Current Affairs January 13, 2024: Classical Languages, Antibiotic Resistance, Anti-Defection Law and 10th Schedule of IC, Swachh Survekshan Awards, 2023, SAMBHAV (Secure Army Mobile Bharat Version)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – A&C – Languages} Classical Languages
- Context (TH): WB CM requests PM to recognize ‘Bengali’ as a classical language officially.
- As per scientific research by the State team, Bengali’s origins 2,500 years ago.
- Bengali is the 2nd most spoken language in India (after Hindi) and the 7th most spoken language globally.
Classical Language
- It is a language with original, independent literary tradition and a large body of ancient written literature.
- India recognizes six classical languages: Tamil (declared in 2004), Sanskrit (2005), Kannada (2008), Telugu (2008), Malayalam (2013) and Odia (2014).
- All the Classical Languages are listed in the Eighth Schedule of the IC.
Criteria for declaring a language as ‘Classical’
- The Ministry of Culture provides guidelines regarding Classical languages. They are:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over 1500-2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts is considered a valuable heritage by generations of speakers.
- The literary tradition should be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
- Classical language and literature are distinct from modern, but there may also be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or offshoots.
Benefits of being a Classical Language
- The Ministry of Education provides specific benefits to promote the classical languages:
- Two major annual international awards for scholars of eminence in classical Indian languages.
- Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages.
- The University Grants Commission is requested to create several professional chairs for classical languages in the Central Universities.
{GS2 – IR – Africa} Emergency in Ecuador
- Context (IE): The Ecuadorian President recently announced a 60-day nationwide emergency.
- The drastic measures come as authorities scramble to recapture the fugitive drug leader.
Ecuador
- Ecuador is in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west.
- The country’s capital is Quito, but its largest city is Guayaquil – the centre for drug violence.
- Its landscapes include the Amazon jungle, Andean highlands, and the wildlife-rich Galápagos Islands.
- Ecuador’s role in the drug trade dates back to the 1980s, when it was a transit route for Peruvian coca base trafficked into Colombia.
Ecuador and its drug war
- After Colombia – Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia or FARC peace accord (2020), the group’s control of cocaine trafficking ended.
- With the resulting power vacuum, the networks began moving to Ecuador.
- Two neighbouring cocaine producers – Colombia and Peru – have contributed to the country becoming a central shipment point for the drug.
- The COVID-19 pandemic then added to economic woes, making the situation ripe for young and unemployed people to become involved in the drug war.
- Recently, Adolfo Macías Villamar, the leader of the Los Choneros criminal gang, disappeared from the prison where he was serving a 34-year sentence; violence has risen after that.
Adolfo Macías Villamar
|
Government steps
- Ecuador’s new President, Daniel Noboa, started the “Phoenix Plan” to counter the drug menace.
- The $800 Mn plan will include a new intelligence unit, tactical weapons for security forces, new high-security prisons and reinforced security at ports and airports, with U.S. support.
- Noboa declared a 60-day state of emergency – enabling military patrols, including in prisons, and setting a national nighttime curfew.
{GS2 – IR – India-USA} India-US Trade Policy Meeting
- Context (IE): India and the US are set to take up some sticky trade issues in the upcoming meeting.
Significance of meet
- The US is India’s single largest trade partner and has a trade balance favourable to India.
- India is also banking on the US-led Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) trade pact to counter China’s influence on trade in Asia.
- US firms adopting China plus one policy and the ongoing supply chain reset, India can attract more foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Such trade policy forum meetings are crucial without an India-US free trade agreement (FTA).
Issues at the table
Generalised System of Preferences (GSP)
- India lost GSP benefits in 2019 during the protectionist policy of the US.
- Before that, India was the largest beneficiary of the GSP policy.
|
India’s laptop policy
- After the “monitoring system” replaced the “ban” on laptop import, the US has raised the issue.
- Such measures are seen as “non-tariff measures”.
