Presiding Officer of Lok Sabha
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
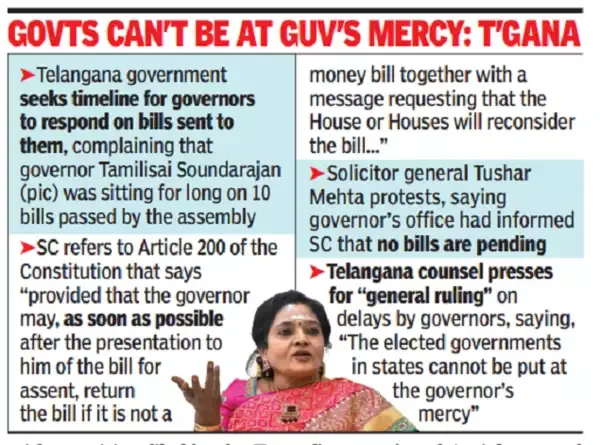
- Context (IE): The US House has been without a speaker for three weeks.
Speaker of the United States House of Representatives
|
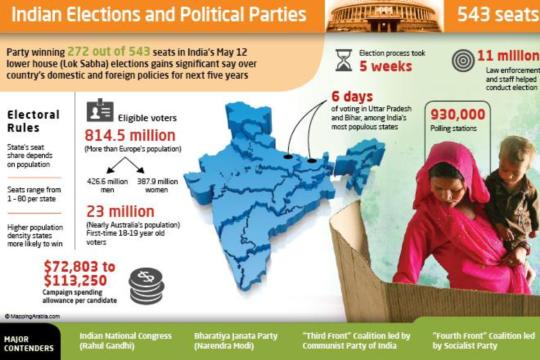
Speaker of Lok Sabha (LS)
- The Speaker of the LS is the presiding officer and the highest authority of the LS.
- The LS must choose one of its members (MPs) to be the Speaker as soon as possible.
- To be elected speaker, a candidate must receive a majority of votes from the MPs present and voting.
- When the post of Speaker is vacant:
- The House must choose a new member to fill the vacancy.
- The Deputy Speaker presides over the Lok Sabha.
- If the post of both the Speaker and Deputy Speaker is vacant, the President can appoint a member of the LS as the Speaker pro tem.
- When the speaker is absent:
- The Deputy Speaker presides over the LS.
- If both the Speaker and Deputy Speaker are absent, anyone from the Panel of Chairpersons can preside over the house.
Panel of Chairpersons
|
- After the dissolution of LS:
- The Speaker remains in office until just before the first meeting of the new House.
- When the LS meets after the election, the President appoints a member of the LS as a pro-tem speaker for the conduct of the house.
- The President himself administers oath to the pro tem speaker.
- Pro tem speaker administers the oath to MPs and enables the house to elect the new speaker.
Vacating the Speaker’s Office
- The speaker has to vacate his office:
- If he ceases to be a member of the LS
- If he resigns by providing written notice to the Deputy Speaker
- If he is removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all the members of the LS.
Role of Speaker under IC
- As the presiding officer of the LS at the Centre and the Legislative Assembly in the States, the Speaker must act impartially.
- The speaker is the custodian of the rights & privileges of the House, its committees, and its members.
- Apart from the traditional roles with respect to the conduct of business, important functions of the Speaker include:
- Certifying a Bill to be a Money Bill.
- Deciding on disqualification under the Tenth Schedule for defection.
- Suspension of members for misconduct in the House.
- Referring a bill to the standing committee.
