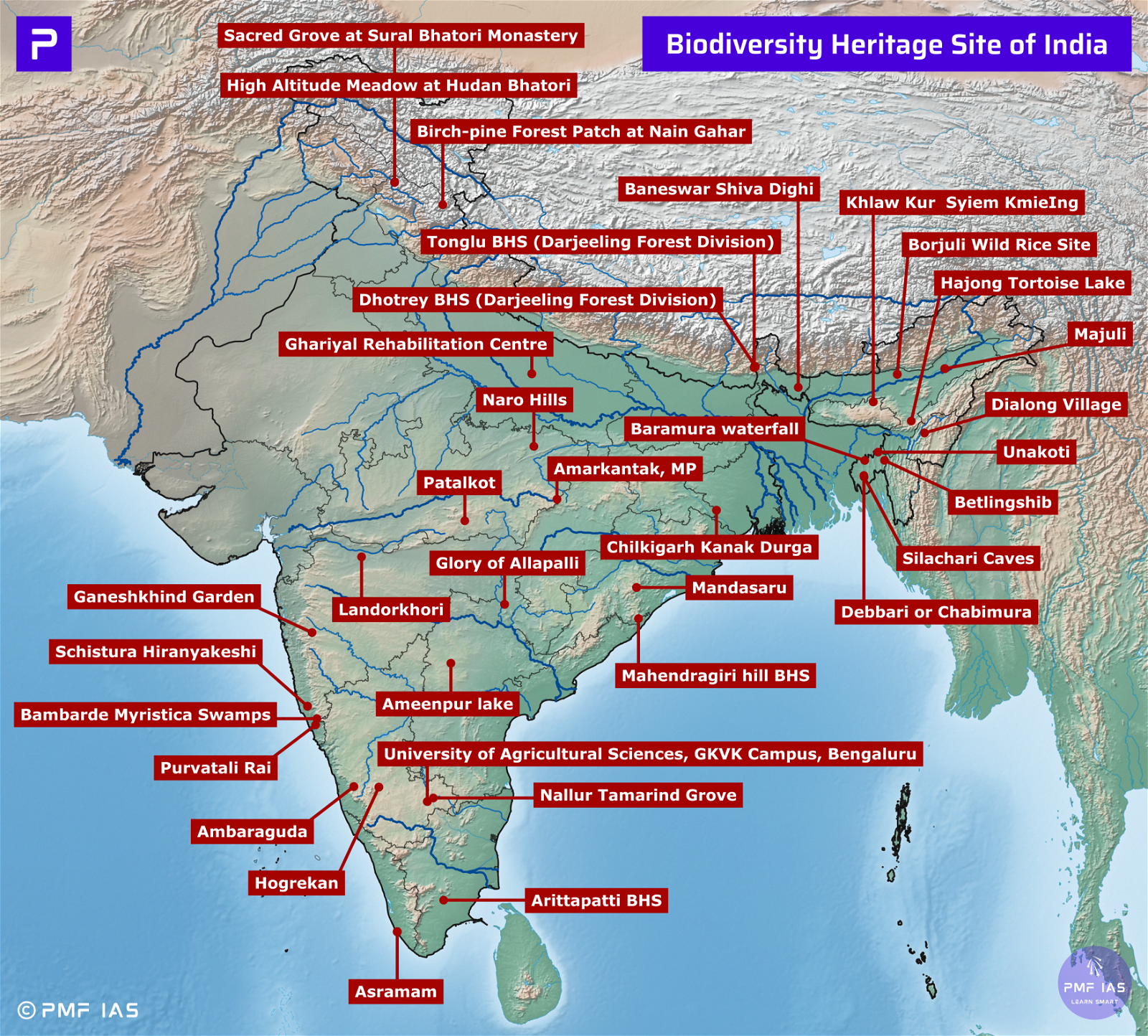
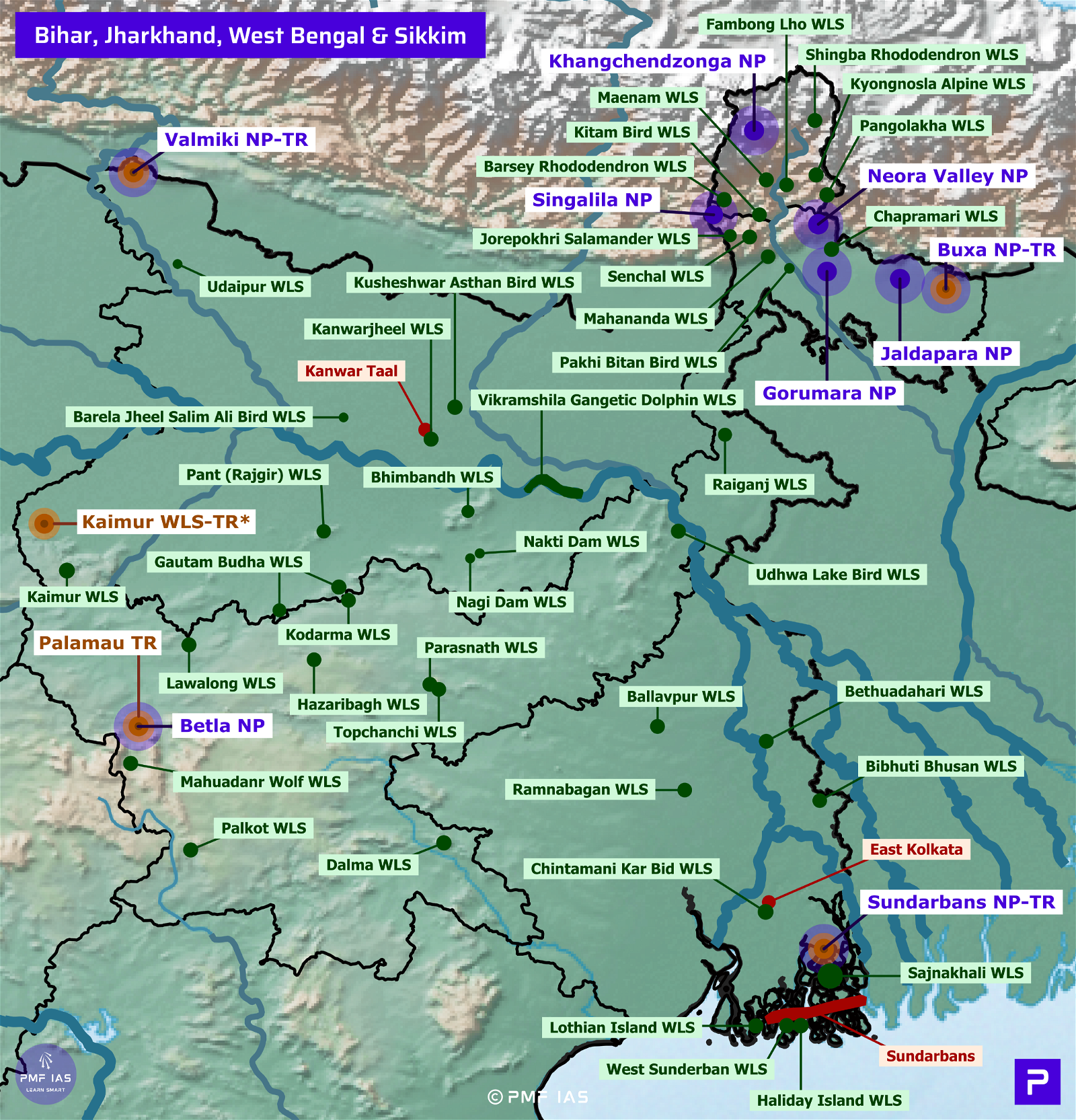
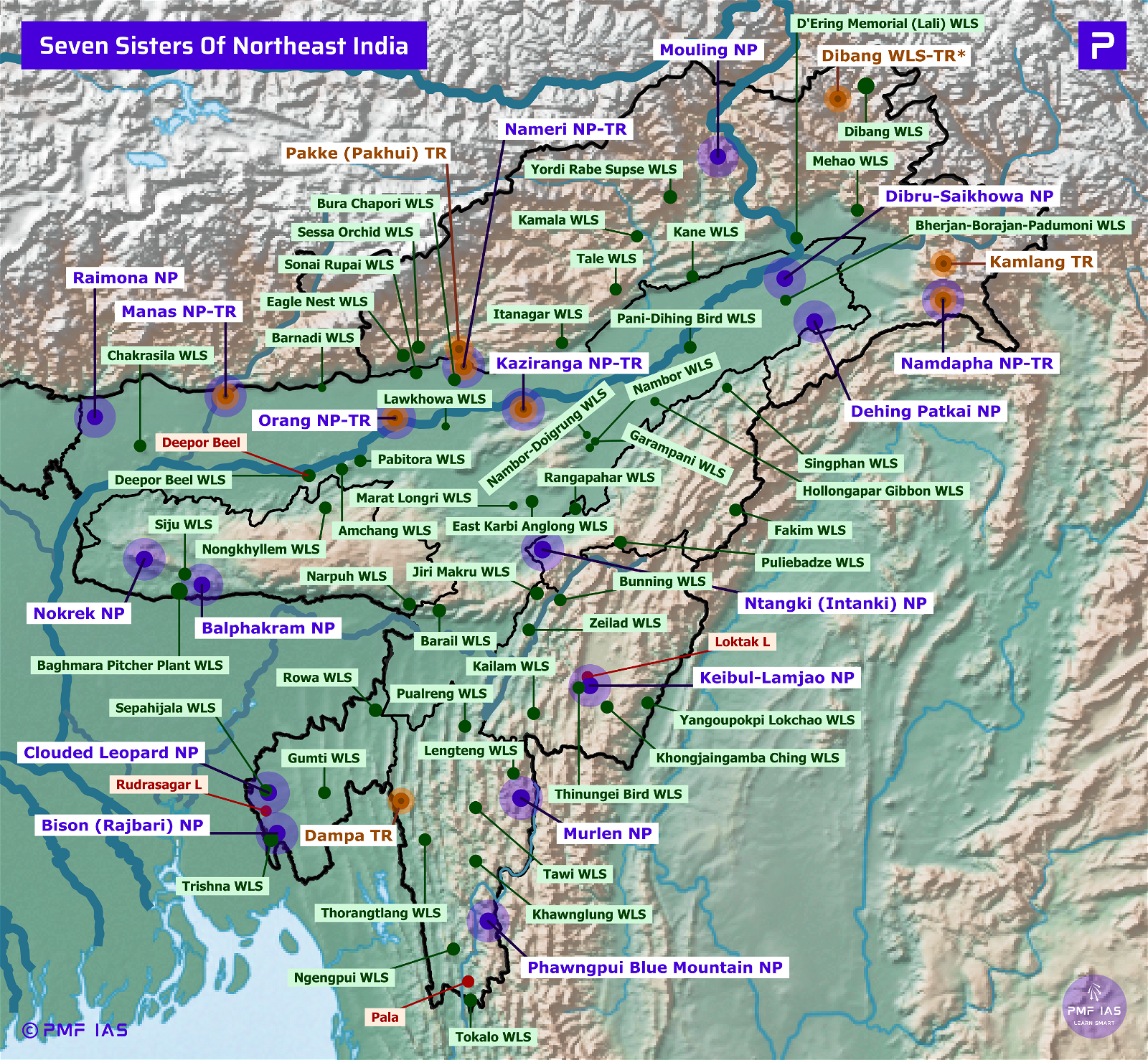
Uttarakhand National Parks, Tiger Reserves, Wildlife Sanctuaries & Ramsar Sites
