Current Affairs February 09, 2024: DigiReady Certification, Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project, Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana, Vote on Account vs Interim Budget, White Paper & Black Paper, Child Pornography, RBI’s action on Paytm Payment Bank
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – IR – India-Myanmar} Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project
- Context (TH): Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP) has “almost died” after the rebel Arakan Army (AA) captured the Paletwa township near the Mizoram border in January.
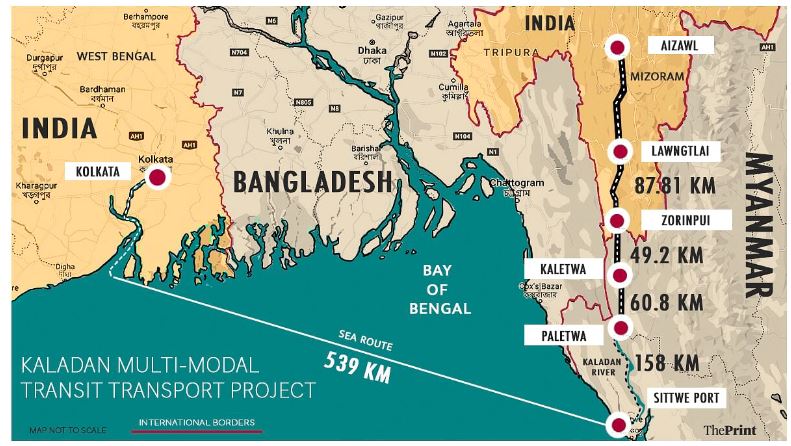
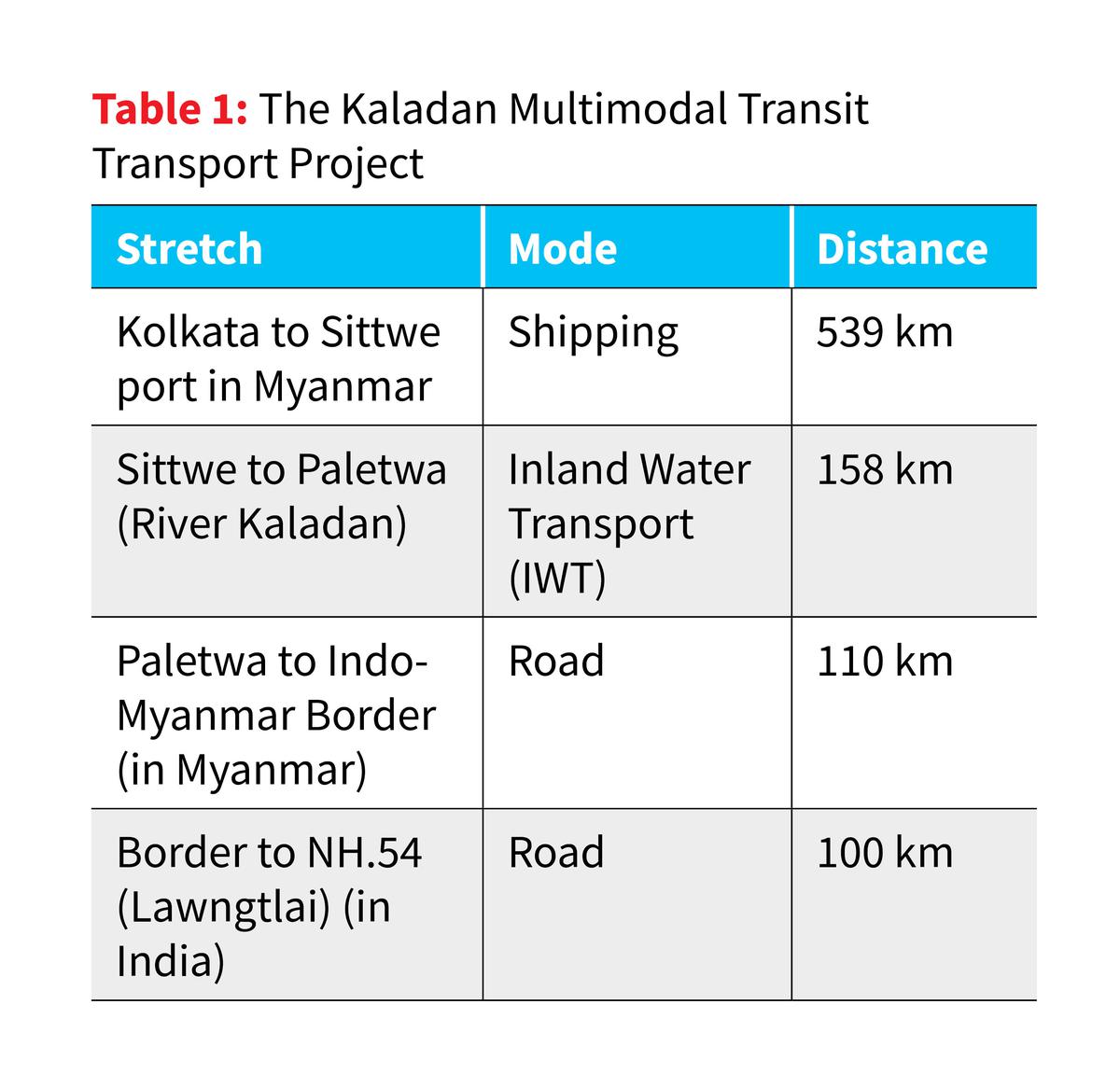
- The Kaladan Multi Modal Transit project was conceived in 2008 jointly by the Governments of India and Myanmar.
