Current Affairs August 18, 2023: Registration of Birth and Death (Amendment) Bill, 2023, Tuberculosis, UDGAM Portal, MGNREGS, Matti banana, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Herons
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Governance – Misc – 2023/08/18} Police verification of SIM card dealers
- Context (TH): The government has made police verification of SIM card dealers mandatory.
- Earlier, the rule did not prescribe detailed documentation of the dealer.
- The licensee or the respective telecom operator will carry out the verification of dealers.
- A penalty of ₹ 10 lahks will be imposed on violators.
- Department of Telecommunications has also discontinued the provision of issuing bulk connections, and instead, a new concept of Business Connection will be introduced.
- Besides the KYC of businesses, the KYC of the person taking handover of SIM will also be done.
{GS2 – Governance – Misc – 2023/08/18} Registration of Birth and Death (Amendment) Bill, 2023
- Context (TH): Lok Sabha passed the Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Bill, 2023.
- Registration of births and deaths is already compulsory under the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969; violating it is a punishable offence.
- Through the amendment, the government intends to improve compliance.
- The objective is to create a National and State database of registered births and deaths.
- The database would help update other databases resulting in efficient and transparent delivery of public services and social benefits.
|
Salient features
Use of birth certificate
- Birth certificates are mandatory to access basic services such as:
- Admission to an educational institution
- Registration of marriage
- Preparation of voter lists
- Appointment to a government post
- Any other purpose determined by the central government.
Database of births and deaths
- The Registrar General will maintain a national database of registered births and deaths.
- The Chief Registrars (appointed by states) and Registrars (appointed by states for local area jurisdiction) will be obligated to share data of registered births and deaths to the national database.
Connecting database
- The national database may be made available to other authorities preparing or maintaining other databases. Such databases include:
- Population Register
- Electoral rolls
- Ration card
- Any other national databases as notified.
Aadhaar details of parents and informants
- In cases of births, informants and parents shall provide Aadhaar numbers.
Issues
- The Bill requires the birth certificate of persons for certain purposes.
- Some of these purposes are citizens’ constitutional rights, and making them conditional on a birth certificate may violate those rights.
- Denying admission to school to a child without a birth certificate may violate the fundamental right to education under Article 21A.
- The Bill links the Aadhaar details of the parents and informant.
- This provision may violate the informant’s right to privacy.
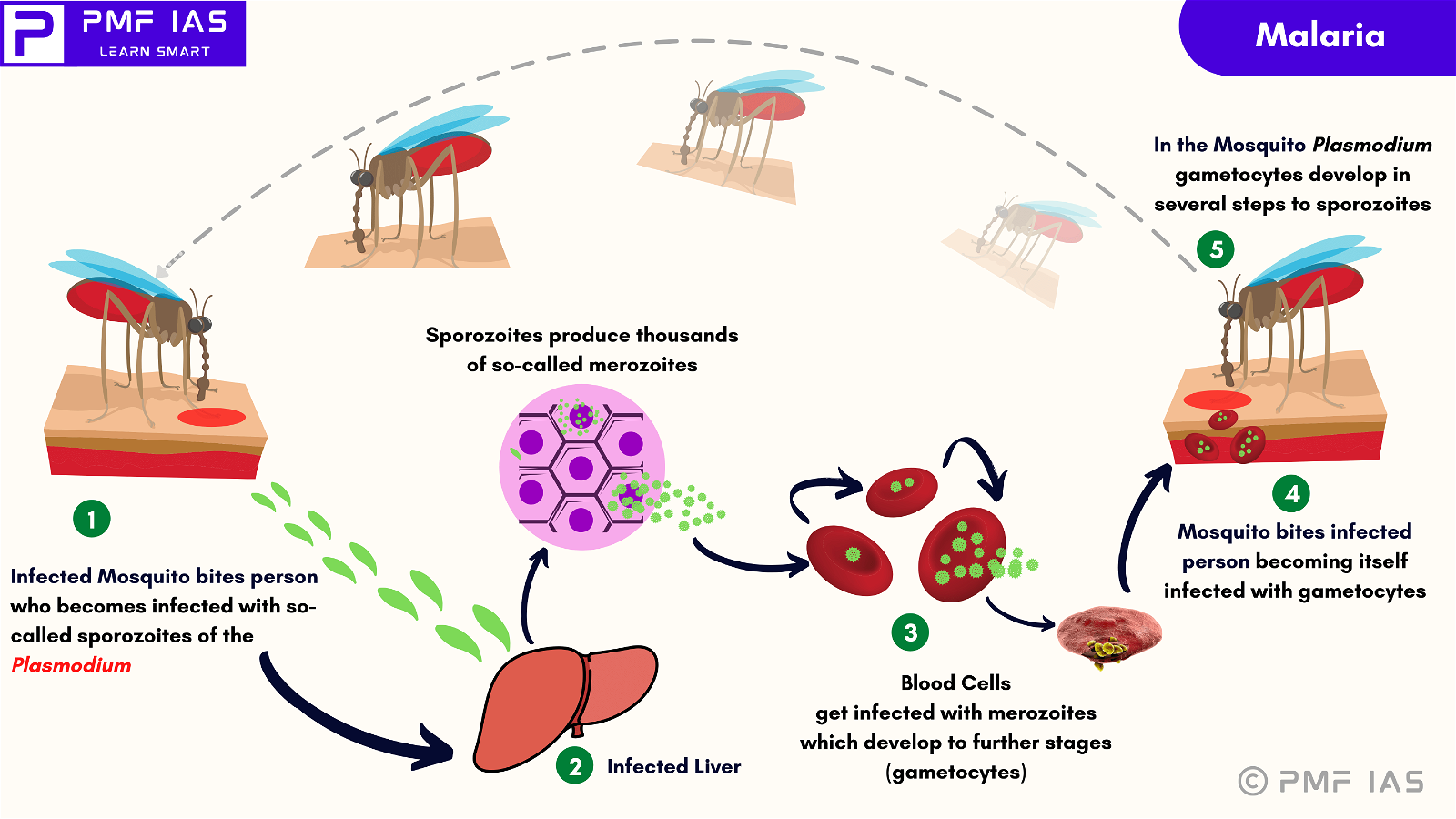
{GS2 – Health – Diseases – 2023/08/18} Tuberculosis (TB)