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 22, 2024 11:32 PM
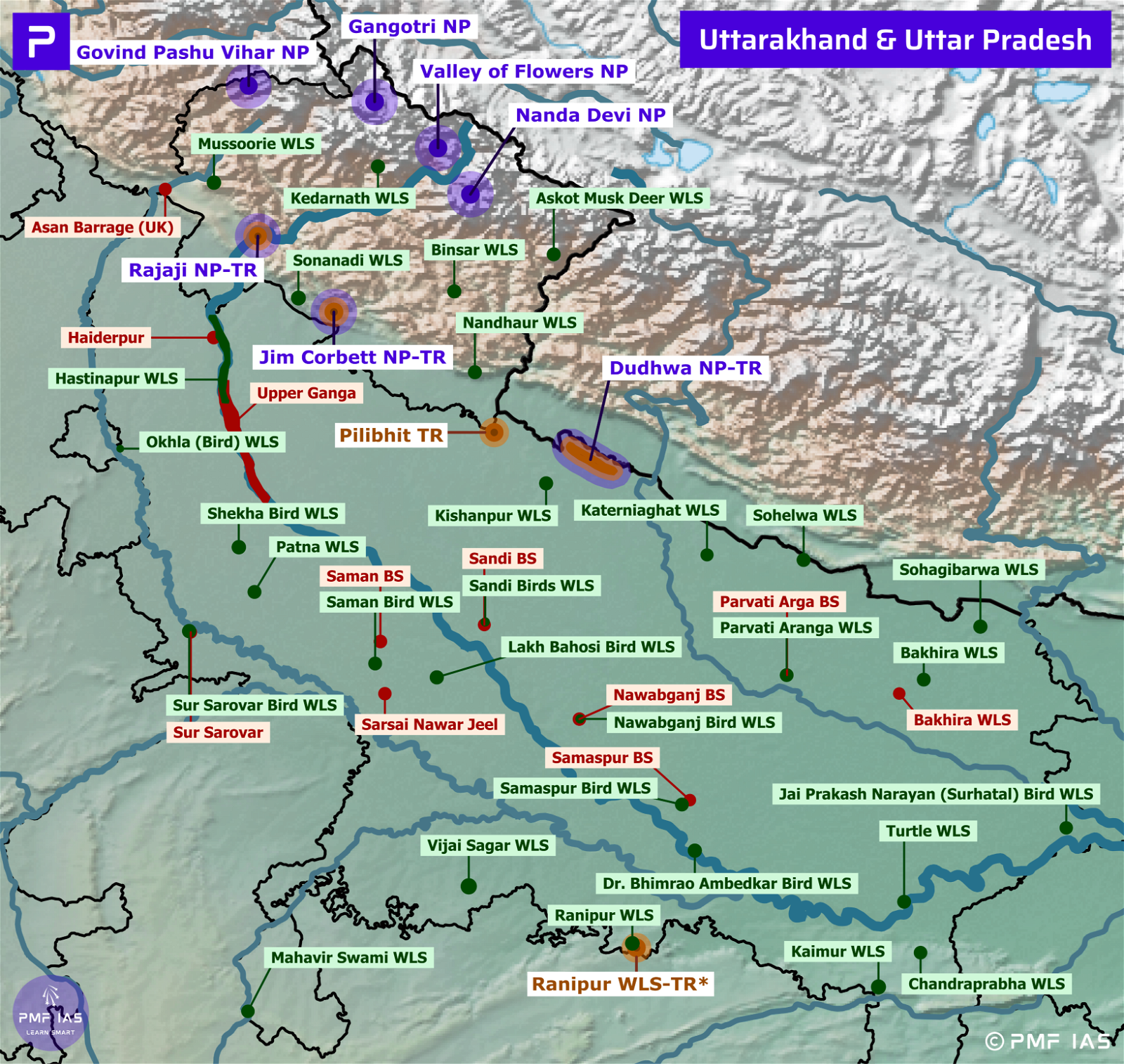
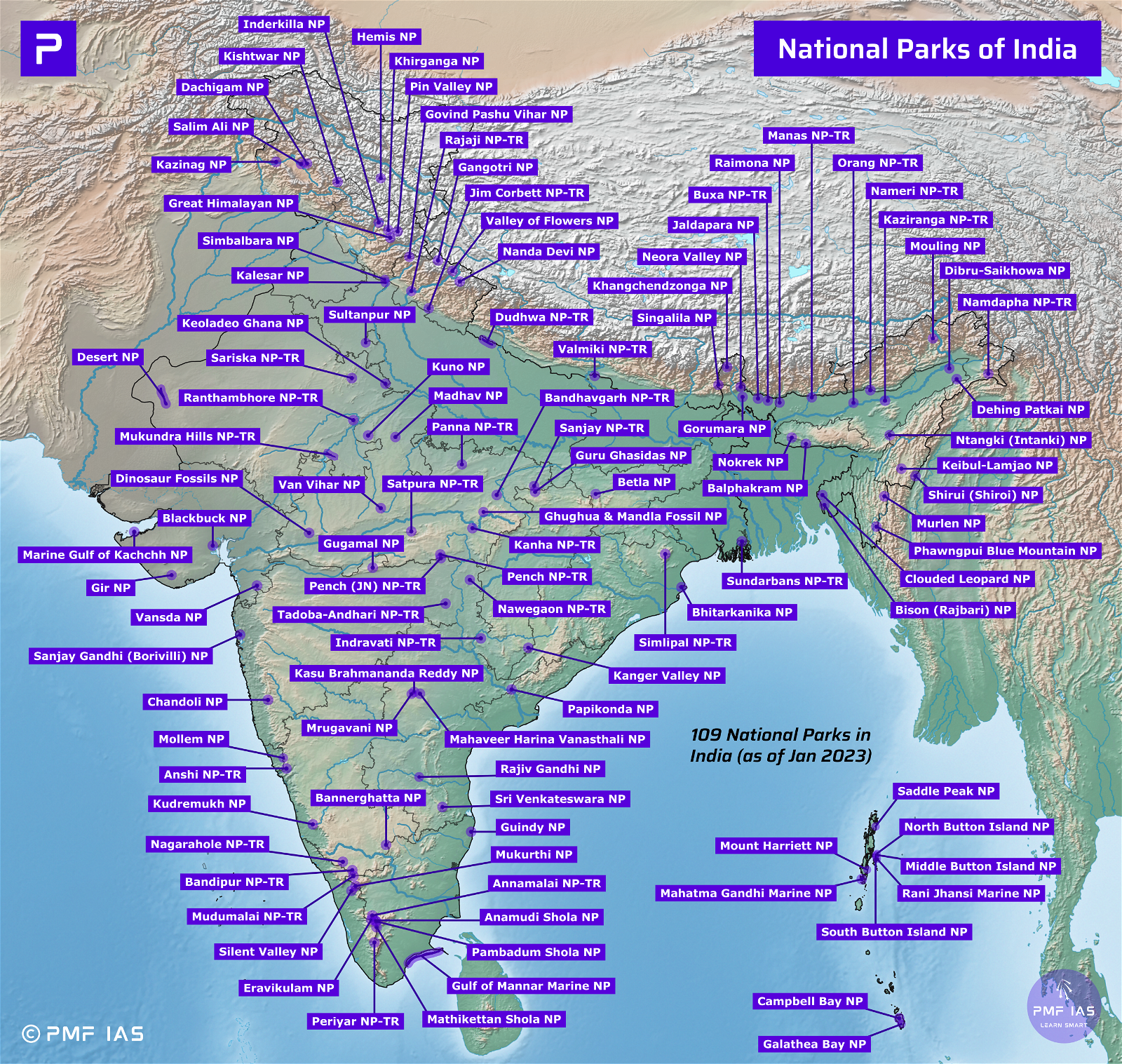
Gangotri National Park
- It is located in the upper catchment of Bhagirathi river.
- The park area forms a continuity