- It is aimed at connecting the port of Kolkata with the port of Sittwe in Rakhine or Arakan State which would then be connected to Mizoram by road and the Kaladan river which flows by Paletwa.
- The project will be entirely funded by India and the Inland Waterways Authority of India has been appointed as project development consultant.
- Components: Involves sea, river, and road transportation:
- Sea Route: From Kolkata to Sittwe (539 km).
- River Route: Sittwe to Paletwa via the Kaladan River (158 km).
- Road Component: Paletwa to Indo-Myanmar border (110 km), and further into Mizoram.
Significance
- The project offers India’s northeastern states access to the sea and an opportunity to develop greater economic linkages with Southeast Asia.
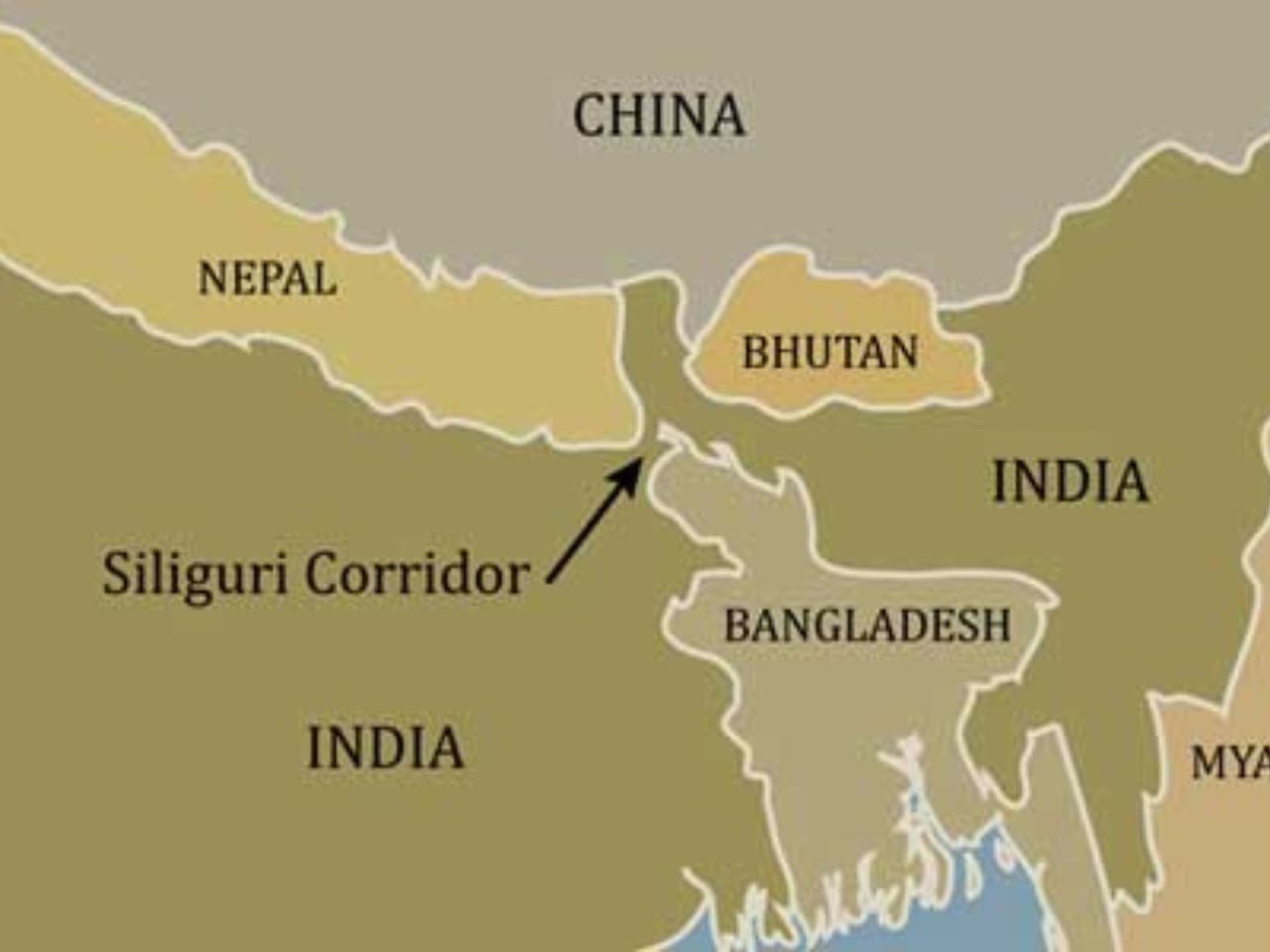
- It will reduce the traffic-load over the only connecting link by land through the narrow Siliguri corridor and substantially reduce the distance between Kolkata and the Northeast.
