Current Affairs August 19, 2023: Arunachaleswarar temple, Landslides, Sanchar Saathi portal, National Policy for Rare Diseases, E-Courts Mission, Hawaii Wildfires, Debt-for-nature swap, Seven Volcanic Summits
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – A&C – Architecture – 2023/08/19} Arunachaleswarar temple
- Context (TH): The State government said that it cannot ban the operation of non-vegetarian hotels along the Girivalam path at Arunachaleswarar temple.
|
- It sated that choice of food is the preference of an individual and no one can interfere with it.
- Arunachalesvara Temple (or Annamalaiyar Temple) is a Hindu temple dedicated to the Lord Shiva.
- It is located at the base of Arunachala hill in the town of Tiruvannamalai in Tamil Nadu, India.
- It is one of the Pancha Bhoota Stalams (temples dedicated to the five elements). It is dedicated to the element of fire (Agni).
- It was built by the Chola dynasty in the 9th century.
- The Arunachaleswarar Temple is renowned for its impressive Dravidian architecture.
Right to Choice of Food (GS2, Polity)
|

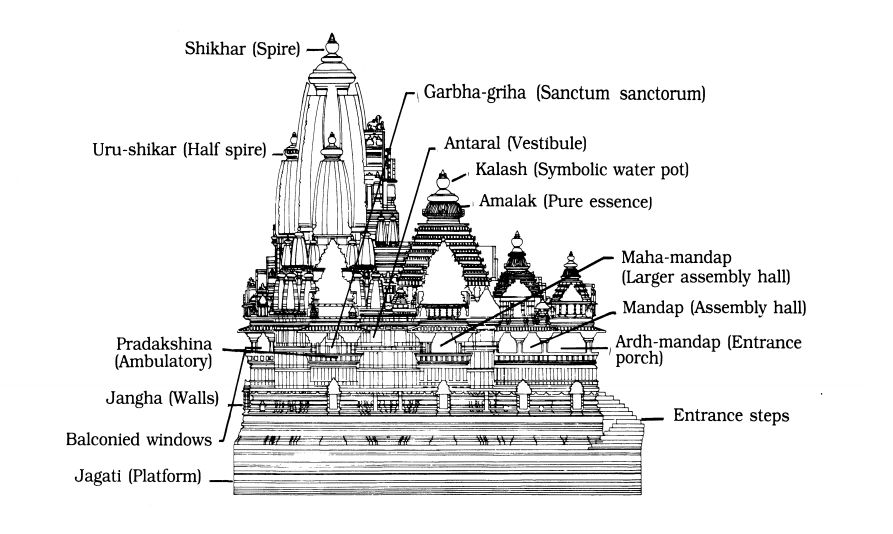
Dravidian Temple Architecture
- Dravidian temple architecture is a Hindu temple architectural style that developed in South India.

Salient Features of Dravidian Temple Architecture
- Panchayatan style: In Panchayatan style, a central shrine surrounded by four subsidiary shrines.
- Compund wall: The Dravidian temple is enclosed within a compound wall (inlike Nagar Style temples).
- Gopurams: The front wall has an entrance gateway in its centre, which is known as a Gopuram. They often rise in multiple tiers.
- Vimana (Shikhara): The vimana is the central and tallest tower of the temple. It typically houses the main deity’s sanctum. It is pyramidal in shape.
- Mandapams: Mandapams are pillared assembly halls used for various ceremonial and religious purposes.
- Garbhagriha (Inner Sanctum): The innermost chamber of the temple is the garbhagriha (or sanctum sanctorum) where the main deity is enshrined. Its entrance is adorned with sculptures of Dwaarpal, Mithun, and Yakshas.
- Antarala: It is a small rectangular hall that connects the assembly hall to the garbhagriha.
- Water Tanks: The presence of a water tank inside the temple enclosure is a distinguishing feature of Dravidian architecture.
- Sculptures and Carvings: Dravidian temples are renowned for their exquisite sculptures and carvings. These carvings depict deities, mythological scenes, dancers, animals, etc.
- Courtyards: Dravidian temples often have spacious courtyards.

