
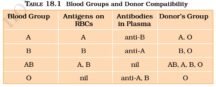
Non-Renewable Sources Of Energy
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Non-Renewable Sources Of Energy

- Fossil fuels represent stored solar energy captured by plants in the past geological times.
- Coal, petroleum and natural gas are called fossil fuels, as they are the remains of prehistoric plants, animals and microscopic organisms that lived millions of year ago.
- During the Carboniferous period 275-350 million years ago, conditions in the world were suitable for formation of large deposits of fossil fuels.
Coal
- Coal is formed from plants and vegetation buried, ‘in situ’ or drifted in from outside to a place, which got covered by deposits of sediments.
- Coal is a solid fossil fuel and a sedimentary rock composed primarily of carbon. There are three basic grades of coal: i) lignite (brown coal), ii) bituminous (soft coal) and iii) anthracite (hard coal).
Formation of coal
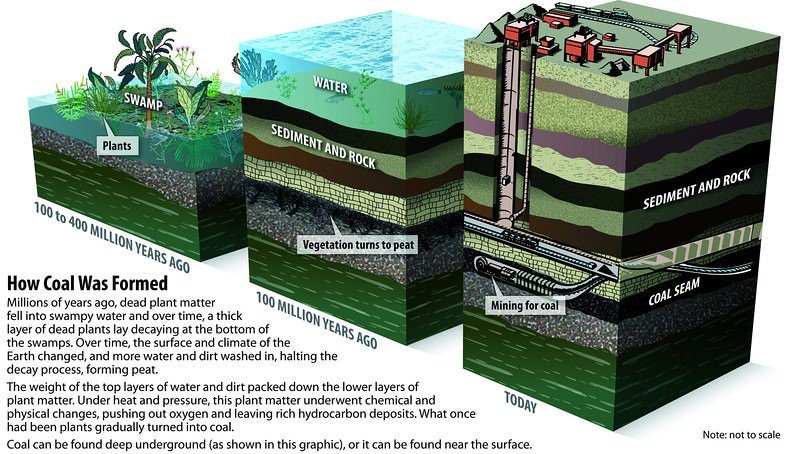
- Coal is the result of plant material that grew in fresh water swamps approximately three hundred million years ago.
- As this plant material died and accumulated, peat also called peat bog was formed.
- Since the plant material accumulated under water, in the swamps decay was inhibited due to lack of oxygen.
- Oceans inundated many of the areas of peat and sediments from the sea were deposited, over the peat.
- The weight of these sediments and the heat of the earth gradually changed the composition of the peat bog and coal was formed.
- Today peat also is used as source of fuel in some parts of the world though its high water content makes it a low-grade fuel.
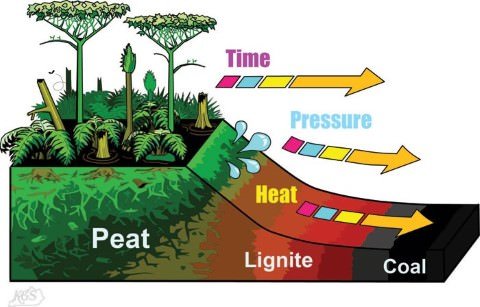
- Peat is changed into coal after many centuries of being compressed by the weight of sediments. It first changes into a low-grade coal known as lignite (brown coal).
- The percentage of carbon in the lignite is higher than in peat. Continued pressure and heat from the earth changes lignite into bituminous soft coal.
- If the heat and pressure were great enough then anthracite coal (hard coal) would be formed which has the highest heat and carbon content.
- Accordingly energy content is greatest in anthracite coal and lowest in lignite.
- The sulphur content of coal is important because on burning low sulphur coal emits less sulphur dioxide (SO2) so more desirable as a fuel for power plants.
Problems with Coal Mining
- Coal is most abundant fossil fuel on earth, but there are problems associated with its mining, transportation and use.
- Coal is mined from both (i) surface mines, and (ii) underground mines.
Surface mining
- Surface mining disrupts and drastically changes the natural landscape and destroys the natural vegetation and the habitat of many species, some of which may already be endangered.
- Mining operations, involving digging, blasting, removal of rocks and soil lying over the coal seam, cause serious problems of air and noise pollution.
- Surface mining may also cause soil erosion and silt loading (the discharge of silts into streams) and canals that disrupt and pollute the aquatic ecosystems as well as ground water in places where aquifers are located near or associated with coal seams.
Underground mining
- Underground mining may cause collapse or land subsidence in the mining areas during or after mining operations are over.
- In case of some mines acid mine drainage from the mine waste pollutes long stretches of streams.
- Coal bed methane in underground mines causes fires.