|
- The Sittwe port offers quicker access to the largest Myanmarese market – the most densely populated regions of Irrawaddy basin and Yangon.
- It enables traders and businessmen from Northeast India to explore markets in Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore and vice-versa.
- With the operationalization of the Sittwe port, food-starved Mizoram will get sufficient quantities of rice from Myanmar and this would further enhance border trade between the two countries.
{GS2 – MoFAH – Schemes} Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana
- Context (PIB): PM has approved the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- PM-MKSSY will be implemented as a Central Sector Sub-scheme under the Central Sector Component of the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Funding: 50% of funding from public finance, including the World Bank and Agence Française de Development (AFD). Remaining 50% is expected from beneficiaries/private sector.
- Components:
- Formalization of fisheries sector.
- Adoption of aquaculture insurance.
- Support for microenterprises.
- Adoption and expansion of safety and quality assurance systems.
- Beneficiaries: Include fishers, aquaculture farmers, workers, vendors, and related enterprises. Micro and small enterprises, FPOs, and startups in fisheries and aquaculture are eligible.
- Duration: It will be implemented for 4 years from FY 2023-24 to FY 2026-27 across all the States and UTs.
- Objective: To formalise the fisheries sector and support micro and small fisheries enterprises with an investment of over Rs. 6,000 crores over the next four years.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Parliament} Vote on Account vs Interim Budget
- Context (DH | TH): On February 8, Diya Kumari, the Deputy Chief Minister and Finance Minister of Rajasthan, presented the Vote on Account in the Assembly.
- During an election year, the incumbent government cannot present a full Union Budget. Hence, an interim budget is announced.
- Both terms interim budget & vote on account are interchangeably used, but they are different.
- Under Article 116 of the Constitution, a vote on account is presented to meet essential government expenditure for a limited period until the Budget is approved.
- It is granted for a few months for an amount equivalent to one-sixth of the total estimates.
Interim Budget vs Vote on Account
| Feature | Interim Budget | Vote-on-Account |
| Content | Contains both revenue and expenditure details | Includes only government’s expenditures |
| Validity Period | Valid throughout the year | Valid for a period of two to four months |
| Legislative Process | Discussed and passed in Lok Sabha | Passed without formal discussion |
| Tax Changes | Can propose changes in the tax regime | Cannot change the tax regime |
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Parliament} White Paper & Black Paper
- Context (IE | IE | TH): Recently, FM Nirmala Sitharaman presented a White Paper on the Indian economy in the Lok Sabha.
- It highlighted the “policy misadventures and scams” under the Congress-led UPA government’s 10-year tenure.
- In response to that, the Congress party has released a ‘Black Paper’. It highlighted the failures of the Modi government and alleged that the last 10 years have been a period of injustice.
What is White Paper?
- It provides comprehensive information, analysis, and proposals on a specific topic or issue.
- Stanford Law School says the public can access the document.
- It offers a detailed assessment of economic indicators, reforms, and their implications for various sectors.
- Governments, organisations, or experts often produce it to shape the policy.
- It serves as a crucial tool for informing policymakers, stakeholders, and the public about the government’s policies, initiatives, and their intended impact on the economy.
- There are no specific rules or guidelines regarding the issuance of White Papers in the Lok Sabha.
- The Opposition also has the right to demand a White Paper from the government on matters regarding which it is unclear.
- The state government can also present it in an assembly.
- Modi Govt. has presented 2 white papers in 10 years.
- On the revenue model for the railways in August 2014
- On the rationalisation of freight and fares. (Source: One India)
What is black paper?
- It presents a critical or dissenting viewpoint on a particular topic, issue, or policy.
- It uses analysis, evidence, and alternative proposals to address controversial subjects.
