Elephant Corridors and Elephant Reserves
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (PIB): Elephant corridors and reserves are developed to protect and conserve the elephants.
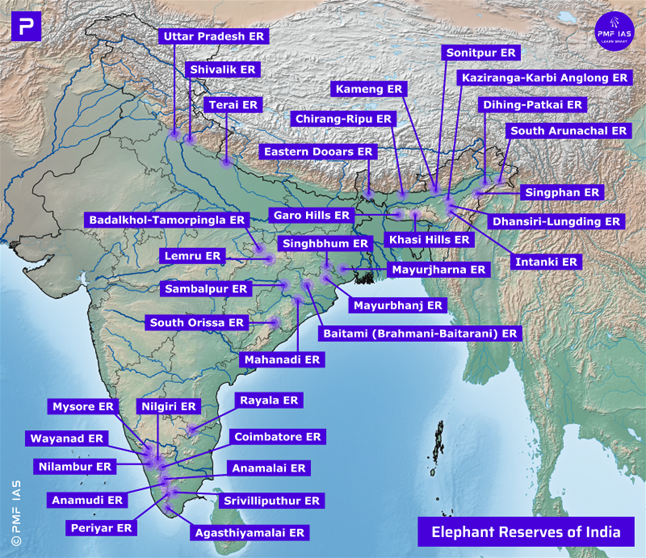
- Elephant Reserves of India with Map (33 Elephant Reserves in India in 2023)
Elephant Corridors
- Elephant corridor is a linear path aiding elephant movement between habitats.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), coordinating with the State Forest Departments, has ground-validated 150 elephant corridors across 15 elephant range states.
Right to Passage of the Animals
|
Benefits of Elephant Corridors
- Genetic diversity: It helps elephants to intermingle and breed with elephants outside their gene pool.
- Reduces human-animal conflict
Elephant Reserves
- There are 33 Elephant Reserves (ER) spread over 10 elephant landscapes in 14 states.
- These ER overlap with Tiger Reserves, Wildlife Sanctuaries, and Reserved Forests protected under the WildLife (Protection) Act, 1972, the Indian Forest Act, 1927, and other local State Acts.
Benefits of Elephant Reserves
Why Elephant Reserves and Corridors Do Little Good for Conservation?
- Elephant reserves and elephant corridors are essentially administrative classifications.
- They don’t promise greater protection of elephant habitats because they are not recognised by law.
- According to the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (WPA 1972), a ‘protected area’ can be one of a ‘national park’, a ‘wildlife sanctuary’, a ‘conservation reserve’ or a ‘community reserve’.
- The prohibited activities in protected areas, including mining, oil and gas drilling, dams, etc., are permissible in an elephant reserve.
- As a result, governments can divert elephant reserves and corridors for various projects.
Asian Elephant
|
- National Parks of India with Map (109 National Parks in India in 2023)
- Tiger Reserves of India with Map (53 Tiger Reserves in India in 2023)
- Biosphere Reserves of India (18 Biosphere Reserves in India (12 Recognized by UNESCO’s MAB))
- Elephant Reserves of India with Map (33 Elephant Reserves in India in 2023)
- Ramsar Sites of India (75 Ramsar Sites in India in 2023)
- Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India (36 Biodiversity Heritage Sites in India in 2023)





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)