- Although India has said that the aim is to ensure that the IT products come from “trusted geographies”.
Visa and immigration
- India is seeking a liberal visa regime to boost service trade.
- Visa delays for Indians surged to record levels during Covid-19.
Totalisation agreement
- Totalisation agreement will provide social security to Indian professionals in the US.
- It will eliminate dual social security deductions in India and the US.
{GS2 – IR – Middle East} US and the UK Strikes on Houthis

- Australia, Bahrain, Canada, and the Netherlands supported the strikes.
- Since November 2023, the Houthis have attacked ships in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden.
- Attacks are to protest the Israeli military’s continuing bombardment of Gaza.
- Strikes are a direct response to the “Houthi attacks against international maritime vessels.
- Last month, the US launched Operation Prosperity Guardian, a coalition of more than 20 countries committed to maritime security in the region.
- However, many partner countries were reluctant to send military ships or personnel in large numbers to the region to avoid the escalation of conflict.
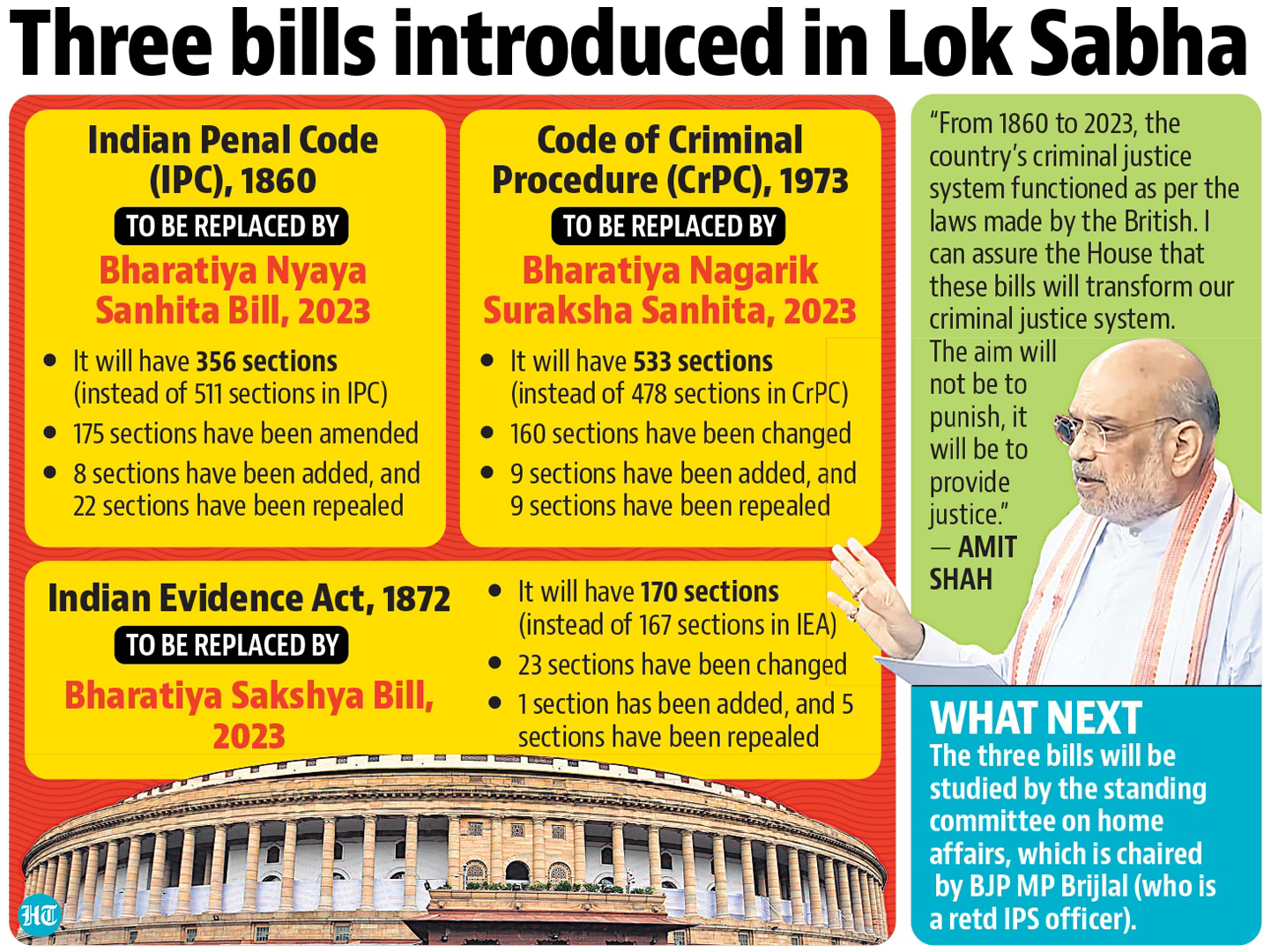
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Parliament} Anti-Defection Law and 10th Schedule of IC
- Context (HT I TH I LL): The Maharashtra Legislative Assembly Speaker has refused to disqualify 16 MLAs of the Eknath Shinde faction and declared the Shinde faction real Shiv Sena.
- The 10th Schedule of the IC gives the power of adjudication to the Speaker, a political appointee.
- The Presiding officer functions as a tribunal while adjudicating disqualification issues; this has been under question for a long time.
Anti-defection law
- It lays down the process by which legislators may be disqualified on the grounds of defection based on a petition by any other member of the House.
- The decision regarding disqualification is referred to the Chairman or the Speaker of such House, and their decision is final.
- The law applies to both Parliament and State Assemblies.
Defection
Defector
|
Relation between Anti-Defection Law and the 10th Schedule
- The 52nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1985, was brought in the name of the ‘Anti-Defection Bill’ and inserted the 10th Schedule in the IC.
