Rajasthan National Parks, Tiger Reserves, Wildlife Sanctuaries & Ramsar Sites
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 25, 2024 6:45 PM
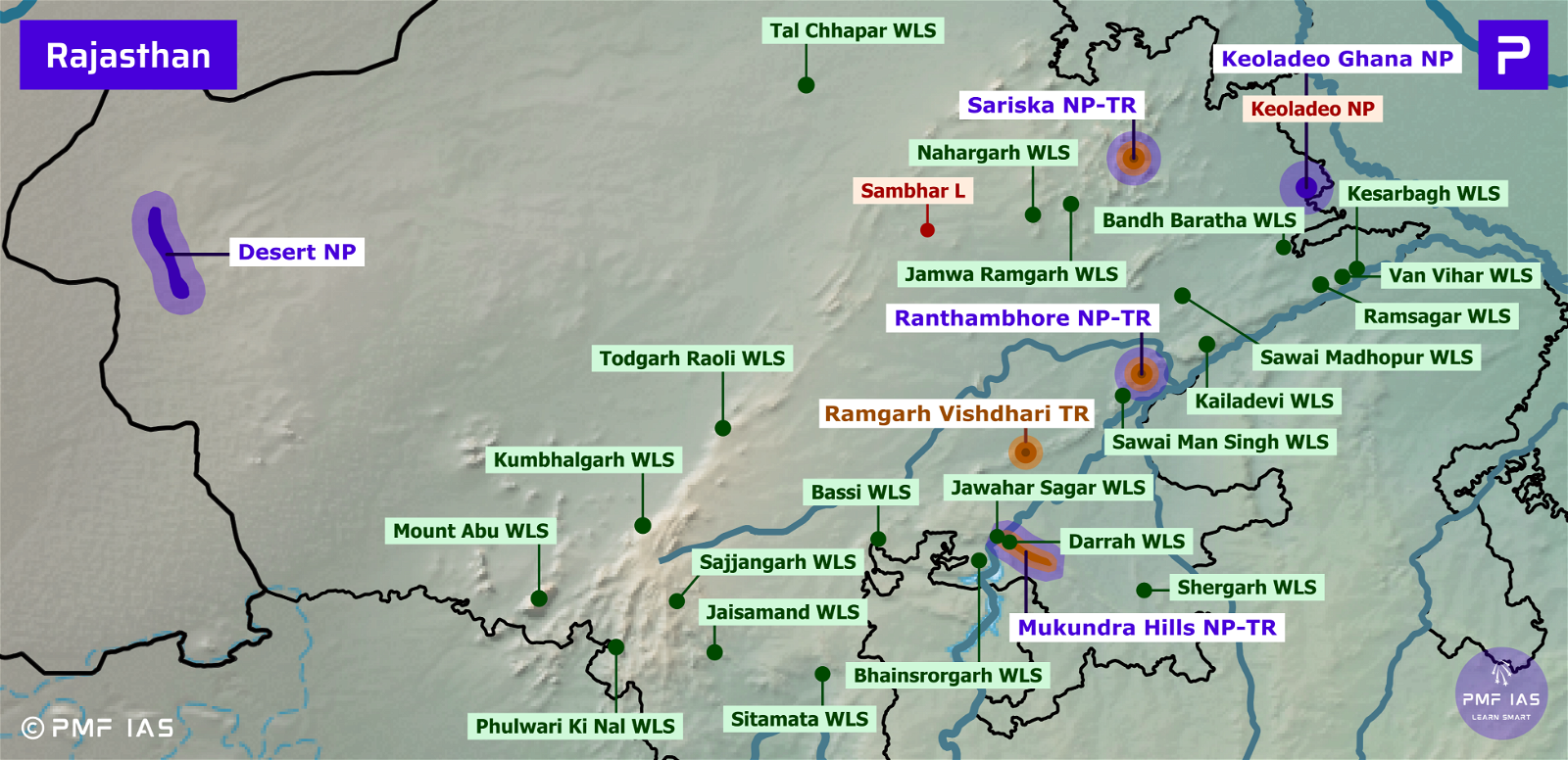
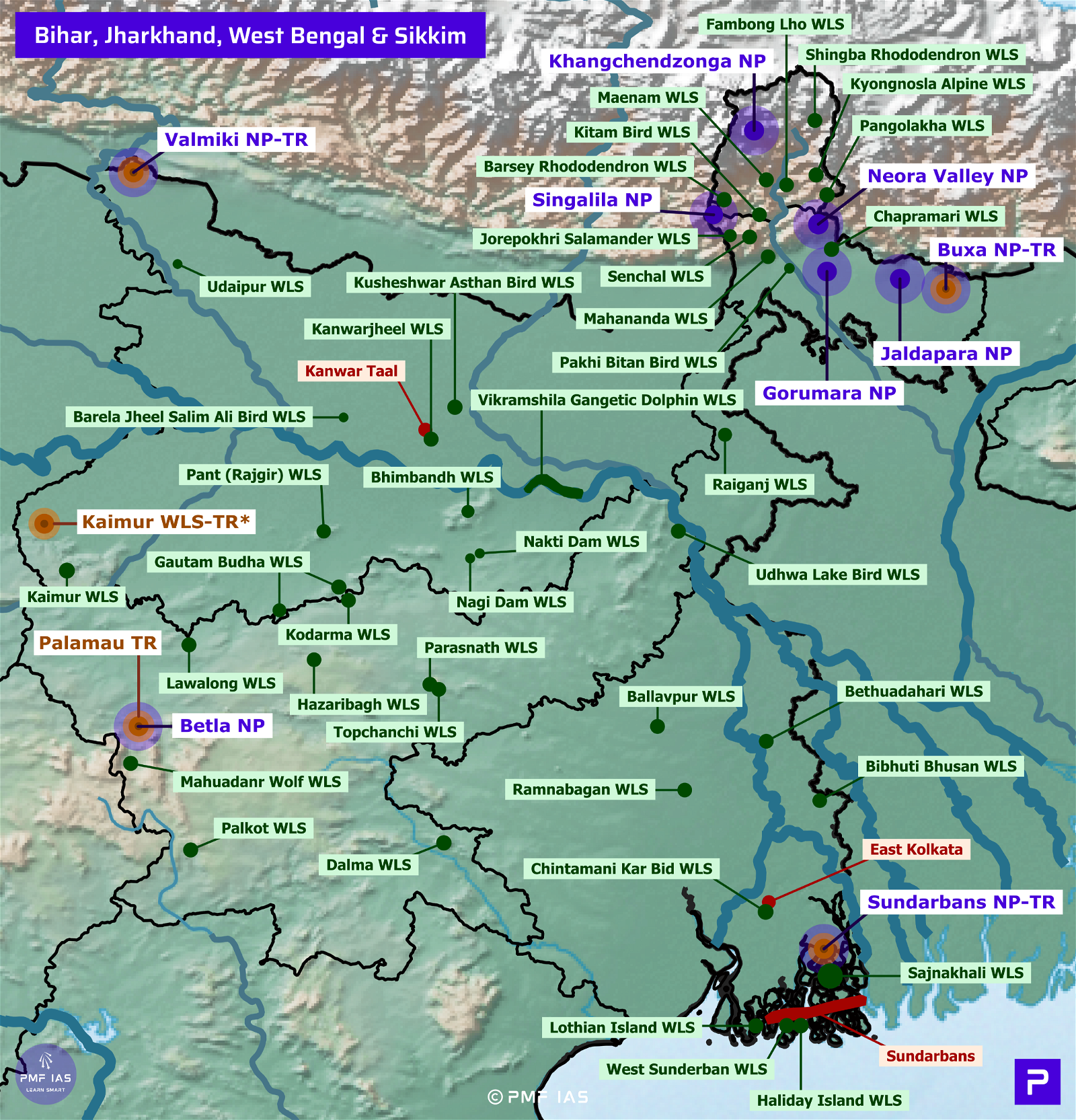
Desert National Park
- It is situated in Jaisalmer and Barmer districts, Rajasthan.
- Vegetation: Open grassland, thorny bushes, and dunes.
- Major Flora: Patches of sewan grass and aak shrub.
- Major Avifauna: Great Indian bustard (CR), eagles, harriers, falcons, buzzards, and vultures.
- Major Fauna: Chinkara or Indian Gazelle, desert fox.
Q. With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below;
Answer: Usually, no human settlements are allowed in a National Park. But there are some exceptions. c) 1 & 3 only. |
Keoladeo Ghana National Park, Ramsar Site
- Formerly known as Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary, it is a freshwater swamp. It gets flooded during the monsoon.
- It is a famous avifauna sanctuary that hosts thousands of birds, especially during the winter season. It is a Ramsar Site and UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Vegetation: tropical dry deciduous forests, dry grasslands and wetlands.
- It is the only regular wintering area in India for the Siberian crane (CR).
- Major Avifauna: Migratory waterfowl, sarus crane (VU) (large non-migratory crane found in parts of India).
- Major Fauna: Blackbuck, hog deer, chital deer, sambar.
