Current Affairs December 30, 2023: India’s Horticulture Sector, X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat), Tripartite Agreement between GoI, ULFA & Assam Government, NVT vs OpenAI, OSIRIS-Rex to study Asteroid Apophis, Huntington’s Disease
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – MoA – Initiatives} Year End Review of AYUSH Ministry
- Context (PIB): Initiatives of the Ministry of Ayush for the year 2023 were discussed.
Initiatives of the Ministry of Ayush
Inclusion of Traditional Medicine in G-20 New Delhi Leaders Declaration
- Ministry of Ayush’s active participation in G20 lead to the mention of “Recognize the potential role of evidence-based Traditional and Complementary Medicine in health, and take note of international efforts in this direction, including WHO’s global and collaborating centres, and clinical trial registries.”
Dedicated vertical for Ayush at BIS
- The Bureau of Indian Standards has created a dedicated vertical for Ayush at BIS.
- A dedicated Working Group for standardization in the field of Ayurveda Informatics has been created to formulate International Standards on Ayush Informatics.
WHO-Global Summit on Traditional Medicine & Gujarat Declaration
- 1st ever Global Summit on Traditional Medicine (August 2023) was organized by the World Health Organisation, and co-hosted by the Ministry of Ayush, in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Gujarat Declaration emphasized that the importance of Traditional Medicine is recognized for the attainment of universal health coverage and WHO’s commitment to work toward it through evidence generation and policy support to member states.
Ayush Visa
- It introduces a special visa scheme for foreigners visiting India seeking treatment under the Indian system of Medicines like therapeutic care, wellness, yoga, etc.
- It boosts medical value travel and is intended to promote India as a medical value travel destination.
- Ministry of Ayush and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare are working together to develop a one-stop ‘Heal in India’ portal to promote India as a Medical Tourism destination of the world.
- Ministry of Ayush and India Tourism Development Corporation signed an MoU in January 2023 to work together for the promotion of Medical Value Travel in the Ayush sector.
SMART (Scope for Mainstreaming Ayurveda Research in Teaching Professionals) Program
- Launched by the National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM) and Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Objective: Regulating medical education and conducting scientific research, boost scientific research in priority healthcare research areas through Ayurveda colleges and hospitals.
Project Collaboration Agreement
- The Ministry of Ayush signed an agreement with WHO.
- Objective: To propel the formulation of a global strategy, focusing on elevating the standards, quality, safety, and effectiveness of traditional and complementary medicines over the next 5 years.
Chintan Shivir
- It provided a roadmap for Ayush’s future, focusing on digital health, strategy, challenges, and collaboration, reinforcing its commitment to growth.
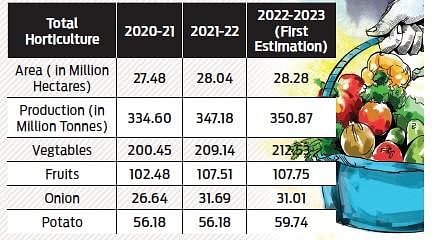
{GS3 – Agriculture – Horticulture} India’s Horticulture Sector
- Context (IE): Litchi Cultivation has expanded to 19 states.
Horticulture Sector in India: Status
- Horticulture includes crops such as fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, plantation crops (Cashewnut, Coconut, Cocoa etc.), floriculture, medicinal and aromatic plants, etc.
- It contributes 30.4% to Agriculture’s Gross Domestic Product, using 13% of gross cropped area, and supports 20% of the agri-labour force.
- Fruits and vegetables account for nearly 90% of total horticulture production in India.
- Global Position of India’s Horticulture Sector:
- Share in total world production: Fruits & Vegetables (12% each).
- Share in global exports: 1.7% in vegetables and 0.5% in fruits.
- 1st in production of Banana, Mango, Lime and Lemon, Ginger and Okra.
- 2nd largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world (after China)
- Largest Producer, Consumer, and Exporter of Spices.
Significance of Horticulture Sector
- Promotes Crop diversification.
- Filip to governments’ goal of doubling farmers’ income by creating employment opportunities.
- Backward and forward linkages to the food processing industry.
- Nutritional security, boosts immunity and maintains overall health.
