Current Affairs July 18, 2023: Global Assessment Report on DRR 2023, Advance Trade Authorization Scheme, Local Currency Settlement
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Polity – Misc – 2023/07/18} Indian Red Cross Society (IRCS)
- Context (PIB): The President of India, Smt. Droupadi Murmu presided over the ceremonial session of the Annual General Meeting of the Indian Red Cross Society (IRCS) at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- Indian Red Cross Society is a voluntary humanitarian organisation.
- It is a member of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement.
- It provides relief during disasters/emergencies and cares for vulnerable people and communities.
Evolution
- IRCS was established in 1920 under the Indian Red Cross Society Act.
- The act was last amended in 1992, and rules were formed in 1994.
Structure
- The President of India is the President, and the Union Health Minister is the Chairman of the Society.
- The National Managing Body is responsible for the supervision of the functions of IRCS committees.
- It consists of 18 members. The President nominates the Chairman and six members. The state and UT branches elect the remaining 12 through an electoral college.
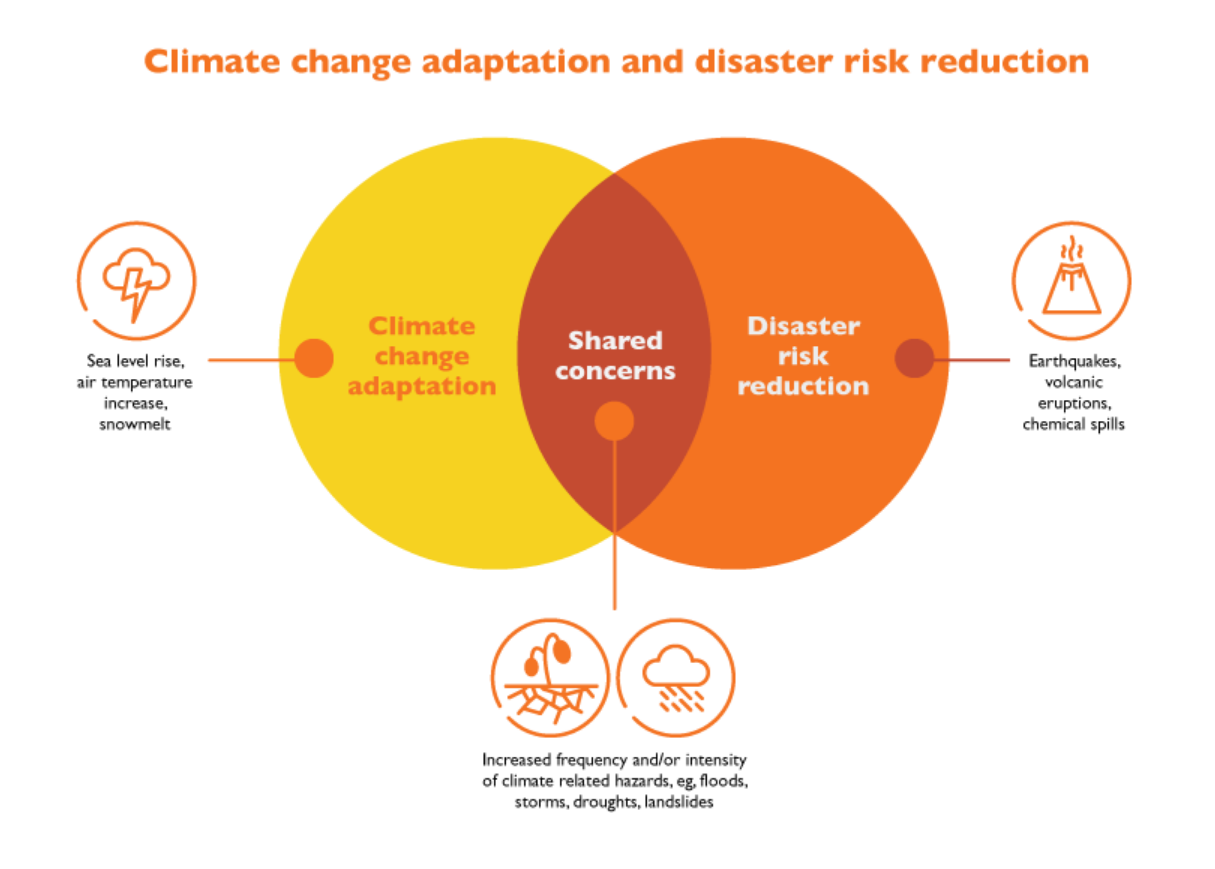
{GS3 – DM – Reports – 2023/07/18} Global Assessment Report on DRR 2023
- Context (UNDRR): United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction published Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2023 (GAR-DRR 2023).
- The theme was Mapping Resilience for the Sustainable Development Goals.
Key Findings
- Global warming will surpass 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels during the next decade.
- The number of people affected by disasters has increased by 50% in the past 30 years.
- The economic losses from disasters have increased by 150% in the past 30 years.
- The GAR-DRR 2023 explores how to build resilience in a complex and risky world.
- It highlights the interconnectedness of risks and how pitfalls can be transformed into opportunities.
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015-2030)
|
{GS3 – IE – Export – 2023/07/18} Advance Trade Authorisation Scheme
- Context (PIB): DGFT implements the Advance Authorisation Scheme under the Foreign Trade Policy.
- Advance Trade Authorisation Scheme provides duty-free import of raw materials for manufacturing export items.
- Manufacturers enjoy exemption from customs duty, education cess, social welfare cess, anti-dumping duty, countervailing duty and safeguard duty, Integrated GST and compensation cess.
List of imports covered under the scheme
- DGFT specifies the number of inputs allowed for any given product by issuing a sector-wise list of standard input-output norms.
- It spells out the required quantity of inputs for specific products while also considering any wastage during manufacturing.