- Context (DD): The WHO South-East Asia Region committed to further accelerate efforts to end tuberculosis by 2030, with member countries adopting the Gandhinagar Declaration.
UN Sustainable Development Goals Target 3.3
|
- The declaration calls for the establishment of a High-Level Multisectoral Commission in each country to coordinate efforts to end TB and other priority diseases.
- This commission would bring together representatives from government, civil society, the private sector, and other stakeholders to work together to develop and implement a National TB Strategy.
- The commission would also monitor progress towards ending TB and ensure all stakeholders are accountable for their commitments.
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- TB commonly affects the lungs (pulmonary TB) but can also affect other parts (extrapulmonary TB).

- Pulmonary tuberculosis is a chronic consumptive disease that can be present as acute pneumonia.
- Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung condition affecting the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli.


- Tuberculosis spreads from person to person through the air when people infected with TB cough, sneeze or otherwise transmit respiratory fluids through the air.
- The most common risk factor associated with TB is HIV and other conditions that impair the immune system.
Tuberculosis Symptomatic Diagnosis
- Most infections do not have symptoms, known as latent tuberculosis.
- About 10% of latent infections eventually progress to active disease that kills about half of those infected if left untreated.
Common symptoms include:
- Chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum
- Loss of weight
- Loss of appetite
- Fever and night sweats
- Fatigue are common symptoms of tuberculosis, etc.
TB Treatment
- The standard 6-month course treatment consists of 2 phases:
- 1st phase lasts 2 months and is called the Intensive phase.
- 2nd phase lasts for 4 months and is called the Continuous phase.
- For new TB cases, the treatment in the intensive phase (IP) consists of four drugs:
- Isoniazid (INH)
- Rifampicin
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
- For previously treated cases of TB, the intensive phase is 12 weeks, where an injection of streptomycin is given for eight weeks along with four drugs.
- A strictly followed 6-month drug regimen cures most people with TB.
Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR-TB)
- CBNAAT (Cartridges Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) is used for early diagnosis of MDR-TB.
- In MDR-TB, the bacteria develop resistance to antimicrobial drugs used to cure the disease.
- MDR-TB does not respond to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful anti-TB drugs.
- Treatment options for MDR-TB are limited and expensive.
- In some cases, even more severe drug-resistant TB may develop.
Causes
- MDR-TB is caused due to mismanagement of treatment and person-to-person transmission.
- Mismanagement of TB treatment involves inappropriate or incorrect use of antimicrobial drugs or ineffective formulations of drugs and premature treatment interruption.
Extensively Drug-Resistant TB (XDR-TB)
- XDR-TB is a form of multidrug-resistant TB with additional resistance to more anti-TB drugs.
