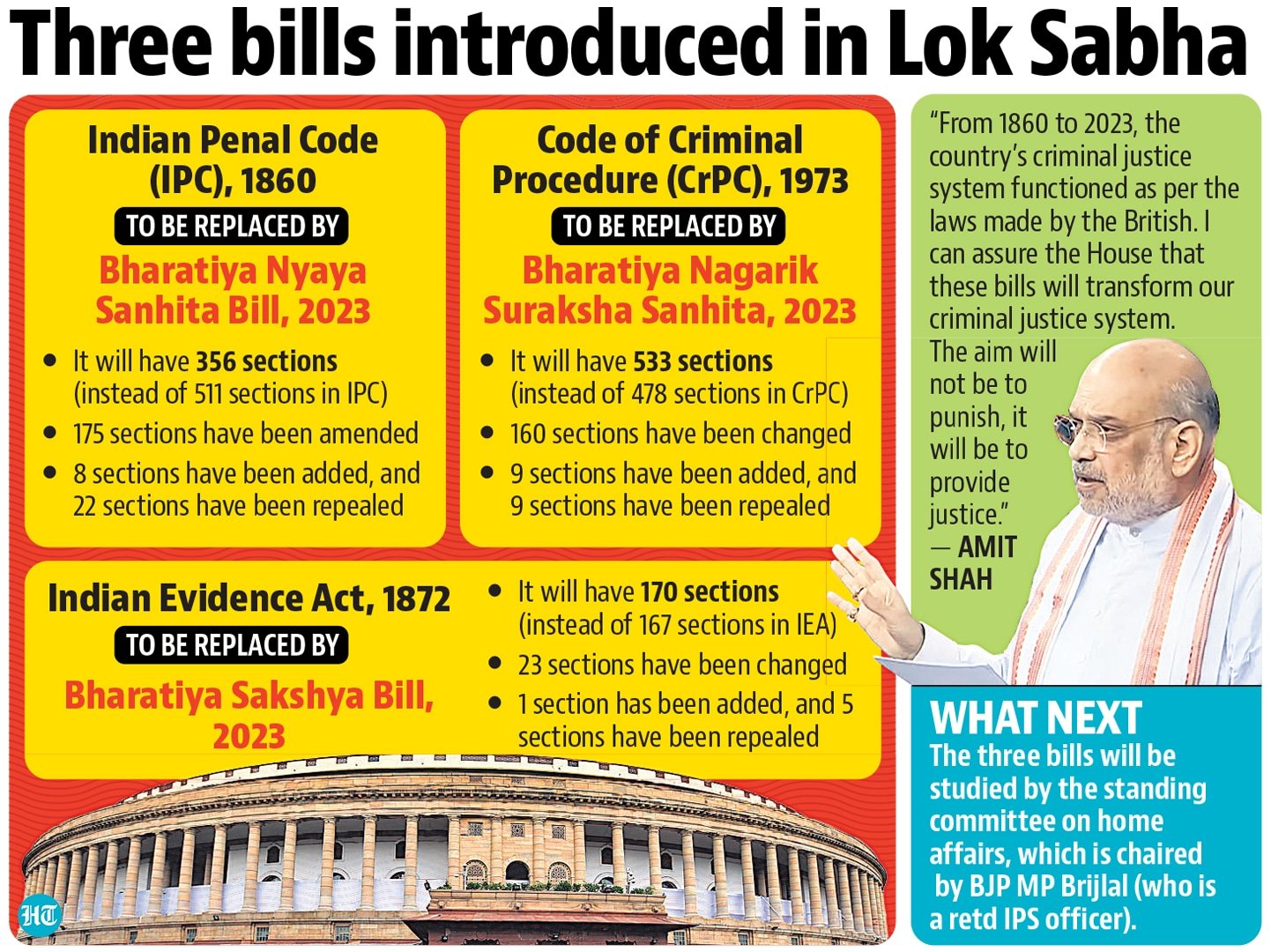
Current Affair July 21, 2023: Prevention of Sexual Harassment (PoSH) Act, India Climate Energy Dashboard, NATO, Nai Manzil, National Biopharma Mission
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Empowerment – 2023/07/21} Prevention of Sexual Harassment (PoSH) Act
- Context (PIB): Provisions of the POSH Act, 2013 apply to all National Sports Federations (NSFs), says the Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports.
- Prevention of Sexual Harassment (PoSH) Act or Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act was enacted in 2013 to implement the Vishakha guideline.
- It defines sexual harassment in the workplace and creates a mechanism to redress complaints.
- The PoSH Act defines sexual harassment to include unwelcome acts such as physical contact and sexual advances, a demand or request for sexual favours, making sexually coloured remarks, showing pornography, and any other unwelcome physical, verbal, or non-verbal conduct of a sexual nature.
- It covers concepts of quid pro quo (a favour or advantage granted in return for something) harassment and hostile work environment as a form of sexual harassment if they occur in connection with the act.
Safeguard mechanisms
Internal Complaints Committee (ICC)
- The law requires any employer with over ten employees to form an ICC.
- Any woman employee can approach ICC and file a formal sexual harassment complaint.
- ICC has to be headed by a woman, have at least two women employees, another employee, and a third party such as an NGO worker with five years of experience, familiar with the challenges of sexual harassment.
Local Area Committee (LAC)
- The Act mandates every district in the country to create a Local Area Committee (LAC) to receive complaints from women working in firms with less than ten employees and from the informal sector, including domestic workers, home-based workers, voluntary government social workers and so on.

