Current Affairs February 17, 2024: Weakening of Gulf Stream, Card Network, Economic Nationalism, Nohar Irrigation Project, Claude AI Chatbot, Twin Technology, Sora by OpenAI, Golden Backed Frog, Hawksbill Sea Turtle, Leith’s Softshell Turtle
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Climatology} Weakening of Gulf Stream
- Context (NDTV | ET): As per a study published in the journal Nature Communications, Gulf Stream could collapse as early as 2025.
- It could lead to more extreme weather events in Western Europe, including colder winters and hotter summers, with devastating effects on agriculture, infrastructure, and public health.
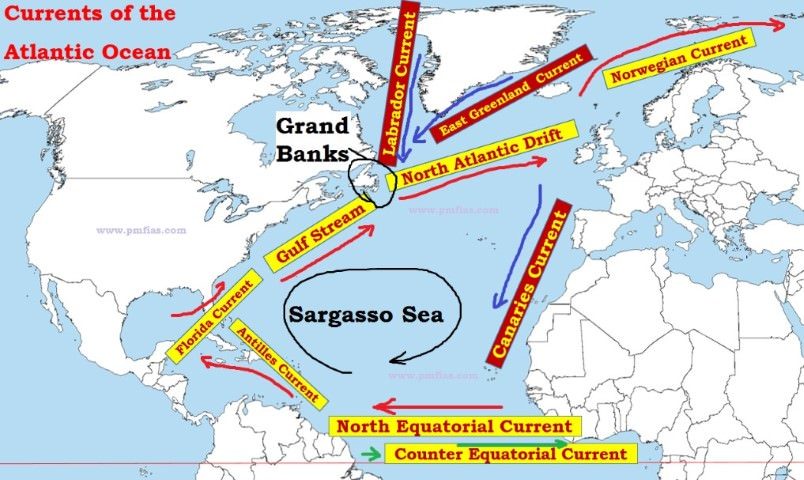
Gulf Stream
- The Gulf Stream is a strong warm ocean current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico into the Atlantic Ocean.
- It extends up the eastern coast of the United States and Canada.
- It is formed from the convergence of the North Atlantic Equatorial Current bringing tropical water from the east, and the Florida Current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico.
- The main portion of the Gulf Stream continues north, veering more to the east and passing close to the Grand Banks, south of Newfoundland, where it breaks up into swirling currents.
- Some of these eddies flow toward the British Isles and the Norwegian seas and form the North Atlantic Current (or Drift).
- In the east, the Gulf Stream merges into the Sargasso Sea.
- It is a small part of ‘thermohaline circulation’ or ‘Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation’.
- With an average speed of 6.4 km/hr, and a maximum speed of about 9 km/hr, it is the fastest current in the world ocean.
Importance of Gulf Stream
- Mingling with the colder waters both on the Grand Banks and off northwestern Europe, contribute to turbulence & availability of nutrient salts making these regions among the most productive commercial fishing grounds in the world.
- The Gulf Stream is like a “river” in the ocean, and it ensures that the climate of Western Europe is much warmer than it would otherwise be.
{GS2 – Governance – Laws} SC struck down amendments in three key laws
- Context (IE): The SC, in addition to the Electoral Bonds Scheme (EBS), struck down various amendments made by the government in crucial laws.
- The Finance Act of 2017 was introduced to amend The Representation of the People Act of 1951 (RPA), The Income-tax Act of 1961, and The Companies Act of 2013.
-
These amendments permitted electoral bonds to bypass many restrictions on political party funding by:
- Eliminating the donation limit for companies.
- Eliminating the need to declare and maintain records of donations through electoral bonds.
-
Before the amendments, political parties had to
- Disclose all contributions exceeding Rs 20,000 without exceptions. (According to Section 29C of the Representation of the People Act).
- Maintain a record of donations over Rs 20,000 for taxation purposes. ( According to Section 13A(b) of The Income-tax Act).
- There was a limit on the amount a company could donate to a political party in a financial year. It was set at a maximum of 7.5% of their average net profits from the previous three years. (According to Section 182(1) of the Companies Act 2013)
- Recent judgment by the SC has restored the status quo that existed before the Finance Act 2017 was passed.
{GS3 – Agri – MSP} NCF Report Recommendations
- Context (IE): On November 18, 2004, the Ministry of Agriculture constituted a National Commission on Farmers (NCF) under Prof Swaminathan.