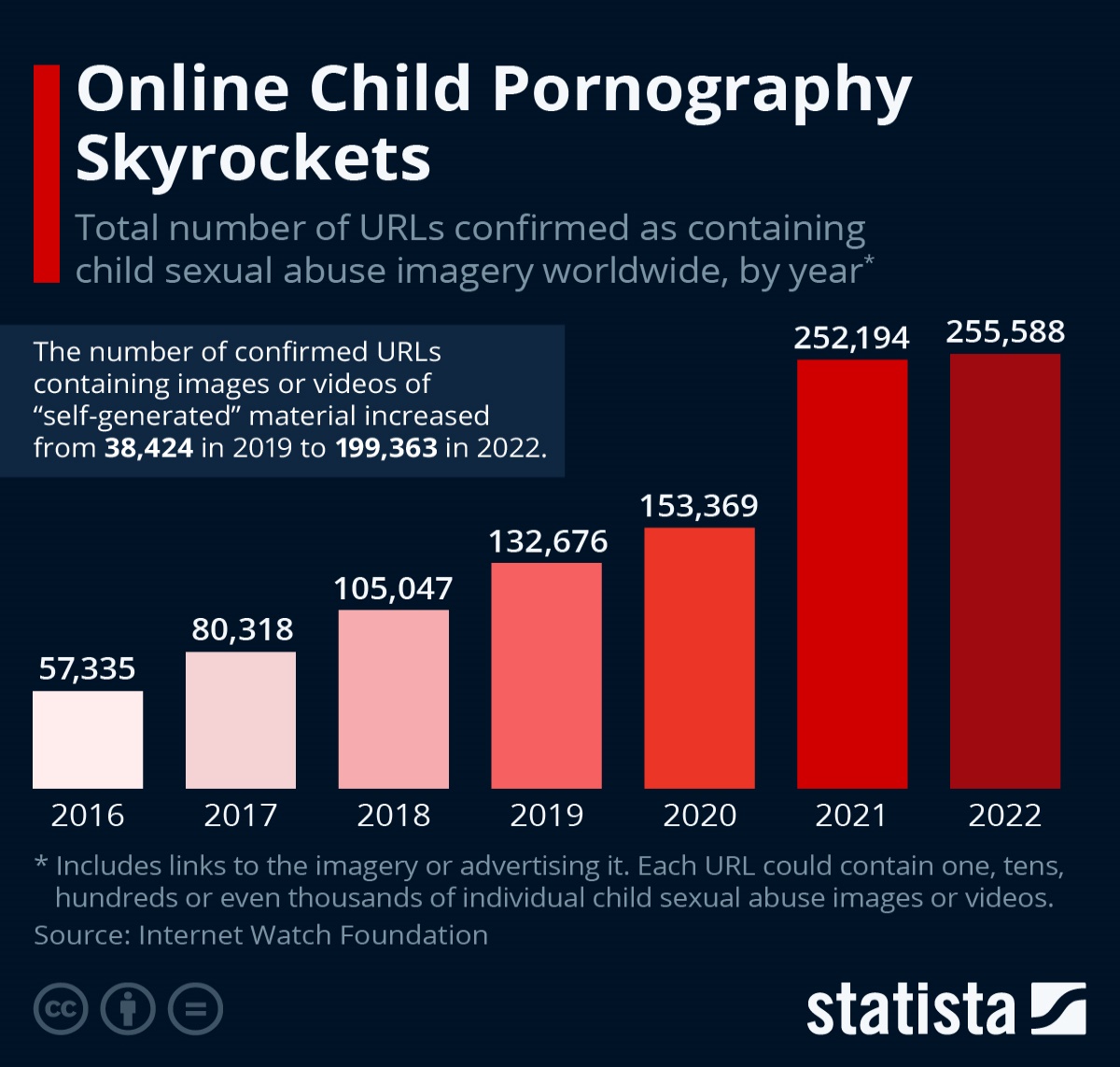
{GS2 – Vulnerable Sections – Children} Child Pornography
- Context (TH): Recently, the Madras High Court, in S. Harish vs Inspector of Police, held that downloading child pornography was not an offence under Section 67B of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000.
|
What is Child Pornography?
- Information Technology Act, of 2000 (IT Act) defines child pornography as any representation through electronic media (including computer-generated images and animations) of a child engaged in sexually explicit conduct.
Laws Governing Child Pornography in India
Information Technology (IT) Act
- The act makes it illegal to produce, create, publish, or possess child pornography in India, and penalties for violating this law include imprisonment and fines.
Protection of a Child From Sexual Offenses (POSCO) Act
- It addresses several forms of sexual abuse, including showing pornography to children, and also includes provisions for prosecuting sexual offenses against boys.
