Current Affairs November 19-20, 2023: Chhath Puja, Halal Branding on Food Products, Stalling of CPEC Project, GI-tagged Onattukara Sesame, Digital Lending Market, Fake Loan Apps, Start-Up, Technical Textiles, Hard Currency, AI-Chemist
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – A&C – Culture} Chhath Puja
- Chhath Puja is a four-day Hindu festival honouring the Sun.
- Devotees observe a rigorous fast, abstaining from water, and make offerings to Usha (the rising Sun) and Pratyusha (the setting Sun) while standing in a water body.
- In this, Chhathi Maiyya (sister of the Sun) who is seen as a demanding, yet benevolent deity is worshipped.
- Chhath Puja begins on the sixth day of the Kartik month, generally in the month of October-November.
- Some people celebrate it in the month of Chaitra (in April), which is called the Chaiti Chhath.
- It is primarily celebrated in Bihar, eastern UP, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, MP, and some parts of Nepal bordering Bihar.
Four Days of Chhath Puja
- First day is Naha Kha
- Second day is Kharna.
- Third day is Sanjh ka Arghya.
- Fourth day is Bhor ka Arghya.
Social Significance of Chhath Puja
- It fosters a strong sense of community and social unity as people from any caste can observe the festival.
- No involvement of priests; devotees fast and pray directly to a visible, apparent God who shines equally on everyone.
{GS2 – Governance – Issues} Halal Branding on Food Products
- The state government cited the following reasons for the ban:
- Creates confusion regarding the quality of food items and is against basic intention of the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- Fosters social animosity.
- The “forged” halal certificates violates public trust.
What does the word ‘Halal’ Mean?
- Halal is an Arabic word that translates to ‘permissible’ in English.
- In the Quran, the term ‘halal’ is contrasted with the term ‘haram’ meaning ‘forbidden’.
- FAO defines Halal as one that is permitted under the Islamic Law.
- The term halal is mainly associated with Islamic dietary laws, referring to food procured, processed, and traded in compliance with Islamic belief.
- The two items of food that are most commonly considered haram (non-halal) are pork (pig meat) and intoxicants (alcohol).
|
When Does the Meat Qualifies as Halal?
- In the Indian context, halal is mainly used to refer to the slaughtering technique used by Muslims.
- This is in contrast to the ‘jhatka’ method, preferred by many Hindus and Sikhs.
Can Non-meat Products Also be Halal?
- Despite its widespread usage for meat products, halal does not have to do with meat.
- So vegetarian food would be considered permissible or ‘halal’ unless it contains alcohol.
Who Issues Halal Certificates in India?
- Halal certificates tell a consumer whether a product meets the requirements of Islamic dietary law.
- They do not indicate the presence of meat.
- India does not have an official regulator for the certification of halal products.
- Rather, there are multiple halal certifying agencies that grant halal certifications to companies, products, or food establishments.
- The GoI neither mandates halal certification nor does it provide a unifying regulatory law.
{GS2 – IR – China-Pakistan} Stalling of CPEC Project
- Context (TH):: The Union Minister for Commerce and Industry participated in the Investor Forum of Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII).
- The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a 3,000-kilometer-long network of infrastructure projects that aims to connect China’s Xinjiang region with Pakistan’s Gwadar Port in Balochistan.
- It is a bilateral project between China and Pakistan to enhance connectivity through:
- Highways
- Railways
- Pipelines
- Various infrastructure developments
- It is part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and was launched in 2015.
What are the reasons for stalling of CPEC Project
Funding Confusion
- The CPEC faced initial hurdles in 2016 due to confusion on funding, contractor selection, delay in the bidding process, differences over tax exemption, and obtaining no-objection certificates.
- Projects like the Gwadar Port and the Gwadar Smart Port City Master Plan ran into issues due to funding uncertainties.
Local Resistance in Balochistan
- Local communities have resisted selling land for the project, fearing loss of livelihoods and expressed discontent with the high profit reaped by Beijing.
- The Pakistani government’s land acquisition practices further aggravated the situation, leading to an insurgency in Balochistan and attacks on Pakistani Army officials protecting Chinese workers.
