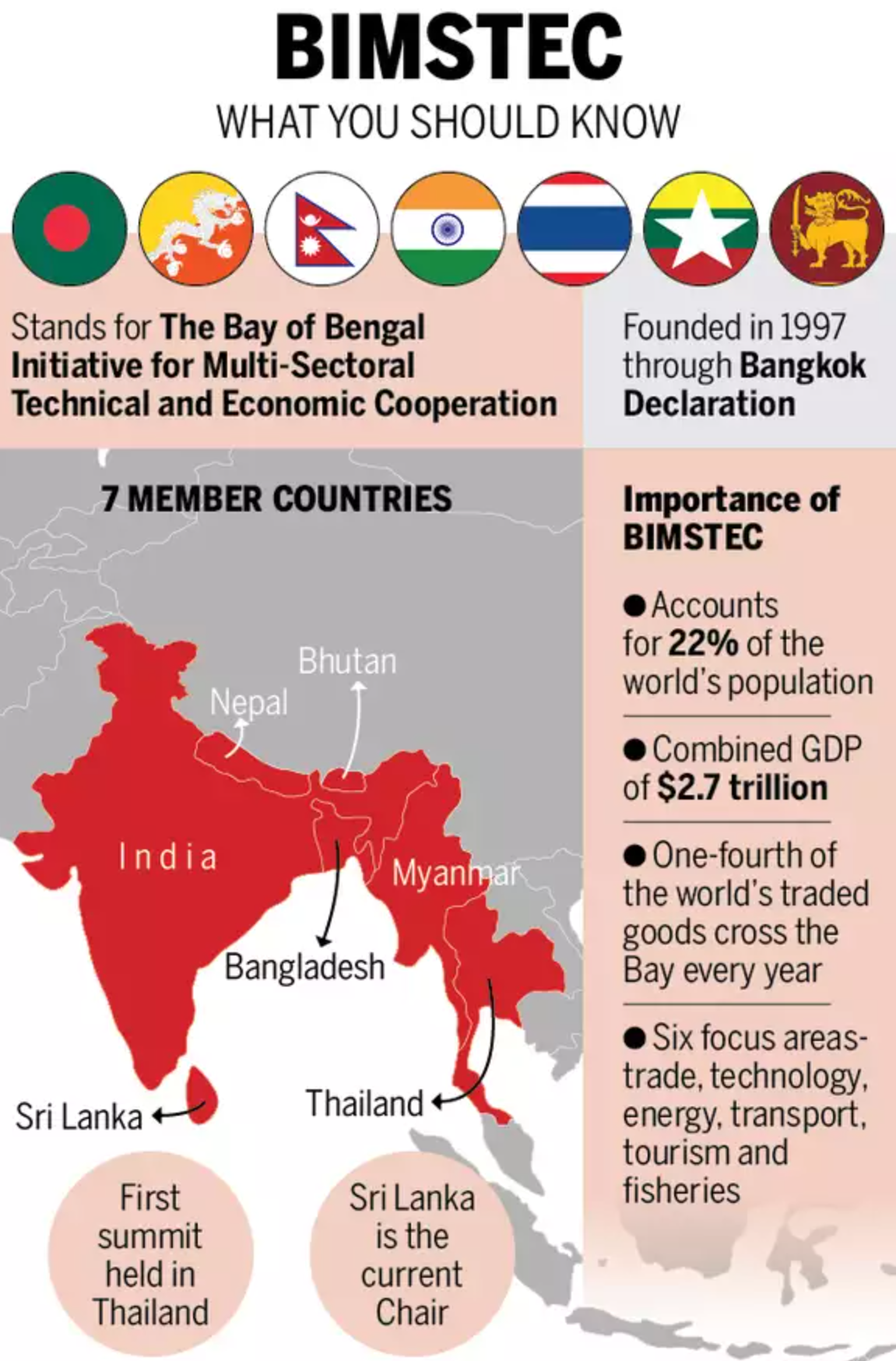
{GS2 – IR – Groupings – 2023/07/19} BIMSTEC
- Context (IE): The first-ever Foreign Ministers meeting of the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) began in Bangkok, Thailand.
- BIMSTEC is an international organisation of seven South Asian and Southeast Asian nations.
- BIMSTEC was formed in 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration.
- Fourteen priority sectors of cooperation have been identified, and several BIMSTEC centres have been established to focus on those sectors.
- Leadership is rotated in alphabetical order of country names.
- The permanent secretariat is in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
{GS2 – IR – India-UAE – 2023/07/19} MoUs
- Context (TH): Three pacts were signed during PM Modi’s visit to the UAE. These are related to:
- Use of local currencies (INR-AED) for cross-border transactions.
- Interlinking of payment and messaging systems.