Mukundra Hills National Park, Tiger Reserve
- Previously known as Darrah Wildlife Sanctuary, it is located within the Kathiawar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.
- Like Sita Mata Wildlife Sanctuary, Mukandara hills National Park was one of the places which were considered for the reintroduction of the Asiatic lion.
- Vegetation: Dry deciduous and grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Bengal tiger, Indian wolf, leopard, chital, sambar, wild boar, sloth bear and chinkara.
- Major Reptilian Fauna: Mugger crocodile and gharial.
Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve
- It acts as a buffer for Ranthambore National Park.
- It will link Ranthambore Tiger Reserve & Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve.
- The government is making efforts to strengthen the prey base by transferring chital (spotted deer) from Ghana Bird Sanctuary (Karauli) to Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, Keoladeo National Park, and Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve.
Ranthambhore National Park, Tiger Reserve
- It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River.
- According to experts, there is overcrowding at the Ranthambore reserve. The Rajasthan government has announced its plan to develop the Bundi Wildlife Sanctuary as a Tiger Reserve to provide a second habitat for tigers in the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
- Vegetation: Dry deciduous forests and grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Bengal Tiger, leopard, nilgai, sambar.
- Major Reptilian Fauna: Mugger crocodile.
- Threats: Poaching, poisoning of tigers by villagers, habitat fragmentation.
Sariska National Park, Tiger Reserve
- It is a part of the Aravalli Range and the Kathiawar-Gir dry deciduous forests’ ecoregion. It is rich in mineral resources, such as copper.
- Vegetation: Arid forests, dry deciduous forests, scrub-thorn and grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Bengal tiger, Indian leopard, golden jackal, chital, sambar deer, nilgai, rhesus macaque.
- Threats: Marble mining, habitat loss and poaching.
- In 2005, it was reported that there were no tigers left in Sariska. In 2008, two tigers from Ranthambhore National Park were relocated to Sariska Tiger Reserve.
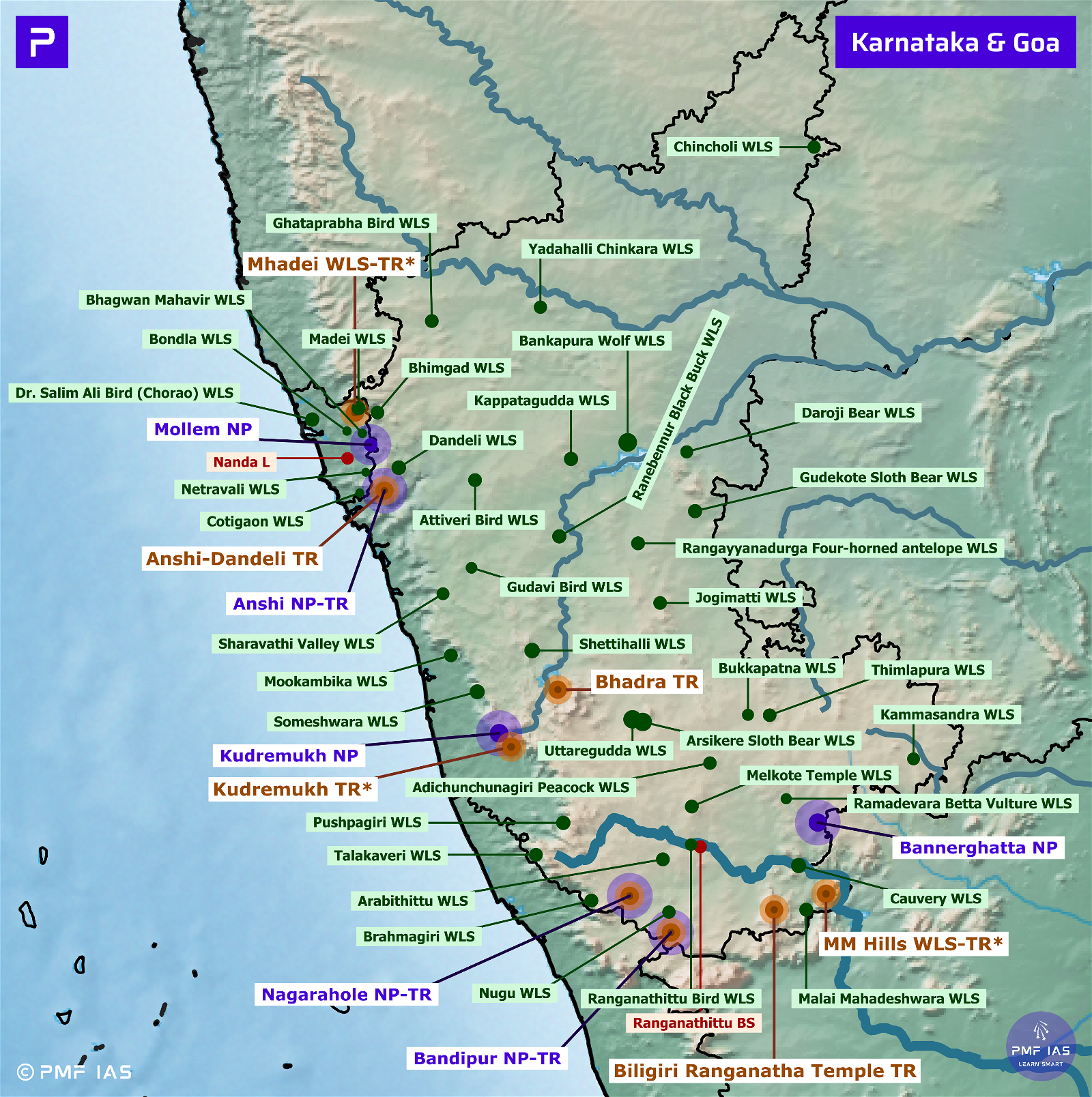
Wildlife Sanctuaries of Rajasthan
Bhensrodgarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- Near Rana Pratap Sagar Dam (on Chambal River).
Mukundara Hills (Darrah) Wildlife Sanctuary
- It consists of three wildlife sanctuaries: Darrah Wildlife Sanctuary, Chambal Wildlife Sanctuary, and Jawahar Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary.
Jaisamand Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located in Udaipur around Dhebar Lake (Jaisamand Lake). Dhebar lake is one of the largest artificial lakes in India. Govind Ballabh Pant Sagar on Rihand River (a tributary of Son River) is India’s largest artificial lake.