Subdivisions of Dravidian Temples
- The subdivisions of Dravidian Temples are basically of five different shapes:
- Kuta or Caturasra: Square
- Shala or Ayatasra: Rectangular
- Gaja-prishta (elephant backed) or Vrittayata: Elliptical
- Vritta: Circular
- Ashtasra: Octagonal
Chola Dynasty (9th – 12th century AD)
- Cholas dynasty established their kingdom in the 9th century after defeating the Pallavas.
- Vijayalaya was the founder of Chola Empire. He was a feudatory of the Pallavas.
- Vijaylaya captured Tanjore in 8th century and this led to establishment of Chola Empire.
- Rajaraja I and Rajendra I are the most celebrated Chola rulers.
- Their rule lasted till they were defeated by the Pandyas in the early 13th century.
- Rajendra III was the last Chola king who was defeated by Jatavarman Sundarapandya II.
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Geomorphology – 2023/08/18} Himachal Landslides Disaster
- Context (TH | TH | NDTV | TH | IE | IE | TH | IE | TH): Heavy rains and cloudbursts in Himachal Pradesh triggered landslides that killed many people and destroyed buildings and infrastructure.


Landslides (GS1, Physical Geography)
- Landslides is a geological event characterized by the rapid movement of a significant amount of soil, rock, and debris down a slope.
- They can range from a small, localized event to large-scale catastroph.
- They are driven by the force of gravity acting on unstable slopes and can be triggered by a variety of factors.
- They are a type of mass wasting, which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.
Factors Triggering Landslides
- Heavy Rainfall: Intense rainfall saturates the soil, reduces its stability and make it more susceptible to sliding.
- Earthquakes: The earthquakes can dislodge soil and rock from slopes, leading to landslides.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanic eruptions can destabilize slopes due to the sudden release of ash, gas, and lava, triggering landslides.
- Human Activities: Construction, excavation, mining, deforestation, and changes in land use can alter the stability of slopes, leading to landslides.
- Erosion: Gradual erosion caused by natural processes (like wind, water, and ice) can weaken slopes over time, eventually resulting in landslide.
- Changes in Water Level: Changes in water level in rivers, lakes, or reservoirs at the base of a slope can exert pressure on the slope, leading to slope failure.
- Undercutting of Slopes: Natural processes or human activities that remove materials from the base of a slope can undermine its stability, causing a landslide.
Types of Landslides
- Fall: Falls are landslides that involve the collapse of rocks or debris from a cliff or steep slope. E.g. rock fall, debris fall.
|

- Slide: A slide-type landslide is a downslope movement of material that occurs along a distinctive rupture or slip surface. E.g., rock slide, debris slide, mud slide.

- Flow: Flows are landslides that involve the movement of material down a slope in the form of a fluid. E.g., debris flow, mud flow.
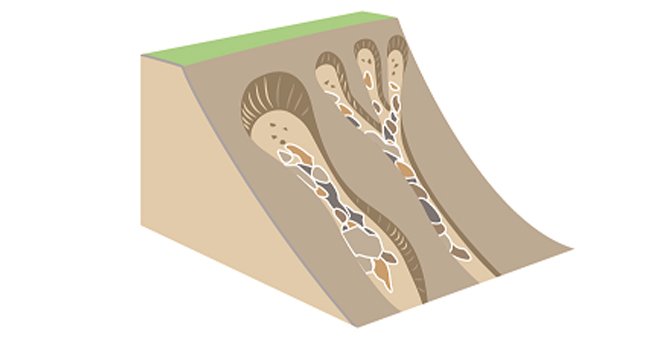
- Topple: Topple involve the forward rotation and movement of a mass of rock, earth or debris out of a slope. This kind of slope failure occurs around an axis (or point) at or near the base.

- Slump: It occurs when a mass of soil or rock rotates and moves downslope along a curved surface.

What is the Cause of Heavy Rainfall which Triggered the Landslides? (GS1, Climatology)
- Heavy rainfall has occurred in Himachal Pradesh due to a surfeit of western disturbances.
- Western disturbances are extratropical storms (low-pressure systems) that originate over the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean and move from west to east.
- They are formed as a result of temperature and pressure contrasts between the mid-latitudes and higher latitudes.
- These weather systems enter the Indian subcontinent from the northwest and bring heavy rainfall, particularly during the winter months.
- They usually peak in winter and are sparse and weaker in warmer months. Their frequency decreases sharply between June and September when the subtropical westerly jet stream migrates northwards.
- But this year there are an unusually high number of western disturbances even during pre monsoon and monsoon.
What is the Reason of Increased Western Disturbances during Monsoon?
- The increased number of western disturbances during monsoon is due to Arctic Warming.
- The Arctic warming causes the polar jet stream to deviate from its regular path and bring the disturbances to north India during the monsoon.
|

