Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – March 19, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Vulnerable Sections – Women} Gender Inequality Index, 2022
- Context (ANI): The Gender Inequality Index (GII) for the year 2022 has been released within the Human Development Report 2022.
- India made significant progress, leaping 14 ranks in the Gender Inequality Index 2022. It now stands at 108th place out of 193 countries, with a GII value of 0.437.
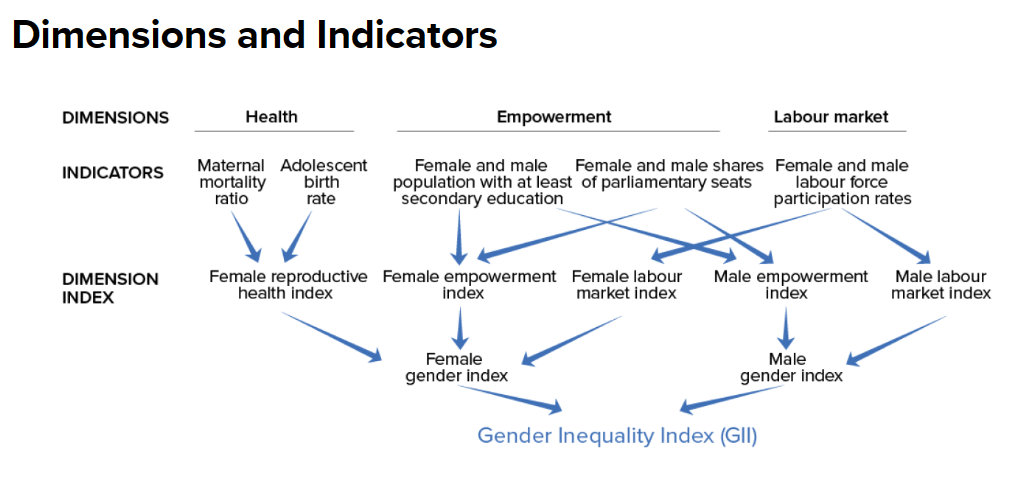
What is the GII?
- Published by: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- India’s Rank: 108 (2022) out of 193 countries (Earlier 122 with a score of 0.490(2021)).
- Top ranking country: Denmark
- The Gender Inequality Index (GII) is a composite metric that measures gender inequality across 3 dimensions:
- Reproductive Health: The GII considers maternal mortality rates and adolescent fertility rates.
- Higher maternal mortality rates and early pregnancies contribute to a higher GII value, indicating greater gender inequality in reproductive health.
- Empowerment: It evaluates women’s participation in political decision-making and their educational attainment.
- It includes indicators such as the percentage of parliamentary seats held by women and the proportion of women with at least secondary education.
- Labour Market: The GII examines labour force participation rates for both men and women.
- Disparities in employment opportunities, wage gaps, and the share of women in professional and technical roles impact this dimension.
- Reproductive Health: The GII considers maternal mortality rates and adolescent fertility rates.
- It reflects the loss in potential human development due to gender-based inequality.
- Interpretation: Each dimension is assigned a value between 0 and 1, where 0 represents perfect gender equality, and 1 signifies maximum inequality.
- Calculation: The GII combines the 3-dimension scores using a geometric mean.
- Comparison with neighbouring countries: Bangladesh fares better, standing at 59th place on the index.
- Bhutan (103), China (107), Sri Lanka (115), Nepal (116).
- Pakistan ranks 142nd on the GII, indicating higher gender inequality.
- Impressions:
- Maternal mortality ratio (deaths per 100,000 live births) – 103 (remains the same from 2020).
- Adolescent birth rate (births per 1,000 women ages 15–19) – 16.3 (17.23 (2021))
- Share of seats in parliament (% held by women) – 14.6 (13.4 (2021))
- Population with at least some secondary education (% ages 25 and older)- Female-41.0(40.51 (2021)) Male- 58.66(58.71(2021))
- Labour force participation rate (% ages 15 and older)- Female- 28.3(27.04(2021)), Male- 76.1(75.1(2021))
- The GII serves as a vital tool for policymakers and organizations to track progress and identify areas where interventions are needed to achieve gender equity.
- Long-Term Improvement: Over the years, India’s GII rank has consistently improved, reflecting the nation’s commitment to advancing gender equality. (From 127 in 2014 to 108th rank).
{GS3 – Envi – CC Impact} Missing Spring in India
- Context (TH): Indian states have been experiencing a gradual withdrawal from spring.
- Spring, characterized by weather between the winter of January and the scorching summers of April, is showing signs of disappearing.
- The analysis of meteorological records spanning 50 years reveals that every region in India has witnessed a net warming during winter.
- This warming trend during the winter months is impacting traditional seasons and potentially leading to the disappearance of spring.
- Human-caused climate change is a significant factor behind the dramatic warmer temperatures observed in February.
- Global mean temperatures have risen by more than 1.3 degrees Celsius since 1850, setting a new record in 2023.
- This warming trend affects the timing and characteristics of seasons, including spring.
What are the effects of missing spring?
- Ecological Disruptions: The missing spring disrupts the natural cycles of plants, animals, and insects.
- Flowering Plants: Many flowering plants rely on spring for pollination and seed production. The absence of spring affects their reproductive success.
- Bird Migration: Spring is when migratory birds return to their breeding grounds. The missing spring can impact their arrival timing and availability of food.
- Insects and Pollinators: Insects, including bees and butterflies, depend on spring for their life cycles. Delayed or absent spring affects their survival.
- Agricultural Challenges:
- Crop Timing: Spring is crucial for planting crops. Delayed spring affects sowing schedules, leading to yield losses.