- Between December 2004 and October 2006, the NCF submitted five reports.
Key Recommendations by the NCF reports
- Causes of Farmer suicide: Insufficient public investment and inadequate public actions were the reasons for the acute agricultural distress leading to farmer suicides.
-
For Women in Agriculture
- Support services and access to timely credit and extension services should be ensured.
- It proposed the establishment of a National Board for Women in Agriculture.
-
Pro-market reforms
- The NCF suggested a code of conduct for contract farming.
- The Commission recommended amending State Agriculture Produce Marketing Acts to facilitate private sector or cooperative involvement in establishing markets, developing marketing infrastructure, and providing support services.
- It also suggested rationalising market fees and other charges while enabling marketing without the obligatory involvement of APMC/licensed traders.
- Need to reassess the Essential Commodities Act, considering that certain laws may have become outdated.
- Promote the formation of farmer groups or organisations to negotiate with buyers and safeguard the interests of small-scale farmers.
- The Commission suggested allowing futures and options trading in agricultural commodities, supervised and regulated by an autonomous body similar to SEBI.
-
Recommendations regarding MSP
- It emphasised the need to avoid delays in issuing the MSP, especially for Kharif crops.
- Highlighted the necessity for improving the implementation of MSP across different regions.
- The Swaminathan Commission did not recommend the fixing of MSP based on C2 (actual cost of production) plus 50 per cent, as demanded by the protesting farmers.
- MSP should be the minimum benchmark for both government and private traders procurement.
- Government purchases should include MSP plus the cost escalation since its announcement, reflecting the prevailing market price.
- The government should also procure staple grains for the Public Distribution System (PDS) at a price equivalent to what private traders offer to farmers.
-
Other Suggestions
- Creation of Farm Schools in the fields of innovative farmers to disseminate their practices.
- Establishment of a grain bank and community food and fodder banks.
- Advocated for the promotion of insurance and the creation of a national network of advanced soil testing labs.
- CACP should function as an independent statutory body, primarily tasked with recommending profitable prices for key agricultural commodities in both dry and irrigated areas.
{GS3 – IE – Banking} Card network
- Context (IE): The RBI has directed a specific card network to cease unauthorised payments made with business cards. The name of the card network was not explicitly mentioned.
What is a card network?
- A card network is a system that links banks, merchants, and card users, facilitating secure and smooth transactions. It operates in the background whenever a card is used for payment.
- In India, there are five authorised card networks: Visa, Mastercard, RuPay, Diners Club, and American Express.
Issue
-
A card network had an unauthorised arrangement allowing businesses to use intermediaries for card payments to entities not accepting cards.
- The intermediary accepted card payments from companies for commercial transactions and transferred the funds through IMPS, RTGS, or NEFT to recipients not accepting cards.
- Such an arrangement qualified as a payment system requires authorisation under Section 4 of the PSS Act, which was not obtained in this case.
- The intermediary collected a substantial sum of funds into an account not designated by the PSS Act.
- Additionally, transactions processed in this setup failed to meet the originator and beneficiary information requirements specified in the RBI’s Master Direction on KYC.
|
{GS3 – IE – Industry} Economic Nationalism
- Context (PIB): Recently, the Vice-President addressed the Bharat Startup and MSMEs Summit in New Delhi.
- The Vice-President emphasised the negative consequences of not embracing economic nationalism.
- He advocated for the importation of only essential items to safeguard India’s foreign exchange, preserve employment opportunities, and foster entrepreneurial growth.
- He also cautioned that neglecting value addition would result in a loss of job creation and hinder the growth of entrepreneurship.
- He also urged the corporates to fuel, finance, promote and sustain research and development in the country,
What is Economic nationalism?
|
{GS3 – Infra – Initiatives} Nohar Irrigation Project
- Context (TH): The Nohar irrigation project in Rajasthan is set to receive a boost through the repairing of the Ferozepur feeder in neighbouring Punjab.
- The canal’s capacity will increase from 226 cusecs to 332 cusecs after the completion of the repair.
- The Central Water Commission initiated this work.
- Infrastructure repair enhances water availability, improves crop yield, reduces dependence on monsoons, boosts livelihoods, mitigates water stress, and fosters economic growth.
Nohar Irrigation Project
- Previously known as the Sidhmukh Nohar Irrigation Project, it is situated in the Nohar region of the Hanumangarh district in the state of Rajasthan.