Lacunae
- PoSH act is not Gender Neutral. Men also face Sexual harassment, but POSH Act protects only women. Therefore, the safeguards under the POSH Act do not apply to ‘men victims’.
Vishaka Guidelines
SHe-Box
|
{GS2 – Envi – RE – 2023/07/21} India Climate Energy Dashboard (ICED)
- Context (PIB): NITI Aayog released the India Climate Energy Dashboard (ICED) 3.0.
- ICED is NITI Aayog’s flagship initiative developed in association with the Vasudha Foundation.
- It provides access to datasets (since 2005) for climate and energy-related modelling and research.
- The platform analyses India’s energy, climate, and economic aspects.
- It supports decision-making to help India transition to clean energy.



{GS2 – IR – Grouping – 2023/07/21} NATO Summit 2023
- Context (TH): 2023 NATO summit was held in Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. The highlights include:
- Creation of NATO-Ukraine Council
- Inclusion of Finland
- Changing stance of the USA

North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- NATO is a political and military alliance created in the aftermath of World War II by 12 countries from Europe and North America in 1949.
- The Washington Treaty (North Atlantic Treaty) forms the basis of NATO.
- The headquarters of NATO is in Brussels, Belgium, while the Allied Command Operations headquarters is near Mons, Belgium.
- During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union (USSR).
- The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact.
Functioning
- North Atlantic Council is NATO’s principal political decision-making body.
- The principle of collective defence (an attack against one Ally is an attack against all) is enshrined in Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty, which commits NATO members to mutual defence.
Member States


- Currently, NATO comprises 31 countries (29 European + 2 North American).
- NATO makes its decisions by consensus. Hence, if a new country wants to join NATO, it must be supported by all other members. Any of its member countries can veto a new member.
- For example, Turkey opposes Sweden’s wish to join NATO due to its alleged support of Kurdish militants.
Post-Cold War Era
- When the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, questions were raised about NATO’s relevance and future.
- NATO succeeded in refashioning from collective defence to collective security.
- It has been a mutually beneficial arrangement, offering security to Europe at a low price.
- For the U.S., NATO has been an ideal vehicle for power projection worldwide.
- NATO has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa.
Warsaw pact
Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO)
|
NATO Summit 2023
NATO-Ukraine Council
- It replaced the NATO-Ukraine Commission.
- It is a joint body where NATO Allies and Ukraine participate as equals.
- It provides for joint consultations, decision-making and activities.
- It also serves as a crisis consultation mechanism between NATO and Ukraine.
The inclusion of Finland and approval of Sweden as NATO members
- Turkey previously opposed Sweden and Finland joining NATO because of their alleged support for Kurdish militants. Now, Turkey has changed its stance and no longer holds that opposition.
USA’s stance on NATO
- At the summit, President Biden strongly supported NATO and Ukraine.
- This is significant because President Trump had a different approach and considered leaving NATO.
{GS2 – MoCI – 2023/07/21} Government e-Marketplace (GeM)
- Context (PIB): Coal Ministry bags the “Best Engagement” Award for Procurement through GeM Portal.
- Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is the Public Procurement Portal for procuring goods and services for all Central and State Government Ministries, Departments, Public Sector Units (PSUs), etc.
- It was launched in 2016 to bring transparency and efficiency to the government buying process.
- It is a 100 per cent GoI-owned company set up under the aegis of the Ministry of Commerce.
- In 2017, GoI made it mandatory for all ministries to procure goods/services from the GeM.
Advantages of GeM
- Increased Public Savings: An independent assessment by the World Bank reported that GeM enabled an average savings of 9.75% on the median price between February 2019 and January 2020.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat: In 2020, GeM made it mandatory for sellers to enter the Country of Origin while registering products on GeM to promote ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
- Enabling MSMEs to Scale Up: The portal allows MSMEs to scale up their business and increase sales.
{GS2 – MoMA – 2023/07/21} Nai Manzil Scheme
- Context (PIB): The Ministry of Minority Affairs implements various schemes for the socio-economic and educational empowerment of the six centrally notified minority communities.
- Nai Manzil Scheme was launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- The scheme is supported by the World Bank.
- The scheme aims to benefit the minority youths who do not have a formal school leaving certificate, i.e., school dropouts or those educated in community education institutions like Madarsas.
- It aims to provide them with formal education and skills to seek employment in the organised sector.
|
{GS2 – MoST – 2023/07/21} National Biopharma Mission
- Context (PIB): National Biopharma Mission is an industry-academia collaborative mission for accelerating discovery research to the early development of Biopharmaceuticals.
- It is a collaborative mission of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and the World Bank.
- It is implemented by the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The program will specifically focus on the development of new vaccines, bio-therapeutics, diagnostics and medical devices to address the rising burden of diseases in the country.
Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC)
|
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Parliament – 2023/07/21} Vice-Chairpersons of Rajya Sabha
- Context (PIB): The Chairman of Rajya Sabha has nominated four women Parliamentarians to the panel of Vice-Chairpersons.
- The reconstituted panel contains a total of eight names, out of which half are women.
- This is the first time in the history of the Upper House that equal representation has been given to women members in the panel of Vice-Chairpersons.
Panel of Vice-Chairpersons
- As per Rajya Sabha rules, the Chairman nominates a panel of vice-chairpersons from among the members of Rajya Sabha.
- The panel consists of a maximum of six vice-chairpersons.
- One of the members may preside over the Council in the absence of the Chairman or the Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha.
- A vice-chairperson shall hold office until a new panel of vice-chairpersons are appointed.
Panel of Chairpersons in Lok Sabha
|
{GS3 – Infra – Energy – 2023/07/21} India’s Nuclear Power Capacity
- Context (PIB): The installed nuclear power capacity will increase from 7,480 MW (7.48 GW generated by 23 nuclear power reactors) to 22,480 MW (22.48 GW) by 2031.
- The share of nuclear power is 2.8% of total electricity generation in 2022-23.
| State | Nuclear Plant | No. of Reactors | Capacity (GW) |
| Tamil Nadu | Kudankulam | 2 | 2.00 |
| Maharashtra | Tarapur | 4 | 1.40 |
| Rajasthan | Rawatbhata | 6 | 1.18 |
| Gujarat | Kakrapar | 3 | 1.14 |
| Karnataka | Kaiga | 4 | 0.88 |
| Tamil Nadu | Kalpakkam | 2 | 0.44 |
| Uttar Pradesh | Narora | 2 | 0.44 |
| Total | 7.48 | ||