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015
- It includes provisions for rehabilitation as well as reintegration of child sexual abuse victims.
Indian Penal Code
- Section 292 of the IPC addresses the dissemination of obscene materials, including those involving children.
- Section 293 prohibits the sale, distribution, or exhibition of obscene objects, which also covers child pornography.
- Section 354A deals with sexual harassment and includes actions such as capturing or recording images of a person engaging in a private act without consent.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- It is a statutory body established under the Commission for Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.
- It works towards ensuring the rights and well-being of children, including protection from exploitation and abuse such as child pornography.
Cyber Crime Cells
- Cybercrime cells established by state police departments employ trained professionals who specialize in digital forensics and cybercrime investigation to identify and track individuals involved in the production, distribution, and consumption of child pornography.
Effects of Child Pornography
Immediate effects on child victims
- Physical injury and pain, including sexually transmitted diseases;
- Feelings of shame, unworthiness, anger, and confusion;
- Withdrawal and isolation;
- Anxiety, depression, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), including nightmares, flashbacks, etc.
Long-term effects on child victims
- Depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental illness;
- Feelings of worthlessness & low self-esteem;
- Distorted and unhealthy sexuality;
- Difficulty establishing healthy relationships;
- Risky behaviors, including substance abuse, promiscuity, self-mutilation, and suicidal attempts;
- Greater risk of getting ensnared in commercial sexual exploitation;
- Ongoing humiliation and lack of privacy;
Other negative effects
- Fuels the demand for child pornography.
- Desensitize children and normalize sexual activity in an effort by offenders to engage in sexual abuse or create new child pornography.
- Gateway to hands-on child sexual abuse, or may be used by sex offenders to reduce their inhibitions and prepare themselves to offend.
- Normalize and increase behaviors by minors such as sexting and other risky sexual behaviors.
- Contributes to the hyper-sexualization of children in American culture.
Landmark Judgements Related to Child Pornography
State of Tamil Nadu v. Suhas Katti (2016)
- SC emphasized that even mere possession of child pornography is a punishable offense.
- The court recognized the importance of protecting children from sexual exploitation and reiterated the need for strict action against offenders.
Shibu Soren v. Central Bureau of Investigation (2007)
- The Jharkhand High Court ruled that a person can be prosecuted for promoting or transmitting child pornography through electronic media.
- This case expanded the scope of child pornography offenses to include online dissemination and distribution.
Pardeep Kumar v. State of Himachal Pradesh (2014)
- The Himachal Pradesh High Court held that viewing or accessing child pornography is an offense under the POCSO Act, regardless of whether the person downloaded or possessed the content.
- This judgment clarified that mere consumption of child pornography is punishable under the law.
Challenges in Enforcing Child Pornography Laws in India
- Many people, including parents, caregivers, and even law enforcement personnel, lack awareness about child pornography & and its implications hampering timely reporting and proper handling.
- Overburdened courts and lengthy legal procedures can lead to delayed justice for child pornography victims, causing frustration and discouraging others from reporting similar incidents.
- The proliferation of encrypted platforms and dark web networks makes it harder for law enforcement to detect and track child pornography activities.
- Jurisdictional challenges arise when the offender and victim are located in different countries, requiring cooperation and coordination among law enforcement agencies from different jurisdiction.
- Lack of coordination between law enforcement, child protection agencies, and other stakeholders leads to inefficiencies in handling cases and providing support to victims.
Way Forward
- Using specialist cybercrime units, increase training and resources for law enforcement authorities to efficiently investigate and prosecute child pornography cases.
- Conduct extensive awareness efforts to inform the public, parents, and kids about the risks associated with child pornography & necessity of reporting such events right away.
- Establish dedicated fast-track courts to expedite child pornography cases, ensuring swift justice for victims and discouraging offenders through timely convictions.
{GS2 – Vulnerable Sections – Migrant workers} Schemes for Migrant Workers
- Minimum wages
- Section 13 of the Inter-State Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Service) Act, 1979 stipulates that the Inter-State migrant workmen shall in no case be paid less than the wages fixed under the Minimum Wages Act, 1948.
- Acts/Rules to address the human right violations of the inter-state migrant workers
- The Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Act, 1970,
- The Inter-State Migrant Workmen Act, 1979,
- The Building and Other Construction Workers Act, 1996,
- The Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008,
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948,
- The Bonded Labour System (Abolition) Act, 1976,
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act, 2013,
- The Prevention of Atrocities (Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribes) Act, 1989
- The Indian Penal Code, 1860.
- Covid measures
- Direct benefit transfers (Income support).
- Food relief packages.
- Control Rooms to resolve the grievances of workers including migrant workers during lockdown.