- Export opportunities
Challenges of Horticulture Sector
- Poor marketing of horticulture crops.
- Huge post-harvest losses due to perishable nature of crops.
- High price fluctuations of produce.
- Stiff competition from the international market.
- Limited availability of market intelligence, especially exports.
GoI Initiatives for Horticulture Sector
Horticulture Cluster Development Programme (CDP)
- It is a central sector programme launched to enhance the global competitiveness of the Indian horticulture sector.
- National Horticulture Board (NHB) provides financial assistance and supervise its implementation.
- A government/ public sector entity shall be appointed as a Cluster Development Agency (CDA) for each identified cluster for the implementation of CDP.
Price Stabilization Fund for Perishable Horticulture Products
- To help regulate price volatility of important agri-horticultural commodities.
Operation Greens
- Launched during Budget 2018-19 to address price fluctuations in tomato, onion, and potato (TOP) and for benefit of farmers and consumers.
- It was later extended to all crops (from TOP to TOTAL).
HORTINET App
- Launched by APEDA (Agriculture and Processed Food Export Development Authority), providing online services such as farm registration, testing and certification, real time details of farmers, farm location, etc.
Horticulture Data Centre
- Set up by the Department of Agriculture to collect regular data on area, production and productivity of horticulture crops.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme for holistic growth of horticulture sector.
- Contribution: 60:40 (Centre: States), for North-Eastern and Himalayan states, Centre contributes 90%.
- Schemes under it:
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
- Horticulture Mission for North-East and Himalayas (HMNEH)
- National Horticulture Board (NHB)
- Coconut Development Board (CDB) – to focus on development of the coconut sector.
- Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH), Nagaland
National Horticulture Board (NHB)
- Set up in 1984, it is headquartered in Gurugram.
- It provides financial assistance for horticulture schemes such as cold storage, bio-pesticides, mushroom cultivation and coconut farming.
CHAMAN (Coordinated Programme on Horticulture Assessment and MANagement using Geometrics)
- It aims to develop a digital inventory of horticultural zones by mapping the area and output through Geo-Spatial studies and remote sensing technology.
{GS3 – Envi – Species} National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- Context (PIB): The Centrally Sponsored Scheme – Project Tiger, which has completed 50 years of successful implementation.
- NTCA administers Project Tiger.
Achievements of NTCA
India is now home to more than 70% of the world’s wild tigers
- India has around 3167 tigers and is now home to more than 70% of the world’s wild tiger population.
- The tiger reserves in India cover 78,000 square kilometres of land.
Launch of International Big Cats Alliance (IBCA)
- IBCA will focus on protecting and conserving seven primary big cats worldwide.
- The alliance aims to reach 97 range countries covering the natural habitat of 7 big cats.
- IBCA would further strengthen global cooperation and efforts to conserve the big cats.
- What are the ‘big seven cats’?
| S.No | Name of Big Cats | IUCN Status |
| 1 | Tiger | Endangered |
| 2 | Lion | Vulnerable |
| 3 | Jaguar | Near Threatened |
| 4 | Snow Leopard | Vulnerable |
| 5 | Leopard | Vulnerable |
| 6 | Cougar | Least Concern |
| 7 | Cheetah | Vulnerable |
Amrit Kaal Ka Vision For Tiger Conservation
- The vision plan aims to sustain tigers while preserving tangible and intangible gains from tiger reserves through landscape-level planning, sectoral integration and convergence.
Successful reintroduction of cheetah
- Cheetah is the only large carnivore that has been eradicated in India over historical times
- The first batch of cheetahs has been successfully translocated from Namibia to Kuno National Park.
- The translocation of cheetahs from South Africa to Kuno National Park has also occurred.
- More cheetahs will be imported soon for introduction in Gandhisagar Wildlife Sanctuary.
Management Effectiveness Evaluation (MEE) of Tiger Reserves
- NTCA has been undertaking “Management Effective Evaluation” (MEE) for four years.
- MEE has been adopted from the framework of the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN).
Reintroduction of tigers
- The initiative of reintroducing tigers has been undertaken to rebuild the wild tiger population in tiger reserves where tigers have recently become locally extinct.
