Current Affairs February 10, 2024: Fair Price Shops on ONDC, Kilkari Scheme, Save Bandipur | Golden IT Corridor, Private Sector Contribution to R&D, Logistics Performance Index 2023, Bharat Ratna for MS Swaminathan, Hypervelocity Expansion Tunnel Test Facility
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – MoCAFPD – Initiatives} Fair Price Shops on ONDC
- Context (PIB | TH): As a part of Digital India, Fair Price Shops of Una and Hamirpur districts of HP are the first to onboard Open Network Digital Commerce (ONDC).
Fair Price Shops (FPSs)
- A FPS is licensed under the Essential Commodities Act, 1955, to distribute essential commodities to ration card holders under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- The term is defined in the National Food Security Act, 2013 (NFSA 2013).
- State Governments must establish institutionalised licensing arrangements for FPSs according to provisions of the Public Distribution System (Control) Order, 2001, under the Essential Commodities Act, 1955.
- Every local authority or any authority designated by the State Government can conduct periodic social audits on FPSs, the TPDS, and other welfare schemes.
- They may publicise their findings and take prescribed actions.
- The State Government can fix an amount as the FPS owner’s margin.
- The State Governments may allow the sale of commodities other than the foodgrains distributed under the TPDS at the FPSs to improve their viability.
- Accounts of an FPS must be sent to the designated authority of the State Government with a copy to the local authority at the end of the month.
Open Network Digital Commerce (ONDC)
- ONDC is a first-of-its-kind initiative that aims to democratise digital commerce and reduce the dominance of online retail giants (like Amazon, Walmart-owned Flipkart, etc.).
- It is an initiative of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It is incorporated as a private, non-profit company.
- It aims to streamline transactions between buyers and sellers, irrespective of the platforms (intermediaries) they are affiliated with.
- Just like the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) enables smooth money transfers across diverse payment platforms, ONDC enables smooth transactions between buyers and sellers across platforms.
Objectives of ONDC
- Democratisation & decentralisation of e-commerce
- Inclusivity and access for sellers
- Increased choices and independence for consumers
- Making goods and services cheaper
Significance of FPSS Onboarding ONDC
- It will provide additional avenues of income generation for FPS dealers by providing:
- Visibility of FPS dealers in the digital marketplace
- Access to a larger customer base beyond NFSA beneficiaries
- Ability to compete on an equal footing with large retailers and e-commerce platforms
- It will also enhance beneficiary satisfaction.
{GS2 – MoCAFPD – Initiatives} Initiatives for Consumer Protection
- Context (PIB): Steps taken towards consumer protection and empowering consumers.
- Progressive legislation: The Consumer Protection Act of 1986 was repealed, and the Consumer Protection Act of 2019 was enacted.
- The aim is to modernise the framework in the new era of globalisation, technologies, e-commerce markets, etc.
- Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules, 2020 were notified under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 to safeguard consumers from unfair trade practices in e-commerce.
- edaakhil.nic.in an Online application portal has been developed to file consumer complaints.
- Guidelines for Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements, 2022 has been notified by the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA).
- Guidelines for Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns, 2023, has been issued by CCPA.
Dark patterns
|
- Framework on Online Consumer Reviews, Principles and Requirements for their Collection, Moderation and Publication has been notified by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) for safeguarding and protecting consumer interest from fake and deceptive reviews in e-commerce.
{GS2 – MoCI – Initiatives} Ease of Doing Business
- Context (PIB): Initiatives taken to improve Ease of Doing Business in India.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) is the nodal Department for coordinating the initiatives under Ease of Doing Business (EoDB).
- Reducing Compliance Burden on Businesses and Citizens by Simplifying, Rationalizing, Digitizing and Decriminalizing Government to Business and Citizen Interfaces.
- E.g. The Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Act, 2023, has effectively decriminalised 183 provisions in 42 Central Acts.