- This Act Amended Articles 101, 102, 190 and 191 of the IC regarding vacation of seats and disqualification from membership of Parliament and State legislatures.
- These articles are for the disqualification of MPs under Article 102(2) and MLAs under Article 191(2).
History of the 10th Schedule
|
Features of Anti-Defection Law
Grounds for Disqualification
- If the Legislator voluntarily gives up their membership of a Political Party.
- If The Legislator voluntarily joins any other Political Party.
- Violation of Instructions: If the legislator votes or abstains from voting in the House contrary to a direction issued by the political party he belongs to, they are deemed disqualified.
- An Independent legislator can be disqualified if they join a political party.
- A nominated legislator will be disqualified if they join any political party six months after the day they become a legislator.
-
Exceptions under the Law
- The law allows a party to merge with another party if at least two-thirds of the party’s legislators favour such a merger.
- Neither the members who decide to merge nor those who stay in the original party will face disqualification.
- The law exempts the presiding officer of the House (speaker, chairman, and deputy chairman) who voluntarily gives up their party membership or rejoins it after they cease to hold that office.
- This exemption has been provided, given the dignity and impartiality of the office.
- Anti-defection laws do not apply to violations of party whips during presidential polls.
- The law allows a party to merge with another party if at least two-thirds of the party’s legislators favour such a merger.
Whip
|
Powers to disqualify
- The Chairman or the Speaker of the House decides to disqualify a member.
- If a complaint is received concerning the defection of the Chairman or Speaker, a member of the House elected by that House shall take the decision.
-
Role of Speaker as Quasi-Judicial Authority
- The decision of the presiding officer is subject to the Judicial Review.
- The law initially stated that the decision of the Presiding Officer is not subject to judicial review.
- Kihota Hollohon vs. Zachilhu and Others (1992): SC held that the office of the Speaker is a quasi-judicial authority whose decisions are amenable to judicial review.
- It is also incumbent upon the Speaker of the House to follow the principles of natural justice while adjudicating proceedings under the 10th Schedule.