What is a Cloudburst? (GS1, Climatology)
- A cloudburst is a localised but intense rainfall activity.
- However, not all instances of very heavy rainfall, are cloudbursts.
- Rainfall of 10 cm or more in an hour over a roughly 10 km x 10 km area is classified as a cloudburst.
- During a cloudburst event, a place receives about 10% of its annual rainfall within an hour.
- While it can occur in plains, the phenomenon is most common in hilly regions.
- In hilly regions, the local topology, wind systems, and temperature gradients between the lower and upper atmosphere facilitate the occurrence of such events.
- Because of the nature of the terrain of hilly regions, cloudbrusts often trigger landslides and flash floods, causing extensive destruction downstream.
Reason Behind the Himachal Disaster Caused by Landslides
- The main reason behind the landslide induced Himachal disaster is unplanned and unscientitic infrastructure development.
- The Himalayan region is a region of young orogeny because of which it has a fragile ecology.
- The young mountains are geologically active and the region has a long history of landslides.
Road Building and Widening
- In recent years, Himachal Pardesh has gone on a road building and widening spree. E.g. Char Dham road building project.
- But unplanned excavation and poorly executed construction are happening while doing so.
- While cutting the mountains, slope stability is not taken into consideration.
- The near-vertical cutting (of the mountains) has destabilised the slopes.
- Vertical cutting means the slope of the mountain gets very close to 90°, whereas, the slope should be less than 60° to maintain slope stability.
|
Way Ahead
- National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) should go for more tunnelling instead of widening the roads.
- The mountains should be cut more scientifically, keeping in consideration of slope stability.
Construction of Buildings
- Large scale construction of buildings is taking place in this Himalayan state due to growing tourism.
- But ill-thought and haphazard constructions practices have increased the vulnerability of the region.
- Unplanned and unauthorised construction has blocked of the natural flow of rivers water resulting in frequent landslides.
- During building constructions also the factor of slope stability is overlooked.
- Moreover, hilly region is over burdened with structures built without any regard for the land’s load-bearing capacity.
- The buildings are constructed with poor drainage system. Due to which drainage water is going into the hills and making them more fragile.
Way Ahead
- The nature of infrastructure development should be scrutanised by concerned authorities.
- If need be, restrictions must also imposed in the larger interest of minimising hazards.
Hydroelectric Projects
- A series of run-of-the-river (RoR) hydropower projects have been pushed in all Himalayan states, despite the region being ecologically fragile.
|
- ROR projects are susceptible to landslides because they involve the construction of diversion channels, which can alter the natural flow of water and make slopes more unstable.
Way Forward
- A proper vulnerability assessment must be done before constructing ROR projects.
- The construction of such projects must strictly adhere to scientific methods.
Other Factors Responsible for the Himachal Disaster Caused by Landslides
- Weak Municipal Laws: The State Municipal Acts in the Indian Himalayan Region state are not very focused on landslide problems. They are not adequate for regulation construction activities.
- Deforestation
- Changes in agriculture crops: Change to crops requiring more intense watering had disturbed the equilibrium of the hills and made it fragile.
- Failure of Early Warning Systems: In Kangra, the EWS failed to alert people of a landslide. Such failures may result in catastrophic events.
Damage to Shimla-Kalka Railway Bridge (GS1, A&C, Architecture)
- Heavy rains and floods have badly damaged the Shimla-Kalka railway bridge near Summer Hill.
- 120-year-old Kalka-Shimla rail track is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The Railways blamed uncontrolled discharge of drains from the highway towards the track by the NHAI and the cutting of slopes for damage.
- The Kalka Shimla Railway was built during the British Raj with an aim to connect by Shimla (the summer capital of British India) with Kalka (which is already accessible from Delhi).
- This narrow-gauge railway line, often called the toy train line, was opened in 1903.
- It was considered the “crown jewel” of the Indian National Railways during British times.

{GS2 – MoCommu – 2023/08/19} Sanchar Saathi portal
- Context (TH): Sanchar Saathi portal is launched to reduce cyber frauds performed through fraudulently acquired SIM cards.
- Sanchar Saathi portal is a citizen-centric initiative of the Department of Telecommunications under the Ministry of Communication to empower mobile subscribers, security and increase awareness.
- It has been to prevent frauds such as identity theft, forged KYC, banking frauds etc.
- The portal allows mobile phone users to:
- Check the connections registered on their names.
- Report fraudulent or unrequired connections.
- Block the mobile phones which are stolen/lost
- Check IMEI genuineness before buying a mobile phone.