- Establishing an IIT-Delhi campus in Abu Dhabi.
- The first two were memorandums of understanding (MoUs) signed between the RBI and its counterpart, the Central Bank of the UAE.
Use of local currencies (INR-AED) for cross-border transactions
- India and the UAE have signed a pact to establish a framework to promote using the rupee and UAE Dirham (AED) for cross-border transactions.
- It aims to implement a Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS), enabling exporters and importers to invoice and pay in their respective domestic currencies.
- It will cover all current and permitted capital account transactions.
Impact of the move
- It would help promote investments and remittances between the two countries.
- It would help optimise transaction costs and settlement time for transactions.
- India will likely use this mechanism to pay for crude oil and other imports from the UAE. Hence, it will reduce dependence on the dollar.
- It is part of a policy effort by India to internationalise the rupee.
India-UAE Bilateral Trade (FY23)
Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
|
Interlinking of payment and messaging systems
- Under the MoU on Payments and Messaging Systems, the two central banks agreed to cooperate on the following:
- Linking their Fast Payment Systems – UPI of India with Instant Payment Platform (IPP) of UAE.
- The UPI-IPP linkage would enable users in either country to make fast and cost-effective cross-border fund transfers.
- Linking the respective Card Switches (RuPay switch and UAESWITCH).
- It will facilitate the mutual acceptance of domestic cards and the processing of transactions.
- Exploring the linking of payments messaging systems, i.e., the Structured Financial Messaging System (SFMS) of India, with the messaging system in the UAE.
- Linking their Fast Payment Systems – UPI of India with Instant Payment Platform (IPP) of UAE.
Recent developments in India-UAE relations
|
{GS2 – Polity – RPA – 2023/07/19} Allocation of Airtime
- Context (TH): The ECI has made the process of allotting airtime to political parties for campaigning on Akashvani and Doordarshan entirely online.
- Till now, the political parties had to send their representatives to the commission’s offices to collect the time vouchers during elections. Now, the parties will be issued digital time vouchers.
Section 39A of RPA: Allocation of airtime to political parties
- The scheme for allotment of time on public broadcasters during campaigning got a statutory basis in 2003 under Section 39A of the RPA, 1951.
- It provides for the allocation of equitable sharing of time on the cable TV network/electronic media.
- The EC, based on the past performance of a recognised political party, allocates airtime time during the election.
In India, the electoral exercise mainly rests on the following pillars
Representation of the People Act (RPA), 1951
|
{GS3 – Land Reforms – 2023/07/19} Land Records: DILRMP
- Context (TH): President of India presented the Bhoomi Samman awards to several officials for their achievements in implementing the Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP).
- Bhoomi Samman Award acknowledges the efforts of individuals/ teams in implementing the DILRMP.
Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP)
- DILRMP was launched in 2008 to digitise and modernise land records systems. It involves:
- Computerisation of Land Records (CLR)
- Strengthening of Revenue Administration
- Updating of Land Records
- DILRMP is a central sector scheme implemented by the Department of Land Resources, Ministry of Rural Development.
Grade Categories for districts
- Platinum: 99% and above
- Gold: 95% and above till 99%
- Silver: 90% and above till 95%
- Others: Less than 90%
Components for Grading
- Computerization of Land Records
- Digitization of Maps
- Linkage of Record of Rights with maps
- Computerization of Registration
- Integration of Registration with Land Records
- Modern Record Room
Important components of DILRMP
Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar number
- Bhu-Aadhaar is a 14-digit alphanumeric ID based on geo-coordinates assigned to a land parcel.
- It is a pan-India number for obtaining ownership details of a plot along with its size and geolocation.
Records of Rights
- Records of Rights have been transliterated into all the 22 scheduled languages mentioned in the IC.
- It will address the problem of linguistic barriers in land governance in the country.
Importance of DILRMP
- It will help to resolve the long pending arbitration cases and boundary-related disputes amicably, thus reducing the burden on the judiciary and the administration.
- It will facilitate various services such as online information on crop profiles, crop insurance, and e-linkages to credit facilities/banks.
- It will Improve access to credit and other financial services
Svamitva Scheme (Survey of Villages Abadi and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas)
|
{Prelims – S&T – Tech – 2023/07/19} TCRM Matrix Framework
- Context (PIB): NITI Aayog unveils TCRM Matrix Framework.
- The Techno-Commercial Readiness and Market Maturity Matrix (TCRM Matrix) framework is a tool to help in enhancing the commercialisation of innovation and technology.
- TCRM Matrix framework presents an integrated assessment model that offers in-depth insights and actionable intelligence to stakeholders at every stage of the technology development cycle.
- It will provide analytics to policymakers, strategists, academicians, and investors to unlock their full potential and drive meaningful change.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)