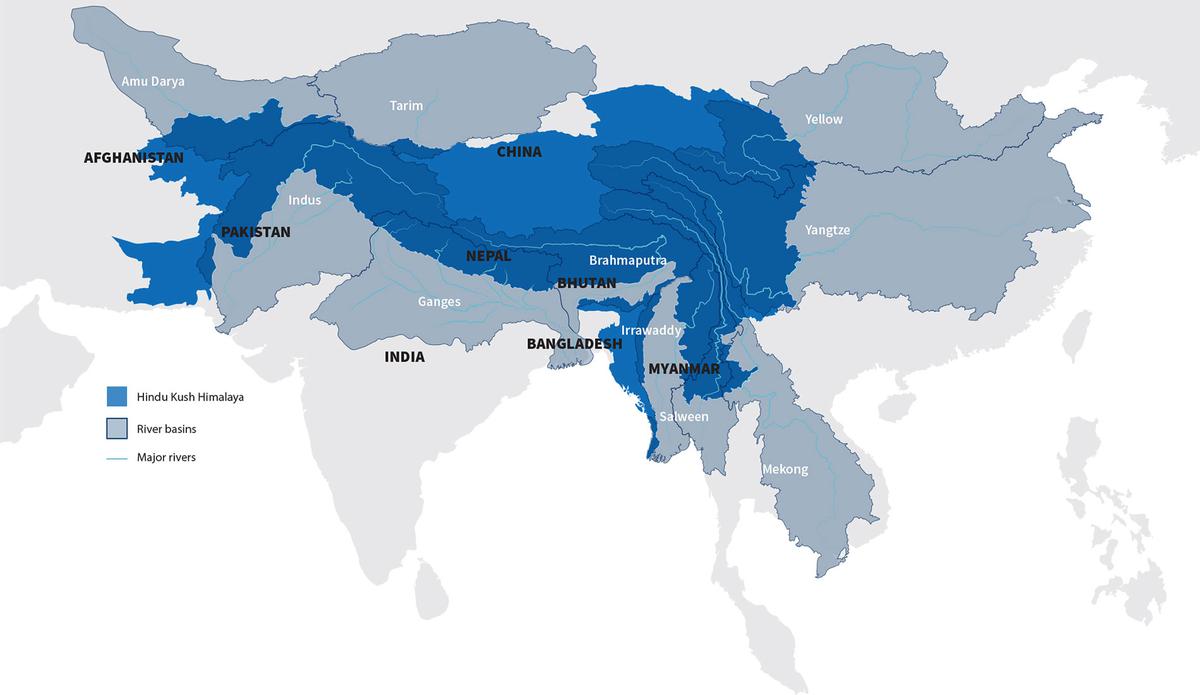
{GS3 – Envi – Conservation} Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region
- Context (IE): Scientists declare Hindu Kush Himalaya a biosphere on the brink of ‘collapse’.
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya region stretches 3,500 kilometres and spans eight countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- It is often referred to as the ‘Third Pole’, on Earth.
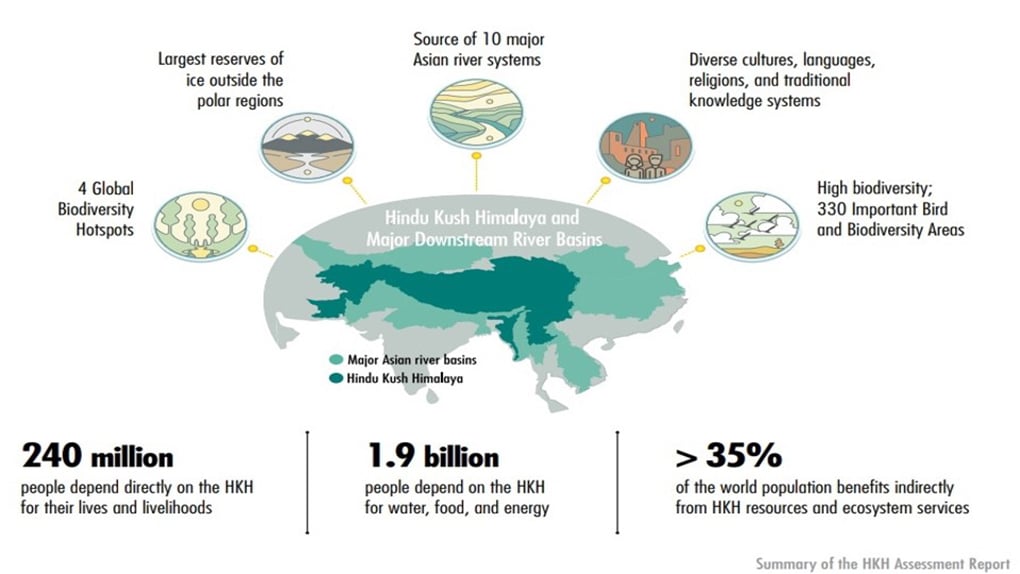
- The HKH is the world’s most important ‘water tower’, being the source of ten of Asia’s largest rivers as well as the largest volume of ice and snow outside the Arctic and Antarctica.