- Business Reform Action Plan (BRAP) for annual assessment of States/UTs based on implementation of designated reform parameters.
- Implementation of National Single Window System (NSWS), a one-stop Shop for investor-related approvals and services.
{GS2 – MoHFW – Schemes} Kilkari Scheme
- Context (PIB): The Kilkari Project expanded to include Maharashtra and Gujarat, now serving a total of 20 States and Union Territories in India.
Kilkari Scheme
- Kilkari (meaning ‘a baby’s gurgle’) is a centralised interactive voice response (IVR)-based mobile health service launched in 2016.
- Launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW)
- Objective: To provide essential health information to pregnant women and new mothers, encouraging healthier choices for newborn care.
- It delivers free, weekly, time-appropriate audio messages (related to pregnancy, maternal, neonatal, childbirth, and childcare) directly to beneficiaries’ mobile phones.
Mobile Academy
|
{GS2 – Social Sector – Health} Under-Prescription of ORS
- Context (TH): The misconceptions about Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) led to their reduced prescription for diarrhoea treatment.
Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)
- ORS is a medical formulation used to treat dehydration caused by diarrhoea, vomiting, and excessive sweating.
- It consists of a precise balance of water, electrolytes (salts), and sugar.
- The typical formulation, as recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), includes Sodium chloride (salt), Glucose (sugar), Potassium chloride, and Trisodium citrate.
How Does ORS Work?
- Electrolytes: These minerals, primarily sodium and potassium, aid in fluid absorption and maintain proper bodily functions.
- Sugar (Glucose): It helps the intestines absorb water and electrolytes more efficiently.
Uses of ORS
- To prevent or treat dehydration caused by diarrhoea, which can be life-threatening, especially in children and the elderly.
- To replace fluids lost through sweating during intense physical activity or heatstroke.
Reasons for under-prescription of ORS
- Provider Misconceptions: Healthcare providers may incorrectly believe that patients do not want ORS, perhaps due to its taste or the perception that it is not a “real” medicine.
- Financial Incentives: There is a financial motive to prescribe more profitable medications over ORS.
- Antibiotics and other treatments can be more expensive, potentially generating more profit for the provider or healthcare facility.
- Stock-outs: Instances where ORS is not available due to stock-outs lead to under-prescription.
Programs Promoting ORS Usage
National Health Mission (NHM)
- The government provides ORS packets and Zinc tablets free of cost at public health facilities.
- Promotes ORS along with Zinc supplementation for managing diarrhoea in children.
Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
- Promotes ORS for treating dehydration caused by diarrhoea.
Intensified diarrhoea Control Fortnight (IDCF)
- Focuses on reducing child deaths due to diarrhoea by promoting ORS and Zinc therapy.
{GS3 – Envi – Conservation} Save Bandipur | Golden IT Corridor
- Context (DTE): The plan for Nilambur-Nanjangud railway line through Bandipur National Park evokes protests over ecological impact.
- The Nilambur-Nanjangud railway line will connect Nilambur in Kerala to Nanjangudi in Karnataka, which is known as the Golden IT Corridor.