- Tigers have been re-introduced in the Rajaji Tiger Reserve (Uttarakhand), Madhav National Park (Madhya Pradesh), Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve and Ramgarh Vishdhari (Rajasthan).
- Efforts are being made to reintroduce tigers to the Buxa Tiger Reserve soon.
Declaration of new Tiger Reserves
- A new tiger reserve, “Rani Durgavati” in Madhya Pradesh, has been declared.
- The county’s total number of tiger reserves has increased to 54.
Conservation Assured Tiger Standards (CA|TS) accreditation of Tiger Reserves in India
- CA|TS is a set of criteria that allows tiger sites to check if their management will lead to successful tiger conservation as per international standards.
- In the current year, six tiger reserves, namely Kali, Melghat, Navegaon – Nagzira, Pilibhit and Periyar, have been awarded CA|TS accreditation.
Bilateral co-operation with Tiger Range Countries
- To foster the transboundary conservation of tigers across India and Bangladesh in the Sundarban landscape.
- To promote tiger conservation in Cambodia, India and Cambodia have signed a MoU on “Cooperation in biodiversity conservation”.
International award to tiger reserves
- During 2022-23, Pench Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) and Pench Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) jointly and Satpura Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) have been awarded the Tx2 award.
|
For detailed Information > Tigers, Project Tiger, National Tiger Conservation Authority.
{GS3 – IS – Issues} Tripartite Agreement between GoI, ULFA & Assam Government
- Context (TH l PIB l IE): The pro-talks faction of the United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) signed a historic tripartite peace deal with the GOI and the state government of Assam.
- ULFA aimed to create an Independent and Socialist Assam through an arms struggle.
- ULFA claims that Assam was never a part of India as the Treaty of Yandabu was signed between two imperial powers (i.e. Burma and Britishers) without the involvement of the Assamese people.
Treaty of Yandabu
|
Tripartite Peace Agreement
Significance of the Deal
- The agreement between the pro-talks ULFA faction, the GOI, and the Assam state government marks a significant step towards peace.
Expert Opinions
- Experts view the deal as a positive development but acknowledge uncertainties regarding its completeness and effectiveness.
ULFA and Assam’s Struggle
Formation of ULFA
- The ULFA was established in 1979 by radical thinkers amidst growing concerns over the identity and resources of the indigenous Assamese population.
Cultural and Economic Shifts
- Assam’s tea, coal and oil economy attracted migrants from all over.
- The Partition and the subsequent exodus of refugees into the state from the erstwhile East Pakistan.
Assam Accord of 1985
- Aiming to resolve the issue of foreigners in Assam, the Accord responded to a prolonged mass movement but failed to address all concerns.
Four Decades of Violence and State Response
ULFA’s Armed Struggle
- The group sought a sovereign Assamese nation through armed conflict, resulting in kidnappings, extortion, and loss of life.
Operation Bajrang and AFSPA
- In response, the GOI launched Operation Bajrang in 1990, imposing President’s rule and the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) in Assam.
- The GOI banned the organisation 1990 under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, citing it as a terrorist organisation.
Internal Divisions and State Allegations
- ULFA faced internal divisions, with one faction (SULFA) surrendering and allegedly conducting state-backed ‘secret killings’ of other ULFA members.
ULFA’s External Support and Links
Camps in Neighboring Countries
- ULFA maintained camps in Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Bhutan, using them to train, shelter, and launch cross-border operations.
- The organisation established ties with the Nationalist Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN) in 1983.
Connections with Global Terror Groups
- The outfit established links with Islamic terror groups and Pakistan’s ISI, with its military chief reportedly meeting Osama Bin Laden.
- ULFA openly supported Pakistan during the Kargil War.
Efforts Towards Peace
Peace Talks
- In 2005, ULFA formed a ‘People’s Consultative Group’ for peace talks, but discussions broke down, leading to renewed violence.
- Post-2008, some ULFA commanders sought peace talks, leading to a significant organisational split.
Pro-Talks Faction’s Demands
- The pro-Talks faction submitted a 12-point charter of demands in 2012, leading to recent discussions and the historic tripartite peace agreement.