- Initiated by Rajiv Gandhi in 1989 but was officially launched in 2002.
- Funding for the project was received from the European Economic Community.
- Its primary objective is to improve irrigation facilities in the region, thereby increasing agricultural productivity and supporting the livelihoods of local farmers.
- The project employs canal irrigation and involves the construction of check dams, reservoirs, and water storage facilities.
- The project draws water from the Indira Gandhi Canal, which is situated near the Ghaggar-Hakra River—a seasonal river originating in the Shivalik Hills.
Indira Gandhi Canal (IGC)
|
{GS3 – S&T – AI} Claude – AI Chatbot
- Context (IE): Claude, the AI chatbot, is developed by Anthropic, a San Francisco-based artificial intelligence startup.
What is Claude?
- Claude is a group of large language models (LLMs) designed to assist with various tasks.
- It can handle text, voice messages, and documents effectively.
- It generates faster and context-aware replies compared to other chatbots.
- It efficiently summarises PDFs and transcripts, effortlessly extracting specific data points from various documents, including scientific papers, legal documents, and novels.
- Claude’s uniqueness is from its foundation in “Constitutional AI,“ allowing developers to define a set of values, ensuring a clear distinction between its technical capabilities and socially responsible actions.
-
Claude has been trained using two methods:
- Supervised Learning (SL): The LLM produces responses based on guiding principles and self-assesses them.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): The model learns from AI-generated feedback, aiming to reduce harmful effects in its outputs.
| LLMs are powerful artificial intelligence models designed to understand and generate human-like text. |
{GS3 – S&T – AI} Digital Twin Technology
- Context (PIB): The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has introduced the Sangam: Digital Twin initiative.
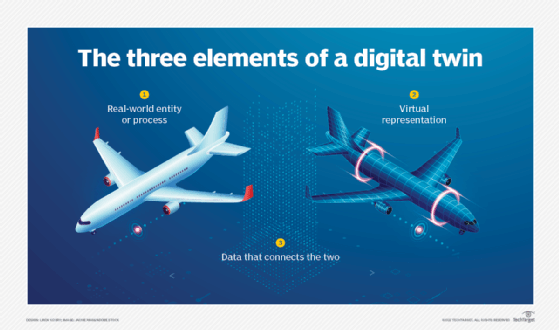
What is Digital Twin technology?
- A digital twin is a digital representation of a physical asset or environment, such as a car, a bridge, or a building.
- Digital twins learn, update, and communicate with their physical counterparts by exchanging data throughout the asset’s lifecycle using AI, machine learning, and IoT technologies.
- Digital twins use real-time data, allowing stakeholders to monitor the performance and lifecycle of a project.
-
Cities around the world are now using technology to collect and interpret data that will make them more resilient in the face of climate change and other emergencies.
- The Virtual Singapore project 3D digital platform lets users from different sectors create tools to solve the city’s complex challenges.
- In India, the state of Andhra Pradesh’s new capital, Amaravati Smart City, is being created using a digital twin.
About Sangam: Digital Twin initiative
- It aims to revolutionise infrastructure planning and design by integrating Digital Twin technology with AI, ML, and IoT.
-
Currently, in the proof-of-concept stage, it is distributed in two stages.
- The first stage would be exploratory, followed by a practical demonstration of specific use cases.
- In November 2023, Survey of India, National Mapping Agency, and Genesys joined hands for a 3D Digital Twin mapping program in India to aid the Smart Cities Mission, along with other schemes such as PM GatiShakti and SVAMITVA.
{GS3 – S&T – AI} OpenAI launches Sora
- Context (IE): OpenAI has introduced an impressive AI model called Sora, which can generate videos directly from text prompts.
What is Sora?
- Sora is a text-to-video model developed by OpenAI.
- Its purpose is to create realistic and imaginative scenes based on descriptive text instructions.
- Sora can generate videos for up to a minute while maintaining visual quality and adhering to the user’s prompt.
- It understands and simulates the physical world in motion, making it valuable for solving problems that require real-world interaction.
Applications
- Sora could revolutionize creative industries, including filmmaking, advertising, graphic design, and game development.
- It also has applications in social media, influencer marketing, and education technology.
What are some other AI models developed by OpenAI?
|
{Prelims – Envi – Species} Golden-backed frog (Indosylvirana aurantiaca)
-
Context (IE | TOI): Scientists made a surprising discovery in the foothills of the Western Ghats in India, a mushroom growing out of the side of Golden-backed frog.