Jamwa Ramgarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is a man-made lake near Jaipur; to its north-east lies the Sariska Tiger Reserve.
Jawahar Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located near the Jawahar Sagar Dam (over the Chambal River) in Kota. Jawahar Sagar Dam is the third dam in the Chambal Valley Projects. It is located upstream of Kota Barrage and downstream of Rana Pratap Sagar.
Kailadevi Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is an extension of the Ranthambore National Park. It is bounded on west by Banas River and on south by Chambal River.
Mount Abu Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located in the Aravalli range. In altitude, it ranges from 300 to 1,722 m at Guru Shikhar (highest peak in Rajasthan).
National Chambal Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located on the Chambal River near the tripoint of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located in Bundi and is recently upgraded to Tiger Reserve.
Sawaimadhopur Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is a part of Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
Sawai Man Singh Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is a part of Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
Sitamata Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated in Pratapgarh and Chittaurgarh. It was once considered for the reintroduction of the Asiatic lion.
Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Located in Churu district, it is known for blackbucks (LC).
Others
- Bandh Baratha Wildlife Sanctuary: Surrounds Baretha Dam in the Bharatpur district.
- Bassi Wildlife Sanctuary: Located to the west of Mukundra Tiger Reserve, in Chittorgarh district.
- Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary: Located in the vicinity of Nahargarh Fort on the outskirts of Jaipur.
- Kesarbagh Wildlife Sanctuary: Dholpur District.
- Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary: extends across the Aravalli Range in Rajsamand District.
- Phulwari Ki Nal Wildlife Sanctuary: Udaipur district, in the southern Aravalli Hills bordering the state of Gujarat.
- Ramsagar Wildlife Sanctuary: Dholpur district.
- Sajjangarh Wildlife Sanctuary: Udaipur district in the southern Aravalli Hills.
- Shergarh Wildlife Sanctuary: Located to the east of Mukundara Hills National Park.
- Todgarh Raoli Wildlife Sanctuary: Aravallis of Ajmer, Pali and Rajsamand districts.
- Van Vihar Wildlife Sanctuary: Van Vihar Wildlife Sanctuary and Ramsagar Wildlife Sanctuary are located in Dholpur district.
Ramsar Sites of Rajasthan (2)
Keoladeo National Park
- It is a complex of ten artificial seasonal marshes. Vegetation is scrub and open grassland.
- The invasive growth of the grass Paspalum distichum has reduced its suitability for certain waterbird species, notably the Siberian Crane (CR).
- Placed on the Montreux Record in 1990 due to water shortage and an unbalanced grazing.
Sambhar Lake
- It is India’s largest inland saltwater lake. It is a key wintering area for Flamingos (LC).
Last updated on April 25, 2024 6:45 PM