- However, it held that there may not be any judicial intervention until the Presiding Officer gives his order.
- Shrimanth Balasaheb Patil vs Honble Speaker Karnataka (2019): SC laid down grounds for review of the decision of the speaker-
- If it violates constitutional mandate.
- If it is made in a mala fide way.
- If the decision of the speaker is perverse.
- If it is non-compliance with the rules of natural justice.
- The decision of the presiding officer is subject to the Judicial Review.
-
Changes after the 91st Constitution Amendment Act, 2003
- The provision about exemption from disqualification in case of a split by one-third of legislature party members was deleted. (Only a Merger was possible; a Split was not possible).
- Earlier, a defection by one-third of the elected members of a political party was considered a ‘merger’. The amendment changed it to at least two-thirds.
- It limited the size of the Council of Ministers to debar defectors from holding public offices and preventing defecting legislators from joining the Council of Ministers until their re-election.
- An MP/MLA disqualified for being a member under the 10th Schedule shall also be disqualified from being appointed as a Minister
- From the date of their disqualification till the expiry of the membership of Parliament/Assembly,
- If they contest any election to Parliament/Assembly before the expiry of such period, till the date they are elected.
Number of Council of Ministers at Union & State Level After 91st CAA, 2003.)
|
Need of law
- Subversion of electoral mandates: Defection is the subversion of electoral mandates by legislators due to the lure of ministerial berths or financial gains.
- Affects the normal functioning of government: The defection leads to instability in the government and affects the administration.
- Promotes horse-trading: Defection also promotes horse-trading of legislators, which goes against the mandate of a democratic setup.
Significance of the Law
- It prevents defections motivated by the lure of office, material advantages, or other considerations.
- It made legislators liable to be penalised for their conduct inside (voting against the party’s whip) and outside (making speeches, etc.) the legislature.
- It maintains stability in the party system and prevents the threat of toppling the governments.
- It promotes party discipline by ensuring the legislators vote for the party whip.
- It permits the merger of political parties without disqualification of members.
- It strengthens the institution of democracy and keeps corruption in check.
Various Supreme Court Judgments on Anti-defection Law
Kihota Hollohon vs. Zachilhu and Others (1992)
- Issue: If the 10th schedule curtails the freedom of speech and expression and subverts the democratic rights of the elected members in parliament and state legislatures.
- SC Judgement: The 10th schedule neither impinges upon the freedom of speech and expression nor subverts the democratic rights of elected members and is thus constitutionally valid.
- Issue: Is paragraph 7 of the Schedule barring the jurisdiction of courts in disqualification cases constitutional?
- SC Judgement: The paragraph seeks to change the operation and effect of Articles 136, 226 and 227 of the IC, which gives the HCs and SCs jurisdiction in such cases.
- Any such provision is required to be ratified by state legislatures as per Article 368(2).
- Issue: Is paragraph 6 of 10th Schedule granting finality to the decision of the Speaker/ Chairman valid?
- SC Judgement: To the extent that the provisions grant finality to the orders of the Speaker, the provision is valid.
- However, the HCs and the SCs can exercise judicial review under the IC.
Dr. Kashinath G Jhalmi vs Speaker, Goa Legislative Assembly (1993)
- Issue: Can a Speaker review his decision to disqualify a member under the Tenth Schedule?
- SC Judgement: The Speaker of a House does not have the power to review his decisions to disqualify a candidate. Such power is not provided under the Schedule or implicit in the provisions.
G. Vishwanathan v. Speaker, Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly (1996)
- Issue: If a member is expelled from an old party and joins another party after being expelled, will it be considered to have voluntarily given up his membership?
- SC Judgement: Once a member is expelled, he is treated as unattached in the house but continues to be a member of the old party as per the 10th Schedule.
- Joining a new party after expulsion amounts to voluntarily giving up membership of his old party.
