Strategic Projects in Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): Andaman and Nicobar (A&N) Islands are seeing a major strategic security upgrade.
Recent strategic upgradations in A&N
- Enhanced infrastructure: Revamped airfields and jetties, additional logistics and storage facilities, habitat for troops, robust surveillance infrastructure, etc., are being constructed.
- Capacity for greater deployment: Such upgradation will facilitate the deployment of additional military forces and warships, aircraft, missile batteries and troops.
- Road construction: A road from the north of the islands to Port Blair in the south is being proposed.
- Expansion of IAF station: Includes expansion of the runway and station. It can result in the holding of fighter squadrons for longer durations.
- Great Nicobar Island Project: A project that includes an international container transhipment terminal, a greenfield international airport, and a township development is being proposed.
- Naval capabilities: Upgrades in hangers, Precision Approach Radar (PAR), Surveillance System at INS Utkrosh in Port Blair and Naval Communication Network (NCN) Centres enhanced naval capacities.
- Remote Sensing: The National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) will increase its manpower to analyse satellite imagery and technical capacity to improve surveillance in the A&N Islands and Lakshadweep.
Strategic Importance of A&N Islands
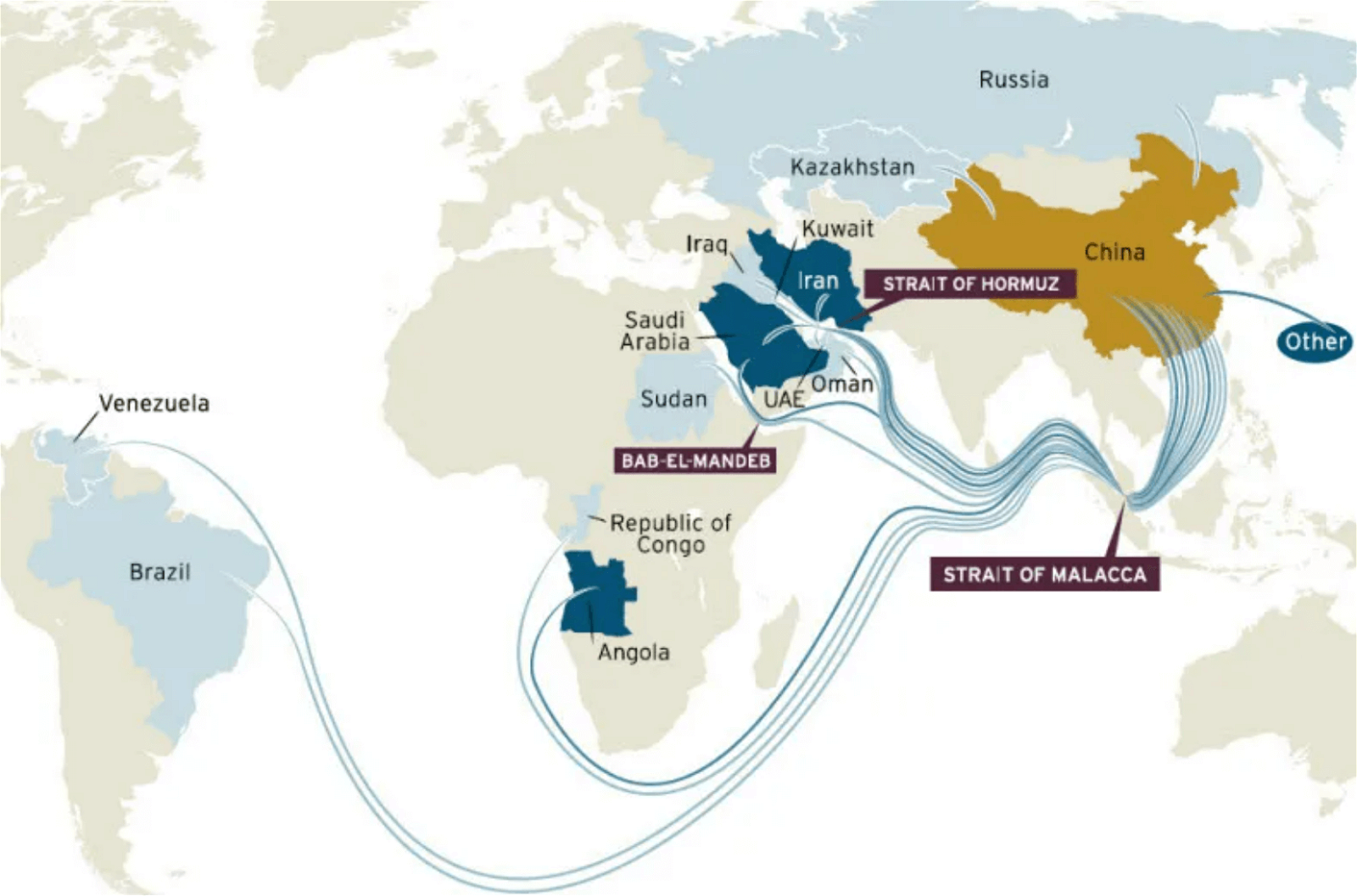
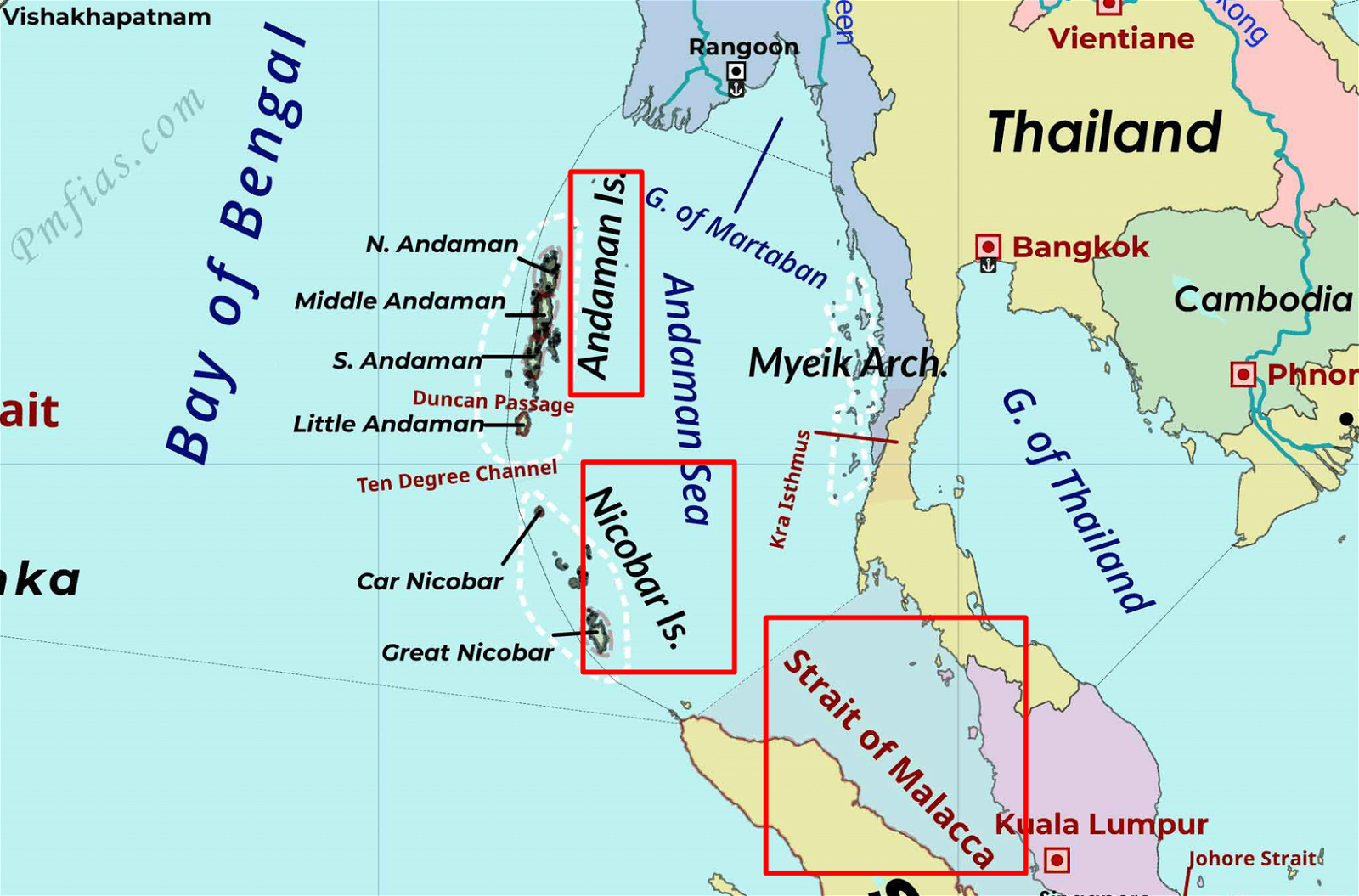
- Closeness to maritime chokepoint: Its location at the western entrance/exit of the Strait of Malacca makes it essential in case of a “Malacca Dilemma”.
- India’s opportunity: It allows India to monitor the flow of traffic from the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean) to the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean).
- Closer to other nations: The A&N islands are closer to Myanmar, Indonesia, and Thailand than to the Indian cities of Chennai and Kolkata.
