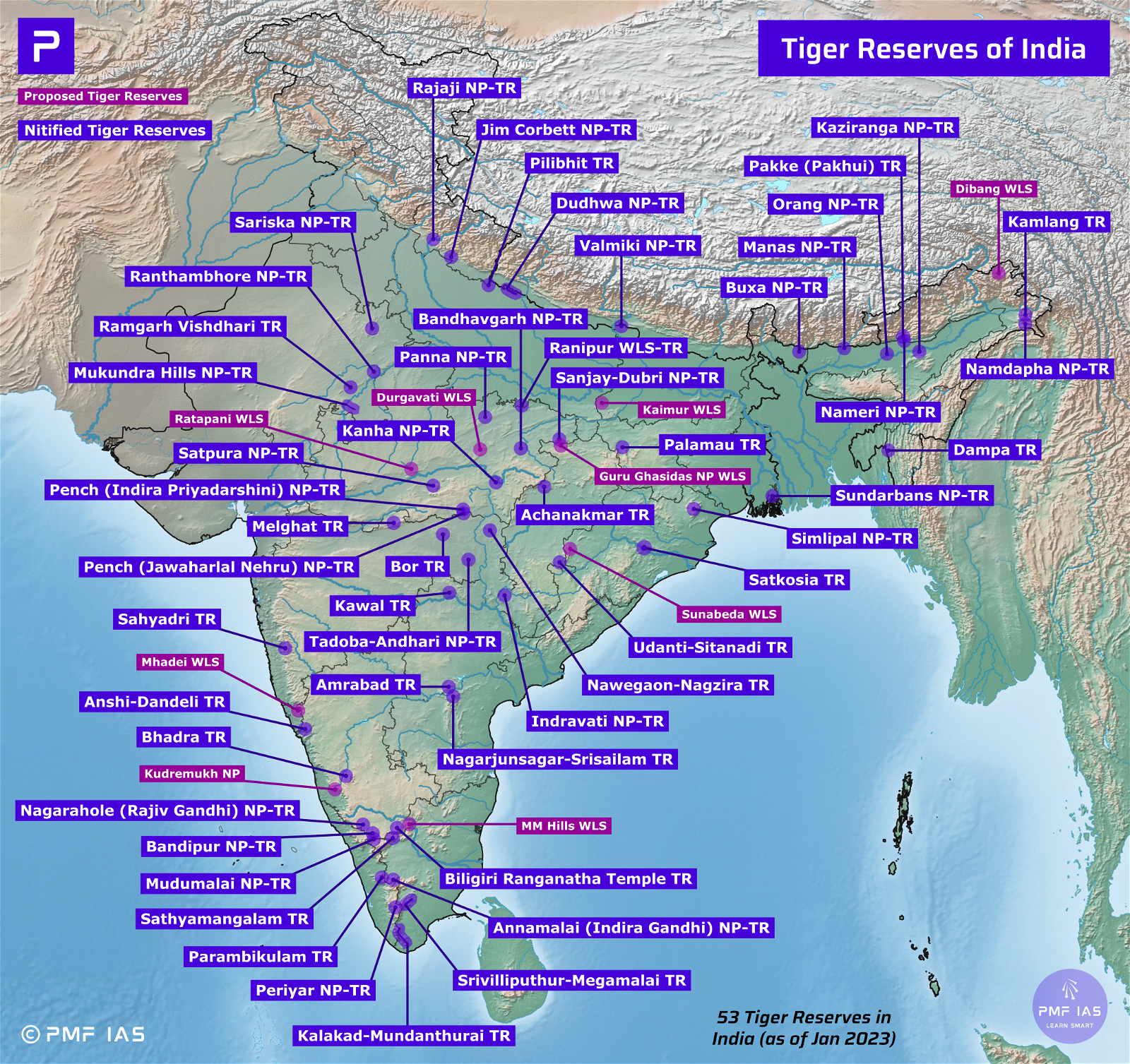
Current Affairs July 17, 2023: Right to Silence, Internationalization of UPI, PM MITRA, Global Minimum Tax, Exercise Nomadic Elephant
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – MoSPI – 2023/07/17} Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS)
- Context (TH): The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has replaced the Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES) with the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS).
- SCoS has ten official members and four non-official members who are eminent academics. It can have up to 16 members.
- SCoS will review the framework and results of all surveys conducted under the aegis of the National Statistical Office (NSO).
- It will advise the Ministry on technical aspects of all surveys, such as sampling frame, design, survey methodology, and finalisation of results.
Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES)
|
SCoS vis-à-vis SCES
- SCoS has a broader mandate than SCES. It will advise the government on technical aspects of all surveys against the SCES, whose mandate is restricted to economic data only.