Operation All Clear
- In 2003, Operation All Clear was launched by the Royal Bhutanese Army, with the `logistical support’ of the Indian security forces.
- The objective was to clear southern Bhutan of camps of the ULFA, the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB), and the Kamatapur Liberation Organisation (KLO).
- Several senior ULFA, NDFB and the KLO leaders were captured and handed over to the Indian Army.
{GS3 – MoF – Initiatives} Initiatives by the Department of Revenue
- Context (PIB): A year-end recap of Department of Revenue (Ministry of Finance) initiatives was released.
Mera Bill Mera Adhikaar (MBMA) Scheme
- It has been launched as a pilot project in select States/ UTs.
- It will reward consumers for uploading B2C GST invoices to the MBMA application.
Indian Customs Electronic Commerce/Electronic Data Interchange (ICEGATE 2.0)
- ICEGATE 2.0 is a bilingual website that provides a contemporary user interface.
ICEDASH
- It is the Ease of Doing Business monitoring dashboard of the Indian Customs, helping the public witness the daily customs clearance times of export and import.
ICETRACK
- This App allows trade stakeholders to track the bill and shipping status, GSTN enquiry, etc., with QR code functionality.
{GS3 – S&T – AI} NVT vs OpenAI
- Context (IE): The New York Times (NYT) has filed a lawsuit against OpenAl and Microsoft, accusing them of unlawful use of copyrighted content for building their Al models.
- The lawsuit claims that responses manufactured by the Al models, especially ChatGPT, illegally leverage the NYT’s original journalistic content and substitute for The Times, thus stealing its audience depriving it of potential revenue.
- Generative Al platforms like ChatGPT and Google’s Bard have instigated debate on internet IP rights over original content, which these platforms use as a foundation for creating their responses.
- The case could shape the legal boundaries around intellectual property (IP) rights in the context of generative Al platforms which synthesize original content creators’ works through algorithms, producing new information.
- The definition of ‘author’ under the Indian Copyright Act of 1957 doesn’t consider that Al systems merely work on the base dataset prepared using copyrighted work from other authors. It’s suggested that such laws worldwide need reimagining considering Al applications.
A Brief History of OpenAI
- OpenAI was set up in 2015 as a non-profit AI research organisation to develop artificial general intelligence (AGI).
- Around 2017, OpenAI introduced the idea of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs).
- In 2019, OpenAI ‘transitioned’ into two organisations:
- OpenAI Global LLC: A ‘capped-profit’ organisation (with a maximum return on investment capped at 100 times the original amount).
- OpenAI Inc: The non-profit sole controlling shareholder in OpenAI Global LLC.
- OpenAI made headlines in 2022 after it released ChatGPT, based on the GPT-3.5 architecture.
- Currently, ChatGPT based on GPT-4 architecture is also available.
|
Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT)
|
|
For details on Language Models and Machine Learning > {GS3 – S&T – AI} Lack of Safety Guardrails in AI-Language Models
Laws Governing IPR in India
|
ACTS |
DEPT./ MINISTRY |
|
The Copyright Act, 1957 |
Registrar of Copyrights Dept for Promotion of Industry & Internal Trade (DPIIT) (Min. of Commerce) |
|
Indian Patents Act, 1970 |
Controller General of Patents, Designs & Trade Marks, DPIIT (Min. of Commerce) |
|
The Designs Act, 2000 |
|
|
Trade Marks Act, 1999 |
|
|
Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection Act) 1999 |
Geographical Indications Registry, DPIIT |
|
Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout-Design Act, 2000 |
Ministry of Information Technology |
|
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001 |
Ministry of Agriculture |
|
Biological diversity Act, 2002 |
National Biodiversity Authority, Ministry of Environment |
For detailed information on IPR >Intellectual Property Rights.
{GS3 – S&T – ISRO} X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat)
- It is a project of ISRO and the Raman Research Institute (RRI), Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- XPoSat mission, in its five years of life, will measure the orientation of vibration in the light wave.
- The mission will capture the degree and angle of polarisation.
Mission Payloads
- POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays), the primary payload, will measure the degree and angle of polarisation in the medium X-ray energy range originating from astronomical sources.
- The XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) payload will provide spectroscopic information.