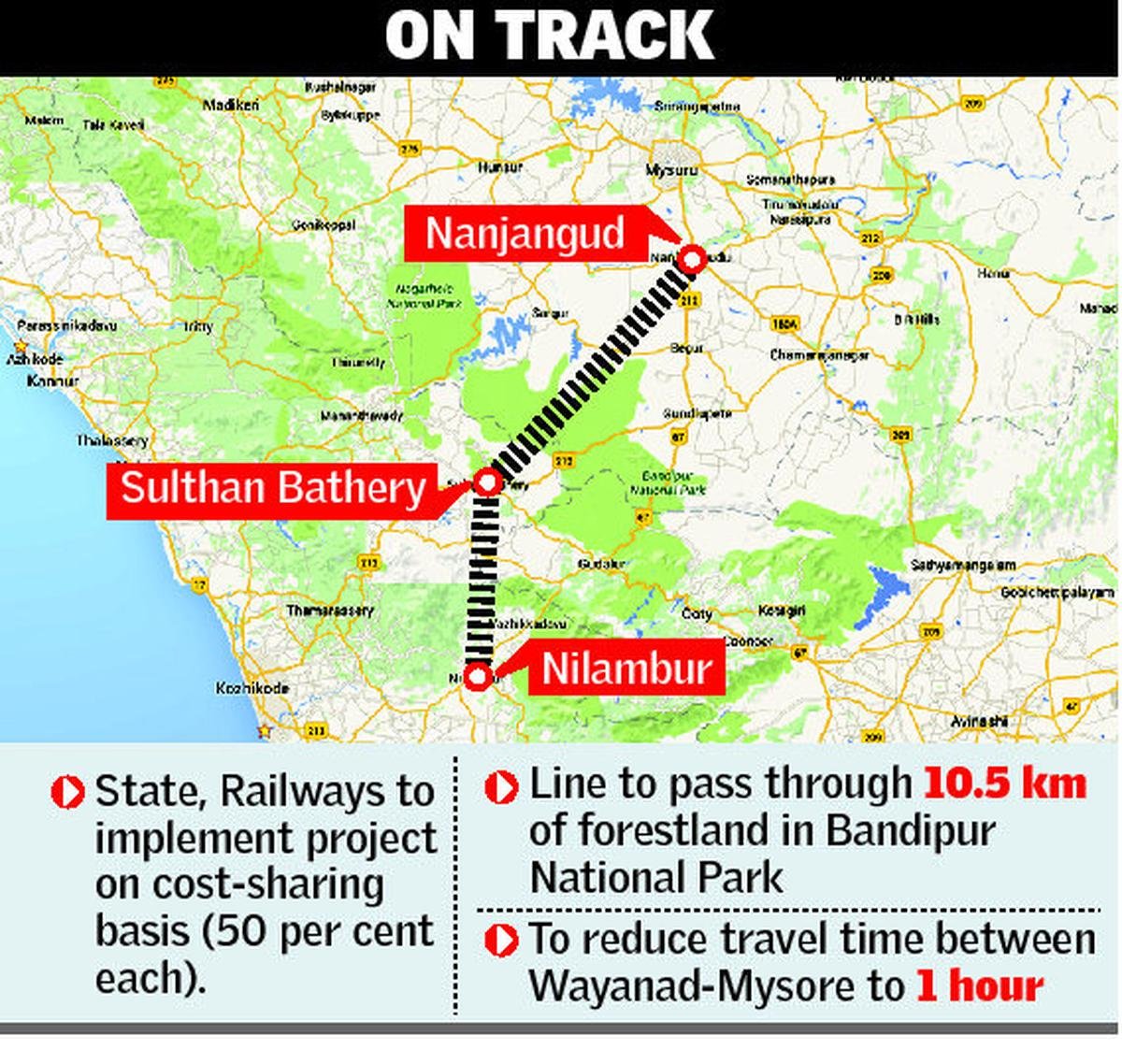
Significance of the Corridor
- Improve interstate connectivity while significantly reducing travel time and distance.
- Alleviate traffic congestion on National Highway-766, which connects Kozhikode in Kerala to Kollegal in Karnataka’s Chamarajanagar district.
Bandipur National Park
- It is situated at the intersection of the Deccan Plateau and the Western Ghats, on the Mysore-Ooty highway in Karnataka.
- Declared a tiger reserve in 1973 as a part of Project Tiger, Bandipur is an extension of the Venugopal Wildlife Park that was founded by the Maharajas of Mysore in 1931.
- It is an important part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve and one of the 12 UNESCO Biosphere Reserves in India.
- It is the largest national park in the state of Karnataka.
- It shares its borders with:
- Nagarhole National Park in Karnataka,
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu, and
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala.