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
|
{GS2 – Polity – IC – FR – 2023/07/17} Right to Silence
- Context (HT): All accused have the Right to silence and cannot be forced to speak up or admit guilt.
- The Right To Silence emanates from Article 20(3), which states that no one can be compelled to be a witness against himself. The provision gives an accused the right against self-incrimination.
- The protection of the right to silence is limited to criminal proceedings.
- It does not apply to other types of proceedings, such as those under the Customs Act or the Foreign Exchange Management Act.
- This is because these laws do not define the person being interrogated as an “accused” and therefore do not entitle them to a lawyer.
Provision for the Right To Silent
Can a law curtail Fundamental Rights?
|
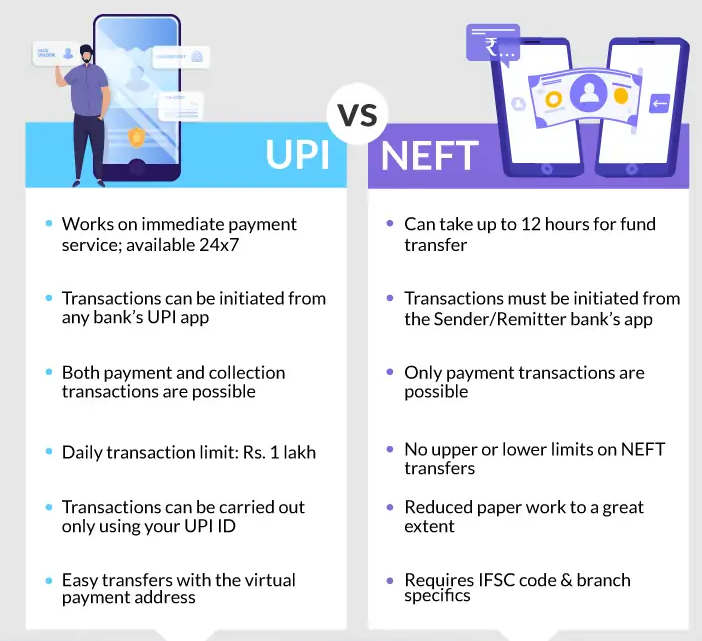
{GS3 – IE – Banking – 2023/07/17} Internationalisation of UPI
- Context (TOI): India and France have agreed to use the UPI mechanism, allowing Indian tourists to make rupee payments using UPI while in France.
- The international use of UPI has several benefits, including faster and cheaper remittance services, enhanced security, and the ability to bypass intermediaries.
- NPCI has taken steps to promote the international use of UPI, such as allowing NRIs in Singapore, Australia, Canada, Oman, Qatar etc., to use the platform from their international mobile numbers.
- RBI has announced extending UPI to allow visitors from G20 countries to use it to make merchant payments when they are in India.
UPI Limits
- At present, users can make up to 20 transactions or 1 lakh Rupees in a single day — either all at once or throughout the day.
- For certain specific categories of transactions, such as the capital markets, collections (such as bills, among others), insurance and forward inward remittances, the limit is ₹2 lakh.
- In December 2021, the limit for the UPI-based ASBA (Application Supported by Blocked Amount) IPO and retail direct schemes was increased to ₹5 lacks for each transaction.
National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI)
- NPCI is an umbrella organization for operating retail payment settlement systems in India.
- NPCI was established jointly by the RBI and the Indian Bank’s Association (IBA) under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act of 2007 to create a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India.
- NPCI is registered as a non-profit organisation under the Companies Act of 2013.
Functions of NPCI
- NPCI operates the RuPay card network, India’s domestic card network.
- NPCI operates the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), a real-time payments system that allows instant payments between bank accounts.
- NPCI acts as National Automated Clearing House (NACH), an offline web-based system for bulk push and pull transactions.
- NACH provides an electronic mandate platform to register mandates facilitating paperless collection processes for corporates and banks. It provides for both account-based and Aadhaar-based transactions.
- NPCI manages the National Financial Switch (NFS) — the largest network of shared Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) in India, facilitating interoperable cash withdrawal, card-to-card funds transfer and interoperable cash deposit transactions, among other value-added services in the country.
Major NPCI Products
- RuPay: RuPay is India’s first domestic Debit and Credit Card payment network, carrying out the RBI’s vision of a “less-cash” economy.
- RuPay card has been introduced in Bhutan, Maldives, UAE, Bahrain, and Saudi Arabia.
- Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM): BHIM is a mobile payment app that allows users to make quick transactions using Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS): It allows people to carry out financial transactions on a Micro-ATM using the Aadhaar authentication.
- Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS): BBPS is an interoperable platform that allows customers to pay water, telephone, gas, DTH and electricity bills at a single location — electronic or physical.

{GS3 – IE – Industry – 2023/07/17} Textile Industry: PM MITRA
- Context (PIB): In March 2023, GoI approved seven PM MITRA Parks for the Textile industry.
Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Regions and Apparel (PM MITRA) Parks
- PM Mitra aims to make India a global hub for textile manufacturing and exports.
- It will create a modern and integrated textile value chain at one location.
- It accommodates the complete value chain of the textiles and apparel industry.
- PM Mitra Parks will enable the Indian textile industry to achieve a larger size and scale and be globally competitive by creating world-class infrastructure and attracting significant investments.
- MITRA parks can be either Greenfield or Brownfield.
- Greenfield Sites: New independent sites will be developed under this category.
- Brownfield Sites: Sites with partly developed industrial trunk infrastructure and other intended facilities will be taken up for completing the development.

Eligibility and Selection
- MITRA Parks will be set up on sites selected from the proposals sent in by state governments.
- The minimum estimated area per MITRA Park is 1,000 acres.
- The selection depends on critical criteria, including connectivity, distances from the port/Dedicated Freight Corridor/industrial corridor/textiles cluster, reliable power supply and water availability and wastewater disposal system, effective single window clearance, etc.
Governance
- The Ministry of Textiles will oversee the execution of these projects.
- Each MITRA park will be led by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). The SPV will be a joint venture between the state and central governments, and it will be registered under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Central Government will pay for 49% equity of the paid-up capital of SPV, and participating State Government will pay for 51% of the paid-up capital.

Financial Support
- The GoI will provide financial support in the form of Development Capital Support (DCS) to the Park SPV to make the MITRA Parks commercially viable.
- The DCS will finance the development of Core Infrastructure comprising Incubation Centres, Plug and Play facilities, Developed Factory Sites, Roads, Power, Water and Waste Water system, etc.
- A Competitiveness Incentive Support (CIS) of up to Rs 300 crore per park to the units in MITRA Park on a first-come-first-serve basis shall be provided to incentivise speedy implementation.
|
{GS3 – IE – Reports – 2023/07/17} UNCTAD’s “A World of Debt” Report
- Context (UNCTAD): The UNCTAD report examines the global debt burden.
Key findings of the report
- Global public debt reached a record USD 92 trillion in 2022, up from USD 22 trillion in 2000.
- Debt has increased faster in developing countries than in developed countries over the past decade.
- Almost 30% of global public debt is owed by developing countries.
- Half of developing countries devote more than 1.5% of their GDP and 6.9% of their government revenues to interest payments than to education or health.
- Developing countries rely more on private creditors now, making credit more expensive and debt restructuring more complex.
- The report identifies several factors that have contributed to the rise in public debt in developing countries, including:
- COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to a sharp decline in economic growth and tax revenues.
- Cost-of-living crisis, which has pushed up government spending on social protection.
- Climate change, which has increased the cost of disaster relief and adaptation.
Reforms to address the global debt burden
- Reform of the international financial architecture to make it more inclusive and equitable.
- Greater investment in sustainable development to reduce the need for debt financing.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
|
{GS3 – IE – Taxes – 2023/07/17} Global Minimum Tax (GMT)
- Context (TH): India has proposed to raise the share of taxes MNCs pay to countries where they earn excess profits.
Need for Global Minimum Tax (GMT)
- Large MNCs are taxed where they declare their profits rather than where they do business.
- This allowed several MNCs to avoid paying high taxes in countries where they do most of their business by shifting their profits to low-tax jurisdictions (the unethical practice of profit shifting).
- So, an American company like Apple, for instance, can avoid paying high taxes in the United States by declaring its profits as belonging to a subsidiary company in Ireland, where tax rates are lower.
- Due to such practices and competition between governments to spur economic growth, the Global corporate tax rates have fallen from over 40% in the 1980s to under 25% in 2020.
Global Minimum Tax (GMT) Agreement
- It is framed by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
- It consists of two pillars.
First Pillar (25% tax on excess profit in addition to a minimum of 15%)
- Pillar 1 addresses the taxing rights, i.e., the basis for collecting taxes.
- It gives taxing rights to the counties where MNCs conduct a significant part of their business.
- It ensures that 25% of residual profits are allocated to the relevant foreign country to tax.
Second Pillar (Minimum 15% tax)
- It allows the governments to impose a minimum tax rate of 15% on MNCs.
- It authorises a government to impose top-up taxes on the company if it declares profits in another country and pays less than 15% taxes on those profits.