- Additionally, the leasing of the Gwadar port to the China Overseas Ports Holding Company fueled anti-China sentiments among Baloch residents.
Suspension of Funding Due to Corruption Concerns
- China halted funding for key road projects over suspicions of corruption. These included Dera Ismail Khan-Zhob Road, Khuzdar-Basima Road, and Karakoram Highway.
Insistence on Using Yuan as Legal Tender
- China’s insistence on using the Yuan as legal tender in the region and
Financial Challenges
- The high costs of construction and debt servicing fees (up to 7% by Sinosure) for CPEC projects financed by commercial Chinese loans have placed a significant economic burden on Pakistan.
- Pakistan’s inquiry into the operations of the China Overseas Ports Holding Company without valid security clearance led to the near stall of the port construction and refusal by China to further expand cooperation in areas like energy, water management, and climate change under CPEC.
For details on the topic > China Pakistan Economic Corridor.
{GS3 – Agri – Crop} Expansion of Cultivation of GI-tagged Onattukara Sesame
- Context (TH): Onattukara Vikasana Agency, the registered owner of the Geographical Indication (GI)-tagged Onattukara sesame, plans to increase the area under its cultivation.
Onattukara Sesame
- Onattukara sesame is a sesame seed native to the Onattukara region of Kerala.
- It is known for its high oil content, rich aroma, and nutty flavour.
- It is rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and anti-cancer properties.
- It is a good source of protein, fibre, and calcium.
Sesame
- Sesame seed is one of the oldest oilseed crops known.
- Its wild relatives are found in Africa and Asia.
Favourable Conditions for Growing Sesame
- Temperature: Between 25 and 35°C.
- Rainfall: It is relatively drought-tolerant but requires about 450 to 600 mm of rainfall.
- Soil: Sesame prefers well-drained, fertile soils with a pH between 6.0 and 7.5. It is not tolerant of acidic or saline soils.
Sesame Production
- India and Myanmar are among the largest producers of sesame.
Sesame Production in India
- Sesame is the oldest indigenous oil plant with a long history of cultivation.
- It is grown in all seasons, i.e., kharif, rabi, and zaid season. But 75% of the production comes from the kharif season.
- More than 85% of sesame production comes from WB, MP, Rajasthan, UP, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
For details on GI Tag > {Prelims – IPR – GI} Products from Uttarakhand Bags GI Tag
{GS3 – IE – Banking} Digital Lending Market
- Context (IE): Recently, it has been seen that fraud loan apps are jeopardizing the digital lending market.
Digital Lending
- Digital lending refers to providing loans through digital channels like websites, mobile apps, and online platforms.
- Banks, NBFCs, and fintech companies provide digital lending services.
Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC)
Fintech Companies
|
Benefits of Digital Lending
- Increased accessibility and convenience.
- Faster.
- Improved risk assessment through data analytics.
Concerns with Digital Landing
- Data privacy and security.
- Fraud and scams.
- Over-indebtedness: Borrowers can easily take on too much debt through digital lending, which may lead to bankruptcy.
- Predatory lending practices like charging high-interest rates or hiding fees.
- Poor regulation and consumer protection
Digital Lending vs Traditional Lending
| Feature | Digital Lending | Traditional Lending |
| Application process | Online and mobile apps | In-person at a bank branch |
| Approval process | Automated and streamlined | Manual and time-consuming |
| Interest rates | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | More flexible terms and options | Less flexible terms and options |
| Convenience | Accessible 24/7 from anywhere | Limited to bank hours and branch locations |
| Transparency | Borrowers have access to all loan information online | Borrowers may need to request information from the bank |
| Data privacy | Concerns about how borrower data is collected and used | Borrowers have more control over their data |
| Fraud risks | More susceptible to fraud | Less susceptible to fraud |
Digital Lending Market
- Globally, in the past 11 years, the digital lending market has surged, projected to reach $350 billion by 2023, with a nearly 40% compound annual growth rate.
- Of this, the illegal digital lending market can be at least $700-800 million.
- In 2023, digital lending in India is projected to reach $80 billion. Ten years ago, it was $5 billion.
How Fraud Loan Apps are Jeoparadising the Digital Lending Market?
- Digital lending apps are typically owned by banks and NBFCs or have partnerships with NBFCs.