Apart from these problems, burning of coal in thermal power plants for generation of electricity and in industry is the prime source of air pollution.
Petroleum Or Mineral Oil
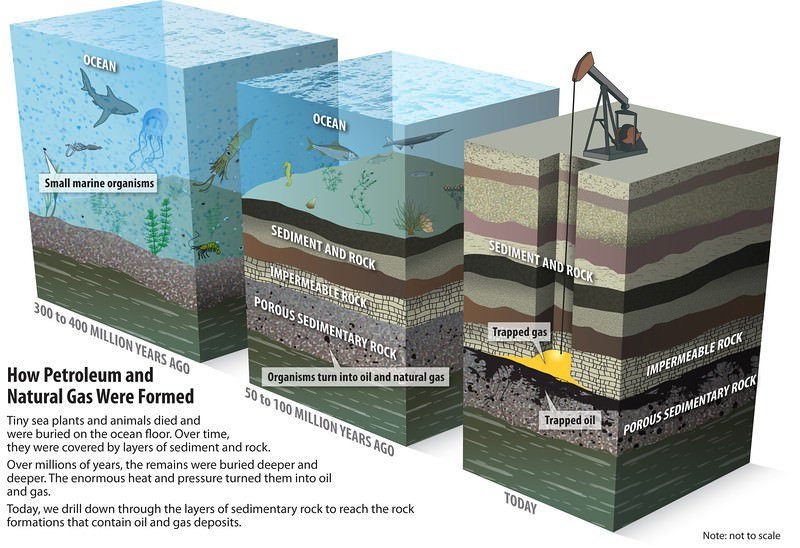
- Oil and gas were formed from the remains of plants and animals that once lived in the sea.
- For over millions of years these remains remained buried under mud and rock under great pressure and at high temperatures.
- Under these conditions marine biomass gradually changed into oil and gas.
- Oil and gas are primarily found along geologically young tectonic belt at plate boundaries, where large depositional basins are more likely to occur.
- Petroleum or crude oil (oil as it comes out of the ground), is a thick dark liquid consisting of a mixture hundreds of combustible hydrocarbons along with small amounts of sulphur, oxygen and nitrogen impurities. It is also known as conventional oil or light oil.
- Deposits of crude oil and natural gas are usually trapped together under the sea floor or earth’s crust on land.
- After it is extracted, crude oil is transported to a refinery by pipelines, trucks or ships (oil tanker).
- In refineries oil is heated and distilled to separate it into components with different boiling points. The important components are gases, gasoline, aviation fuel, kerosene, diesel oil, naphtha, grease and wax and asphalt.
- Some of the products of oil distillation are called petro-chemicals which are used as raw material for the manufacture of pesticides, plastics, synthetic fibers, paints and medicines etc.
Natural Gas
- Natural gas, primarily consist of methane, is often found above reservoirs of crude oil.
- The natural gas is a mixture of 50 to 90% by volume of methane (CH4), the simplest hydrocarbon.
- It also contains small amounts of heavier gaseous hydrocarbons such as ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10) and also small amounts of highly toxic hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
- Natural gas is formed through geological processes similar to the processes of crude oil formation described earlier except the organic material gets changed to more volatile hydrocarbons than those found in oil.
- Almost every oil well produces liquid petroleum along varying amounts of natural gas. However, there are large gas deposits without any liquid petroleum being associated with them.
Conventional natural gas
- It lies above most reservoirs of crude oil. These deposits can be tapped/used only through pipeline.
- But the natural gas that comes out along with oil is often looked as unwanted by product and is burned off.
Unconventional natural gas
- It is found by itself in other underground reservoirs. So far it is very expensive to get natural gas from such unconventional sources but technology is being developed to extract the gases economically.
- When a natural gas field is tapped, propane and butane gases, present in natural gas are liquefied and removed as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
- LPG is stored in pressurized tanks or cylinders for use as cooking gas. At a very low temperature natural gas can be converted to liquefied natural gas (LNG).
- Natural gas is used as a source of carbon used in tyre industry. When natural gas is strongly heated, then methane gets in it decomposed to form carbon and hydrogen.
- The carbon thus formed is called carbon black and used as filler in the manufacture of tyres.
Problems associated with oil and gas
- Methane being major component of natural gas, happens to be a greenhouse gas and its leakage contributes to global warming.
- Extraction of oil and gas may cause sinking of land or subsidence.
- Another major problem in the past with onshore oil wells has been brine (salt water). Typically, for every barrel of oil production ten barrels of brine are also extracted.
- In early days the brine was simply discarded into nearby streams or on the soil. Today most brine is reinjected into the well. However, brine can contaminate fresh water aquifers if the casing lining the well is missing or corroded.