- So, if an American company pays only 5% taxes on profits that it declares as that of its subsidiary in Ireland, the U.S. government can now impose a 10% additional tax on these profits.
- In 2022, 136 countries and the EU agreed to implement a minimum 15% tax rate on MNCs.
Effect
- Supporters of the GMT agreement believe it will help stop the “race to the bottom” as countries compete against each other to cut taxes to attract businesses.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
|
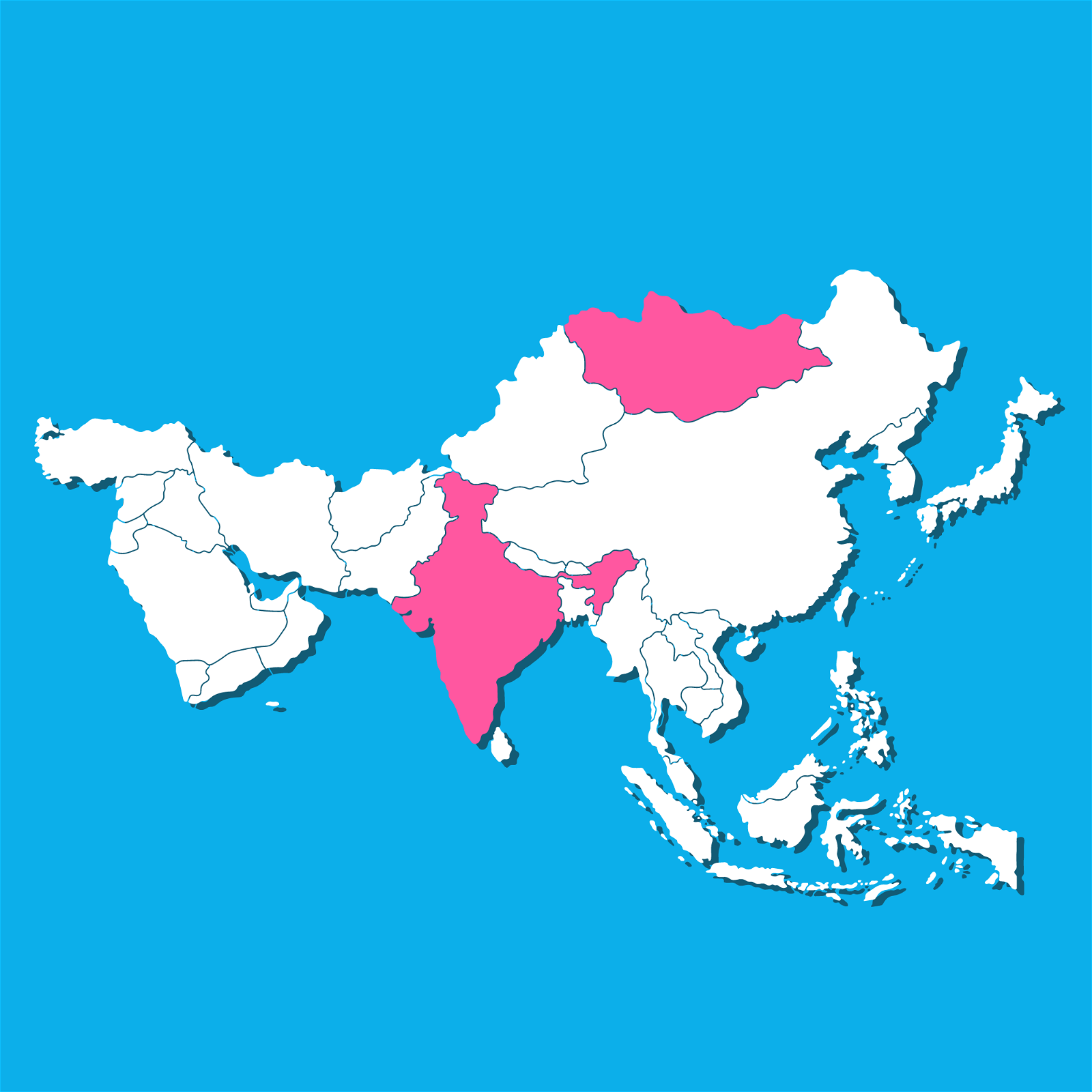
{Prelims – IR – India-Mongolia – 2023/07/17} Military Exercise Nomadic Elephant
- Context (PIB): 15th edition of Nomadic Elephant-23 is scheduled at Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia.
- Exercise Nomadic Elephant is an annual bilateral military exercise between India and Mongolia.
- It is conducted alternatively in Mongolia and India. The last edition was held at Bakloh, HP, in 2019.
- The exercise aims to build positive military relations between the two armies.
- It will focus on counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrain under the UN mandate.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)