The three reforms are being introduced as part of the portal’s framework
- CEIR (Central Equipment Identity Register): It enables the tracking and blocking of lost or stolen phones anywhere in the country.
- Know your mobile connections: It allows users to check the number of mobile connections issued in their name by logging in using their mobile number. This feature helps identify any unauthorized or unwanted connections, which can be blocked immediately.
- ASTR (Artificial Intelligence and Facial Recognition powered Solution for Telecom SIM Subscriber Verification): This AI-based technology facilitates mobile connection analysis and includes features such as IMEI-based phone theft information messaging to law enforcement agencies and the owner.
- It also enables the blocking of any number associated with a particular IMEI and the tracking of stolen mobile devices.
{GS2 – MoHFW – Policy – 2023/08/18} National Policy for Rare Diseases
- Context (TH): Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients and caregivers struggle with multiple issues related to disease.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), (or Lou Gehrig’s disease), is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the motor neurons.
- Motor neurons are a type of the nerve cells (or neurons) in the brain and spinal cord.
- These nerve cells control voluntary muscle movement, such as walking, talking, and eating.
- As the ALS disease progresses, the muscles weakens and leading to paralysis.
- There is no cure for ALS, the average life expectancy after diagnosis of ALS is 3-5 years.
- ALS is qualified to be considered as a rare disease under National Policy for Rare Diseases, 2021.
National Policy for Rare Diseases, 2021 (NPRD 2021)
- NPRD formulated by Ministry of Health and Family Welfare was launched in 2021 for the treatment of rare disease patients.
What is a Rare Disease According to NPRD 2021?
- The average prevalence threshold used by NPRD to define rare diseases is from 1 to 6 in 10,000 people.
|
Salient Features of NPRD 2021
Categoristion of Rare Diseases
- The rare diseases have been identified and categorized into 3 groups namely:
- Group 1: Disorders amenable to one-time curative treatment
- Group-2: Diseases requiring long term/lifelong treatment (but relatively lower cost of treatment)
- Group 3: Diseases for which definitive treatment is available but have challenges like to make optimal patient selection for benefit, very high cost and lifelong therapy.
Centre of Excellence and Nidan Kendras
- Eight Centres of Excellence (CoEs) have been identified for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of rare diseases.
- Five Nidan Kendras have been set up for genetic testing and counselling services.
Financial Support
- Up to Rs. 50 lakhs will be provided to the patients suffering from any category of rare diseases and for treatment in any of the CoE, outside the Umbrella Scheme of Rashtriya Arogaya Nidhi.
- In order to receive financial assistance, the patient may approach the nearest CoE.
Umbrella scheme of Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN)
|
{GS2 – MoL&J – 2023/08/19} E-Courts Mission
- Context (TH): E-courts Mission was launched as part of a National e-Governance Plan to modernise the court system in the country.
- The Mission comes under the “National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of ICT in the Indian Judiciary – 2005” for District & Subordinate Courts.
- The Department of Justice, under the Ministry of Law and Justice with the e-Committee of the SC executes the project.
- With the successful completion of Phase II and the announcement of Phase III, the nation is moving closer to paperless, online courts.
E-committee of SC
|
Phase I (2011-15) E-Courts Mission
- Basic computerisation and local network connectivity were achieved at Rs 639.41 crore.
Phase II (2015-2023)
- Focus on further development with an outlay of Rs 1,670 crore.
- 18,735 district & subordinate courts were computerised in this phase.
Virtual Justice Clock
- It is an initiative to exhibit vital statistics of the justice delivery system at the Court level giving the details of the cases instituted, cases disposed and pendency of cases on a day/week/month basis.
- The effort is to make the functioning of the courts accountable and transparent by sharing with the public the status of case disposals by the court, accessible on the District Court’s website.
JustIS Mobile App 2.0
- It is a tool available to judicial officers for effective court and case management by monitoring the pendency and disposal of not only his court but also individual judges working under them.
- This App is also made available to HC and SC Judges who can now monitor the pendency and disposal of all the States and Districts under their jurisdiction.
Digital Court
- It is an initiative to make the court records available to the judge in digitised form to enable the transition to Paperless Courts.
S3WaaS Websites
- S3WaaS is a cloud service developed for government entities to generate Secure, Scalable & Sugamya (Accessible) S3WaaS websites.
- Its framework helps to manage websites for publishing information related to the district judiciary.
- It is multilingual, citizen-friendly and disability friendly.
Phase III
- The eCourt project has planned Phase III which aims to further ease the justice system by moving towards digital, paperless, and online courts.
- The budget allocation for this phase is Rs 7,000 crore, as announced in Union Budget 2023-2024.