- About half of the oil that contaminates the ocean comes from natural seepage from offshore deposits.
- 20% of the oil contaminating the ocean comes from oil well, blowouts, pipeline breaks and tankers.
Nuclear Energy Sources
- Radioactive minerals are used to generate nuclear energy through high technological methods.
- There are two methods which can be used to release energy from radioactive minerals:
- Nuclear fission – In this process, the nucleus of heavy atom namely of uranium (U 235) or plutonium (P239) breaks apart into smaller fragments, releasing an enormous amount of energy.
- Nuclear fusion – In this process, small nucleus like those of isotopes of hydrogen, namely deuterium and tritium fuse or join together to form heavier nuclei, releasing vast amounts of energy.
Nuclear fission
- Radioactive mineral, which generates nuclear energy through fission, may be considered a non-renewable alternative source of energy as it is an ore and is found in limited quantities.
- Nuclear fission occurs because the atom of radioactive minerals contains nuclei that are unstable and break or split apart releasing energy.
- Whenever a neutron strikes a nucleus of U-235, energy is released, krypton and barium are produced, and several neutrons are released.
- These new neutrons may strike other atoms of U-235 to produce a chain reaction.
- When this nuclear disintegration takes place particles from the nucleus including neutrons fly out.
- The neutron may cause other atomic nuclei to split releasing more neutrons and more energy.
- Once begun this chain reaction continuous to release energy until the fuel is spent or the neutrons are prevented from striking other nuclei.
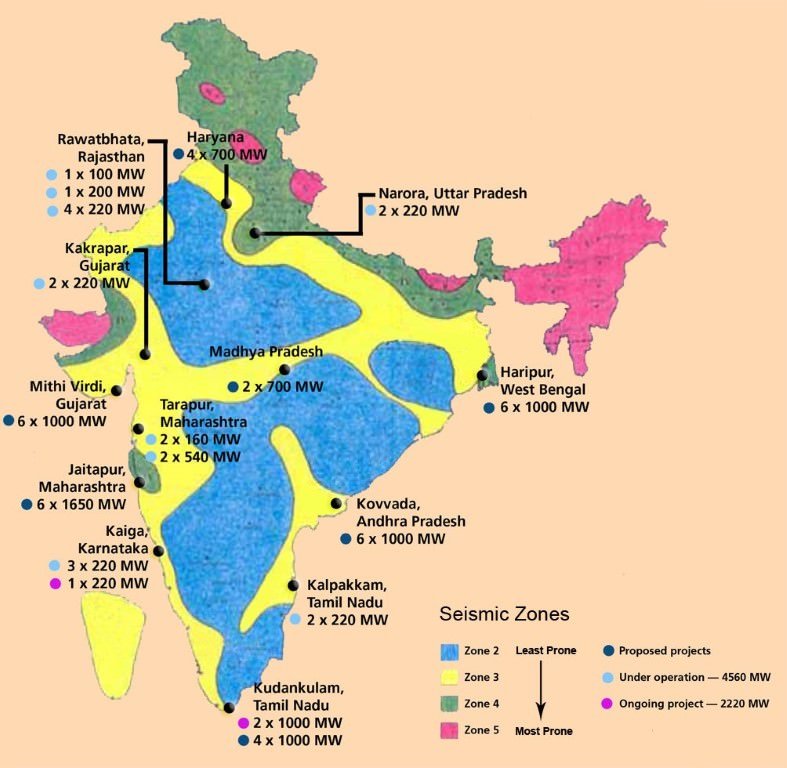
- In the reactor of a nuclear power plant, the rate of nuclear chain reaction is controlled and the heat generated is used to produce high pressure steam, which spins turbine that generate electricity.
- Heat produced here is carried away by water coolant and transferred by way of heat exchanger to the water in a steam-generating unit.
- The steam produced powers a turbine that produces electricity. Cooling water is used to condense the steam after it has gone through the turbine
- Two other nuclear technologies for generating electricity from nuclear fuel in a safe and economic way have also been proposed, but so far they have not proved operationally successful. These are: (i) nuclear breeder reactor, (ii) fusion reactor.
Nuclear breeder reactor
- The nuclear reactors operating today use uranium very inefficiently. About 1% uranium is actually used to produce steam for generating electricity.
- A nuclear reactor that can utilize between 40% and 70% of its nuclear fuel is called a breeder reactor.
- Breeder reactors convert more abundant uranium -238 or thorium -232 fissionable isotopes, Plutonium- 239 or Uranium -233 respectively, that can sustain a nuclear chain reaction.
Nuclear fusion reactor
- The principle for nuclear fusion involves, as you are aware, uniting two small atoms to form a large atom with the release of an enormous amount of energy.
