
Category Indian Geography
West Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Narmada, Tapti, Sabarmati, Mahi, Luni & Ghaggar
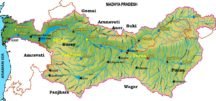 Read MoreWest Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Narmada, Tapti, Sabarmati, Mahi, Luni & Ghaggar
Read MoreWest Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Narmada, Tapti, Sabarmati, Mahi, Luni & GhaggarEast Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Cauvery, Pennar, Subarnarekha, Ponnaiyar & Vaigai
 Read MoreEast Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Cauvery, Pennar, Subarnarekha, Ponnaiyar & Vaigai
Read MoreEast Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Cauvery, Pennar, Subarnarekha, Ponnaiyar & VaigaiEast Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Godavari, Krishna & Mahanadi
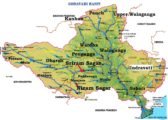 Read MoreEast Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Godavari, Krishna & Mahanadi
Read MoreEast Flowing Peninsular Rivers: Godavari, Krishna & MahanadiPeninsular River System vs. Himalayan River System
 Read MorePeninsular River System vs. Himalayan River System
Read MorePeninsular River System vs. Himalayan River SystemGanga-Brahmaputra River System: Major Tributaries of The Ganga & Brahmaputra
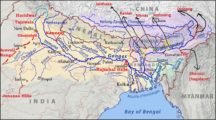 Read MoreGanga-Brahmaputra River System: Major Tributaries of The Ganga & Brahmaputra
Read MoreGanga-Brahmaputra River System: Major Tributaries of The Ganga & BrahmaputraIndus River System: Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas & Satluj
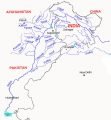 Read MoreIndus River System: Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas & Satluj
Read MoreIndus River System: Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas & SatlujClassification of Drainage Systems of India
 Read MoreClassification of Drainage Systems of India
Read MoreClassification of Drainage Systems of IndiaDrainage patterns: Discordant drainage patterns & Concordant Drainage Patterns
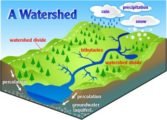 Read MoreDrainage patterns: Discordant drainage patterns & Concordant Drainage Patterns
Read MoreDrainage patterns: Discordant drainage patterns & Concordant Drainage PatternsIndian Islands: Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands & New Moore Island
 Read MoreIndian Islands: Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands & New Moore Island
Read MoreIndian Islands: Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands & New Moore IslandCoastline of India | Coastal Plains of India
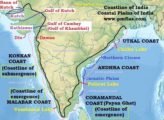 Read MoreCoastline of India | Coastal Plains of India
Read MoreCoastline of India | Coastal Plains of IndiaHills of Peninsular India: Aravalis, Vindhyas, Satpuras, Western & Eastern Ghats
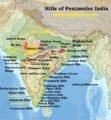 Read MoreHills of Peninsular India: Aravalis, Vindhyas, Satpuras, Western & Eastern Ghats
Read MoreHills of Peninsular India: Aravalis, Vindhyas, Satpuras, Western & Eastern GhatsPeninsular Plateau (Deccan Plateau) | Plateaus in the Peninsular Region
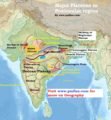 Read MorePeninsular Plateau (Deccan Plateau) | Plateaus in the Peninsular Region
Read MorePeninsular Plateau (Deccan Plateau) | Plateaus in the Peninsular RegionDivisions of Indo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plains
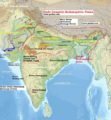 Read MoreDivisions of Indo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plains
Read MoreDivisions of Indo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra PlainsIndo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plain | Bhabar, Terai, Bhangar, Khadar
 Read MoreIndo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plain | Bhabar, Terai, Bhangar, Khadar
Read MoreIndo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plain | Bhabar, Terai, Bhangar, KhadarMajor Mountain Passes in India & Himalayas
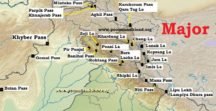 Read MoreMajor Mountain Passes in India & Himalayas
Read MoreMajor Mountain Passes in India & Himalayas