Range of inputs covered
- It covers inputs that are physically incorporated into the final product.
- It also includes fuel, oil and other catalysts consumed or used to produce the export product.
- Biotechnological items are allowed if the Department of Biotechnology approves and issues a NOC.
Eligibility
- The scheme is open to
- Manufacturer exporters
- Merchant exporters
- Suppliers to the UN and other aid programmes, who act as subcontractors of the projects
- In the case of pharma imports, the authorisation will be extended only to manufacturer-exporters.
Value-addition Requirement
- The raw materials imported under the scheme can be exported after a value-addition of at least 15%.
- For tea, the value-addition requirement is 50%.
Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT)
|
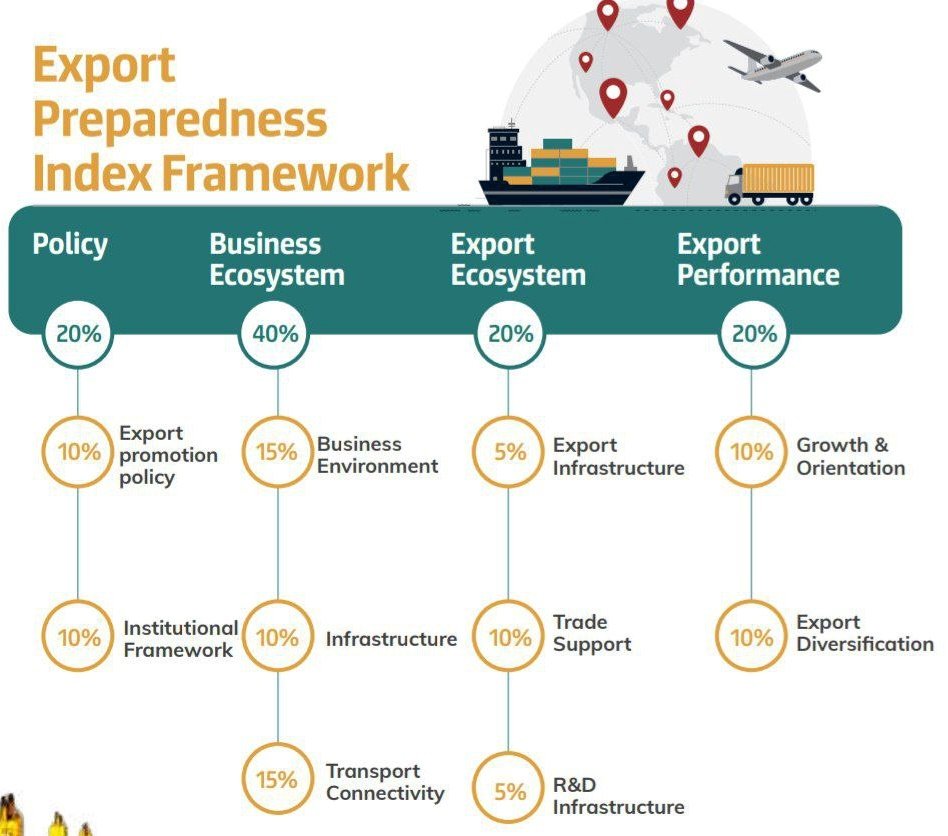
{GS3 – IE – Exports – 2023/07/18} Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2022
- Context (PIB): NITI Aayog has released the third edition of the ‘EPI’ for States/UTs of India.
- Export Preparedness Index (EPI) is an annual report released by NITI Aayog.
- EPI 2022 presents a comprehensive analysis of India’s export performance in FY22, along with its sector-specific and district-level merchandise export trends.
- The report evaluates the performance of the states across four pillars:
- These four pillars are further based on ten sub-pillars.
Highlights of the report
- The EPI 2022 Report observed that most ‘Coastal States’ have performed well.
- Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Gujarat are the top performers.
- Haryana is the best-performing state among the landlocked states.

- Gujarat’s Jamnagar and Surat are among the top-performing districts.

- Agriculture exports in FY2022 touched US$ 50 billion in value, an increase of 20% over 2020-21.
- Top five states in terms of overall exports are Gujarat, Maharashtra, TN, Karnataka, and UP.


Importance
- The EPI delves deeper beyond states and examines exports at the district level.
- It empowers the State governments with region-specific insights to assist decision-making.
- It can catalyse competitive federalism, elevating the export performance of every state.
{GS3 – IE – Reforms – 2023/07/18} Local Currency Settlement (LCS) System
- Context (IE): India and UAE signed an MoU on the Local Currency Settlement (LCS) system.
- This system will allow for the use of the Indian rupee and UAE dirham in bilateral trade, marking India’s first-ever LCS arrangement.
- Both sides agreed to link India’s UPI with UAE’s Instant Payment Platform (IPP).
- The LCS system is expected to bring a number of benefits to both India and the UAE, including:
- Reduced transaction costs
- Faster processing times
- Increased stability in the exchange rate
- Increased reliance on local currencies
Significance of the UAE to India:
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)