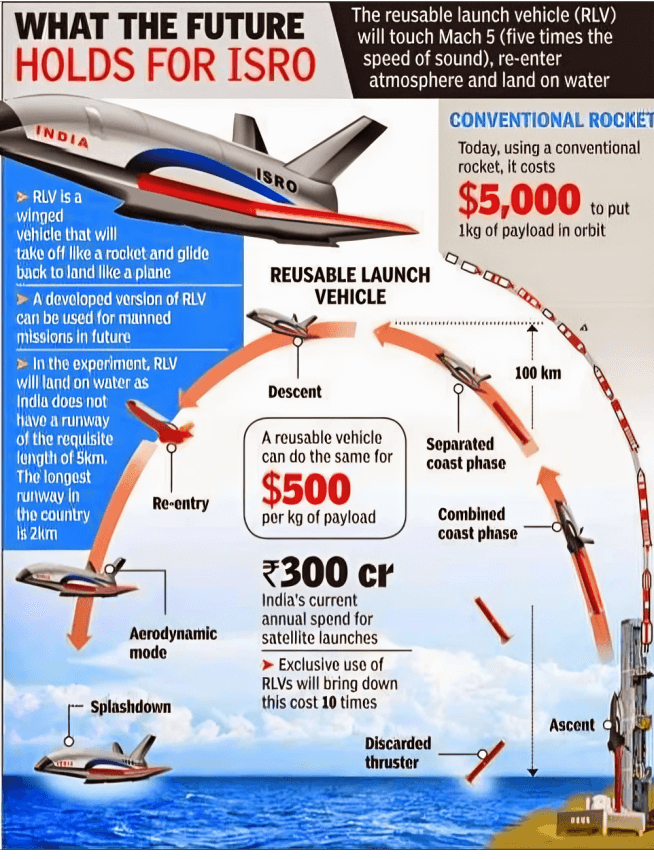
Reusable Launch Vehicle ‘Pushpak’
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (ET | NDTV | TH): ISRO has successfully carried out the landing mission of ‘Pushpak’ Reusable Landing Vehicle Landing Experiment (RLV LEX) 02 from the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR) in Challakere near Karnataka’s Chitradurga.
- The RLV LEX 02 landing experiment is the second of the series of experiments conducted by the space agency under the Reusable Launch Vehicle Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) programme.
- RLV-LEX-02 demonstrated the autonomous landing capability of RLV off-nominal initial conditions at the release from a Chinook helicopter.
- The winged body and all flight systems used in RLV-LEX-01 were reused in the RLV-LEX-02 mission.
‘Pushpak’
- Pushpak, dubbed the “swadeshi space shuttle” is India’s futuristic Reusable Launch Vehicle.
- The rocket’s name comes from the ‘Pushpak Viman’ of the Ramayana, which is known as the Vehicle of Kuber, Lord of Wealth.
- It is designed as an all-rocket, fully reusable single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) vehicle, incorporating several major elements such as the X-33 advanced technology demonstrator, the X-34 testbed technology demonstrator and the upgraded DC-XA flight demonstrator.
- In it, the most expensive part, the upper stage, which houses all the expensive electronics, is made reusable by bringing it back safely back to Earth.
- Later, it could even do refuelling of in-orbit satellites or retrieving satellites from orbit for refurbishment.
- It also a step towards India’s aim of “minimising space debris” and sets the stage for establishing the Bhartiya Antariksh Station by 2035.
Reusable Launch Vehicle Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) Programme
- It aims at developing essential technologies for a fully reusable launch vehicle to enable low cost access to space.
- The configuration of RLV-TD is similar to that of an aircraft and combines the complexity of both launch vehicles and aircraft.
- The winged RLV-TD has been configured to act as a flying test bed to evaluate various technologies, namely, hypersonic flight, autonomous landing and powered cruise flight.
- In future, this vehicle will be scaled up to become the first stage of India’s reusable two stage orbital launch vehicle.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)