- The energy produced by stars and the sun is the result of nuclear fusion.
- Generation of energy by this method so far, however, has not been possible though lot of research has focused on the fusion reaction of deuterium (D) and tritium (T) (two isotopes of hydrogen) which fuse at about 100 million degrees.
Problems related to nuclear energy generation
The major problems associated with the generation of nuclear power are
- disposal of nuclear waste,
- contamination of environment with long lasting radioactive materials (radioactive pollution),
- thermal pollution,
- health effects from exposure to low levels of radiation,
- limited supplies of uranium ore,
- high construction and maintenance costs,
- questionable reactor safety,
- human or technical error that could result in a major accidents and vulnerability to sabotage,
- developing nuclear weapons by processing reactor waste.
- Problems of dismantling of a nuclear plant’s, after their useful life of 30-40 years is over.
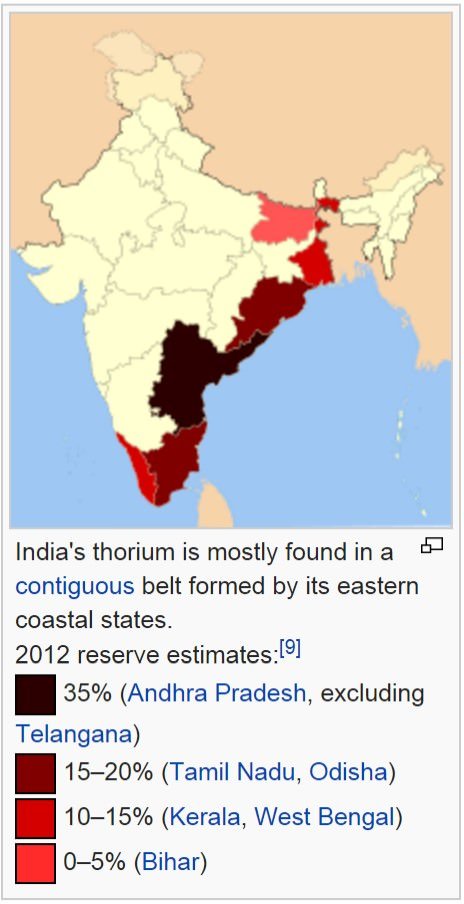
Location of radioactive mineral ore in India
- In India, monazite that is the main source of thorium, is found in commercial quantities on the Travancore coast between Kanya Kumari and Quilon, while uranite or pitchblende mineral of uranium is found in Gaya (Bihar), Ajmer (Rajasthan) and Nellore (Andhra Pradesh).
Energy conservation
- CFL (compact fluorescent lamps) should be replaced by LEDs as they are much more efficient.
- Replaceing aging old appliances with energy efficient models.
- Alternative resources i.e. renewable energy sources should be used in place of nonrenewable energy sources e.g. solar energy, biogas, wind energy etc.
- Energy audits of homes, buildings, hotels and factories should be done at regular interval.
- Demonstration of projects involving the introduction of appropriate, renewable solar, wind and biogas energy technologies at the community level.
- Collaborative community/academic research and development in order to produce lowcost, sustainable energy options should be given priority.
- Environment friendly public transport system should be promoted to reduce the use of individual motorized transport.
- Installation of photoelectric controls or timers should be used to make sure that outdoor lighting is sufficient during the day.
- Elevators/lifts should be used for going up beyond three floors and for coming down the usage of lifts may be reduced.
- Whenever two elevators/lifts are provided in a building only single should be operated during “non-peak” hours.
- Conservation and sustainable use of water bodies, including watersheds, rivers barriers and coastal zones will be helpful in the energy conservation at community level.
- Training programme about energy efficient repairs should be organized to conserve energy at community level.
- Advocacy to remove subsidies to inefficient and polluting sources of energy should become essential.
- Locally manufactured, improved cook stoves should be introduced to reduce charcoal/fuel consumption.
- Auditing Regular monitoring and audit of energy consumption in industries results in energy conservation.
- Process modification: replacement of old and more energy consuming processes by the new energy efficient processes. Old factories should now employ process modification.
- Use public transportation as much as possible instead of using own vehicles.
- Avoid free frequent starts and stops of vehicles to reduce fuel consumption.
- Appliances and office equipments should be replaced with energy star rated units.
- Building designs and construction practices should promote energy conservation.
Impact of energy use on the environment
- Depletion of energy resources.
- Pollution of environment from emission of green house gases.
Energy And Economic Development
- Energy development is an integral part of economic development.
- Cheap, efficient and environment friendly enegy resources and technologies are must to stay globally competitive.








From Where I can Download and Print this??