- Pests and Diseases: Spring warmth helps control pests and diseases. Without it, farmers face increased challenges in pest management.
- Human Health Implications:
- Allergies: Spring is associated with pollen release. Missing spring may alter pollen patterns, affecting allergy sufferers.
- Cultural and Social Impact:
- Festivals and Traditions: Spring festivals celebrate renewal, growth, and new beginnings. Their absence affects cultural practices.
How does this affect global climate change?
- Feedback Loops: The disruption of spring affects natural feedback loops. For example:
- Snow and Ice Albedo: Delayed spring leads to prolonged snow cover. Reduced albedo (reflectivity) due to snow and ice amplifies warming by absorbing more sunlight.
- Vegetation Changes: Altered spring timing affects vegetation growth and carbon sequestration. Delayed greening can impact the global carbon cycle.
- Regional Climate Patterns:
- Indian Monsoon: Spring influences the onset of the Indian monsoon. Changes in spring dynamics can alter monsoon patterns, affecting agriculture and water availability.
- Temperature Extremes: The absence of spring contributes to more extreme temperature shifts, impacting weather events globally.
- Ocean Circulation and Heat Transport:
- Thermohaline Circulation: Spring affects ocean currents. Disrupted spring patterns may impact the thermohaline circulation, which plays a crucial role in heat transport worldwide.
- Shifts in Phenology and Biodiversity:
- Mismatched Timing: Spring cues various biological events (flowering, migration, breeding). Disruptions can lead to mismatches (e.g., flowers blooming before pollinators arrive).
- Species Vulnerability: Some species may struggle to adapt to altered spring conditions, affecting biodiversity.
- Permafrost Thaw and Methane Release:
- Warmer Winters: Prolonged winter warmth accelerates permafrost thaw. Thawed permafrost releases stored methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
{GS3 – S&T – BioTech} Genetic Modification of Fruit Fly
- Context (TH): Scientists have genetically modified a sexually reproducing fruit-fly species, Drosophila melanogaster, to reproduce asexually.
- Parthenogenesis was induced in the fruit fly species Drosophila melanogaster.
- The researchers identified genes responsible for parthenogenesis in another fruit fly species, Drosophila mercatorum, and modified the D. melanogaster genome to express these genes.
- This genetic manipulation resulted in 1.4% of the fruit fly eggs being parthenogenetic, with offspring surviving to adulthood.
- In regular fertilization, polar bodies, which are by-products of chromosome transmission, are discarded.
- Altering protein levels of specific genes likely affected polar body disposal, allowing them to substitute for the missing male pronucleus and initiate embryonic development in unfertilized eggs.
|
Implications
- The findings have implications for controlling insect pests by releasing sterilized males or males with edited genomes to disrupt progeny development.
- This approach may inadvertently select facultatively parthenogenetic individuals, limiting its long-term effectiveness.
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
Comparative Analysis
|
{Prelims – In News} Shillekyata Tribe
- Context (TH): The Shillekyata fishers, a tribal community, are asserting their fishing rights in Kundapura taluk.
- The Shillekyatha community migrated from Maharashtra to Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, particularly during the era of Shivaji.
- Also addressed as the Killekyata community, they are nomadic in nature.
- They commonly find shelter in various places such as temples, bus stands, railway stations, schools, college fields, and charity chathras.
- Language: Marathi is spoken at home, but Kannada is used for interaction with other communities. The script used for writing is Kannada.
- Artisanal Traditions: Known for their craftsmanship in leatherwork, including making dolls, puppets, and whistles.
- The tradition of leatherwork is traced back to ancient times and is found in various regions like China, Thailand, and Java.
- Religion: Hinduism.
- Food: Their diet consists of rice, chapati, roti, fish, chicken, mutton, and other items.
- They prepare their remedies using Ayurvedic plants for various ailments, including snake and scorpion bites. They also provide medicines for animals.
- Economic Activities: In addition to their nomadic lifestyle, they are involved in hunting and fishing activities, which supplement their livelihoods.
- Traditional Occupation: The primary traditional occupation of the Killekyatas is “Togalubombeyata,” a form of puppetry and storytelling.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} 25T Bollard Pull (BP) Tug ‘Baljeet’
- Context (PIB): The 25T Bollard Pull (BP) Tug, Baljeet, was launched at M/s Shoft Shipyard Pvt Ltd in Gujarat.
- These Tugs are being built under the classification rules of the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS).
- The availability of these Tugs will provide impetus to the Indian Navy’s operational commitments by assisting naval ships and submarines during berthing, un-berthing, turning, and manoeuvring in confined waters.
- The Tugs will be capable of conducting limited Search and Rescue Operations and providing afloat firefighting assistance to ships alongside and at anchorage.
|
- The contract for constructing and delivering three 25T BP Tugs was awarded to M/s Shoft Shipyard Pvt Ltd (M/s SSPL), an MSME, aligning with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
|
Indian Register of Shipping
- It is an internationally recognized, independent ship classification society.
- It is a not-for-profit entity was founded in 1975.
- It operates as a public limited company incorporated under the Indian Companies Act 1956 (now the Indian Companies Act 2013).
- It is a member of the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS), which represents classification societies worldwide.
- IRClass provides ship classification and certification services, conducting technical inspections and environmental and quality standards encompassing structural integrity, safety equipment, and environmental protection measures.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} Exercise Tiger Triumph
- Context (PIB): A bilateral tri-service Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR), Exercise Tiger Triumph– 24 between India and the USA is scheduled for the Eastern Seaboard.
- The exercise aims to enhance coordination and interoperability between the armed forces of both countries for conducting HADR operations.
- By refining Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), they intend to enable rapid and smooth coordination during disaster relief efforts.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)