- But many fraud digital apps have also emerged and are trapping consumers.
How do illegal loan apps trap people?
- They inundate social media platforms with advertisements, falsely advertising their relationship with prominent NBFCs, and trap users with promises of offering quick loans, even to those with low credit scores.
- Once a user downloads the app, it gets access to their personal information.
How Do Fake Loan Apps Survive?
- Inefficient regulation: In 2022, the RBI issued digital lending guidelines for regulated entities like banks and NBFCs, but it doesn’t address fraudulent apps without bank or NBFC associations.
- Deceiving appearance: Fake apps skillfully deceive Google and Apple by presenting themselves as loan calculators, aggregators, or even unrelated services like a food recipe recorder.
- Effective marketing: Dubious loan apps advertise on Instagram and Facebook; despite whatever filters they claim to use.
- Desperation of borrowers.
Way Ahead
Enhance Regulatory Oversight
- Formulating clear guidelines outlining permissible practices, interest rate caps, and data privacy standards for digital lending platforms.
- Mandatory licensing and regular audits of digital lending platforms.
- Know Your Digital Finance App (KYDFA): The Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) suggested that the RBI design detailed KYDFA norms for lending apps.
Other Measures
- Promoting awareness among the consumers.
- Provide easily accessible reporting mechanisms for consumers.
- Strengthen app store review processes.
{GS3 – IE – Industry} Start-Up
- Context (IE): According to the Chief Economic Advisor to the GoI, Startups will play an important role in helping India become 3rd largest economy.
Start-up
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) defines startups as:
- An entity, incorporated or registered in India,
- Not established prior to 10 years.
- Annual turnover not exceeding INR 100 crore in any preceding financial year, and
- Working towards innovation, development or improvement of products, processes or services or, if it has a scalable business model with a high potential of employment generation or wealth creation.
Challenges Faced by Start-ups
- Lack of diversification: >90% of startups concentrated in technology/ IT/App sectors that are capital intensive.
- Regional concentration: Mostly concentrated in Bengaluru, Mumbai, Delhi/NCR.
- ‘Out-migration of startups’: Startups like Flipkart, Grofers have moved their registered office from India in order to save on taxes and ensure access to capital.
- Other challenges: Infrastructure deficit, lack of skilled workforce and funding, etc.
- Red tape, corruption, and bureaucratic inefficiencies.
- Expenditure on R&D stagnated at 0.7% in the last 2 decades.
Achievements of Startups
- India now adds the largest number of start-ups globally (4 start-ups/hour).
- India as a Unicorn Hub: From 10 unicorns in 2016, India now is the 3rd largest Unicorn community in the world.
- Pan India Presence: There is at least 1 recognised Startup in each State and UT, with 45% of start-ups having bases in Tier 2 and 3 cities, working as the brand ambassadors of the local products.
- Employment booster: Generated >6 lakh jobs in sectors like IT, healthcare, education, and food and beverages.
- Inclusive growth: 45% of Startups recognized by DIPP have at least 1 woman director.
Way Forward
- Offering flexible business models by adapting to local regulations.
- Developed cutting-edge platforms to connect consumers and businesses to optimize logistics and delivery operations for reshaping the way goods and services are delivered in India.
- Introduce single window clearance, reduce bureaucratic red-tapism,
- Promote online registration, and fillings to automate processes.
- Strengthening incubation and acceleration programs by fostering collaboration between startups, research institutions, and academia.
{GS3 – IE – Industry} Technical Textiles
- Context (TH): India’s market for technical textiles is targeted to touch $40 billion by 2030 from the current $23 billion.
- Technical Textiles are manufactured for their technical performances and functional properties rather than aesthetic and decorative features.
- They are a niche segment of textiles.