Opposition to India’s Nuclear Plan
- In 2010, India planned to reach a nuclear power capacity of 63 gigawatts (GW) in 2032.
- However, after the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, protests halted the Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project (Maharashtra) and the expansion at the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (Tamil Nadu).
- A proposed nuclear power plant near Haripur was refused permission by West Bengal.
- A PIL has also been filed against the government’s civil nuclear programme at the Supreme Court.
Power Sector at a Glance (as of 31-05-2023)
| Category | Installed Generation Capacity (MW) |
% of Share in Total |
|||
|
Fossil Fuel (56.8%) |
|||||
| Coal | 2,05,235 (205 GW) |
49.1% |
|||
| Gas | 24,824 (24.8 GW) |
6.0% |
|||
| Lignite | 6,620 (6.6 GW) |
1.6% |
|||
| Diesel | 589 (0.58 GW) |
0.1% |
|||
| Total Fossil Fuel | 2,37,269 |
56.8 % |
|||
|
Non-Fossil Fuel (43%) |
|||||
| Solar | 67,078 (67 GW) |
16.1 % |
|||
| Wind | 42,868 (42.8 GW) |
10.3 % |
|||
| Biomass Power/Cogen | 10,248 (10 GW) |
2.5 % |
|||
| Small Hydro Power | 4,944 (4.9 GW) |
1.2 % |
|||
| Waste to Energy | 554 (0.55 GW) |
0.1 % |
|||
| Wind, Solar & Other RE | 1,25,692 (125 GW) |
30.2 % |
|||
| Hydro | 46,850 (46 GW) |
11.2 % |
|||
| Renewables (Incl. Hydro) | 173,619 (173 GW) |
41.4% |
|||
| Nuclear | 6,780 (6.7 GW) |
1.6% |
|||
| Total Non-Fossil Fuel | 179,322 (179 GW) |
43.0% |
|||
| Total Installed Capacity | 4,17,668 (417 GW) |
100% |
|||
|
Coal (49%) > Solar (16%) > Hydro (11%) > Wind (10%) > Gas (6%) > Biomass (2.5%) > Nuclear (1.6%) Lignite (1.6%) > Small Hydro (1.2%) > Diesel (0.1%) > W2E (0.1%) [Source] |
|||||
|
|||||
For more information on Nuclear Reactors (PMF IAS)
For more information on India 3 stage Nuclear Programme (PMF IAS)





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)