- The Golden backed frog, also known as Trivandrum frog, common wood frog, or small wood frog, is a small-sized amphibian.
- They are notable for their bright golden coloration on their backs, which contrasts with their dark brown or black colored legs. They have white-colored underbelly.
- They are endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
- They are partially arboreal and partially aquatic.
- Habitat: Predominantly found in evergreen and semi-evergreen forests in the Western Ghats. They prefer to reside near water bodies, where they can lay their eggs and find their food.
- Diet: They are primarily insectivorous and feed on a range of small insects and arthropods such as ants, beetles, and crickets.
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, pollution of water bodies, and the introduction of non-native species.
{Prelims – Envi – Species} Hawksbill Sea Turtle | Common Angelshark
- Context (DTE): Draft resolution for conservation of hawksbill turtle and angelshark adopted at CMS COP14.
Hawksbill Turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata)
- One of the smaller sea turtle species, the hawksbill turtle gets its name from its narrow, elongated head which tapers sharply with a V-shaped lower jaw.
- It is the only extant species in the genus Eretmochelys.
- The carapace is orange, brown or yellow and hatchlings are mostly brown with pale blotches on scutes.
- Hawksbills are solitary nesters, they nest at intervals of 2-3 years, about 2 to 4 times per season.
- Habitat: Typically found around coastal reefs, rocky areas, estuaries, and lagoons.
- Range: Most tropical of all sea turtles. Found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
- Diet: The hawksbill’s narrow head and jaws shaped like a beak allow it to get food from crevices in coral reefs. They eat sponges, anemones, squid, and shrimp.
- Threats: Harvesting for their prized shell, referred to as “tortoise shell.” Bycatch in fishing gear, Climate change, Direct harvest of turtles and eggs, Loss and degradation of nesting habitat, Ocean pollution/marine debris, etc.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Critically Endangered | WPA: Schedule I | CITES: Appendix I

Common Angelshark (Squatina squatina)
- Angelshark is a cartilaginous fish similar to a ray or skate.
- It can be distinguished from other angelsharks by its simple and conical nasal barbels, high and wide pectoral fins, and small spines that are present on the snout and above the eyes.
- Diet: They eat mostly bony fish, other demersal animals, such as skates, crustaceans, mollusks, and cephalopods.
- Habitat: They are found in coastal and outer continental shelf sediment habitats in the Mediterranean Sea and eastern Atlantic. They may also be found in estuaries and brackish water.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Critically Endangered | CITES: Appendix I

{Prelims – Envi – Species} Leith’s softshell Turtle (Nilssonia leithii)
- Context (IE): Critically endangered Leith’s soft-shell turtle was sighted in Cauvery.
- Leith’s softshell turtle is a large freshwater soft-shelled turtle, endemic to peninsular India.
- It is found in all major rivers of the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Odisha.
-
Physical description
- The adults are olive green or greyish in colour on the carapace and white off-cream on the plastron.
- Many have a striking head pattern where the black stripes run along the head near the lips and blotches of red colour patterned in between.
- Threats: Poaching, hunting, illegal consumption.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Critically Endangered | WPA: Schedule IV | CITES: Appendix I

{Prelims – Envi – Species} New species of marine amphipod discovered
- Context (DTE): Reseaerchers have discovered a new species of marine amphipod, a shrimp-like crustacea of genus Parhyale.

|
- The new species has been named Parhyale odian after Odisha’s native language, Odia, as the species was collected there.
- The newly discovered species differs from all other 15 species by having a stout robust seta — a spine-like structure on the surface of the propodus of the male gnathopod (first pair of legs)
- They are mostly found underneath stones with attached vegetation and also in the burrows of isopods.
Chilika Lake
|
{Prelims – In News} ‘Sagar Aankalan’ Guidelines
- Context (PIB): The “Sagar Aankalan” guidelines have been introduced for the National Benchmarking of Indian Ports Performance.
- These guidelines apply to all Indian seaports.
Objectives
- Mapping and benchmarking of Indian port logistics performance and efficiency.
- Harmonization of standards, definitions, and performance with global benchmarks.
- Improving competitiveness, efficiency, and overall performance of the port sector with a focus on enhancement, productivity, sustainability, and customer satisfaction.
World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (LPI) Report
Major Performance Indicators for Indian Ports
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)