- Fauna: It is one of the last refuges of the endangered Asiatic wild elephant. Other species found are Sloth bears, gaurs, Indian rock pythons, jackals, muggers, and four-horned antelopes.
- Flora: It is characterised by a mix of deciduous and evergreen forests.
{GS3 – IE – Industry} Initiatives for Textile Industry
- Context (PIB): A total Capital Investment subsidy of Rs. 1,416.50 crore has been released under the Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS) in the last three years.
Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS)
- It is a credit-linked Capital Investment Subsidy (CIS) scheme for technological upgradation and modernisation of the textile industry.
- Approved in 2016 and implemented through the web-based iTUFS platform.
- Capital outlay Rs. 17822 crores.
- Period 2016 to 2022.
- Significance
- Promotes ease of doing business.
- Promotes exports through Make in India with Zero Effect and Zero defects in manufacturing.
- Promotion of Technical Textiles, a sunrise sector.
- Background
- The Ministry of Textiles introduced the Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (TUFS) in 1999 as a credit-linked subsidy scheme.
- Since then, the scheme has been implemented in different versions.
Eligibility of ATUFS
- The following entities are eligible to get the credit-linked subsidy under this scheme:
- Handloom sector.
- Silk sector.
- Jute sector.
- Technical textiles.
- Madeup/garment manufacturing.
- Processing fibres, fabrics, made-up, garments and yarns.
- Weaving preparatory and knitting.
To know more about the textile industry, visit > Textile industry.
{GS3 – IE – R&D} Private Sector Contribution to R&D
- Context (TH): The Union Finance Minister announced in the interim Budget that a corpus of one lakh crore rupees would be established.
- This corpus aims to provide fifty-year interest-free loans for long-term financing or refinancing.
- The goal is to encourage the private sector to scale up research and innovation in sunrise domains. This announcement is worth examining for its potential impact.
Why this initiative is important?
R&D Expenditure is quite low in GDP terms
- Overall expenditure on R&D is on the rise in absolute terms (increasing from ₹1.1 lakh crore in 2009-10 to ₹1.27 lakh crore in 2020-21).
- As a fraction of GDP there has been a steady decline from 0.82% to around 0.64% during the same period.
Private sector contribution in India is low compared to other super powers
- In comparison to global science superpowers like Germany, South Korea, and the United States, India’s private sector contribution is notably lower, standing at 36.4%.
- In these superpowers, the private sector’s share of national gross expenditure on R&D (GERD) is significantly higher, ranging from 67% to 79%.

India’s GERD-to-GDP in Comparison to global is also quite low
- Advanced countries typically allocate at least 1% of their GDP to GERD.
- Even countries like Brazil (1.16%) and South Africa (0.83%) have a higher GERD-to-GDP ratio compared to India.
{GS3 – Infra – Transportation} Logistics Performance Index 2023
- Context (PIB): India has ranked 38th out of 139 countries in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index Report 2023.
- India’s rank has improved by six places from 44 in 2018 and sixteen places from 54 in 2014.
Logistics Performance Index (LPI)
- LPI is an interactive benchmarking tool developed by the World Bank to help countries identify trade logistics challenges and opportunities and improve performance.
- It considers six parameters to evaluate the logistics performance of the countries:
- Customs performance
- Infrastructure quality
- Ease of arranging shipments
- Logistics services quality
- Consignment tracking and tracing
- Timeliness of shipments
- The survey report is usually released every two years.