Ravi S Naik v. Union of India AIR 1994
- Issue: Does judicial review by courts extend to rules framed under the Tenth Schedule?
- SC Judgement: Rules under the Tenth Schedule are procedural. Any violation of those would be a procedural irregularity. Procedural irregularity is immune from judicial scrutiny.
- Issue: If only resignation constitutes “voluntarily giving up” political party membership.
- SC Judgement: There is a broader meaning of “voluntarily giving up membership”. The inference can also be drawn from the conduct of the members.
Rajendra Singh Rana and Ors. vs. Swami Prasad Maurya and Ors. (2007)
- Issue: When can a court review the Speaker’s decision-making process under the Tenth Schedule?
- SC Judgement: If the Speaker fails to act on a complaint or accepts claims of splits or mergers without making a finding, he fails to act as per the Tenth Schedule.
- Ignoring a petition for disqualification is not just an irregularity but a violation of constitutional duties.
Keisham Meghachandra Singh vs. the Hon’ble Speaker Manipur Legislative Assembly & Ors. (2020)
- Issue: Do courts have the power to direct speakers to decide petitions seeking disqualification within a fixed time frame?
- SC Judgement: The Speaker should decide 10th Schedule disqualifications within a “reasonable period”.
- ‘Reasonableness’ would depend on the facts of each case, and Unless there are “exceptional circumstances”, disqualification petitions under the 10th Schedule should be decided within three months.
Various Decisions by the Presiding Officers
- Issue: Does public criticism of one’s political party amount to defection?
- Decision of the Presiding Officer: The Speaker held that a person getting elected as a political party candidate also gets elected because of the party’s programs.
- If the person leaves the party, he should return before the electorate.
- Issue: Can stories in print or electronic media be taken as evidence of defection?
- Decision of the Presiding Officer: There is no reason why news clippings and stories in the media would be untruthful.
Drawbacks of Anti-Defection Law
- By preventing parliamentarians from changing parties, it reduces the accountability of the government to the Parliament and the people.
- It emphasises the government’s stability more than ensuring its accountability, which is the crucial feature of Parliamentary Democracy.
- The Law dilutes the separation of powers between the Executive and the Legislature – and centralises power in the hands of the cabinet.
- The law has also been criticised because it infringes on members’ elemental powers, privileges and immunities in exercising their freedom of speech and action, including voting.
- The law does not specify a period for the Presiding Officer to decide on a disqualification plea.
- The role of a presiding officer as an adjudicator is questionable, given they are a political nominee.
- The incumbent’s challengers do not anticipate by-elections – and as a result, the incumbent candidate has a clear head start.
Various Recommendations to Overcome the Drawbacks
Dinesh Goswami Committee on Electoral Reforms,1990
- Disqualification should be limited to the following cases:
- A member voluntarily gives up the membership of his political party
- A member abstains from voting or votes contrary to the party whip in a vote of confidence or motion of no-confidence.
- Political parties could issue whips only when the government was in danger.
- The President/Governor should decide on the Election Commission’s (EC) advice on disqualification.
Halim Committee on Anti-defection Law, 1998
- The words ‘voluntarily giving up’ political party membership’ be comprehensively defined.
- Restrictions like the prohibition on joining another party or holding offices in the government be imposed on expelled members.
- The term political party should be defined clearly.
Law Commission 170th Report, 1999
- Provisions that exempt splits and mergers from disqualification are to be deleted.
- Pre-poll electoral fronts should be treated as political parties under anti-defection.
- Political parties should limit the issuance of whips to instances only when the government is in danger.
Election Commission
- President/Governor should make decisions under the Tenth Schedule on the binding advice of the EC.
NCRWC/Venkatchalliah Committee, 2002
- Defectors should be barred from holding public office or any remunerative political post for the remaining term.
- The vote cast by a defector to topple a government should be treated as invalid.
- ‘Block vote’ proposal to correct lacunae in the concept and implementation of the anti-defection law.