between Govind National Park and Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary. The Gaumukh glacier, the origin of the river Ganges is located inside the park.
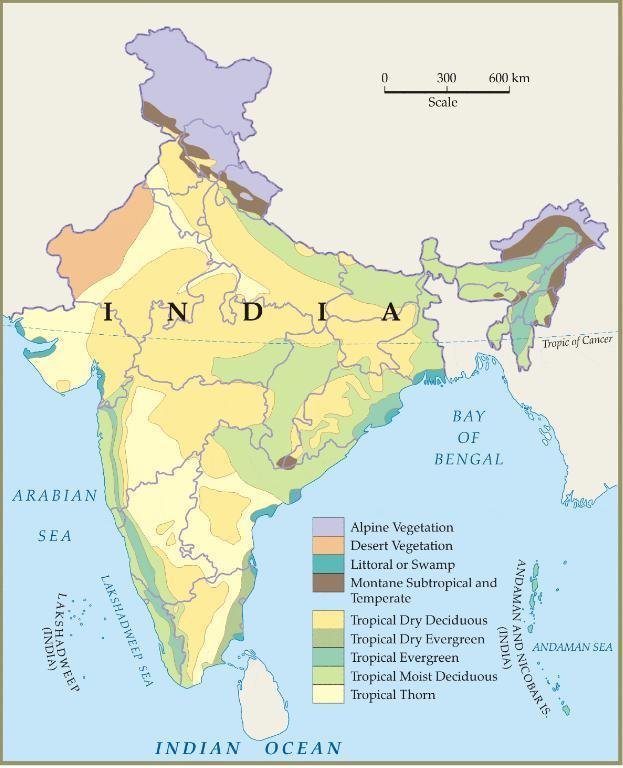
- Habitat: Coniferous forests, alpine meadows and glaciers.
- Vegetation: Pine, deodar, fir, and rhododendrons.
- Major Fauna: Snow leopard, Asian black bear, brown bear, musk deer, blue sheep, Himalayan tahr.
Govind Pashu Vihar National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary
- Named after Indian freedom fighter and politician, Govind Ballabh Pant, it is located in the Garhwal Himalayas.
- The Snow Leopard Project started by the Government of India is being managed at this sanctuary.