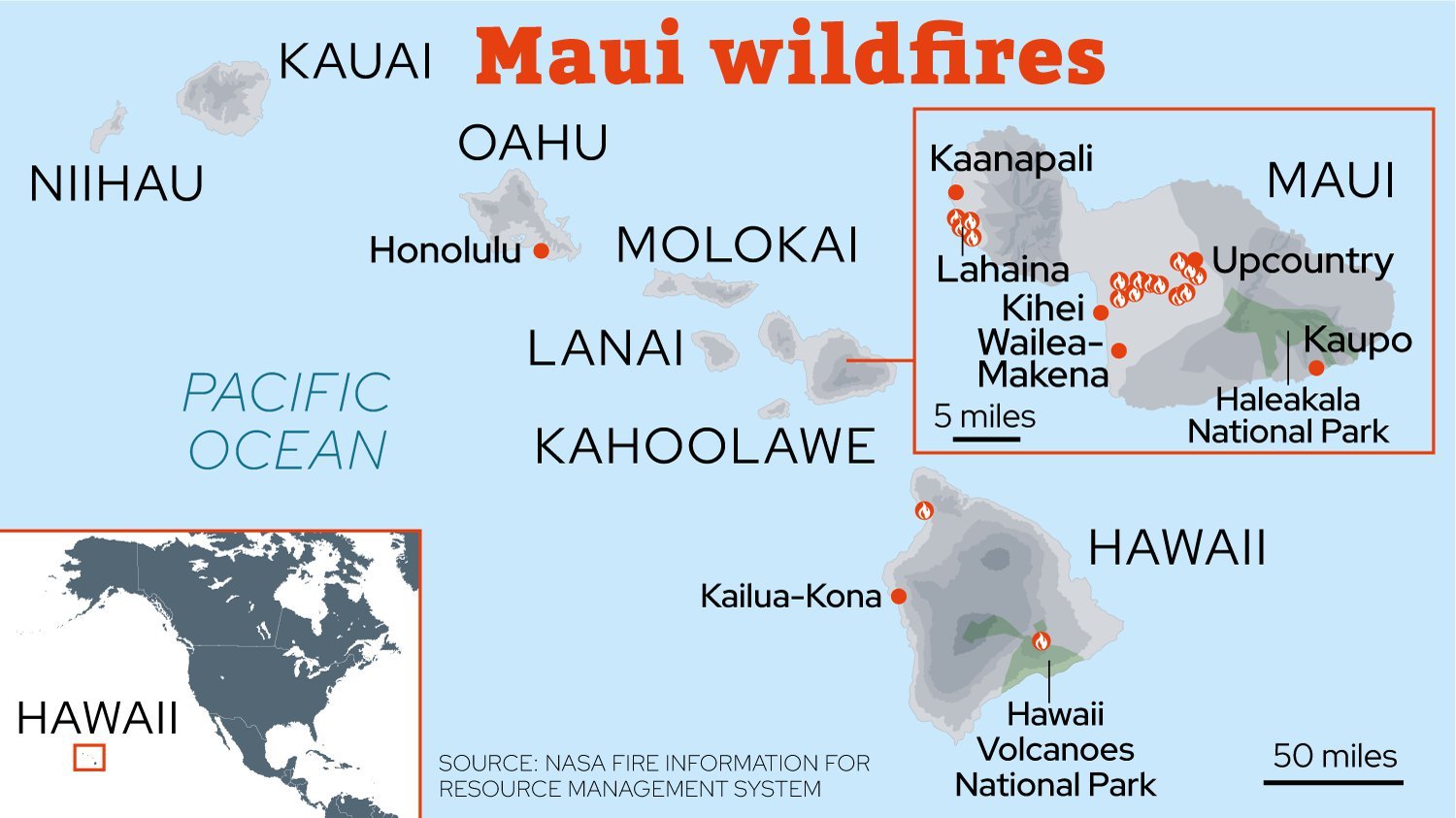
{GS3 – Envi – CC Impact – 2023/08/19} Hawaii Wildfires
- Context (DTE | IE | IE | IE | IE | TH): Large-scale wildfires sweeping the US state of Hawaii have become the deadliest US wildfire in more than a century.
- The most affected region by these wildfires is Maui Island, with significant damage to the town of Lahaina (a site of historical and cultural importance).
- Parts of another island, called Hawaii (or Big Island), have also been burnt by the fire.
Hawaii Islands (USA)
|
Wildfires
- Wildfires (also known as forest fires and bushfires) are uncontrolled fires that spread rapidly through vegetation, including grasslands, forests, and other natural landscapes.
- Wildfire seasons occur during periods when weather conditions are favourable for the ignition and rapid spread of fires. These conditions include hot temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds
Necessity of Wildfires
- Be it natural or human-made, wildfire is a critical part of the ecosystem.
- A healthy wildfire ensures that forests remain robust and resilient as it:
- Aids the natural replenishment of nutrients in the soil
- Helps sunlight reach the forest floors
- Encourages the germination of seeds
Adverse Effects of Wildfires
- The increasingly intense nature of the wildfires is a cause of worry because:
- Loss of biodiversity and habitat destruction: Wildfires destroy or damage natural habitats of species and also kill the species. This lead to a decline in biodiversity.
- Loss of life and property: Wildfires can directly threaten human lives, property, and infrastructure.
- Air pollution: Wildfires release large amounts of smoke and particulate matter, which degrade air quality and pose health risks to nearby communities.
- Increases carbon emission: Wildfires release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This contributes to global warming and climate change.
- Soil Erosion: The removal of vegetation by fire can expose soil to erosion by wind and water.