- A group of parties registering itself as a pre-election coalition shall have one block vote during the term of the House.
- Deletion of the 10th Schedule provision regarding exemption from disqualification in case of a split.
SC, 2020
- Speakers, members of a particular political party, and insiders in the House should not be the “sole and final arbiter” in disqualification cases.
- The SC suggested amending the IC to redefine the Speaker’s role as a quasi-judicial authority in handling disqualification petitions under the anti-defection law.
- A mechanism outside Parliament or Legislative Assemblies should adjudicate disqualification petitions under the 10th schedule.
- A permanent tribunal headed by a retired SC judge or a former HC CJ as a new mechanism.
Issue related to the Merger of Political Parties
-
P.D.T Achary
- There should be a merger between two original political parties.
- 2/3rd of the house members belonging to that party should accept the merger.
- If 2/3rd of the members do not accept it, then the merger doesn’t happen as per the law.
Subhash Kashyap
- Party that sets up candidates for the election is the party that has to merge under the 10th Schedule.
- 2/3rd MLAs of that party should agree to the merger.
Faizan Mustafa
- Disagreed and questioned the concept of a merger between the two original parties.
- He emphasised the significance of the Legislature Party, which is defined as a ‘group consisting of all the members of that House’, As per the definition in the 10th Schedule.
- The merger has to be seen “locally” and not at the national level, and nowhere does the Tenth Schedule talk about how a ‘national party’ or a ‘regional party’ should split.
Previous Similar case
- In 2019, the Vice President (RS Presiding Officer) issued orders to “merge” the Telugu Desam Party (TDP) with the ruling BJP in Rajya Sabha after four of TDP’s five MPs defected.
- TDP argued that a “merger” can only occur at the party’s organisational level, not in the House.
Regulation of defection in some countries
- Bangladesh: A member shall vacate his seat if he resigns from or votes against the directions given by his party. The Speaker refers the dispute to the Election Commission.
- Kenya: A member who resigns from his party has to vacate his seat. The Speaker decides, and the member may appeal to the High Court.
- Singapore: A member must vacate his seat if he resigns or is expelled from his party. Parliament decides on any question relating to the disqualification of a member.
- South Africa: The Constitution provides that a member loses membership of the Parliament if he ceases to be a member of the party that nominated him.
- USA, UK, Australia, Canada: No law on Defection.
- Several democracies have not adopted an anti-defection law, even though legislators often switch to the other side.
- In the U.K., Australia and the U.S., parliamentarians and senators often take positions contrary to their parties or vote against the party’s view yet continue within the same party.
{GS2 – Social Sector – Health – Issues} Antibiotic Resistance
- Context (TH): Development of new drugs to tackle Antibiotic resistance.
- Zosurabalpin: It offers a potential new way to tackle drug-resistant Acinetobacter infections.
- Wockhardt’s cefepime-zidebactam: It is India based and is currently in international Phase 3 trials.
- Cefiderocol: Developed by a Japanese firm, already approved for use in various countries.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobials include antibiotics, antiviral, antifungal & anti-parasitic medication.
- Antimicrobial resistance is defined as a microorganism’s resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism.
- For example, in Multi-Drug Resistant TB (MDR-TB), the TB bacteria are resistant to two of the essential TB drugs, isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RMP).
Causative Factors behind AMR
- Microorganisms can develop resistance and become Superbugs mainly in two ways:
- Intrinsic resistance: It refers to the inherent resistance of certain bacteria to specific antibiotics.
- Acquired resistance: It refers to the resistance developed in bacteria due to genetic mutation.
Causes behind Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance
- Overuse and improper use of antimicrobials.
- Greater access to over-the-counter antibiotic drugs in developing countries.
- Using broad-spectrum antibiotics over narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Inadequate dumping of pharmaceutical industry effluents.
- Antibiotic use in livestock feed.

Suggestions to Improve India’s fight against AMR
- Provide a supportive environment for startups: E.g. Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine was developed by the relatively small German startup BioNTech.