Significance
Threats to HKH
- HKHs are warming about three times faster than the global average.
- Glaciers lost ice 65% more quickly between 2010 and 2019 than they did between 2000 and 2009 and could lose up to 80% of their volume by 2100 if GHG emissions aren’t sharply reduced.
Impact of CC on HKH and associated hydrological consequences
- Increased drought-like situations due to an overall decrease in the number of rainy days.
- Increased flood events due to an overall increase in the rainy day intensity.
- Effect on groundwater quality in alluvial aquifers due to increased flood and drought events.
- Influence on groundwater recharge due to changes in precipitation and evaporation.
- Increased saline intrusion of coastal and island aquifers due to rising sea levels.
Steps Taken to Protect HKH Region
- International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): A regional intergovernmental organisation working to make the HKH region greener, more inclusive, and climate-resilient.
- Resilient Mountain Solutions (RMS): Initiative developed by ICIMOD to equip people in the region with simple and affordable technologies and knowledge required to build long-term resilience.
- Hindu Kush Himalayan Monitoring and Assessment Programme coordinated by ICIMOD.
- National Mission on Sustaining Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE): One of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
Way Forward
- Promote public–private–civil society partnerships: Incentives to be provided for green initiatives and other innovative financing ventures applying corporate social responsibility principles.
- Strengthen institutions: National and regional institutions to be strengthened to facilitate upstream-downstream knowledge exchange, transboundary cooperation, and capacity building.
- Evidence-based actions to reduce disaster risk, mitigate and adapt to climate change, and adopt good governance, are central to ensuring prosperity in the HKH region.
{GS3 – IE – Banking} RBI’s action on Paytm Payment Bank
- Context (TH): The RBI has taken corrective action against Paytm Payments Bank Ltd (PPBL).
- This comes after an audit report uncovered ongoing issues and non-compliance in the bank.
What has the RBI instructed?
- PPBL is prohibited from accepting more deposits, top-ups, or credit transactions in its wallets or accounts starting February 29.
- This restriction includes prepaid instruments for FASTags and National Common Mobility Cards.
- However, existing customers are allowed to use their current balances for services.
- PPBL was terminated from performing any banking services, bill payments, or UPI transactions.
- It was asked to terminate nodal accounts of its parent company.
|
Concerns
- RBI guidelines for payments banks prohibits them from engaging in lending activities. Though, PPBL doesn’t lend directly but offers credit-dispensing products from third parties, raising licensing concerns.
- Previous Penalties and Money Laundering Concerns
- RBI penalized PPBL ₹5.39 crore for violating KYC norms.
- Over 1,000 accounts linked with the same PAN raised concerns about money laundering.
Impact of RBI’s action
- May impact Paytm’s revenue and profitability in the medium to long term. (According to Macquire Capital).
- The severe restrictions hamper Paytm’s ability to retain customers and sell payment and loan products. (According to Researchers)
- Paytm’s parent company (One97 Communication) anticipates an annual EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation) impact of ₹300 to ₹500 crore.