- Loss of Ecosystem Services: Forests provide various ecosystem services, such as water filtration, flood regulation, and pollination. So, forest loss due to wildfire disrupt these services.
- Invasive Species: After a fire, disturbed areas are vulnerable to colonization by invasive plant species that can outcompete native vegetation and disrupt ecosystem balance.
- Displacement: Communities living in or near fire-prone areas may be forced to evacuate their homes, leading to temporary or permanent displacement.
What has Started the Hawaii Wildfires?
- The reason which has started the wildfires is still under investigation.
- The causes which starts wildfires can be classified into two types:
- Natural Causes: volcanic activity and lightning strikes.
- Humans Causes: campfires, garbage burning, malfunctioning equipment, cigarettes,etc.
Climate Change and Lightning Induced Wildfires
|
How Hawaii Wildfires have become a Catastrophe due to Climate Change?
Drought Conditions
- Maui Island is experiencing severe drought conditions due to climate change.
- Flash droughts which results in rapid drying of moisture from the atmosphere, have aided the spread of the fires.
|
Invasive Species
- Changes in rainfall due to climate change has affected the distribution of plants in Hawaii.
- It has harmed some unique native species such as silversword and helped in the growth of some invasive grass species.
- These invasive grass species are often highly flammable, and provide a lot of fuel for wildfires.
Hurricane Dora
- Climate change is a major factor in the increasing intensity and frequency of hurricanes.
- As the Earth’s atmosphere warms, the oceans also warm, which provides more energy for hurricanes to form and intensify.
- Hurricane Dora was a tropical cyclone that formed in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- Due to the affect of climate change, Hurricane Dora quickly intensified into Category 4 storm.
|