- Exclusive economic zone (EEZ): It adds 300,000 sq km to India’s EEZ and promises undersea hydrocarbon and mineral deposits.
- Uninhibited islands: Less than 40 of the archipelago’s 836 islands and islets are inhabited, leaving a possibility of surreptitious occupation — a la “Kargil heights” — by a covetous neighbour.
- China’s expanding influence: China is building a military facility at Myanmar’s Coco Islands north of the A&N Islands, which raises concerns.
Malacca Dilemma
|
Historical evolution of security presence in A&N
- British Period: Dark symbolism of Kalapani to Cellular jail in A&N island in the aftermath of the 1857 revolution led to long neglect of the island chain.
- Liberated by INA: Japan occupied it during World War II. For a brief period, it remained liberated under the Provisional Government of INA.
- Part of independent India: Despite some British advisors suggesting it to be retained as the Crown’s possession, it became part of India.
- A&N Naval garrison: In 1962, after a reported sighting of a Chinese submarine, India stationed a few navy personnel in the A&N islands.
- Post-Kargil war: India’s first unified theatre operational command, the Andaman Nicobar Command (ANC) in Port Blair, was established in 2001 after the Kargil security review report.
Way forward: India’s future role in A&N
- Extension of defensive and diplomatic capabilities: A security infrastructure upgrade will not only extend India’s defensive perimeter but also bestow the ability to project power or extend a hand of friendship to maritime neighbours.
- Peace in the region: India, with the cooperation of like-minded partners, can contribute to maintaining peace and tranquillity in the Indo-Pacific.
- Transhipment hub: Port Blair could become a regional hub for navies to acquire interoperability in areas such as disaster relief, medical aid, countering piracy, and human smuggling.
To know more, visit > Andaman and Nicobar Islands.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)