- Vegetation: Himalayan broadleaf forests, conifer forests, alpine shrub and meadows.
- Flora: Pine, deodar, cedar, oak, maple, walnut, horse chestnut, hazel and rhododendron.
- Major Fauna: Snow Leopard (VU), leopard, musk deer, Himalayan tahr, steppe eagle, bearded vulture.
Jim Corbett National Park, Corbett Tiger Reserve
- It is the oldest National Park in India and is located in the Nainital.
- In 1936, it was established to protect the Bengal tiger. It was named after Jim Corbett, a well-known hunter and naturalist. The park was the first National Park to come under the Project Tiger initiative.
- Corbett Tiger Reserve’s core area is formed by Jim Corbett National Park, while the buffer contains Sonanadi Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Ramganga, Sonanadi and Kosi are the major rivers flowing through the National Park and Ramganga Reservoir is located within the National Park.
- Vegetation: Dense, moist deciduous forests, marshy depressions and grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Bengal tigers, elephants, leopards, Himalayan black bears, Himalayan goral, rhesus macaqu.
- Local crocodiles and gharials were saved from extinction by captive breeding programs that subsequently released crocodiles into the Ramganga river.
- Threats: Invasive weeds, and poaching.
- Corbett National Park is one of the thirteen protected areas covered by the Worldwide Fund For Nature under their Terai Arc Landscape Program.
|
Terai Arc Landscape Program
|
Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, National Park
- It is India’s second Biosphere Reserve and it is under UNESCO’s Man & Biosphere Programme. It’s core area is formed by Nanda Devi National Park and Valley of Flowers National Park.
- The Nanda Devi National Park is situated around the peak of Nanda Devi (7816 m).It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Within the National Park lies the Nanda Devi Sanctuary, a glacial basin surrounded by a ring of peaks.
- Major Flora: Fir, birch, rhododendron and juniper.
- Major Fauna: Himalayan musk deer, mainland serow, Himalayan tahr, Himalayan black bear.
Rajaji National Park, Tiger Reserve
- It spreads over the Shivalik ranges and the Indo-Gangetic plains. The Ganga and Song Rivers flow through the park.
- The National Park has been named after C. Rajagopalachari (second Governor-General of independent India).
- The park is at the north-western limit of distribution for both elephants and tigers in India.
- Major Fauna: Elephants, Bengal tiger, sloth bear, black bear, Indian langur, Indian porcupine.
Valley of Flowers National Park
- It is a high altitude Himalayan valley in the transition zone between Zanskar and Great Himalayas.
- It is known for its meadows of endemic alpine flowers.
- Both the Valley of Flowers National Park and the Nanda Devi National Park forms the core area of Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve.
- Vegetation: Alpine vegetation.
- Major Flora: Orchids, poppies, marigold, daisies, rhododendron and birch.
- Major Fauna: Asiatic black bear, snow leopard, musk deer, brown bear, red fox, and bharal (blue sheep).

Q. Which one of the following National Parks lies completely in the Temperate alpine zone?
|
Wildlife Sanctuaries of Uttarakhand
Askot Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located in Pithoragarh district. This sanctuary has been set up for conserving the musk deer (EN).
Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary
- It has been set up for conserving the musk deer (EN). It stretches from Gaurikund to Kedarnath mountain.
- Mandakini river flows through the Wildlife Sanctuary. It originates from the Chorabari Glacier near Kedarnath. It is fed by Vasukiganga River at Sonprayag.
- Mandakini joins Alaknanda River at Rudraprayag. Alaknanda joins Bhagirathi River at Devaprayag to form the Ganges River.
Nandhaur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Jim Corbett Tiger Reserve lies between Rajaji Tiger Reserve and Nandhaur Wildlife Sanctuary. Nandhaur Wildlife Sanctuary is a part of the Shivalik ER.
Sonanadi Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sonanadi WLS is contiguous with the Jim Corbett Tiger Reserve.
Others
- Binsar Wildlife Sanctuary: Almora district.
- Mussoorie Wildlife Sanctuary: Located close to Rajaji Tiger Reserve.
Ramsar Sites of Uttarakhand (1)
Asan Barrage (Asan CnR)
- It is formed by the damming of the Asan River near its confluence with the Yamuna River in the Dehradun district.
- Avifauna: Red-Headed Vulture (Indian Black Vulture – CR), White-Rumped Vulture (CR), Baer’s Pochard (CR)
Last updated on April 22, 2024 11:32 PM