- People who are resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (amikacin, kanamycin, capreomycin) are said to have XDR-TB.
Treatment for Drug-Resistant TB
- The treatment success in MDR-TB is about 54%, while it is just 30% in the case of XDR-TB patients.
- A combination of eight drugs for over a year is needed for XDR-TB treatment.
- Treatment success in XDR-TB patients depends on the extent of the drug resistance, the severity of the disease, whether the patient’s immune system is weakened, and treatment adherence.
- Drugs used for treating MDR-TB and XDR-TB can cause serious adverse effects such as deafness.
The Goal to End TB by 2025
- Revised National TB Control Programme was renamed the National TB Elimination Programme.
- The name change aligns with the larger goal of eliminating the disease by 2025, five years ahead of the SDG 3.3 target.
National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- 1962: GoI launched National TB Programme (NTP) with BCG vaccination at the district level.
- 1993: WHO declared TB a global emergency and devised the directly observed treatment (DOTS).
- 1993: GOI revitalised NTP as the Revised National TB Control Programme (RNTCP).
- 1997: DOTS was launched as the RNTCP strategy. By 2006 the entire country was covered.
- In its second phase (2006–11), RNTCP improved the quality and reach of services.
- Despite the measures, undiagnosed and mistreated cases continued to drive the TB epidemic.
- A large number of MDR-TB cases were reported every year.
- To address this, National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Control 2012-2017 was documented with the goal of ‘universal access to quality TB diagnosis and treatment’.
- Significant interventions were taken during NSP 2012-2017 regarding mandatory notification of all TB cases, integration of the programme with the National Health Mission, etc.
- To eliminate TB in India by 2025, National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Elimination 2017-2025 involving all the stakeholders was formulated by RNTCP.
- On 01-01-2020, RNTCP was renamed National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
National strategic plan for tuberculosis elimination (NSP) 2017-2025 (NSP)
- TB elimination has been integrated into the four strategic pillars of “Detect – Treat – Prevent – Build”.
Detect
- Early diagnosis and treatment of TB are essential in TB elimination.
- The objective of NSP was to find all drug-sensitive TB cases and drug-resistant TB cases.
- To facilitate TB notification, RNTCP has developed a TB surveillance system called “NIKSHAY” (https://nikshay.gov.in) for government and private healthcare facilities.
- For TB diagnosis, more than 14,000 designated microscopy centres are spread across the country.
- Cartridge Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (CBNAAT) / Line Probe Assay (LPA) has been established at district levels for decentralised molecular testing for drug-resistant TB.
- From 2020, GOI will use the Truenat test for early-stage diagnosis.
Treat
- Screening all patients for rifampicin resistance (and additional drugs wherever indicated) is done.
- For drug-sensitive TB, daily fixed-dose combinations of first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs are given.
Prevent
- Isoniazid Preventive Therapy (IPT) is given to children in close contact with a TB patient.
- BCG vaccination is provided at birth or as early as possible till one year of age. BCG vaccine protects against meningitis and disseminated TB in children.
Build
- Health system strengthening for TB control under the NSP 2017-2025 is recommended in the form of building and strengthening enabling policies, empowering institutions, and human resources.
{GS3 – IE – RBI – 2023/08/18} UDGAM Portal
- Context (TH): RBI has launched the Unclaimed Deposits – Gateway to Access inforMation (UDGAM) portal to search unclaimed people’s deposits across multiple banks at one place.
- Earlier, RBI directed banks to display the name and address of such depositors on their websites.
- At present, users can access the details of their unclaimed deposits from the seven banks presently available on the portal.
- The search facility for remaining banks will be made available in a phased manner by October 15, 2023.
Steps of declaring deposits as unclaimed
- Initially, the bank accounts are categorised as inoperative.
- Once an account becomes inoperative for 10 continuous years (i.e., 2 years post being declared inoperative), they are classified as Unclaimed Deposits.
- On completion of the 10th year, all monies in that account are transferred to The Depositor Education and Awareness Fund (DEAF) maintained by the RBI.
- The unclaimed deposits earn simple interest at a rate the RBI declares, provided and paid by the bank.
|
Refund of unclaimed deposits
- The claimant must contact the home branch and provide necessary documentary evidence like updated KYC and other relevant papers.
- If the account holder is deceased, then the claim can be made by a registered nominee.
- If there is no registered nominee or if the registered nominee is also deceased, then the claim can be made by the beneficiary as per the testamentary document (will) of the account holder.