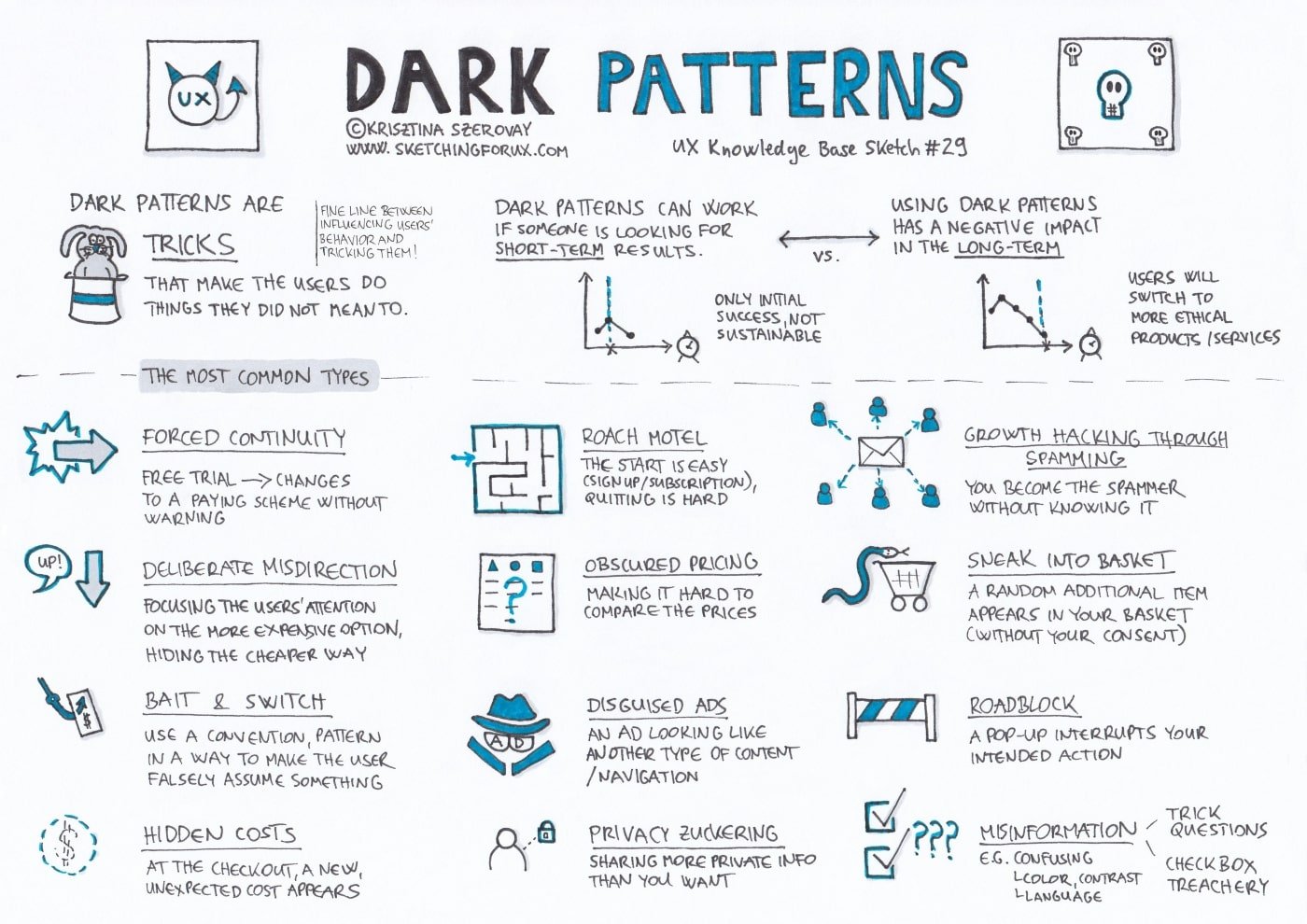
Misuse of the Power
- The LS/Legislative Assembly rules provide for suspension of members for misconduct in the House. The Speakers and the Houses misuse these provisions often against the Opposition members.
- The Speaker can refer to Bills introduced to the Parliamentary Standing Committees. However, even significant Bills that require detailed scrutiny are not referred to such committees.
- There have also been challenges in the Court in recent years against the certification of certain Bills as a Money Bill by the Speaker of the LS.
Authority Under the Tenth Schedule
- The Speaker is the deciding authority on disqualifying members under the Tenth Schedule.
- While he/she is expected to perform this constitutional role neutrally, past instances suggest that the Speakers favour the ruling dispensation.
- The minority judges in Kihoto Hollohan (1992) believed that vesting the power to decide on defections with the Speaker violates the basic democratic principles.
- The SC in Keisham Meghachandra Singh vs The Hon’ble Speaker Manipur (2020) recommended amending the Constitution to vest these powers in an independent tribunal headed by judges.
Way Forward
- Speakers should act impartially & refrain from engaging in any conduct perceived as inappropriate.
- The Indian Parliament must follow British practices to build trust in the Speaker’s role.
Speaker in Britain
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)