{GS3 – S&T – Space} OSIRIS-REx to study Asteroid Apophis
- Context (LM): The former OSIRIS-REx spacecraft sets off on a (seven-year, 4 billion-mile journey) journey to study asteroid Apophis.
Asteroid Apophis
- Asteroid Apophis is better known as the ‘God of Chaos’.
- It is a near-Earth object (NEO) estimated to be about 1,100 feet (340 meters) across.
- Asteroid Apophis is made of silicate materials and nickel-iron (different from carbon-rich, “C-type” Bennu).
- It originated in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Why Study Apophis?
- Discovered in 2004, Apophis gained notoriety as one of the most hazardous asteroids that could impact Earth.
- Apophis is expected to “safely pass close to Earth on April 13, 2029, the closest approach to Earth by an asteroid of this size that scientists have known about in advance.
- Apophis’ close encounter with Earth is expected to change the asteroid’s orbit and the length of its 30.6-hour day.
- It was officially taken off from NASA’s Potentially Hazardous Asteroids list (PHAs).
|

Asteroids
- Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun like planets, but they are much smaller than planets and are irregular shaped (not all round like planets).
- Formed around 4.6 billion years ago, they are remnants of protoplanetary disk- the cloud of gas and dust from which the sun and planets formed.
- Size: Some are tiny, only a few metres across while others can be several kilometres wide.
- Types:
- C-type (Carbonaceous) Asteroids: They make up 75% of the known asteroids.
- S-type (Silicate or Stony) Asteroids: They account for 17% of known asteroids.
- M-type (Metallic) Asteroids: They are made up of nickel-iron and are found in the middle region of the asteroid belt.
- Asteroids are divided into three categories:
- Asteroids in the main asteroid belt, between Mars and Jupiter.
- Trojans (name comes from Greek mythology), which are asteroids that share an orbit with a larger planet.
- Near-Earth Asteroids (NEA): It has orbits that pass close to the Earth.
- Earth Crossers: Those that cross the Earth’s orbit. More than 10,000 such asteroids are known, of which over 1,400 are classified as potentially hazardous asteroids (PHAs).

|
OTHER ASTEROID MISSIONS |
||
|
Galileo mission (NASA) |
It was the first spacecraft to fly past asteroids Gaspara in 1991 and Ida in 1993. | |
|
Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) mission (NASA) |
It was the first spacecraft to successfully orbit Eros, an asteroid near Earth, and also land on the asteroid. | |
|
Mission Lucy (NASA) |
For exploring Jupiter Trojan asteroids. | |
|
Dawn Mission (NASA) |
It aims to study 2 out of 3 protoplanets in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter i.e. Vesta and Ceres (Pallas is 3rd).
|
|
|
Hera Mission (European Space Agency [ESA]) |
It is an asteroid deflection mission which is scheduled to be launched in 2024 to measure the impact crater produced by the DART collision and study the change in the asteroid’s orbital trajectory. It will arrive at the Didymos system in 2027. | |
|
AIDA mission (NASA & ESA) |
It is a technology demonstration of the kinetic impactor concept to deflect a small asteroid and to characterize its physical properties.
|
|
|
Hayabusa Mission (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency [JAXA]) |
By Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
|
|
{Prelims – Sci – Bio – Diseases} Huntington’s Disease
- Context (TH): A paper published by researchers from the University of Szeged has made strides in understanding Huntington’s Disease using fruit flies.
- It is a rare, progressive genetic disorder that causes progressive breakdown of brain’s nerve cells.
- It is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene which is involved in the production of a protein called huntingtin which provides instructions for making the protein.
- Mutated genes provide faulty instructions leading to the production of abnormal huntingtin proteins and the formation of clumps.
- These clumps disrupt the normal functioning of the brain cells, which eventually leads to the death of neurons in the brain, resulting in Huntington’s disease.
- The symptoms often appear when a person is in their 30s or 40s.
- It causes uncontrolled movements, impaired coordination of balance and movement, a decline in cognitive abilities, difficulty in concentrating and memory lapses, mood swings, and personality changes.
- Treatment: No cure exists, but drugs and physiotherapy can help manage some symptoms.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)