- Development of advanced rapid diagnostics: Prompt and precise detection of infections is essential for curbing the spread of resistant microbes.
- Cultivating indigenous phage therapies: India imports high-quality phages from Eastern Europe.
- We need to channel our efforts into developing new, innovative vaccines such as therapeutic vaccines. These are designed to prevent the recurrence of infections.
- Need to prioritise infection control strategies.
- A vast majority of our hospitals lack the requisite policies, committees, and expertise for effectively preventing drug-resistant infection transmission to patients.
- Prescribe antibiotics only when needed and in the right doses. Overusing and misusing antibiotics in humans, livestock, and crops are the main reasons for antimicrobial resistance.
Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP)
|
{Prelims – Awards} Swachh Survekshan Awards, 2023achh
- Context (IE): The President conferred the Swachh Survekshan Awards, 2023 in New Delhi.
- Indore and Surat were jointly awarded the title of the cleanest city.
- Indore achieved the top rank for the seventh consecutive time.
Swachh Survekshan Awards
- It is the world’s largest urban sanitation and cleanliness survey conducted annually.
- It was launched in 2016 as part of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (a nationwide cleanliness campaign).
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) with Quality Council of India (QCI) as its implementation partner.
- Objective: Encourage citizen participation & create awareness amongst all sections of society about the importance of working together towards making towns and cities better places to reside in.
- Theme of 2023: Waste to Wealth”; for 2024, the theme is: “Reduce, Reuse and Recycle”.
- Criteria for rankings:
- Door-to-door collection of waste,
- Segregation at source,
- Cleanliness of public areas,
- Clean water bodies,
- Citizens’ feedback regarding the cleanliness of their cities.
Swachh Survekshan Awards, 2023

What other Cities can learn from Indore?
Focus on sustainable sanitation systems
- Nagar Nigam took over the waste collection process, terminating the private contracts.
- NGOs created awareness about garbage disposal directly to municipality vehicles.
Handling Legacy Waste
- Clearing and treating nearly 13 lakh metric tonnes of legacy waste in about six months.
Infrastructure Development
- Nagar Nigam started converting wet waste into compost and built a treatment plant for dry waste.
Addressing Open Defecation
- NGOs constructed single-household or community toilets in areas in need of urinals ad toilets.
- They also distributed 1,000 accessible dustbins to vehicle owners to discourage littering.
Community Engagement and Awareness
- Administering the cleanliness oath to over four lakh people.
- Issuance of spot fines against people spitting, urinating in public, or littering.
- Public shaming through the publication of offenders’ names in newspapers & broadcasting over radio.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} Indian Army Year of Technology Absorption 2024
- Context (HB): The Indian Army will observe 2024 as the “Year of Technology Absorption”.
- This theme underscores commitment to leveraging technology as a transformative change catalyst.
- It will aim to induct drones and counter-drone systems across infantry, artillery and armoured battalions.
- It will also establish Command Cyber Operations Support Wings (CCOSWs), besides bridging other conventional asymmetries.
Command Cyber Operations Support Wings (CCOSWs)
|
- The Army has identified 355 Army posts to enable 4G connectivity with the telecom ministry.
- The process of replacing animals with drones is also under process.
- The Indian Army is targeting to have 1 lakh drones by 2027.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} SAMBHAV (Secure Army Mobile Bharat Version)
- The ecosystem SAMBHAV operates on state-of-the-art contemporary 5G technology.
- SAMBHAV will have multi-layered encryption with a pan-India secure ecosystem.
- It will ride on a commercial network with inherent security.
- This leverages the potential of indigenous public cellular networks in the country.
- This aligns with the government of India’s efforts towards “dual-use infrastructure”.
- It also manifests “civil-military fusion” in emerging technology.
- This step marks a significant step towards Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- It will secure defence communication from eavesdropping on conventional mobile networks.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)