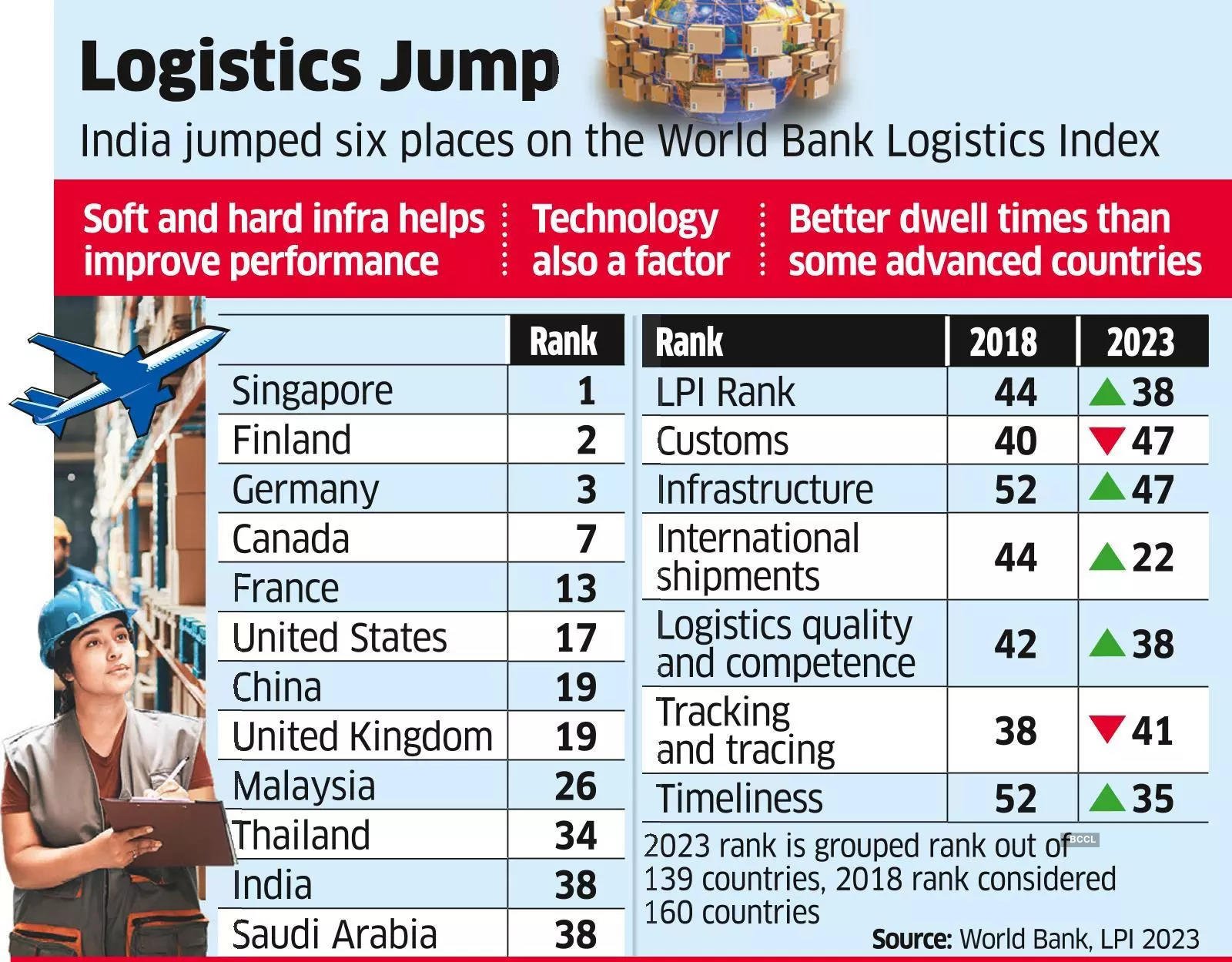
Reasons Behind India’s Improvement in LPI
PM Gati Shakti – National Master Plan for Multi-modal Connectivity
- PM Gati Shakti is a digital platform that brings 16 ministries together for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- It will incorporate the infrastructure schemes of various Ministries and State Governments like Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, dry/land ports, UDAN, etc.

National Logistics Policy (NLP)
- NLP aimed at easing the movement of goods and boosting the trade sector in the Indian economy.