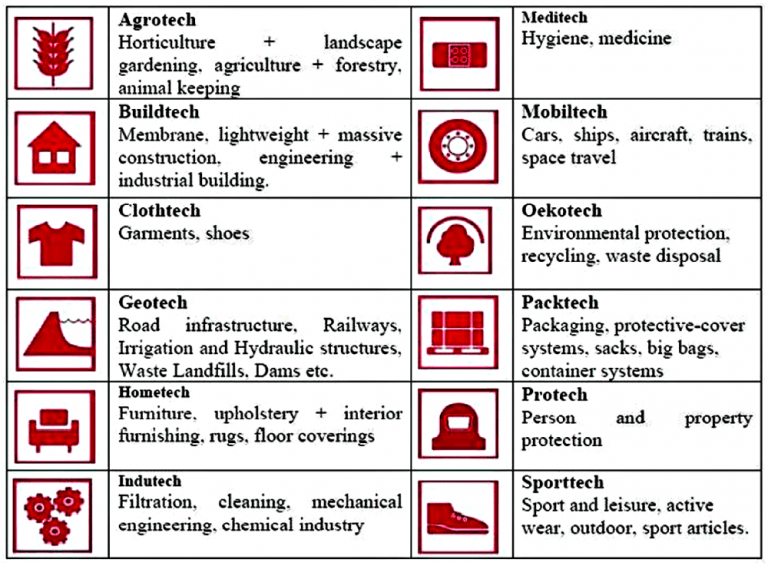
State of Technical Textiles in India
- India is the 6th largest producer of technical textiles with a global share of 6%.
- Contribution to GDP: 0.7%
- The sector grows at a Compounded Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8%, with future growth expected to accelerate to 15-20%.
Challenges of the Technical Textile Sector
- Low level of penetration- Around 5-10% against 30-70% in developed countries.
- Dependence on imports for products like diapers, polypropylene spun-bond fabric for disposables, wipes, protective clothing, hoses, webbings for seat belts, etc.
- Limited Research and Development.
- Lack of awareness about the benefits and applications of technical textiles.
- Infrastructure constraints.
- Fiscal anomalies: Imposition of excise duties on raw materials and no exemption on finished products escalating the cost of production.
Way Forward
- Address trade barriers and promote exports by providing incentives.
- Foster collaborations between raw material producers and manufacturers to ensure a reliable and cost-effective supply chain.
- Standardization and quality control for adopting quality management systems and obtaining certifications.
- Establishing dedicated research centers and providing grants and incentives for industry-academia collaborations.
National Technical Textiles Mission
- Implementation period: FY 2020-21 to 2023-24.
- Objective: To position India as a global leader in Technical Textiles, achieve a market size of $40 billion and export $10 billion in the technical textiles segment by 2024-25.
- Focus: Developing usage of technical textiles in various flagship missions (Swachch Bharat Mission; Ayushman Bharat), and programs of the country including strategic sectors.
- 4 Components of Mission:
- Component I (Research, Innovation and Development),
- Component II (Promotion and Market Development),
- Component III (Export Promotion),
- Component IV (Education, Training, Skill Development).
{Prelims – IE – Money} Hard Currency
- Context (IE): According to the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI), conditions are yet not ripe for Indian Rupee to transform into a Hard Currency.
- Hard currency, often referred to as strong currency, is a currency issued by a nation that is seen as politically and economically stable.
- They:
- Are easily exchangeable,
- Are widely held as foreign exchange reserves by central banks,
- Act as a liquid store of wealth.
Other forms of Money
Hard Money
- Hard money is money issued with the backing of gold or other very credible assets.
- Hard money avoids the risks of inflation.
Soft Money
- Soft money is just paper currency backed by government bonds. Here money is printed without keeping adequate reserves like gold in proportion to the newly issued money.
Hot Money
- “Hot money” refers to funds that are moved quickly and frequently between financial markets to take advantage of fluctuating interest rates, exchange rates, or price movements.
- They influence the balance of payments and strengthen the exchange rate of the recipient country.
Near Money
- “Near money” refers to assets that are not cash but can be easily and quickly converted into cash without significant loss of value.
{Prelims – S&T – AI} AI Achievements
AI-Chemist
- AI-chemist creates oxygen-producing materials from Martian meteorites.
- Significance: It will make future manned missions to Mars cost-effective, which will require oxygen for rocket propulsion and life support.
GraphCast
- Graphcast, Google DeepMind’s AI-weather model, improves 10-day forecasts regarding accuracy, speed, and accessibility.
- Significance:
- It outperformed traditional systems in 90% of tested cases.
- It excelled in forecasting extreme events without direct training for such predictions.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)