- If the account holder died without a will (intestate), then the claim can be made as per applicable succession laws.
The time limit for filing the claims
- There is no time limit for filing claims. Claimants (account holders, nominees, legal heirs/beneficiaries) can lodge their claims with the respective home bank after the deposit is transferred to DEAF.
- A bank must settle such a claim request within fifteen days of the claim being filed with all supporting documentation needed for the legitimacy of the claim.
{GS3 – MoRD – Schemes – 2023/08/18} MGNREGS
- Context (TH): Drones will be used to monitor both the progress and quality of assets produced under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
- MGNREGS is a social security scheme guaranteeing 100 days of work to any rural household willing to do public work-related unskilled manual work at the statutory minimum wage.
- The Ministry of Rural Development (MRD) is monitoring the entire implementation of this scheme in association with state governments.
- The wages are revised according to the Consumer Price Index-Agricultural Labourers (CPI-AL).
|
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 or MGNREGA
- The act obligates the state to give rural households work on demand.
- The applicant becomes eligible for an unemployment allowance if such employment is not provided within 15 days of registration.
- The employment will be provided within a radius of 5 km. If it is >5 km, an extra wage will be paid.
- Under the act, priority shall be given to women, and at least one-third of the beneficiaries shall be women who have registered and requested work.
- All work sites should have crèches, drinking water and first aid facilities.
- Social Audit must be done by the Gram Sabha.
Funding pattern
- 100% of the unskilled labour cost and 75% of the material cost (including wages of skilled and semi-skilled workers) of the programme is borne by the Centre.
- Under the MGNREGS, wages of unskilled workers must be paid within 15 days; if there is a delay, the Centre has to compensate them.
Wages and material cost
- The Act provides for the wage and material costs to be in the proportion of 60:40.
- For instance, if a project costs Rs. 100, the wage expenditure should be at least Rs. 60, and the expenditure on materials should be Rs. 40.
- It should be ensured that the total material cost (including wages of skilled and semi-skilled workers and mates) of all works in the Annual Shelf of Projects should not exceed 40%.
- However, over 80% of the scheme’s funds have been used for wage payments in several labour-rich states.
Mates
- Mates are the site supervisors under MGNREGA.
- They are the frontline supervisors of the programme and are listed as semi-skilled workers because of the specialist nature of their job.
- Their wages come from the “material component“, 60% of which the Union government pays.
- Due to their payment delays, most mates started listing themselves as unskilled workers.
MGNREGS and Poverty alleviation
- MGNREGS was launched as a poverty alleviation instrument for the rural region, providing them with a safety net through guaranteed work and wages.
- But now it is felt that States like UP and Bihar, with a higher poverty level, haven’t been able to utilise the scheme optimally.
Amarjeet Sinha committee
- The Central government has constituted a committee to review the implementation of the MGNREGS, primarily to assess the programme’s efficacy as a poverty alleviation tool.
- Former Rural Development secretary Amarjeet Sinha heads the committee.
- The committee will also study the factors behind the demand for MGNREGA work, expenditure trends and inter-State variations, etc.
Section 27 of MGNREGA
Urban employment guarantee scheme
|
Issues
Technical glitches
- Biometric authentication failure.
- Difficulties in getting payment.
Corruption in MNREGS works
- Machines are being used in place of the workers.
- Many receive wages without doing work.
- Works beyond the approved list being undertaken, etc.
Bogus attendance
- To stop any bogus attendance of workers, the Centre has made the attendance of workers through a mobile application with time-stamped and geo-tagged photographs mandatory.
- However, in most cases, the employees’ families are averse to providing a phone to women. Hence, many women have dropped out of MGNREGS.
MGNREGS expansion proposals
- Extend the duration of employment to 200 days.
- Encompass urban areas.
- Raise the wage rate per the state’s statutory minimum wage.
- Augment the budget allocation for MGNREGA.
{Prelims – IPR – GI Tag – 2023/08/18} Matti banana
- The Matti banana has a sweet fragrance and honey-like taste unique to Kanniyakumari.
- The Matti banana’s fingers do not grow straight like other bunches. Instead, they have a distinct wind-blown appearance.
- The Matti banana is low in Total Soluble Solids Content (TSSC), which makes it a good choice for Baby Food. Hence, also known as the “Baby Banana“.