- The new logistics policy has four features:
- Integration of Digital System (IDS): Under IDS, 30 different systems of seven departments are integrated including road transport, railways, customs, aviation. and commerce departments.
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): It will bring all the digital services related to the transportation sector into a single portal.
- Ease of Logistics (E-Logs): It is a new digital platform for industry associations to resolve issues by reaching out to the government.
- System Improvement Group (SIG)
Measures by Line Ministries
- Expansion of electrification of railway tracks by the Ministry of Railway (MoR).
- The Land Port Authority of India (LPAI) has reduced the average export and import release time through interventions.
- The Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) has launched National Logistics Portal Marine, which is a single window interface platform for port-related logistics operations.
|
{GS3 – S&T – Defence} FDI in Defence Industry
- Context (PIB): Steps taken to increase the FDI in the Defence sector.
- Liberalisation the Defence Industry was opened to private sector participation in May 2001.
- The FDI limit in the defence sector was increased in 2020.
- 74% through the Automatic Route for companies obtaining new defence industrial licenses.
- up to 100% through the Government Route when it facilitates access to modern technology.
- Co-development and co-production of specialised defence technologies with Foreign Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
- FDI received so far Rs 5,077 crore.
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Indigenous Climate Forecasting System
- Context (PIB): The IITM-ESM (Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology Earth System Model) has been indigenously developed at the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- The IITM-ESM is a state-of-the-art Earth System Model.
- It was developed under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It is India’s first ESM and has been used for climate change assessments, including the Sixth Assessment Report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
- It was also utilised in the latest Sixth Assessment Report prepared by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Earth System Model (ESM)
- It seeks to simulate all relevant aspects of the Earth system.
- ESMs incorporate physical, chemical, and biological processes.
- They simulate interactions among the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and biosphere.
- Unlike Global Climate Models (GCM), which focus solely on physical processes (such as winds, clouds, and ocean currents), ESMs account for the broader Earth system.
Components
- ESMs include the atmospheric and ocean components found in GCMs.
- Global carbon cycle: Tracking carbon movement between the atmosphere, oceans, and land.
- Dynamic vegetation: Representing changes in plant growth and land cover.
- Atmospheric chemistry: Modelling chemical reactions affecting air quality.
- Ocean biogeochemistry: Considering nutrient cycles and marine ecosystems.
- Continental ice sheets: Accounting for ice dynamics and sea-level changes.
- Human Influence and Feedbacks: ESMs can simulate how human activities (e.g., deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions) impact the Earth system.
- Feedback loops allow ESMs to represent complex interactions between physical, chemical, and biological components.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
|
{Prelims – Awards} Bharat Ratna for MS Swaminathan
- Context (PIB | IE | TH): The PM today announced that Dr MS Swaminathan, known for his pivotal role in the Green Revolution, will be conferred the highest civilian award, Bharat Ratna.
Significance of MS Swaminathan
- Called the Father of the Green Revolution in India.
- Helped India achieve self-reliance in agriculture during challenging times (1960’s-70’s).
- Efforts towards modernising Indian agriculture.
- Ensured the nation’s food security and prosperity.
- He recommended that the Minimum Support Price should be at least 50 per cent more than the weighted average cost of production.

Early life
- Born in Kumbakonam, Madras Presidency, on August 7, 1925.
- The experience of the Bengal famine in 1943 during the Second World War motivated him to commit his life to ensuring the food security of India.
- In 1944, he earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Agricultural Science from the University of Madras.
- Later, he moved to the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) in New Delhi to study genetics and plant breeding.
- In 1949, he obtained a post-graduate degree in cytogenetics.
- He returned to India in 1954 after completing the Doctor of Philosophy degree in 1952 & post-doctoral research associateship at various universities in abroad.
- He died on September 28, 2023, in Chennai at the age of 98.