Payment banks
|
{GS3 – IE – Employment} Steps Taken to Increase Employment
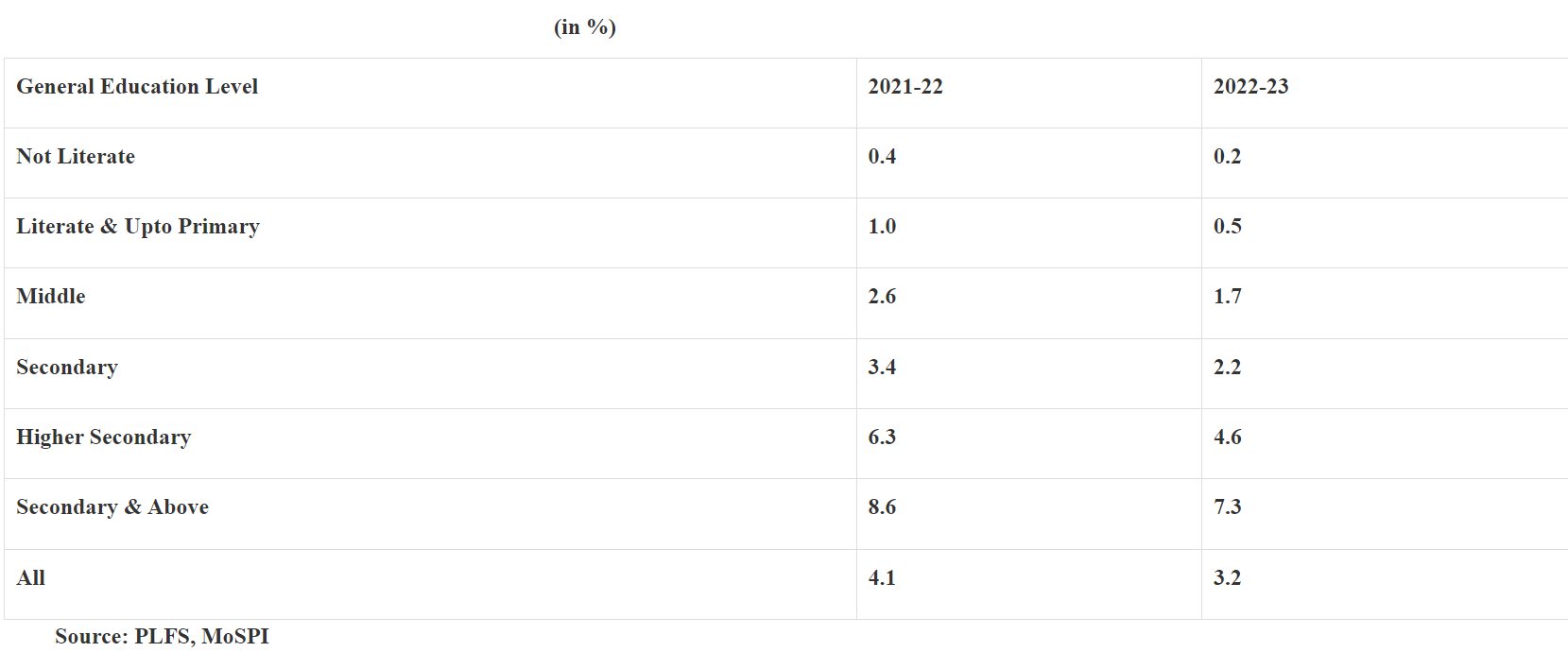
- Context (PIB): According to the Periodic labour force survey, 2022-23 data the unemployment rate is declining across different education levels.
- The estimated Unemployment Rate (UR) on usual status for persons of age 15 years and above of different general education level during 2021-22 and 2022-23 is as follows:
Steps taken to Increase Employment
- Skill India Mission (SIM): Under SIM, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) delivers skill, re-skill and up-skill training through various schemes viz.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- Jan Sikhshan Sansthan (JSS).
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS).
- Craftsman Training Scheme (CTS) through Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Skilling of rural youth for entrepreneurship development through Rural Self Employment and Training Institutes (RSETIs)
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: it aims to integrate vocational education programmes into mainstream education in all educational institutions in a phased manner.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): To facilitate self-employment. Under PMMY, collateral free loans upto Rs. 10 lakhs, are extended to micro/small business enterprises and to individuals.
- PM SVANidhi Scheme to facilitate collateral free working capital loan to street vendors to restart their businesses, which were adversely impacted during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- The Code on Wages, 2019 provides for universal minimum wage and floor wage across employments in organized and unorganized sector.
{GS3 – IE – MSME} DigiReady Certification Portal
- Context (PIB): Recently, the Quality Council of India and Open Network for Digital Commerce launch DigiReady Certification Portal to empower MSMEs and small retailers.
- It is an online platform that aims to evaluate and certify the digital readiness of MSMEs in India.
- The DRC portal contains 7 modules covering the major areas of digital integration that MSMEs need to evaluate before joining an online marketplace.
- By using this online self-assessment tool, small businesses can check how ready they are to join the ONDC platform as sellers. This helps them to enhance their digital skills and business opportunities.
- It is in line with the objectives of the recently launched FIRST (Forum for Internet Retailers, Sellers, and Traders).
FIRST (Forum for Internet Retailers, Sellers, and Traders)
|
{GS3 – IE – RBI} Monetary Policy Committee’s Decision
- Context (IE | TH): RBI’s monetary policy committee has decided to keep the repo rate unchanged at 6.5%.
- Other decisions
- Monetary policy stance withdrawal of accommodation.
- GDP growth for FY 2025 7%
- Headline inflation 5.4% for the current fiscal.
- Reason to keep repo rate and Policy stance unchanged
- Retail inflation continues to remain above the 4% target of the RBI.
- Incomplete transmission of RBI’s monetary policy.
- Impact
- External benchmark lending rates that are linked to the repo rate will not rise. This will provide some relief to borrowers as their equated monthly instalments (EMIs) will not increase.
RBI’s policy stances
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)