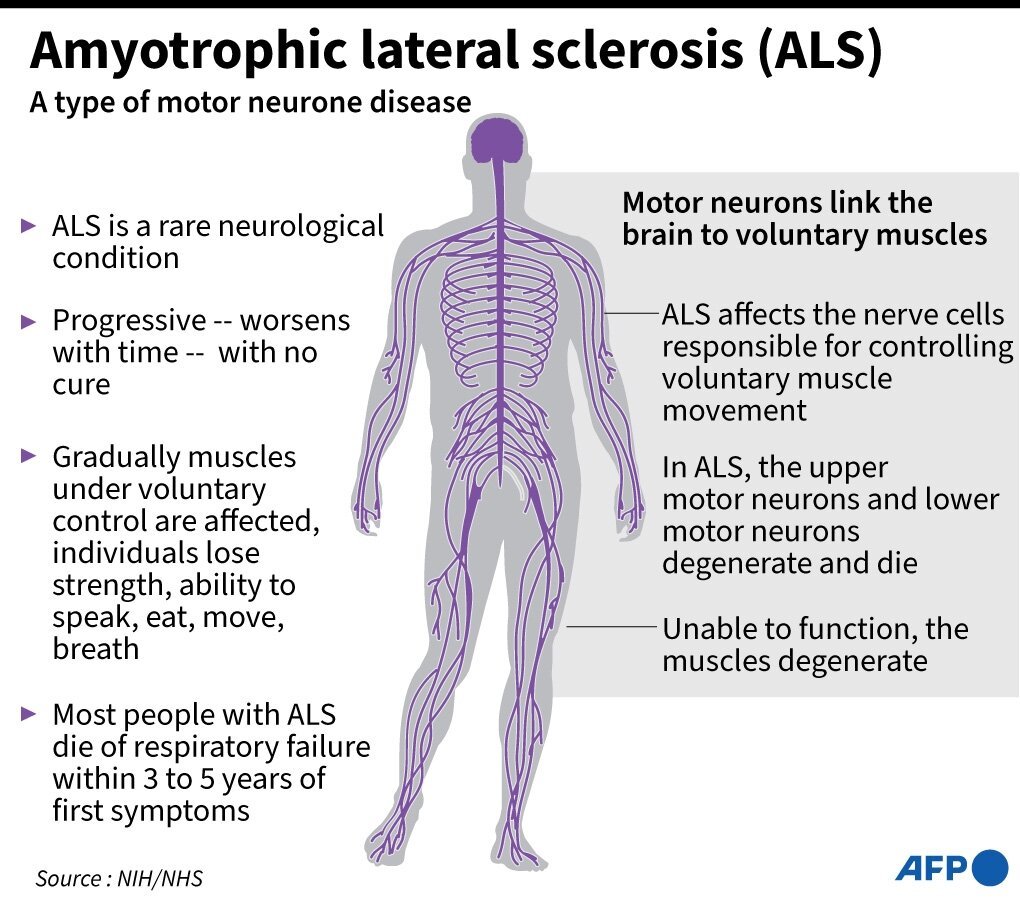
{Prelims – Sci – Bio – Diseases – 2023/08/18} Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Context (TH): Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
- As the nerve cells die, the muscles they control weaken and waste away.
- This causes a variety of symptoms, including muscle weakness, stiffness, twitching, and spasticity.
- There is No Cure For ALS, the average life expectancy after diagnosis of ALS is 3-5 years.
|
{Prelims – Species In News – 2023/08/18} Herons
- Context (TH): The Annual Heronry Count was jointly organised by WWF-India with the Forest department in Thiruvananthapuram district.


- Herons are long-legged wading birds that are found all over the world.
- These generally include several species, usually called “egrets”.
- They are most common in the tropics and feed on frogs, fish, and other aquatic animals.
- Herons nest in colonies called “heronries”, usually located near water.
- Being one of the top predators in the aquatic food chain, monitoring their population can indicate the health of the aquatic ecosystem, freshwater, as well as brackish water.
{Prelims – World PIN – Africa – 2023/08/18} Libya
- Context (TH): Since 2014, Libya has been divided into competing political and military factions.
- Libya is a North African country that gained its independence in 1951.
- Soon after, oil was discovered and earned the country immense wealth.
- Colonel Gaddafi seized power in 1969 and ruled for four decades.
- He was toppled and killed in 2011 in a rebellion assisted by Western military intervention.
- In 2016, following years of conflict, a new UN-backed government was installed in Tripoli.
- Libya borders
- Mediterranean Sea to the north
- Tunisia and Algeria to the west
- Niger and Chad to the south
- Sudan and Egypt to the east.






![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)