His contribution towards Agricultural research
- The first attempt to develop high-yielding varieties: he started working on transferring genes for fertiliser response from Japonica varieties to Indica varieties.
|
- Developing semi-dwarf wheat varieties using mutagenesis: it involves exposing plants to chemicals or radiation to lower the plant height (it didn’t work). The lowering of plant heights led to a simultaneous reduction in the size of the grain-bearing panicles.
His relationship with other stalwarts helped him achieve the Wheat Revolution in India.
American scientist Orville Vogel
- He played a role in developing a dwarf wheat called Gaines, which had a high yield.
- It contained dwarfing genes from a dwarf wheat called the Norin-10.
- Swaminathan contacted him to get help for developing a ‘dwarf wheat’ in India.
- Since Vogel was unsure of the wheat’s potential in the Indian climate, he advised Swaminathan to approach Norman Borlaug.
- Norman Borlaug had incorporated the same dwarfing genes through Vogel’s lines into his spring wheat varieties in Mexico that were better suited for India.
Norman Borlaug
- Swaminathan along with Norman Borlaug toured India and worked seriously on dwarf wheat breeding programme in 1963.
- Within five years, there was what was called the Wheat Revolution. Between 1964 and 1968, annual production of wheat increased from about 10 million tonnes to about 17 million tonnes.
- The government declared India self-sufficient in food production in 1971.
- Indira Gandhi, the then PM, released a special stamp to mark the achievement.
Noteworthy job listings
- After 1971, he was appointed as the director-general of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and a secretary to the Government of India.
- He was made the first Asian director general of the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) in the Philippines in 1982.
- In 1984, he became the president and vice-president of the IUCN and World Wildlife Fund.
- He was the chair of the National Commission on Farmers constituted in 2004.
- He was nominated to the Rajya Sabha by former (late) President APJ Abdul Kalam, where he served from 2007 to 2013.
Awards, contributions, and achievements
- He was awarded the first World Food Prize in 1987, and the prize money was used to set up the MS Swaminathan Research Foundation.
- He established the Nuclear Research Laboratory at the IARI.
- He played a key role in setting up of the
- International Crop Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics in India.
- The International Board for Plant Genetic Resources (Bioversity International) in Italy.
- The International Council for Research in Agro-Forestry in Kenya.
- Swaminathan co-chaired the United Nations Millennium Project on hunger from 2002 to 2005.
- He was the head of the Pugwash Conferences on Science and World Affairs (2002 – 2007).
Recognitions
- 1961: Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award.
- 1965: Mendel Memorial Medal from the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences.
- 1971: Ramon Magsaysay Award.
- 1986: Albert Einstein World Science Award.
- 1987: The first World Food Prize.
- 1991: Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement.
- 2000: Four Freedoms Award.
- 2000: Planet and Humanity Medal of the International Geographical Union.
- 2024: Bharat Ratna.
- He was also awarded the Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Vibhushan awards & the Indira Gandhi Prize.
{Prelims – In News} Hypervelocity Expansion Tunnel Test Facility
- Context (PIB | HT): India’s first Hypervelocity Expansion Tunnel Test Facility was successfully established and tested by the Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur (IITK).
- Now, India is among the few countries with advanced hypersonic testing capability.
- It can generate flight speeds between 3-10 km/s, simulating the hypersonic condition.
- The facility called S2, nicknamed “Jigarthanda”, is a valuable test facility for ongoing missions of ISRO and DRDO, including Gaganyaan, Reusable Launch Vehicle, and hypersonic cruise missiles.
|
{Prelims – In News} Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad Scheme
- Context (TOI): All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) launches the ‘Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad’ scheme.
- Objective: To provide travel assistance registration fees to a team of a minimum 2 to 10 Bachelor students for attending competitions on scientific events at the international level to encourage engineering students to improve their field of technical education
- Eligibility: A team of Students in the field of technical education must be enrolled and undergoing a technical course notified by the council in an AICTE-approved technical institution.
- Nature and Extent of financial support eligible under the scheme: Maximum Rupees one lakh per student.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)