- Hurricane Dora did not hit Hawaii islands.
- Instead, the Hawaii islands were caught between high and low pressure zones due to the hurricane, which resulted in the winds fanning the flames and making these difficult to control.

Other Factors Contributing to Hawaii Wildfires
Rain Shadow Areas
- While Hawaii is home to some of the wettest spots on earth, it also has regions that receive little rain.
- Very steep mountains on each of the main Hawaiian islands block the prevailing NE Trade winds.
- This results in abundant rain on the windward direction and dry rain shadows in the leeward areas.
- Maui’s wildfire infested areas, including Lahaina, are in one of those rain shadows.
Deforestation
- Hawaii islands have lost million acres of native forest, which were natural water and climate regulators, due to development activities and agriculture .
- Due to forest loss, disruptions in weather and temperature patterns are occuring and making the Hawaii islands drier and hotter.
{GS3 – Infra – Bridge – 2023/08/18} Damage to Ram Jhula
- Context (TH): Ram Jhula, the iron suspension bridge, built across Ganga River in Rishikesh, is damaged by floods.
|

- Heavy rains have probably caused soil erosion after which the foundation of the bridge started developing cracks.
- The bridge connects the Sivananda Ashram (Tehri Garhwal district) to Swargashram (Pauri Garhwal district).
- Built in the year 1986, the bridge runs parallel to Laxman Jhula, an older suspension bridge built by the British in 1930 which has been shut since 2022 in view of safety issues.
- The government is constructing Bajrang Setu as an alternative to Laxman Jhula.
{Prelims – Envi – 2023/08/19} Debt-for-nature swap
- Context (DTE): Recently, Gabon announced a $500 million DEBT-FOR-NATURE Swap which is the largest such deal signed by any country.
- Debt-for-nature Swap allows heavily indebted developing countries to seek help from financial institutions in the developed world with paying off their debt if they agree to spend on the conservation of natural resources.
- Debt-for-climate swaps provide benefits for both creditors and debtors:
- Creditors can advance their development cooperation and climate finance goals, improve their chances of debt recovery, and strengthen their diplomatic ties with debtor nations.
- Debtors can reduce their external debt and debt service obligations, allocate fiscal resources towards other development priorities, and promote climate action through domestic investment.

{Prelims – IE – Banking – 2023/08/19} Penal Charges
- Context (IE): The RBI introduced new norms to address the practice of banks and NBFCs using penal interest as a revenue enhancement tool.
- A Penal Charge is an additional charge a lender levies on a borrower in case of delay in payment or default or non-compliance with payment contracts.
What are the key changes in the new norms?
- According to the RBI notification on ‘Fair Lending Practice-Penal Charges in Loan Accounts’, the banks and other lending institutions will not be allowed to levy penal interest (w.e.f. Jan 1, 2024).
- They would levy only penal charges in case of defaults or non-compliance by the borrower with the terms on which credit facilities were sanctioned.
{Prelims – World PIN – 2023/08/18} Seven Volcanic Summits
- Context (TH): Alappuzha woman on a mission to climb Seven Volcanic Summits.
- Seven Volcanic Summits are the highest volcanoes on each of the seven continents.
Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa (5,895 m)
- A dormant stratovolcano located in Tanzania.
- Its three volcanic cones: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira.
- Highest mountain in Africa.
- Highest single free-standing mountain above sea level in the world.
- Highest volcano in Africa and the Eastern Hemisphere.
- Kilimanjaro National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Ojos del Salado, South America (6,893 m)
- An active stratovolcano located on the border between Chile and Argentina.
- Highest peak in both countries.
- Highest volcano in the world.

Pico de Orizaba (Citlaltépetl), North America (5,636 m)
- An active stratovolcano.
- Highest mountain in Mexico.
- Third highest mountain North America.

Mount Elbrus, Europe (5,642 m)
- A dormant stratovolcano.
- Highest peak in Russia and Europe.
- Highest peak of the Caucasus Mountains.
- Highest stratovolcano in Eurasia.

Mount Damavand, Asia (5,671 m)
- A dormant stratovolcano.
- Located near the Caspian Sea.
- Highest peak in Iran.
- Second highest volcano in the Eastern Hemisphere.

Mount Giluwe, Australia (4,367 m)
- A extinct stratovolcano.
- Second highest peak in Papua New Guinea.

Mount Sidley, Antarctica (4,285 m)
- A dormant shield volcano
What is a Stratovolcano?
Shield volcano
|
{Prelims – World PIN – SA – 2023/08/19} Ecuador
- Context (BBC): Candidate in Ecuador’s presidential election Fernando Villavicencio was shot dead. He was campaigning against corruption and gangs in Ecuador.
- Ecuador occupies part of the Andes mountains and part of the Amazon basin.
- It is situated on the Equator, from which its name derives.
- It borders:
- Colombia to the north
- Peru to the east and the south
- Pacific Ocean to the west.

- The country is divided into four main regions:
- Sierra (Andes highlands)
- Costa (coastal lowlands)
- Oriente (Amazon Rainforest)
- Galápagos Islands (volcanic islands)
- Its capital city is Quito. Quito’s historic centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is known for its well-preserved colonial architecture.
- It official language is Spanish.
- The country is one of the world’s largest exporters of bananas and shrimp.
- Ecuador has experienced periods of political instability and changes in government.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)